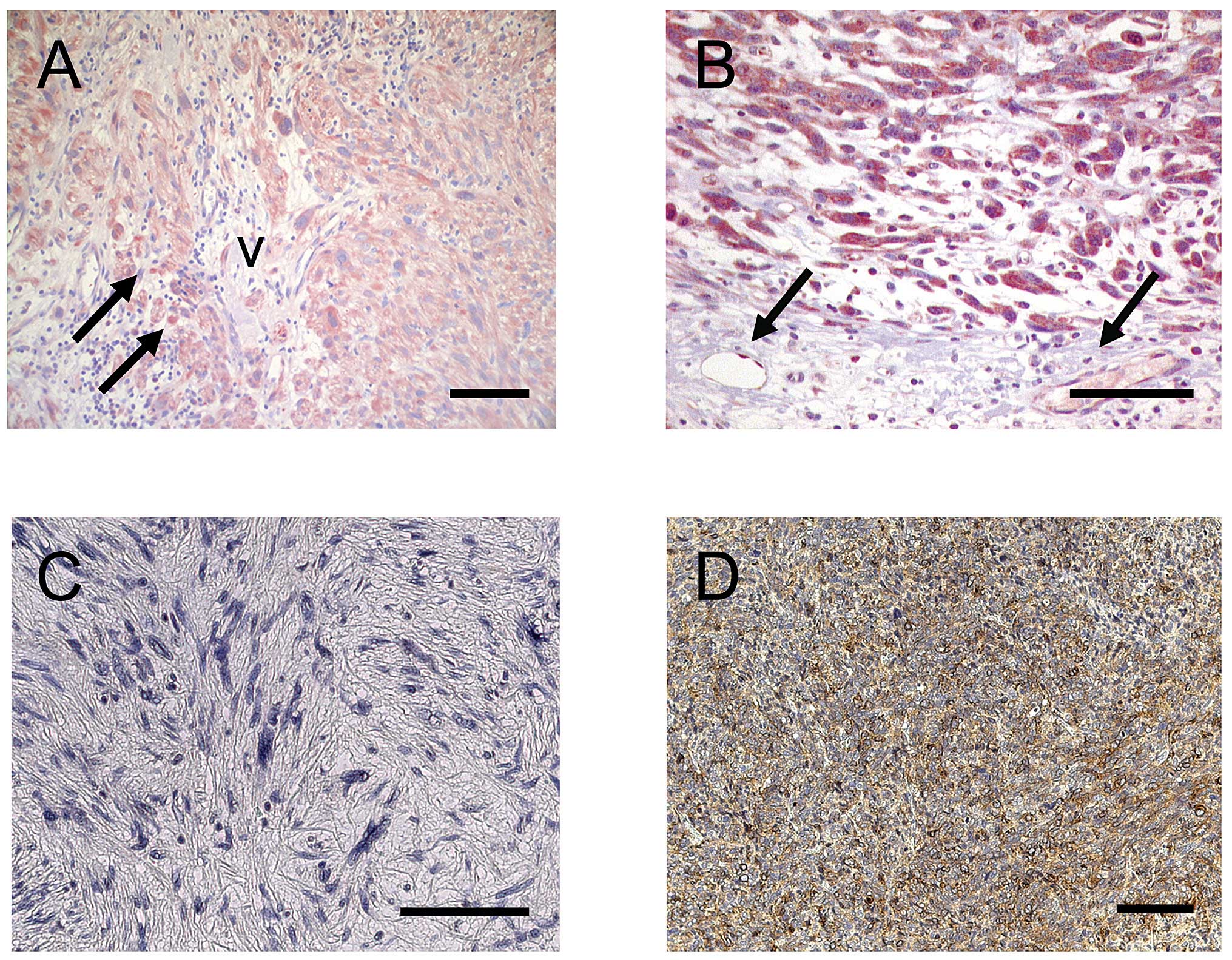
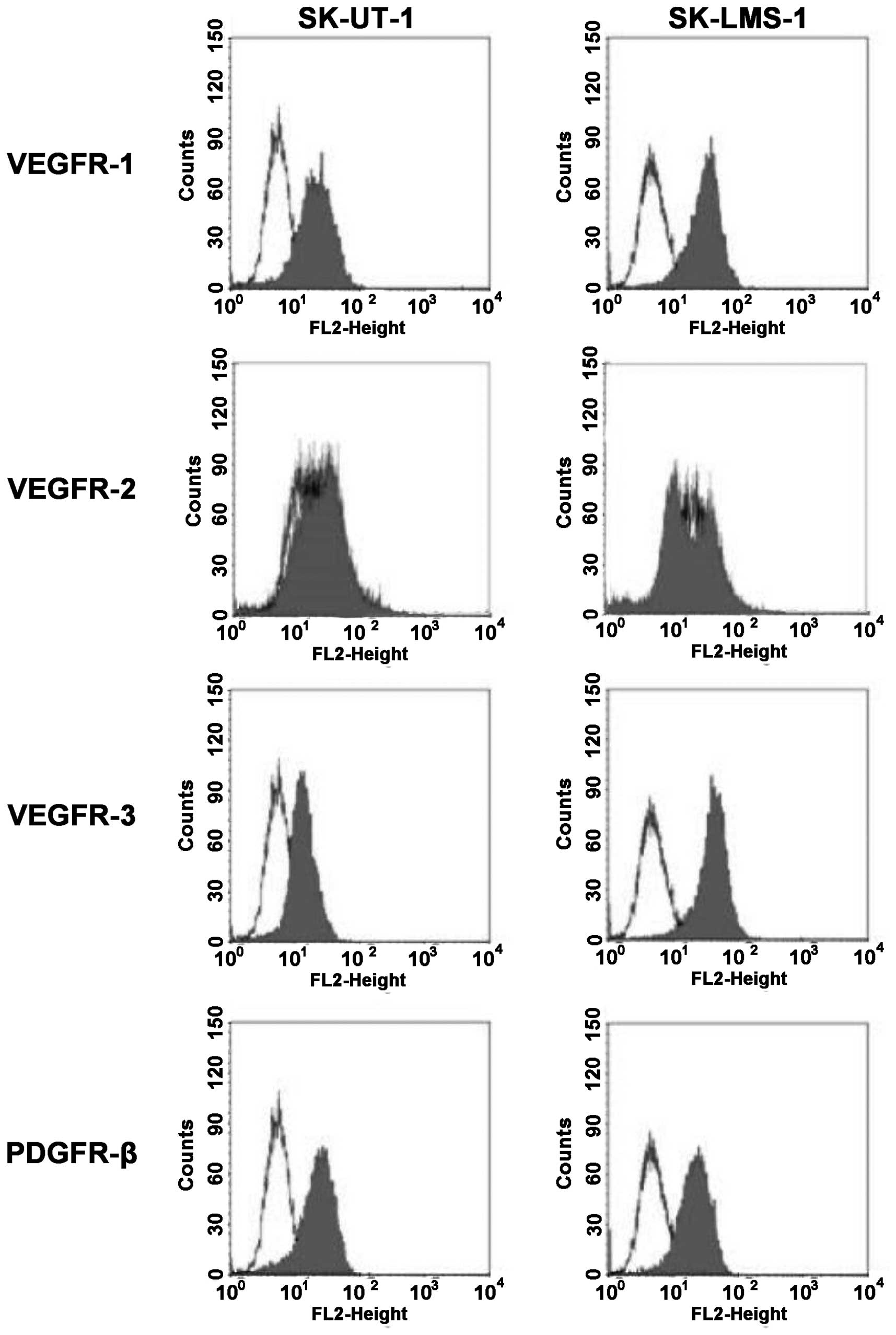
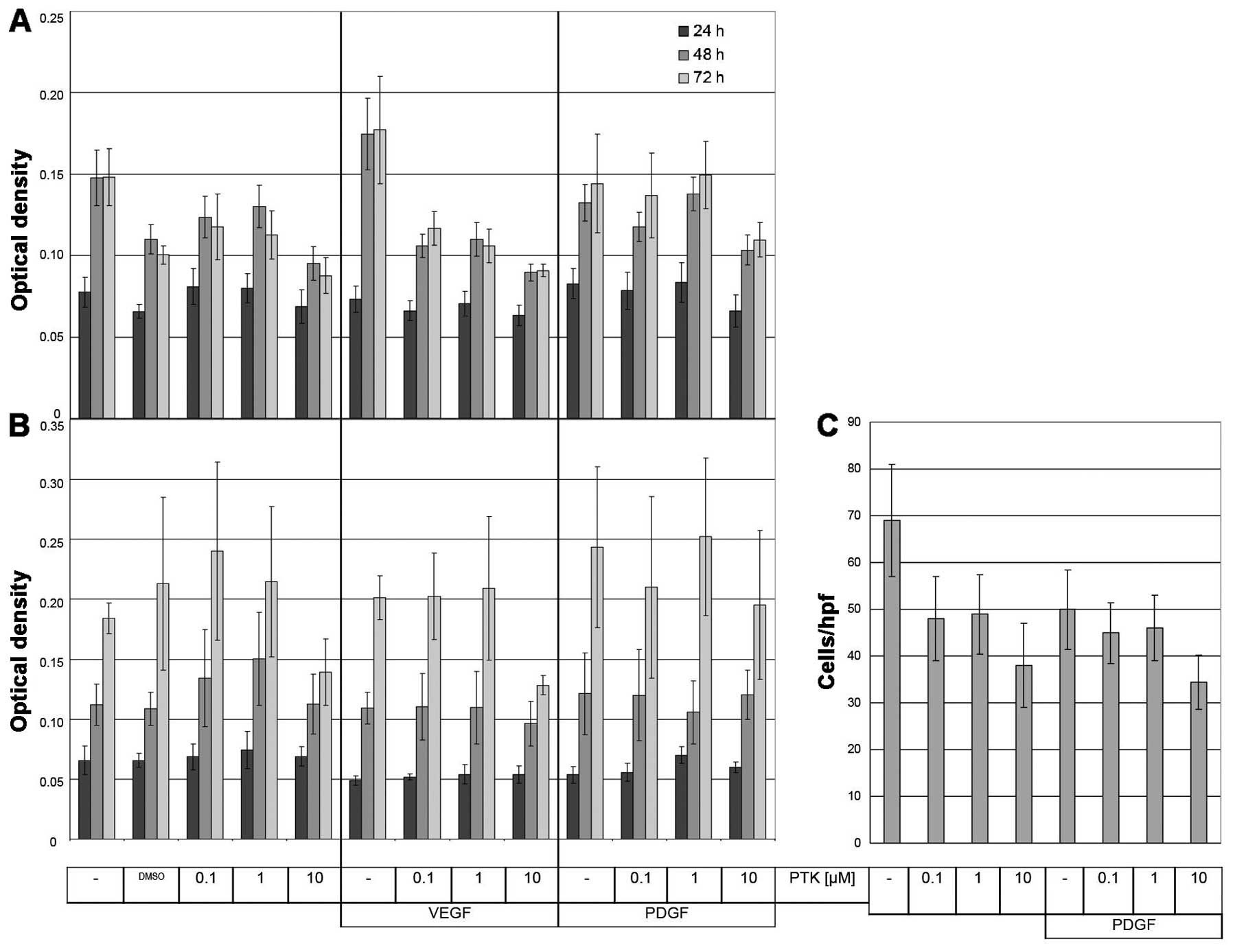
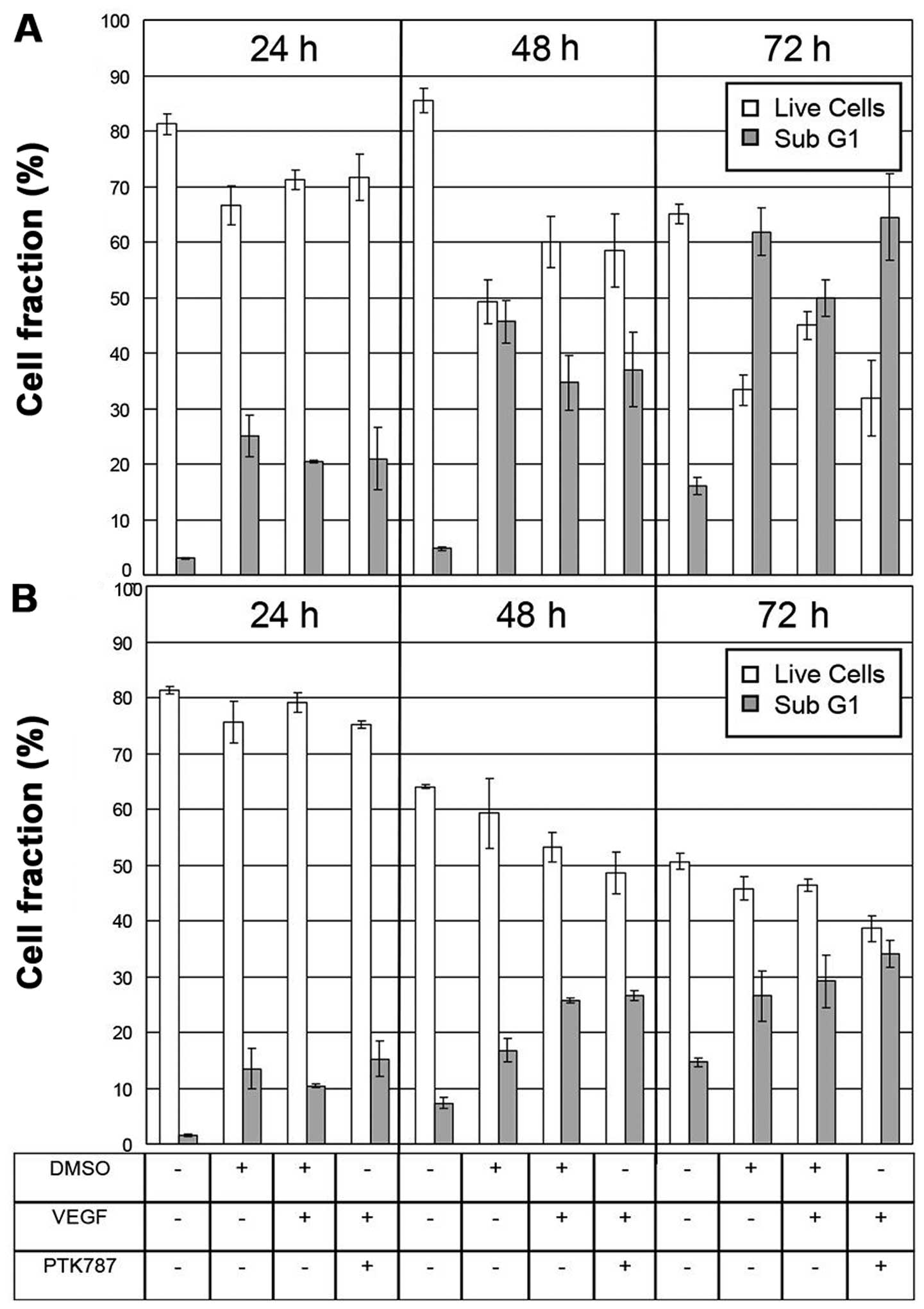
|
1
|
García-Martínez E, Egea Prefasi L,
García-Donas J, Escolar-Pérez PP, Pastor F and González-Martín A:
Current management of uterine sarcomas. Clin Transl Oncol.
13:307–314. 2011.
|
|
2
|
Gaumann AK, Schermutzki G, Mentzel T,
Kirkpatrick CJ, Kriegsmann JB and Konerding MA: Microvessel density
and VEGF/VEGF receptor status and their role in sarcomas of the
pulmonary artery. Oncol Rep. 19:309–318. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Maki RG: Gemcitabine and docetaxel in
metastatic sarcoma: past, present, and future. Oncologist.
12:999–1006. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Carmeliet P and Jain RK: Molecular
mechanisms and clinical applications of angiogenesis. Nature.
473:298–307. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Paesler J, Gehrke I, Gandhirajan RK, et
