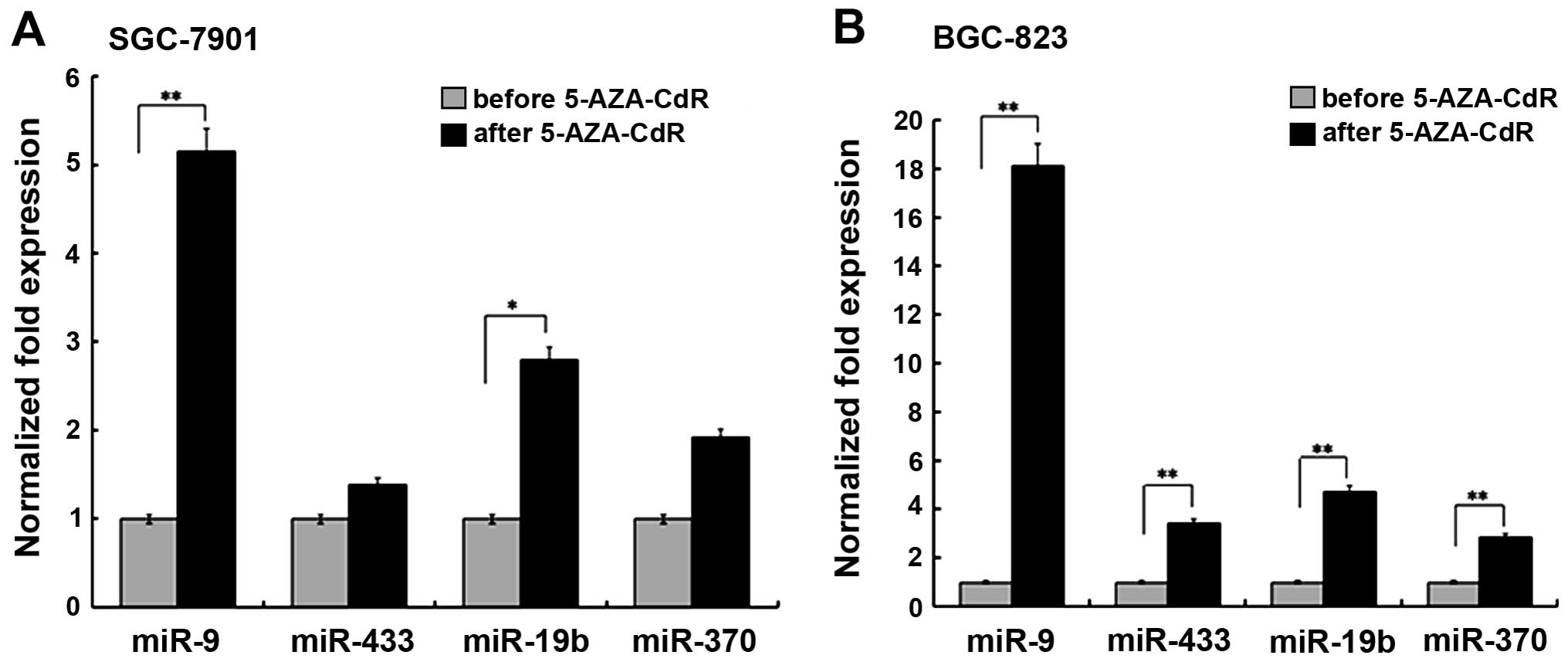
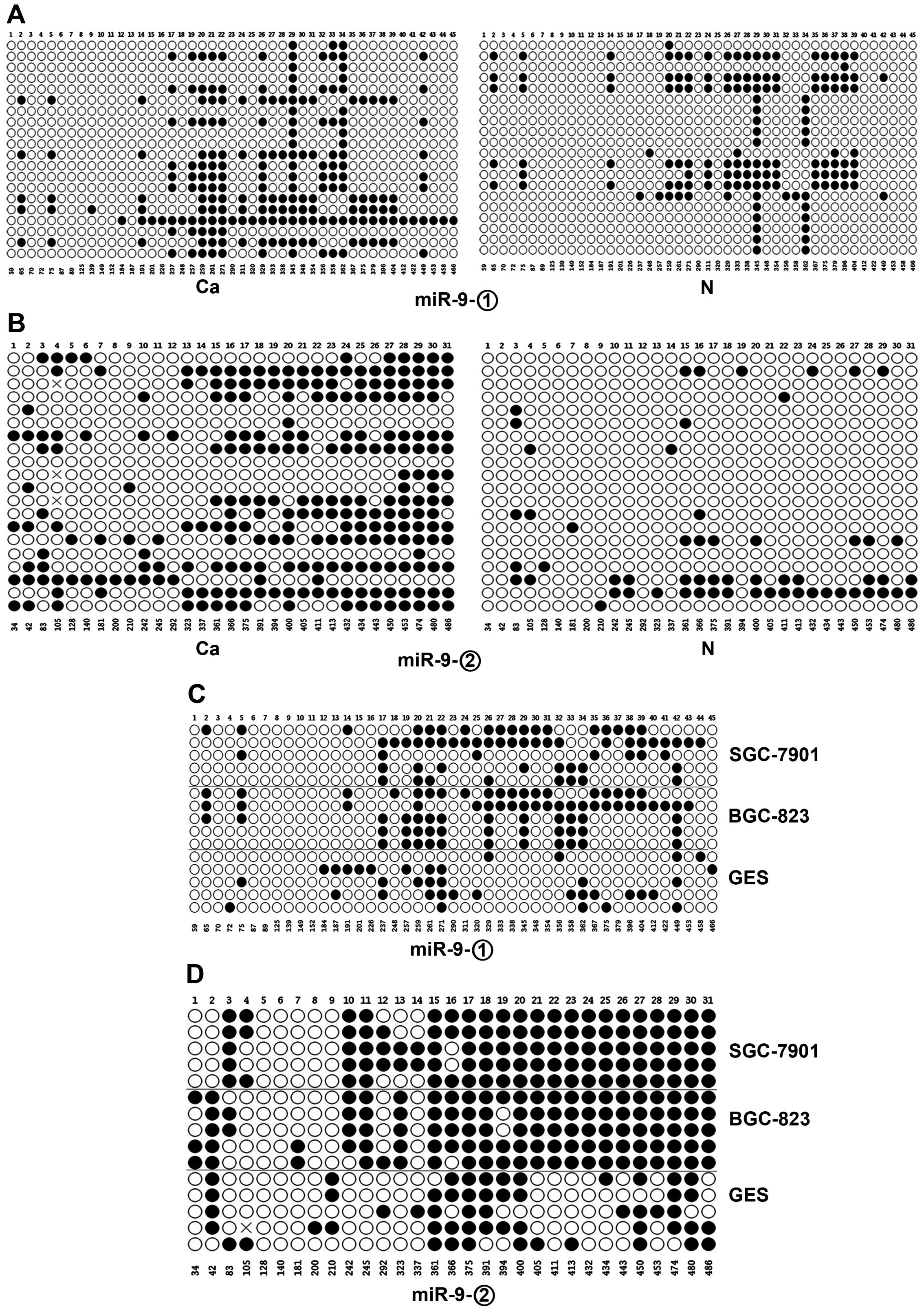
|
1
|
Zhang B, Pan X, Cobb GP and Anderson TA:
microRNAs as oncogenes and tumor suppressors. Dev Biol. 302:1–12.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Finnegan EJ and Matzke MA: The small RNA
world. J Cell Sci. 116:4689–4693. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Weber B, Stresemann C, Brueckner B and
Lyko F: Methylation of human microRNA genes in normal and
neoplastic cells. Cell Cycle. 6:1001–1005. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yanaihara N, Caplen N, Bowman E, et al:
Unique microRNA molecular profiles in lung cancer diagnosis and
prognosis. Cancer Cell. 9:189–198. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Wijnhoven BP, Michael MZ and Watson DI:
MicroRNAs and cancer. Br J Surg. 94:23–30. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Luo HC, Zhang ZZ, Zhang X, Ning B, Guo JJ,
Nie N, Liu B and Wu XL: MicroRNA expression signature in gastric
cancer. Chin J Cancer Res. 21:74–80. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, et al: MicroRNA
expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature. 435:834–838.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Li Z, Lu J, Sun M, et al: Distinct
microRNA expression profiles in acute myeloid leukemia with common
translocations. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 105:15535–15540. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Calin GA, Liu CG, Sevignani C, et al:
MicroRNA profiling reveals distinct signatures in B cell chronic
lymphocytic leukemias. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:11755–11760.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Volinia S, Calin GA, Liu CG, et al: A
microRNA expression signature of human solid tumors defines cancer
gene targets. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:2257–2261. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhang Z, Li Z, Gao C, et al: miR-21 plays
a pivotal role in gastric cancer pathogenesis and progression. Lab
Invest. 88:1358–1366. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Iorio MV, Ferracin M, Liu CG, et al:
MicroRNA gene expression deregulation in human breast cancer.
