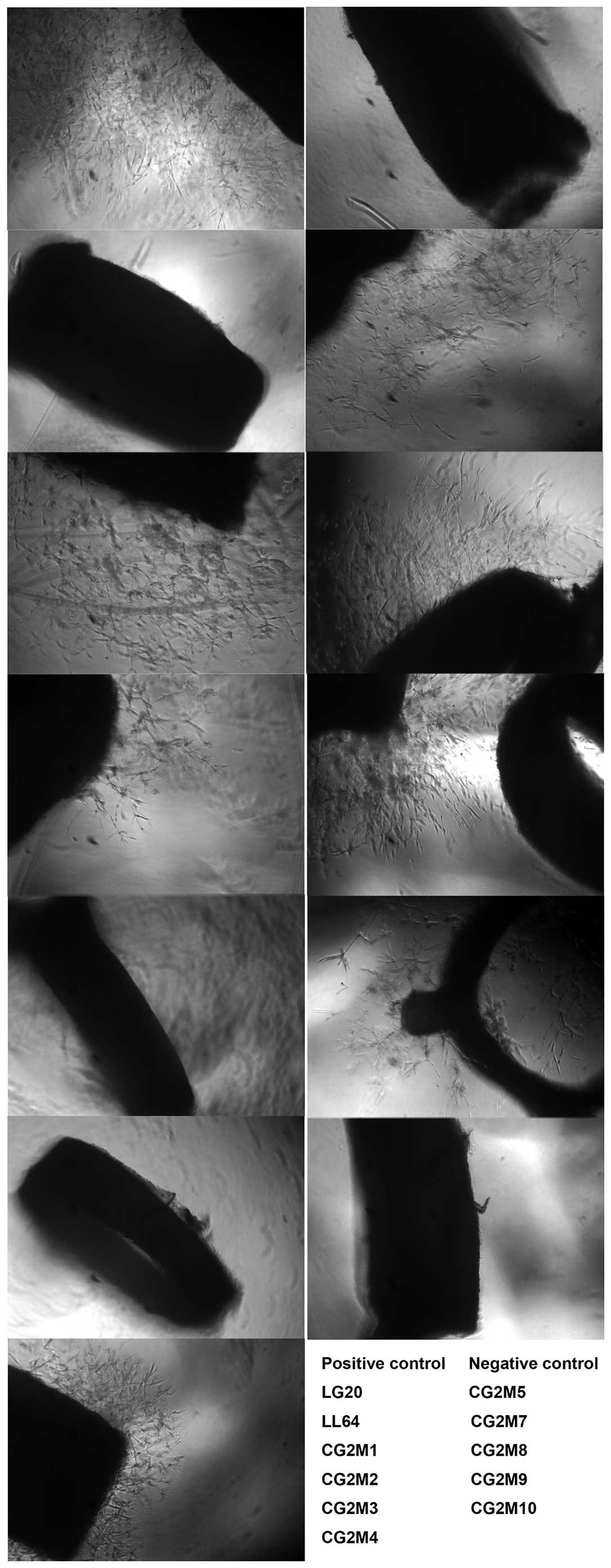
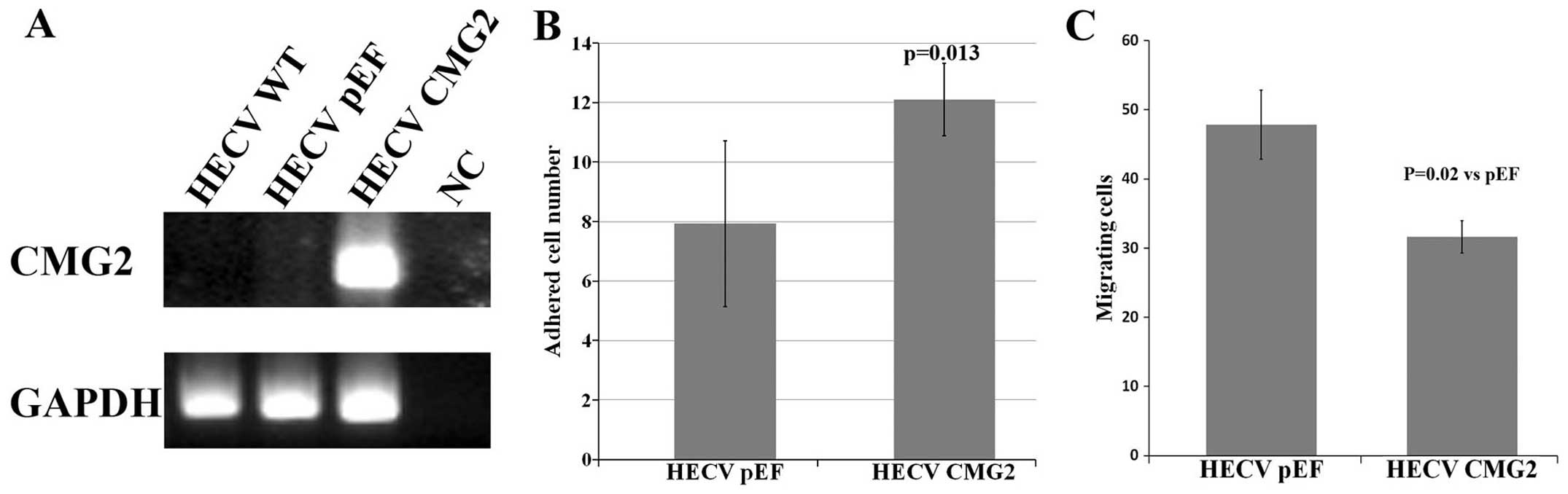
|
1
|
Bell SE, Mavila A, Salazar R, et al:
Differential gene expression during capillary morphogenesis in 3D
collagen matrices: regulated expression of genes involved in
basement membrane matrix assembly, cell cycle progression, cellular
differentiation and G-protein signaling. J Cell Sci. 114:2755–2773.
