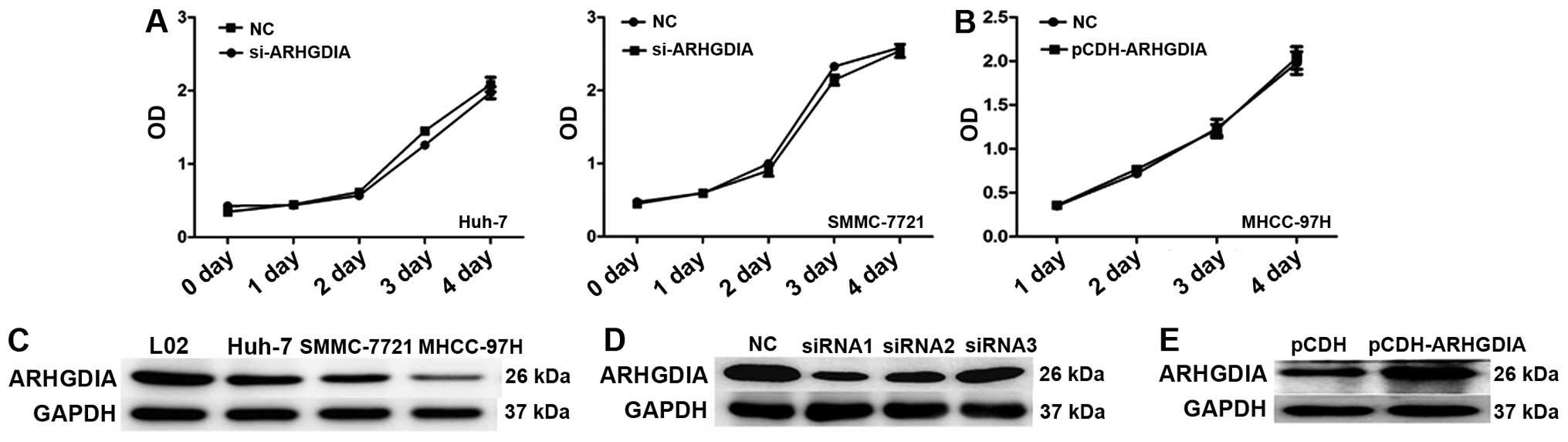
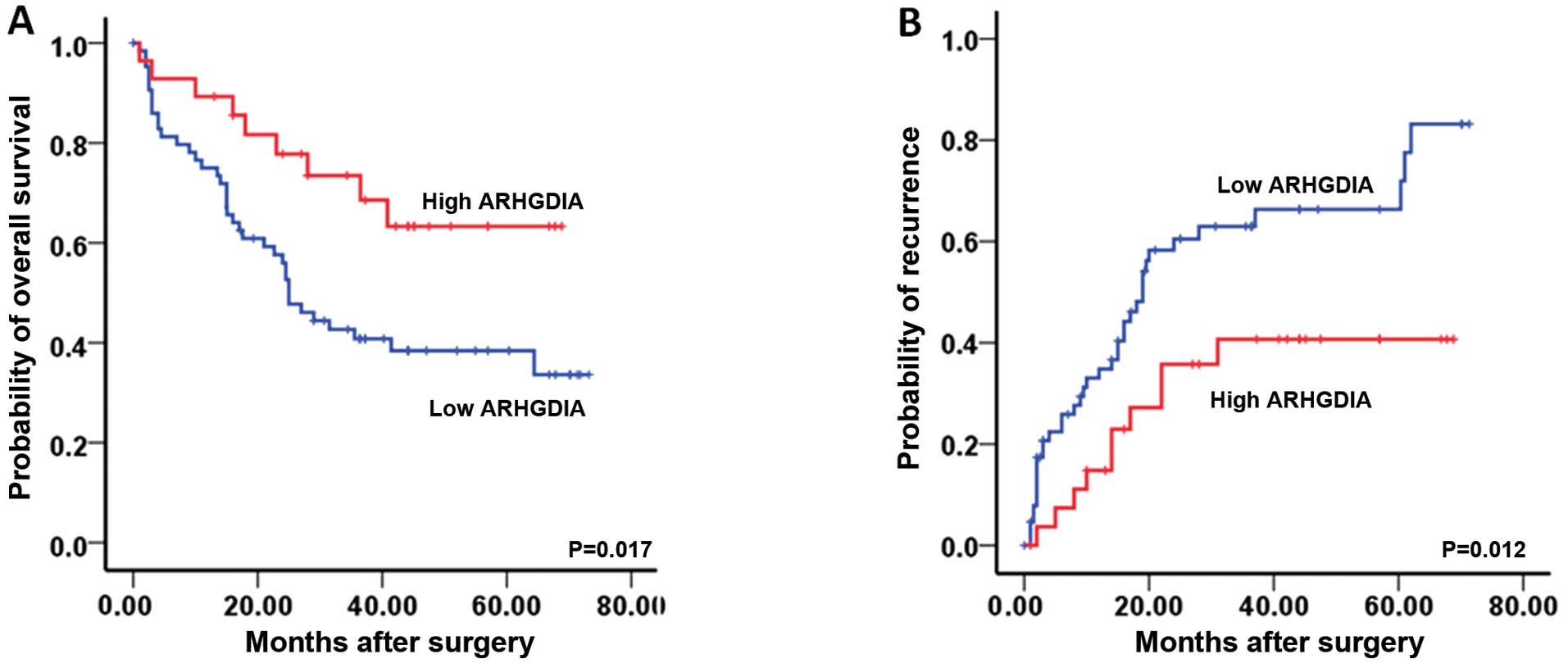
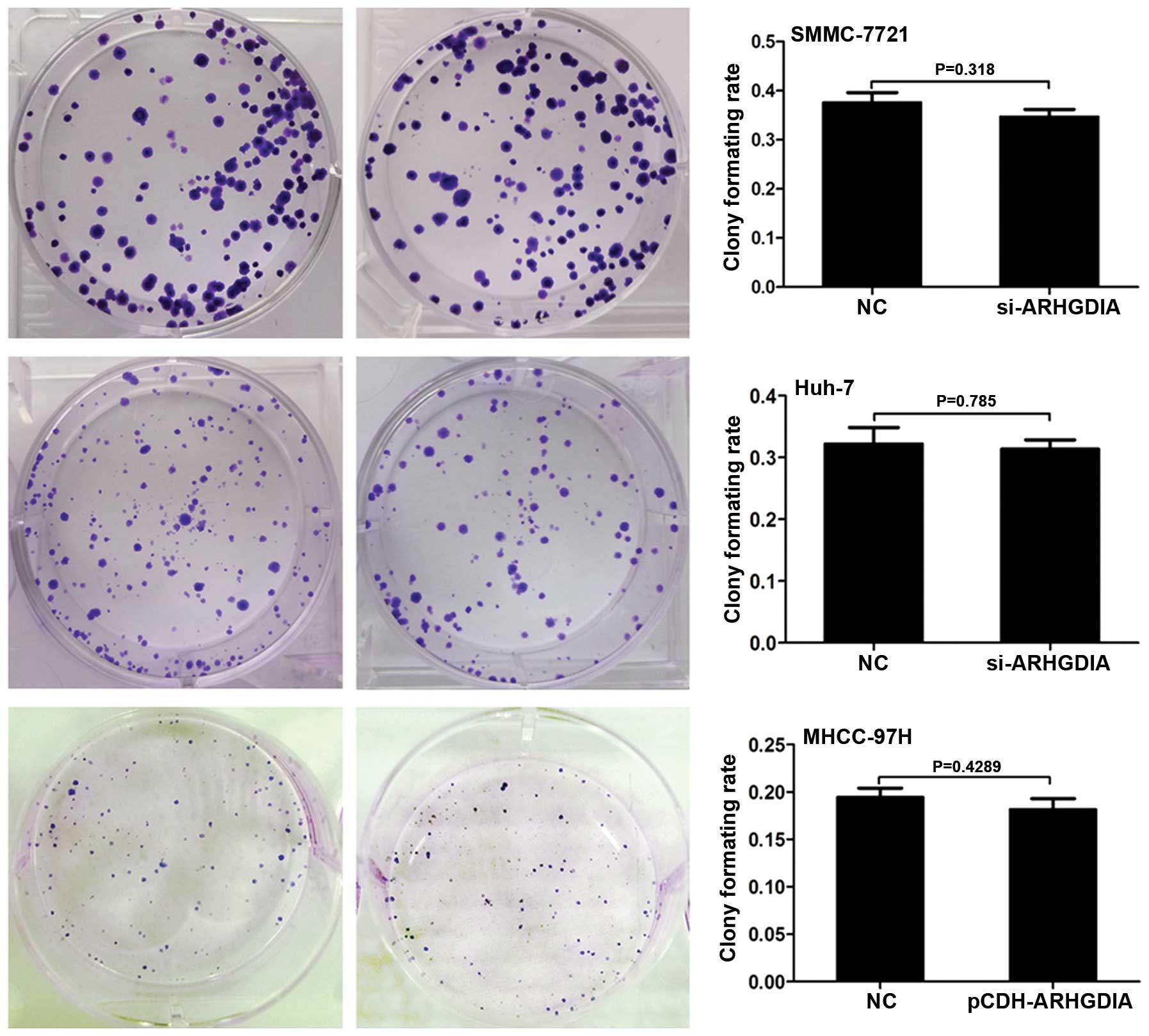
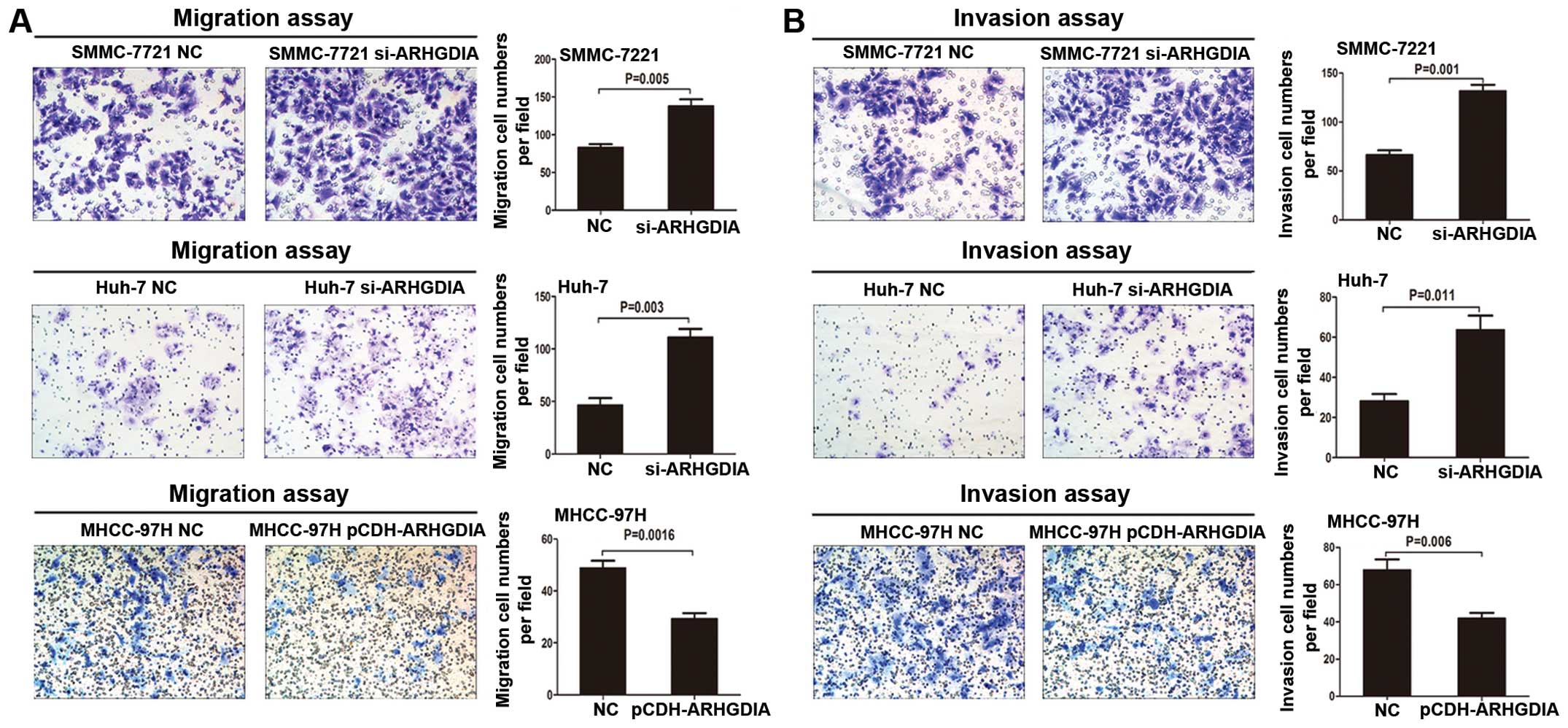
|
1
|
Bosch FX, Ribes J, Díaz M and Cléries R:
Primary liver cancer: worldwide incidence and trends.
Gastroenterology. 127(Suppl 1): S5–S16. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Portolani N, Coniglio A, Ghidoni S, et al:
Early and late recurrence after liver resection for hepatocellular
carcinoma: prognostic and therapeutic implications. Ann Surg.
243:229–235. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bruix J, Boix L, Sala M and Llovet JM:
Focus on hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Cell. 5:215–219. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Takai Y, Sasaki T and Matozaki T: Small
GTP-binding proteins. Physiol Rev. 81:153–208. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Fukumoto Y, Kaibuchi K, Hori Y, et al:
Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel type of
regulatory protein (GDI) for the rho proteins, ras p21-like small
GTP-binding proteins. Oncogene. 5:1321–1328. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Leonard D, Hart MJ, Platko JV, et al: The
identification and characterization of a GDP-dissociation inhibitor
(GDI) for the CDC42Hs protein. J Biol Chem. 267:22860–22868.