Cancer Res. 65:7065–7070. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Takamizawa J, Konishi H, Yanagisawa K, et
al: Reduced expression of the let-7 microRNAs in human lung cancers
in association with shortened postoperative survival. Cancer Res.
64:3753–3756. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Motoyama K, Inoue H, Nakamura Y, Uetake H,
Sugihara K and Mori M: Clinical significance of high mobility group
A2 in human gastric cancer and its relationship to let-7 microRNA
family. Clin Cancer Res. 14:2334–2340. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Varambally S, Cao Q, Mani RS, et al:
Genomic loss of microRNA-101 leads to overexpression of histone
methyltrans-ferase EZH2 in cancer. Science. 322:1695–1699. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Cimmino A, Calin GA, Fabbri M, et al:
miR-15 and miR-16 induce apoptosis by targeting BCL2. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 102:13944–13949. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Costinean S, Zanesi N, Pekarsky Y, et al:
Pre-B cell proliferation and lymphoblastic leukemia/high-grade
lymphoma in E(mu)-miR155 transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
103:7024–7029. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
O’Donnell KA, Wentzel EA, Zeller KI, Dang
CV and Mendell JT: c-Myc-regulated microRNAs modulate E2F1
expression. Nature. 435:839–843. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Murakami Y, Yasuda T, Saigo K, et al:
Comprehensive analysis of microRNA expression patterns in
hepatocellular carcinoma and non-tumorous tissues. Oncogene.
25:2537–2545. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Tsai KW, Liao YL, Wu CW, et al: Aberrant
hypermethylation of miR-9 genes in gastric cancer. Epigenetics.
6:1189–1197. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tanaka N, Toyooka S, Soh J, et al:
Frequent methylation and oncogenic role of microRNA-34b/c in
small-cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 76:32–38. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Suh SO, Chen Y, Zaman MS, et al:
MicroRNA-145 is regulated by DNA methylation and p53 gene mutation
in prostate cancer. Carcinogenesis. 32:772–778. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Balaguer F, Link A, Lozano JJ, et al:
Epigenetic silencing of miR-137 is an early event in colorectal
carcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 70:6609–6618. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhang Y, Wang X, Xu B, et al: Epigenetic
silencing of miR-126 contributes to tumor invasion and angiogenesis
in colorectal cancer. Oncol Rep. 30:1976–1984. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Schiffgen M, Schmidt DH, von Rücker A,
Müller SC and Ellinger J: Epigenetic regulation of microRNA
expression in renal cell carcinoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
436:79–84. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Michael MZ, O’ Connor SM, van Holst
Pellekaan NG, Young GP and James RJ: Reduced accumulation of
specific microRNAs in colorectal neoplasia. Mol Cancer Res.
1:882–891. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Luo H, Zhang H, Zhang Z, et al:
Downregulated miR-9 and miR-433 in human gastric carcinoma. J Exp
Clin Cancer Res. 28:822009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Du Y, Liu Z, Gu L, et al: Characterization
of human gastric carcinoma-related methylation of 9 miR CpG islands
and repression of their expressions in vitro and in vivo. BMC
Cancer. 12:2492012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Minor J, Wang X, Zhang F, et al:
Methylation of microRNA-9 is a specific and sensitive biomarker for
oral and oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinomas. Oral Oncol.
48:73–78. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Tanaka T, Arai M, Wu S, et al: Epigenetic
silencing of microRNA-373 plays an important role in regulating
cell proliferation in colon cancer. Oncol Rep. 26:1329–1335.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lujambio A, Calin GA, Villanueva A, et al:
A microRNA DNA methylation signature for human cancer metastasis.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 105:13556–13561. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Datta J, Kutay H, Nasser MW, et al:
Methylation mediated silencing of MicroRNA-1 gene and its role in
hepatocellular carcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 68:5049–5058. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Toyota M, Suzuki H, Sasaki Y, et al:
Epigenetic silencing of microRNA-34b/c and B-cell translocation
gene 4 is associated with CpG island methylation in colorectal
cancer. Cancer Res. 68:4123–4132. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ando T, Yoshida T, Enomoto S, et al: DNA
methylation of microRNA genes in gastric mucosae of gastric cancer
patients: its possible involvement in the formation of epigenetic
field defect. Int J Cancer. 124:2367–2374. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lehmann U, Hasemeier B, Christgen M, et
al: Epigenetic inactivation of microRNA gene hsa-mir-9-1 in human
breast cancer. J Pathol. 214:17–24. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Grady WM, Parkin RK, Mitchell PS, et al:
Epigenetic silencing of the intronic microRNA hsa-miR-342 and its
host gene EVL in colorectal cancer. Oncogene. 27:3880–3888. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Suzuki H, Maruyama R, Yamamoto E and Kai
M: DNA methylation and microRNA dysregulation in cancer. Mol Oncol.