2001.
|
|
2
|
Scobie HM, Rainey GJ, Bradley KA and Young
JA: Human capillary morphogenesis protein 2 functions as an anthrax
toxin receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 100:5170–5174. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bradley KA, Mogridge J, Mourez M, Collier
RJ and Young JA: Identification of the cellular receptor for
anthrax toxin. Nature. 414:225–229. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Carson-Walter EB, Watkins DN, Nanda A,
Vogelstein B, Kinzler KW and St Croix B: Cell surface tumor
endothelial markers are conserved in mice and humans. Cancer Res.
61:6649–6655. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Emsley J, King SL, Bergelson JM and
Liddington RC: Crystal structure of the I domain from integrin
alpha2beta1. J Biol Chem. 272:28512–28517. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Davies G, Cunnick GH, Mansel RE, Mason MD
and Jiang WG: Levels of expression of endothelial markers specific
to tumour-associated endothelial cells and their correlation with
prognosis in patients with breast cancer. Clin Exp Metastasis.
21:31–37. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Rmali KA, Watkins G, Harrison G, Parr C,
Puntis MC and Jiang WG: Tumour endothelial marker 8 (TEM-8) in
human colon cancer and its association with tumour progression. Eur
J Surg Oncol. 30:948–953. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Rmali KA, Puntis MC and Jiang WG:
Prognostic values of tumor endothelial markers in patients with
colorectal cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 11:1283–1286. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Davies G, Rmali KA, Watkins G, Mansel RE,
Mason MD and Jiang WG: Elevated levels of tumour endothelial
marker-8 in human breast cancer and its clinical significance. Int
J Oncol. 29:1311–1317. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hanks S, Adams S, Douglas J, et al:
Mutations in the gene encoding capillary morphogenesis protein 2
cause juvenile hyaline fibromatosis and infantile systemic
hyalinosis. Am J Hum Genet. 73:791–800. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Dowling O, Difeo A, Ramirez MC, et al:
Mutations in capillary morphogenesis gene-2 result in the allelic
disorders juvenile hyaline fibromatosis and infantile systemic
hyalinosis. Am J Hum Genet. 73:957–966. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tumer L, Kasapkara C, Fong K, Serdaroglu A
and McGrath JA: Hyaline fibromatosis syndrome resulting from a new
homozygous missense mutation, p. Gly116Val, in ANTXR2. J Dermatol.
40:677–678. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Al Sinani S, Al Murshedy F and Abdwani R:
Infantile systemic hyalinosis: a case report with a novel mutation.
Oman Med J. 28:53–55. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang YY, Wen CQ, Wei Z and Jin X: A novel
splice site mutation in ANTXR2 (CMG2) gene results in systemic
hyalinosis. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 33:e355–e357. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yan SE, Lemmin T, Salvi S, et al: In-depth
analysis of hyaline fibromatosis syndrome frameshift mutations at
the same site reveal the necessity of personalized therapy. Hum
Mutat. 34:1005–1017. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Martchenko M, Candille SI, Tang H and
Cohen SN: Human genetic variation altering anthrax toxin
sensitivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 109:2972–2977. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Reveille JD, Sims AM, Danoy P, et al:
Genome-wide association study of ankylosing spondylitis identifies
non-MHC susceptibility loci. Nat Genet. 42:123–127. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Guo C, Xia Y, Yang Q, Qiu R, Zhao H and
Liu Q: Association of the ANTXR2 gene polymorphism and ankylosing
spondylitis in Chinese Han. Scand J Rheumatol. 41:29–32. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chen C, Zhang X and Wang Y: ANTXR2 and
IL-1R2 polymorphisms are not associated with ankylosing spondylitis
in Chinese Han population. Rheumatol Int. 32:15–19. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Peters DE, Zhang Y, Molinolo AA, et al:
Capillary morphogenesis protein-2 is required for mouse parturition
by maintaining uterine collagen homeostasis. Biochem Bioph Res Co.
