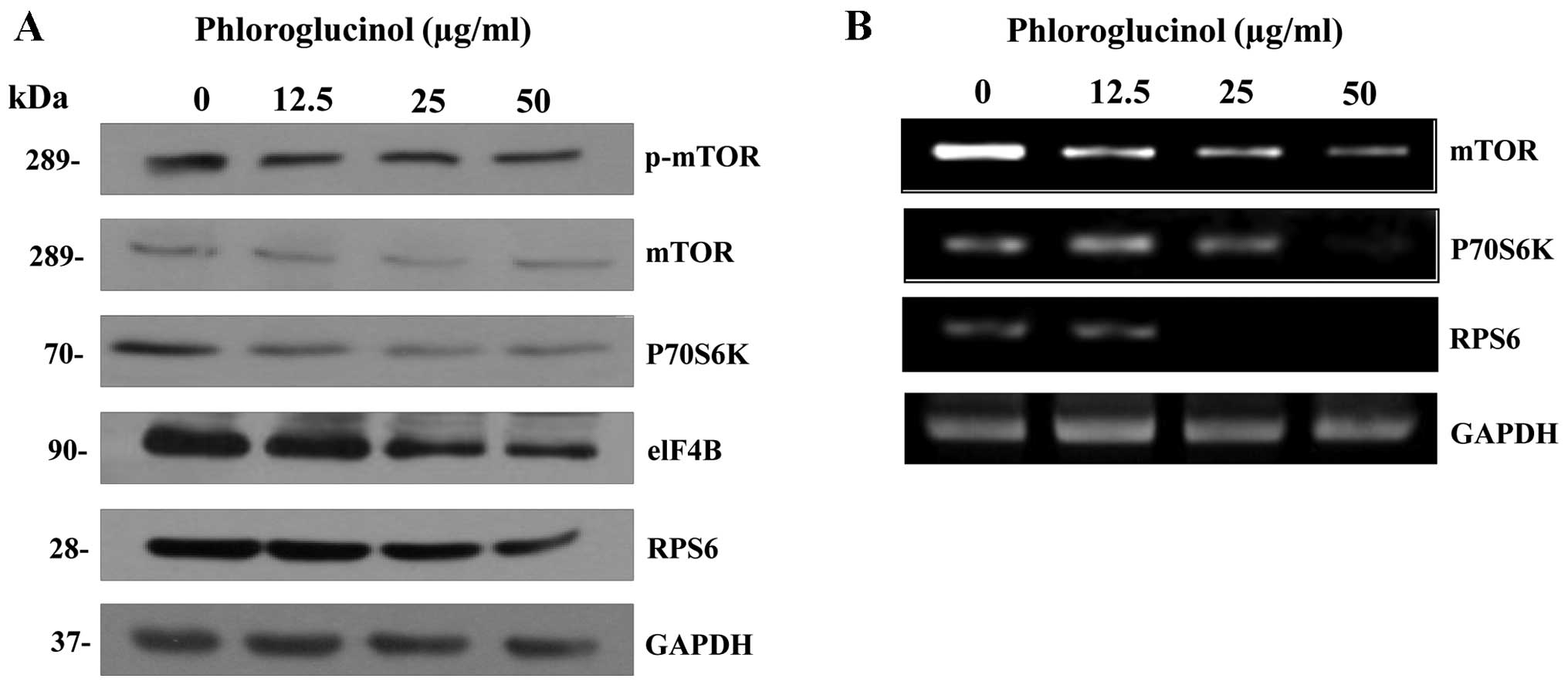
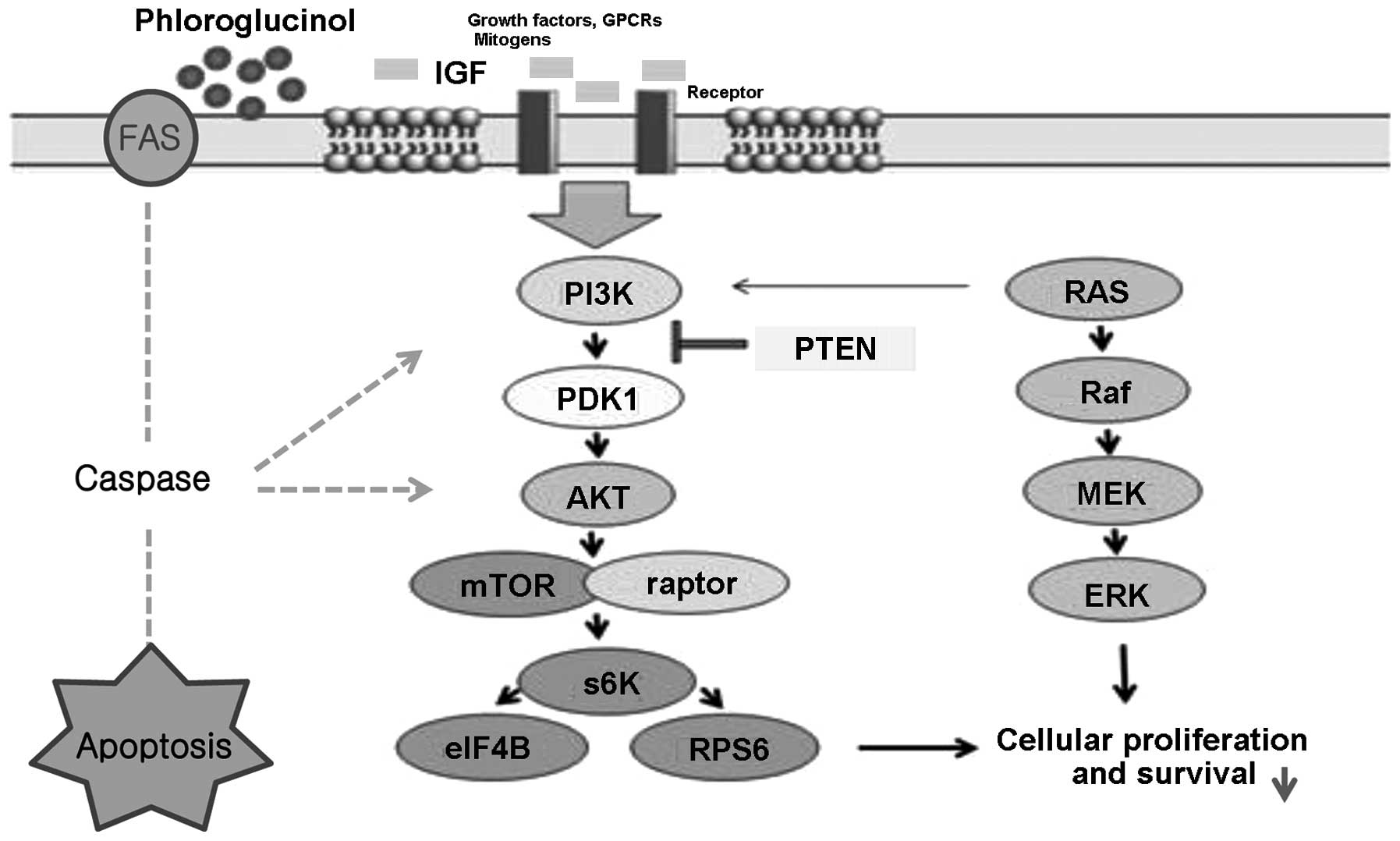
|
1
|
Matsui T, Omura K, Kawakami K, Morita S
and Sakamoto J: Genotype of thymidylate synthase likely to affect
efficacy of adjuvant 5-FU based chemotherapy in colon cancer. Oncol
Rep. 16:1111–1115. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Oehler C and Ciernik IF: Radiation therapy
and combined modality treatment of gastrointestinal carcinomas.
Cancer Treat Rev. 32:119–138. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Nagayama K, lwamura K, Shibata T, Hirayama
I and Nakamura T: Bactericidal activity of phlorotannins from the
brown alga Ecklonia kurom. J Antimicrob Chemother.
50:889–893. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Park EJ and Pezzuto JM: Botanicals in
cancer chemoprevention. Cancer Metast Rev. 21:231–255. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Stan SD, Kar S, Stoner GD and Singh SV:
Bioactive food components and cancer risk reduction. J Cell
Biochem. 104:339–356. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wei A, Zhou D, Xiong C, Cai Y and Ruan J:
A novel non-aromatic β-ring flavonoid: isolation, structure
elucidation and its induction of apoptosis in human colon HT-29
tumor cell via the reactive oxygen species-mitochondrial
dysfunction and MAPK activation. Food Chem Toxicol. 49:2445–2452.
2011.