6:567–578. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Guo LH, Li H, Wang F, Yu J and He JS: The
tumor suppressor roles of miR-433 and miR-127 in gastric cancer.
Int J Mol Sci. 14:14171–14184. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wada R, Akiyama Y, Hashimoto Y, Fukamachi
H and Yuasa Y: miR-212 is downregulated and suppresses
methyl-CpG-binding protein MeCP2 in human gastric cancer. Int J
Cancer. 127:1106–1114. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Hashimoto Y, Akiyama Y, Otsubo T, Shimada
S and Yuasa Y: Involvement of epigenetically silenced microRNA-181c
in gastric carcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis. 31:777–784. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Shen R, Pan S, Qi S, Lin X and Cheng S:
Epigenetic repression of microRNA-129-2 leads to overexpression of
SOX4 in gastric cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 394:1047–1052.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Suzuki H, Yamamoto E, Nojima M, et al:
Methylation-associated silencing of microRNA-34b/c in gastric
cancer and its involvement in an epigenetic field defect.
Carcinogenesis. 31:2066–2073. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Rotkrua P, Akiyama Y, Hashimoto Y, Otsubo
T and Yuasa Y: MiR-9 downregulates CDX2 expression in gastric
cancer cells. Int J Cancer. 129:2611–2620. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Tsai KW, Wu CW, Hu LY, et al: Epigenetic
regulation of miR-34b and miR-129 expression in gastric cancer. Int
J Cancer. 129:2600–2610. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Zhu A, Xia J, Zuo J, et al: MicroRNA-148a
is silenced by hypermethylation and interacts with DNA
methyltransferase 1 in gastric cancer. Med Oncol. 29:2701–2709.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Li P, Chen X, Su L, et al: Epigenetic
silencing of miR-338-3p contributes to tumorigenicity in gastric
cancer by targeting SSX2IP. PloS One. 8:e667822013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Lei H, Zou D, Li Z, et al:
MicroRNA-219-2-3p functions as a tumor suppressor in gastric cancer
and is regulated by DNA methylation. PLoS One. 8:e603692013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Deng H, Guo Y, Song H, et al: MicroRNA-195
and microRNA-378 mediate tumor growth suppression by epigenetical
regulation in gastric cancer. Gene. 518:351–359. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Li Y, Li B, Zhang Y, Xiang CP, Li YY and
Wu XL: Serial observations on an orthotopic gastric cancer model
constructed using improved implantation technique. World J
Gastroenterol. 17:1442–1447. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Momparler RL: Pharmacology of
5-Aza-2′-deoxycytidine (decitabine). Semin Hematol. 42(Suppl 2):
S9–S16. 2005.
|
|
51
|
Takai D and Jones PA: The CpG island
searcher: a new WWW resource. In silico Biol. 3:235–240.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Chen Q, Chen X, Zhang M, Fan Q, Luo S and
Cao X: miR-137 is frequently down-regulated in gastric cancer and
is a negative regulator of Cdc42. Dig Dis Sci. 56:2009–2016. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Yamamoto E, Suzuki H, Maruyama R and
Shinomura Y: Developing technologies for epigenomic analysis and
clinical application of molecular diagnosis. Rinsho Byori.
60:637–643. 2012.(In Japanese).
|
|
54
|
Langevin SM, Stone RA, Bunker CH, et al:
MicroRNA-137 promoter methylation is associated with poorer overall
survival in patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the head and
neck. Cancer. 117:1454–1462. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Furuta M, Kozaki KI, Tanaka S, Arii S,
Imoto I and Inazawa J: miR-124 and miR-203 are epigenetically
silenced tumor-suppressive microRNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Carcinogenesis. 31:766–776. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Li Y, Kong D, Ahmad A, Bao B, Dyson G and
Sarkar FH: Epigenetic deregulation of miR-29a and miR-1256 by
isoflavone contributes to the inhibition of prostate cancer cell
growth and invasion. Epigenetics. 7:940–949. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Momparler RL: Epigenetic therapy of cancer
with 5-aza-2′-deoxy-cytidine (decitabine). Semin Oncol. 32:443–451.
2005.
|