422:393–397. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Reeves CV, Wang X, Charles-Horvath PC, et
al: Anthrax toxin receptor 2 functions in ECM homeostasis of the
murine reproductive tract and promotes MMP activity. PLoS One.
7:e348622012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Reeves CV, Dufraine J, Young JA and
Kitajewski J: Anthrax toxin receptor 2 is expressed in murine and
tumor vasculature and functions in endothelial proliferation and
morphogenesis. Oncogene. 29:789–801. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bonnekoh B, Wevers A, Jugert F, Merk H and
Mahrle G: Colorimetric growth assay for epidermal cell cultures by
their crystal violet binding capacity. Arch Dermatol Res.
281:487–490. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Jiang WG, Davies G, Martin TA, et al:
Targeting matrilysin and its impact on tumor growth in vivo: the
potential implications in breast cancer therapy. Clin Cancer Res.
11:6012–6019. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Jiang WG, Hiscox S, Hallett MB, Scott C,
Horrobin DF and Puntis MC: Inhibition of hepatocyte growth
factor-induced motility and in vitro invasion of human colon cancer
cells by gamma-linolenic acid. Br J Cancer. 71:744–752. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Rosen EM, Meromsky L, Setter E, Vinter DW
and Goldberg ID: Smooth muscle-derived factor stimulates mobility
of human tumor cells. Invasion Metastasis. 10:49–64.
1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Jiang WG, Hiscox S, Singhrao SK, Nakamura
T, Puntis MC and Hallett MB: Inhibition of HGF/SF-induced membrane
ruffling and cell motility by transient elevation of cytosolic free
Ca2+. Exp Cell Res. 220:424–433. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Jiang WG, Martin TA, Lewis-Russell JM,
Douglas-Jones A, Ye L and Mansel RE: Eplin-alpha expression in
human breast cancer, the impact on cellular migration and clinical
outcome. Mol Cancer. 7:712008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Cai J, Jiang WG and Mansel RE: Inhibition
of the expression of VE-cadherin/catenin complex by gamma linolenic
acid in human vascular endothelial cells, and its impact on
angiogenesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 258:113–118. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Grant DS, Tashiro K, Segui-Real B, Yamada
Y, Martin GR and Kleinman HK: Two different laminin domains mediate
the differentiation of human endothelial cells into capillary-like
structures in vitro. Cell. 58:933–943. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Cai J, Jiang WG and Mansel RE: Inhibition
of angiogenic factor- and tumour-induced angiogenesis by gamma
linolenic acid. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 60:21–29.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Jiang WG and Harding KG: Enhancement of
wound tissue expansion and angiogenesis by matrix-embedded
fibroblast (dermagraft), a role of hepatocyte growth factor/scatter
factor. Int J Mol Med. 2:203–210. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Chaudhary A and St Croix B: Selective
blockade of tumor angiogenesis. Cell Cycle. 11:2253–2259. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Liu S, Zhang Y, Hoover B and Leppla SH:
The receptors that mediate the direct lethality of anthrax toxin.
Toxins (Basel). 5:1–8. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Pilpa RM, Bayrhuber M, Marlett JM, Riek R
and Young JA: A receptor-based switch that regulates anthrax toxin
pore formation. PLoS Pathog. 7:e10023542011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Rogers MS, Christensen KA, Birsner AE, et
al: Mutant anthrax toxin B moiety (protective antigen) inhibits
angiogenesis and tumor growth. Cancer Res. 67:9980–9985. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Rmali KA, Puntis MC and Jiang WG: TEM-8
and tubule formation in endothelial cells, its potential role of
its vW/TM domains. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 334:231–238. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Abrami L, Leppla SH and van der Goot FG:
Receptor palmitoylation and ubiquitination regulate anthrax toxin
endocytosis. J Cell Biol. 172:309–320. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Liu S, Leung HJ and Leppla SH:
Characterization of the interaction between anthrax toxin and its
cellular receptors. Cell Microbiol. 9:977–987. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Garlick KM, Batty S and Mogridge J:
Binding of filamentous actin to anthrax toxin receptor 1 decreases
its association with protective antigen. Biochemistry.
51:1249–1256. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Cai C, Che J, Xu L, et al: Tumor
endothelium marker-8 based decoys exhibit superiority over
capillary morphogenesis protein-2 based decoys as anthrax toxin
inhibitors. PLoS One. 6:e206462011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Cryan LM, Bazinet L, Habeshian KA, et al:
1,2,3,4,6-Penta-O-galloyl-beta-D-glucopyranose inhibits
angiogenesis via inhibition of capillary morphogenesis gene 2. J
Med Chem. 56:1940–1945. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Cao S, Cryan L, Habeshian KA, et al:
Phenolic compounds as antiangiogenic CMG2 inhibitors from Costa
Rican endophytic fungi. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 22:5885–5888. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Rogers MS, Cryan LM, Habeshian KA, et al:
A FRET-based high throughput screening assay to identify inhibitors
of anthrax protective antigen binding to capillary morphogenesis
gene 2 protein. PLoS One. 7:e399112012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|