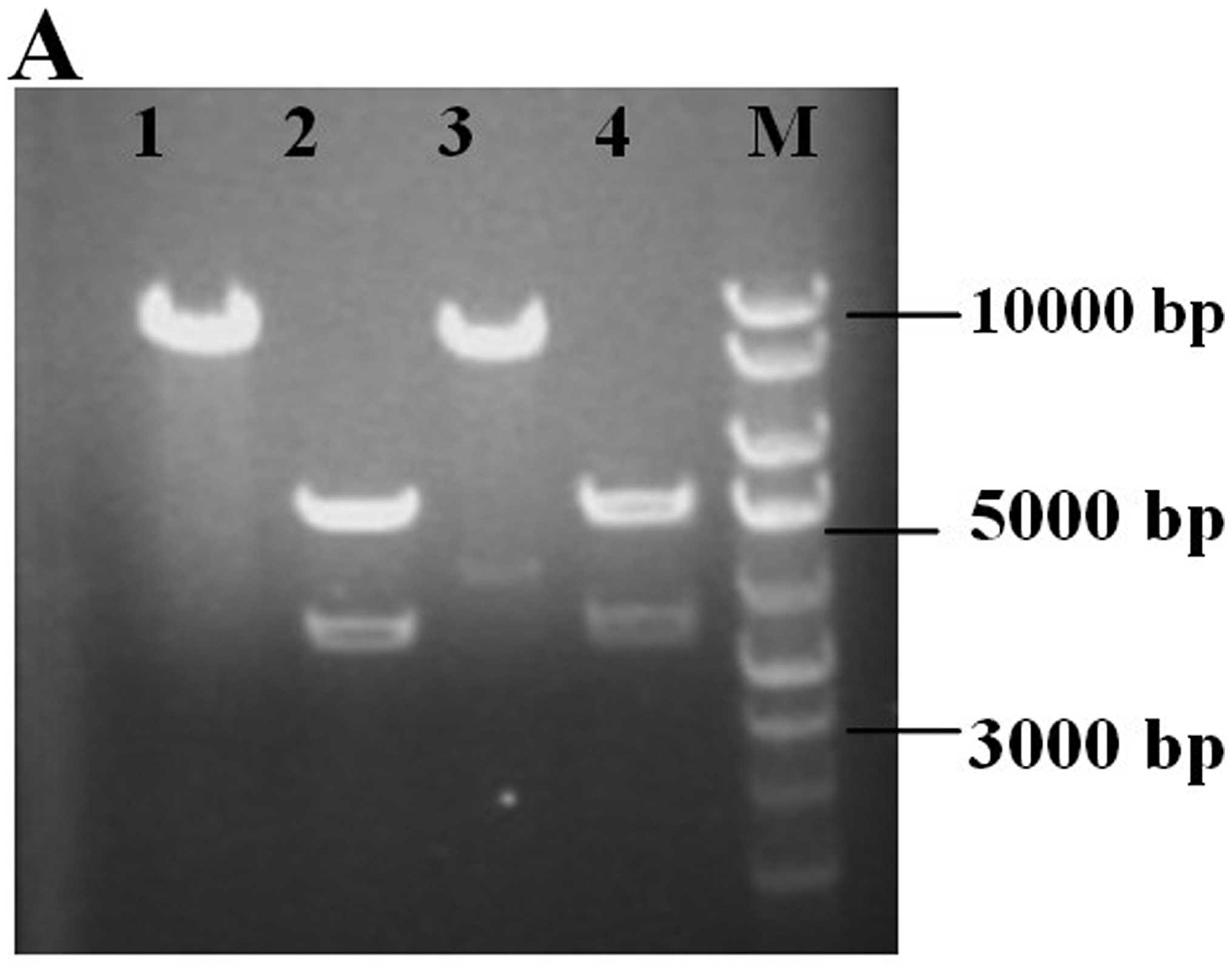
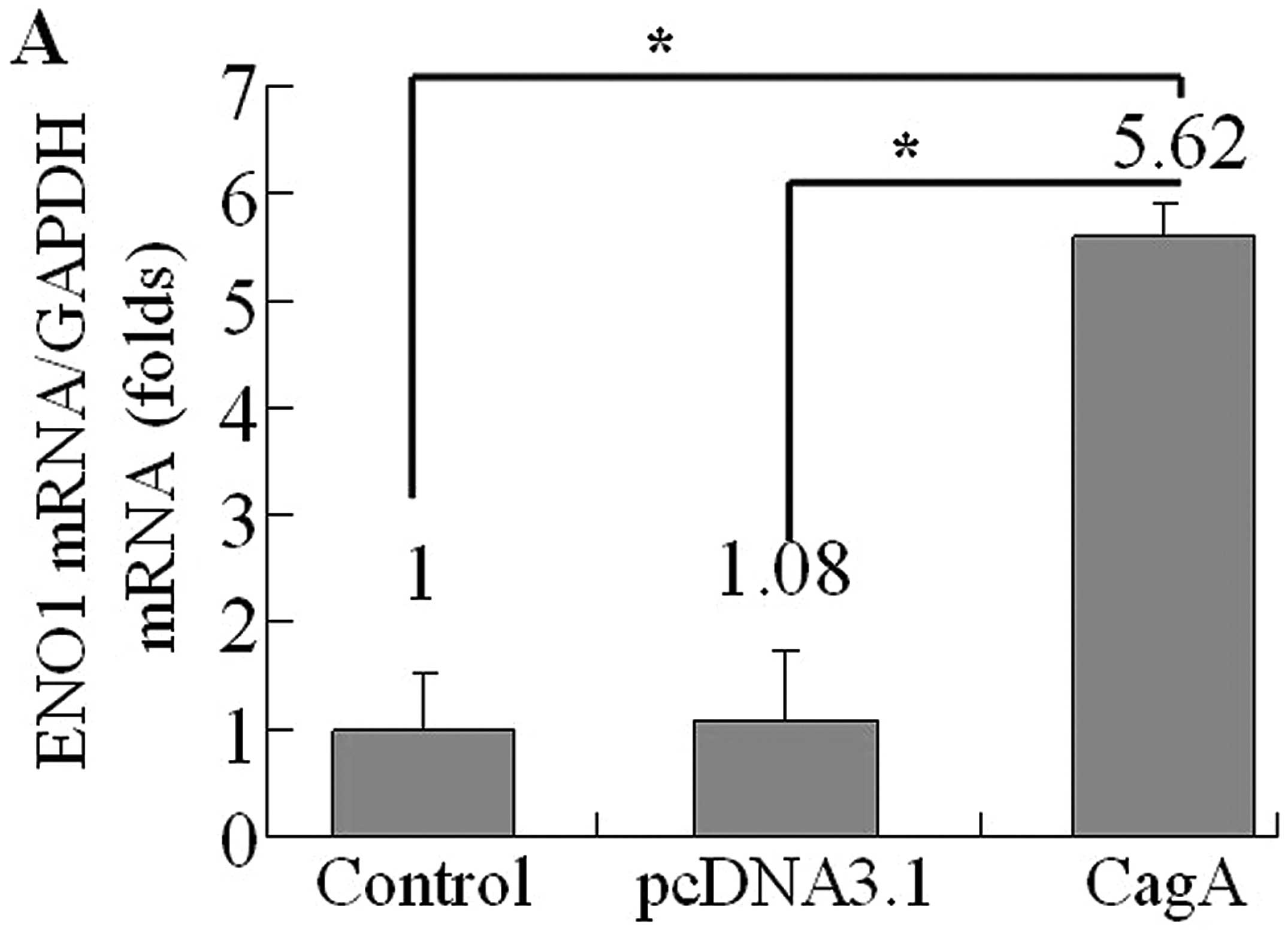
|
1
|
Cavaleiro-Pinto M, Peleteiro B, Lunet N
and Barros H: Helicobacter pylori infection and gastric
cardia cancer: systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer Causes
Control. 22:375–387. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Peek RM and Crabtree JE:
Helicobacter infection and gastric neoplasia. J Pathol.
208:233–248. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Zhu Y-L, Zheng S, Du Q, Qian K-D and Fang
P-C: Characterization of CagA variable region of Helicobacter
pylori isolates from Chinese patients. World J Gastroenterol.
11:880–884. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hatakeyama M: Oncogenic mechanisms of the
Helicobacter pylori CagA protein. Nat Rev Cancer. 4:688–694.
2004.
|
|
5
|
Backert S and Selbach M: Role of type IV
secretion in Helicobacter pylori pathogenesis. Cell
Microbiol. 10:1573–1581. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Saadat I, Higashi H, Obuse C, et al:
Helicobacter pylori CagA targets PAR1/MARK kinase to disrupt
epithelial cell polarity. Nature. 447:330–333. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Brandt S, Kwok T, Hartig R, Konig W and
Backert S: NF-kappaB activation and potentiation of proinflammatory
responses by the Helicobacter pylori CagA protein. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 102:9300–9305. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhao DP, Liu ZF, Ding J, et al:
Helicobacter pylori CagA upregulation of CIP2A is dependent
on the Src and MEK/ERK pathways. J Med Microbiol. 59:259–265. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Churin Y, Al-Ghoul L, Kepp O, Meyer TF,
Birchmeier W and Naumann M: Helicobacter pylori CagA protein
targets the c-Met receptor and enhances the motogenic response. J
Cell Biol. 161:249–255. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Kuipers EJ, Perez-Perez GI, Meuwissen SG
and Blaser MJ: Helicobacter pylori and atrophic gastritis:
importance of the cagA status. J Natl Cancer Inst. 87:1777–1780.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Nomura AM, Lee J, Stemmermann GN, Nomura
RY, Perez-Perez GI and Blaser MJ: Helicobacter pylori CagA
seropositivity and gastric carcinoma risk in a Japanese American
population. J Infect Dis. 186:1138–1144. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Huang ZG, Duan GC, Fan QT, et al: Mutation
of cytotoxin-associated gene A affects expressions of antioxidant
proteins of Helicobacter pylori. World J Gastroenterol.