|
|
7
|
Hsu HF, Houng JY, Kuo CF, Tsao N and Wua
YC: Glossogin, a novel phenylpropanoid from Glossogyne
tenuifolia, induced apoptosis in A549 lung cancer cells. Food
Chem Toxicol. 46:3785–3791. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kang HS, Chung HY, Kim JY, Son BW, Jung HA
and Choi JS: Inhibitory phlorotannins from the edible brown alga
Ecklonia stolonifera on total reactive oxygen species (ROS)
generation. Arch Pharm Res. 27:194–198. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kim MM, Ta QV, Mendis E, Rajapakse N, Jung
WK, Byun HG, Jeon YJ and Kim SK: Phlorotannins in Ecklonia
cava extract inhibit matrix metalloproteinase activity. Life
Sci. 79:1436–1443. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lin ML, Chen SS, Lu YC, Liang RY, Ho YT,
Yang CY and Chung JG: Rhein induces apoptosis through induction of
endoplasmic reticulum stress and Ca2+-dependent
mitochondrial death pathway in human nasopharyngeal carcinoma
cells. Anticancer Res. 27:3313–3322. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Debatin KM and Krammer PH: Death receptors
in chemotherapy and cancer. Oncogene. 23:2950–2966. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hu W, Lee SK, Jung MJ, Heo SI, Hur JH and
Wang MH: Induction of cell cycle arrest and apoptosis by the ethyl
acetate fraction of Kalopanax pictus leaves in human colon
cancer cells. Bio Resour Technol. 101:9366–9372. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Degterev A and Yuan J: Expansion and
evolution of cell death programmes. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
9:378–390. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Tan ML, Ooi JP, Ismail N, Moad Al and
Muhammad TS: Programmed cell death pathways and current antitumor
targets. Pharm Res. 26:1547–1560. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Maddika S, Ande SR, Wiechec E, Hansen LL,
Wesselborg S and Los M: Akt-mediated phosphorylation of CDK2
regulates its dual role in cell cycle progression and apoptosis. J
Cell Sci. 121:979–988. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hengartner MO: The biochemistry of
apoptosis. Nature. 407:770–776. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Grimm S and Brdiczka D: The permeability
transition pore in cell death. Apoptosis. 12:841–855. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Cryns V and Yuan J: Proteases to die for.
Genes Dev. 12:1551–1570. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Cantley LC: The phosphoinositide 3-kinase
pathway. Science. 296:1655–1657. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sachdev D, Li SL, Hartell JS,
Fujita-Yamaguchi Y, Miller JS and Yee D: A chimeric humanized
single chain antibody against the type I insulin-like growth factor
(IGF) receptor renders breast cancer cells refractory to the
mitogenic effects of IGF-1. Cancer Res. 63:627–635. 2003.
|
|
21
|
Segrelles C, Moral M, Lara MF, Ruiz S,
Santos M, Leis H, Garcia-Escudero R, Martinez-Cruz AB,
Martinez-Palacio J, Hernandez P, Ballestin C and Paramio JM:
Molecular determinants of Akt-induced keratinocyte transformation.
Oncogene. 25:1174–1185. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lee ER, Kim JY, Kang YJ, Ahn JY, Kim JH,
Kim BW, Choi HY, Jeong MY and Cho SG: Interplay between PI3K/Akt
and MAPK signaling pathways in DNA-damaging drug-induced apoptosis.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1763:958–968. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Shaw RJ and Cantley LC: Ras, PI(3)K and
mTOR signaling controls tumour cell growth. Nature. 441:424–430.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Bhandari BK, Feliers D, Duraisamy S,
Stewart JL, Gingras AC, Abboud HE, Choudhury GG, Sonenberg N and
Kasinath BS: Insulin regulation of protein translation repressor
4E-BP1, an elF4E-binding protein, in renal epithelial cells. Kidney
Int. 59:866–875. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Oldham S and Hafen E: Insulin/IGF and
target of rapamycin signaling: ATOR de force in growth control.
Trends Cell Biol. 13:79–85. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Bjornsti MA and Houghton PJ: The TOR
pathway: a target for cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 4:335–348.
2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
White MF: The IRS-signaling system: a
network of docking proteins that mediate insulin and cytokine
action. Recent Prog Horm Res. 53:119–138. 1998.
|
|
28
|
Mori H, Inoki K, Opland D, Munzberg H,
Villanueva EC, Faouzi M, Guan KL, et al: Critical roles for the
TSC-mTOR pathway in β-cell function. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab.
297:E1013–E1022. 2009.
|
|
29
|
Wan X, Harkavy B, Shen N, Grohar P and
Helman L: Rapamycin induces feedback activation of Akt signaling
through an IGF-1R dependent mechanism. Oncogene. 26:1932–1940.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
O’Reilly KE, Rojo F, She QB, Solit D,
Mills GB, Smith D, Lane H, Hofmann F, et al: mTOR inhibition
induces upstream receptor tyrosine kinase signaling and activates
Akt. Cancer Res. 66:1500–1508. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Quevedo C, Salinas M and Alcazar A:
Regulation of cap-dependent translation by insulin-like growth
factor-1 in neuronal cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
291:560–566. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Roux PP, Shahbazian D, Vu H, Holz MK,
Cohen MS, Taunton J, Sonenberg N and Blenis J: RAS/ERK signaling
promotes site-specific ribosomal protein S6 phosphorylation via RSK
and stimulates cap-dependent translation. J Biol Chem.
282:14056–14064. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kiaris H and Spandidos D: Mutations of ras
genes in human tumors (review). Int J Oncol. 7:413–421.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Treisman R: Regulation of transcription by
MAP kinase cascades. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 8:205–215. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|