1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sun HC, Zhang W, Qin LX, et al: Positive
serum hepatitis B e antigen is associated with higher risk of early
recurrence and poorer survival in patients after curative resection
of hepatitis B-related hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol.
47:684–690. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Gao Q, Qiu SJ, Fan J, et al: Intratumoral
balance of regulatory and cytotoxic T cells is associated with
prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma after resection. J Clin
Oncol. 25:2586–2593. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ellenbroek SI and Collard JG: Rho GTPases:
functions and association with cancer. Clin Exp Metastasis.
24:657–672. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Harding MA and Theodorescu D: RhoGDI
signaling provides targets for cancer therapy. Eur J Cancer.
46:1252–1259. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Jones MB, Krutzsch H, Shu H, et al:
Proteomic analysis and identification of new biomarkers and
therapeutic targets for invasive ovarian cancer. Proteomics.
2:76–84. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhao L, Wang H, Li J, Liu Y and Ding Y:
Overexpression of Rho GDP-dissociation inhibitor α is associated
with tumor progression and poor prognosis of colorectal cancer. J
Proteome Res. 7:3994–4003. 2008.
|
|
13
|
Zhao L, Wang H, Sun X and Ding Y:
Comparative proteomic analysis identifies proteins associated with
the development and progression of colorectal carcinoma. FEBS J.
277:4195–4204. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Forget MA, Desrosiers RR, Del M, et al:
The expression of rho proteins decreases with human brain tumor
progression: potential tumor markers. Clin Exp Metastasis. 19:9–15.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Jiang WG, Watkins G, Lane J, Cunnick GH,
Douglas-Jones A, Mokbel K and Mansel RE: Prognostic value of rho
GTPases and rhoguanine nucleotide dissociation inhibitors in human
breast cancers. Clin Cancer Res. 9:6432–6440. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Habets GG, Scholtes EH, Zuydgeest D, et
al: Identification of an invasion-inducing gene, Tiam-1, that
encodes a protein with homology to GDP-GTP exchangers for Rho-like
proteins. Cell. 77:537–549. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hordijk PL, ten Klooster JP, van der
Kammen RA, et al: Inhibition of invasion of epithelial cells by
Tiam1-Rac signaling. Science. 278:1464–1466. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Turner SJ, Zhuang S, Zhang T, et al:
Effects of lovastatin on Rho isoform expression, activity, and
association with guanine nucleotide dissociation inhibitors.
Biochem Pharmacol. 75:405–413. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Shibata S, Nagase M, Yoshida S, et al:
Modification of mineralocorticoid receptor function by Rac1 GTPase:
implication in proteinuric kidney disease. Nat Med. 14:1370–1376.
2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Gorovoy M, Neamu R, Niu J, et al: RhoGDI-1
modulation of the activity of monomeric RhoGTPase RhoA regulates
endothelial barrier function in mouse lungs. Circ Res. 101:50–58.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wei L, Imanaka-Yoshida K, Wang L, et al:
Inhibition of Rho family GTPases by Rho GDP dissociation inhibitor
disrupts cardiac morphogenesis and inhibits cardiomyocyte
proliferation. Development. 129:1705–1714. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Li XR, Ji F, Ouyang J, et al:
Overexpression of RhoA is associated with poor prognosis in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur J Surg Oncol. 32:1130–1134. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang D, Dou K, Xiang H, et al: Involvement
of RhoA in progression of human hepatocellular carcinoma. J
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 22:1916–1920. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Fuku K, Tamura S, Wada A, et al:
Expression and prognostic role of RhoA GTPases in hepatocellular
carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 132:627–633. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wu X, Chen H, Gao Q, et al: Downregulation
of JWA promotes tumor invasion and predicts poor prognosis in human
hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Carcinog. 53:325–336. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Takenawa T and Suetsugu S: The WASP-WAVE
protein network: connecting the membrane to the cytoskeleton. Nat
Rev Mol Cell Biol. 8:37–48. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lee TK, Man K, Ho JW, et al: Significance
of the Rac signaling pathway in HCC cell motility: implications for
a new therapeutic target. Carcinogenesis. 26:681–687.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Liu S, Yu M, He Y, et al: Melittin
prevents liver cancer cell metastasis through inhibition of the
Rac1-dependent pathway. Hepatology. 47:1964–1973. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chen L, Chan TH, Yuan YF, et al: CHD1L
promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression and metastasis in
mice and is associated with these processes in human patients. J
Clin Invest. 120:1178–1191. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|