15:599–606. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Plow EF, Herren T, Redlitz A, Miles LA and
Hoover-Plow JL: The cell biology of the plasminogen system. FASEB
J. 9:939–945. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jiang BH, Agani F, Passaniti A and Semenza
GL: V-SRC induces expression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF-1)
and transcription of genes encoding vascular endothelial growth
factor and enolase 1: involvement of HIF-1 in tumor progression.
Cancer Res. 57:5328–5335. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhu Y, Shu X, Chen J, et al: Effect of
Helicobacter pylori eradication on oncogenes and cell
proliferation. Eur J Clin Invest. 38:628–633. 2008.
|
|
16
|
Hirata Y, Maeda S, Mitsuno W, et al:
Helicobacter pylori activates the cyclin D1 gene through
mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway in gastric cancer cells.
Infect Immun. 69:3965–3971. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wu C-Y, Wang C-J, Tseng C-C, et al:
Helicobacter pylori promote gastric cancer cells invasion
through a NF-kappaB and COX-2-mediated pathway. World J
Gastroenterol. 11:31972005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Lee KS, Kalantzis A, Jackson CB, et al:
Helicobacter pylori CagA triggers expression of the
bactericidal lectin REG3γ via gastric STAT3 activation. PloS One.
7:e307862012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Atherton JC and Blaser MJ: Coadaptation of
Helicobacter pylori and humans: ancient history, modern
implications. J Clin Invest. 119:2475–2487. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Selbach M, Moese S, Hauck CR, Meyer TF and
Backert S: Src is the kinase of the Helicobacter pylori CagA
protein in vitro and in vivo. J Biol Chem. 277:6775–6778.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Poppe M, Feller SM, Romer G and Wessler S:
Phosphorylation of Helicobacter pylori CagA by c-Abl leads
to cell motility. Oncogene. 26:3462–3472. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Amieva MR, Vogelmann R, Covacci A,
Tompkins LS, Nelson WJ and Falkow S: Disruption of the epithelial
apical-junctional complex by Helicobacter pylori CagA.
Science. 300:1430–1434. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wroblewski LE, Peek RM and Wilson KT:
Helicobacter pylori and gastric cancer: factors that
modulate disease risk. Clin Microbiol Rev. 23:713–739. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Higashi H, Tsutsumi R, Muto S, et al:
SHP-2 tyrosine phosphatase as an intracellular target of
Helicobacter pylori CagA protein. Science. 295:683–686.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Higashi H, Tsutsumi R, Fujita A, et al:
Biological activity of the Helicobacter pylori virulence
factor CagA is determined by variation in the tyrosine
phosphorylation sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 99:14428–14433.
2002.
|
|
26
|
Pancholi V: Multifunctional alpha-enolase:
its role in diseases. Cell Mol Life Sci. 58:902–920. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Takashima M, Kuramitsu Y, Yokoyama Y, et
al: Overexpression of alpha enolase in hepatitis C virus-related
hepatocellular carcinoma: association with tumor progression as
determined by proteomic analysis. Proteomics. 5:1686–1692. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Feo S, Arcuri D, Piddini E, Passantino R
and Giallongo A: ENO1 gene product binds to the c-myc promoter and
acts as a transcriptional repressor: relationship with Myc
promoter-binding protein 1 (MBP-1). FEBS Lett. 473:47–52. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kim J-W, Zeller KI, Wang Y, et al:
Evaluation of myc E-box phylogenetic footprints in glycolytic genes
by chromatin immunoprecipitation assays. Mol Cell Biol.
24:5923–5936. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kim SY, Lee YC, Kim HK and Blaser MJ:
Helicobacter pylori CagA transfection of gastric epithelial
cells induces interleukin-8. Cell Microbiol. 8:97–106. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Zhu Y, Zhong X, Zheng S, Du Q and Xu W:
Transformed immortalized gastric epithelial cells by virulence
factor CagA of Helicobacter pylori through Erk
mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. Oncogene. 24:3886–3895.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Li Q, Liu N, Shen B, et al:
Helicobacter pylori enhances cyclooxygenase 2 expression via
p38MAPK/ATF-2 signaling pathway in MKN45 cells. Cancer Lett.
278:97–103. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Liu Z, Xu X, Chen L, et al:
Helicobacter pylori CagA inhibits the expression of Runx3
via Src/MEK/ERK and p38 MAPK pathways in gastric epithelial cells.
J Cell Biochem. 113:1080–1086. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|