al: The vascular endothelial growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase
inhibitors vatalanib and pazopanib potently induce apoptosis in
chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells in vitro and in vivo. Clin
Cancer Res. 16:3390–3398. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Lin B, Podar K, Gupta D, et al: The
vascular endothelial growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase
inhibitor PTK787/ZK222584 inhibits growth and migration of multiple
myeloma cells in the bone marrow microenvironment. Cancer Res.
62:5019–5026. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Masood R, Cai J, Zheng T, Smith DL, Hinton
DR and Gill PS: Vascular endothelial growth factor VEGF is an
autocrine growth factor for VEGF receptor-positive human tumors.
Blood. 98:1904–1913. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Dias S, Hattori K, Zhu Z, et al: Autocrine
stimulation of VEGFR-2 activates human leukemic cell growth and
migration. J Clin Invest. 106:511–521. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Podar K, Tai YT, Davies FE, et al:
Vascular endothelial growth factor triggers signalling cascades
mediating multiple myeloma cell growth and migration. Blood.
98:428–435. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Volm M, Koomagi R and Mattern J: Vascular
endothelial growth factor and basic fibroblast growth factor in
primary lung carcinomas and the incidence of metastases. Int J
Oncol. 9:711–714. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Itakura J, Ishiwata T, Shen B, Kornmann M
and Korc M: Concomitant over-expression of vascular endothelial
growth factor and its receptors in pancreatic cancer. Int J Cancer.
85:27–34. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Charnock-Jones DS, Sharkey AM, Boocock CA,
Ahmed A, Plevin R, Ferrara N and Smith SK: Vascular endothelial
growth factor receptor localization and activation in human
trophoblast and choriocarcinoma cells. Biol Reprod. 51:524–530.
1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Liu B, Earl HM, Baban D, Shoaibi M, Fabra
A, Kerr DJ and Seymour LW: Melanoma cell lines express VEGF
receptor KDR and respond to exogenously added VEGF. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 217:721–727. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Los M, Roodhart JM and Voest EE: Target
practice: lessons from phase III trials with bevacizumab and
vatalanib in the treatment of advanced colorectal cancer.
Oncologist. 12:443–450. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Escudier B, Eisen T, Stadler WM, et al:
Sorafenib for treatment of renal cell carcinoma: Final efficacy and
safety results of the phase III treatment approaches in renal
cancer global evaluation trial. J Clin Oncol. 27:3312–3318. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Rini BI, Escudier B, Tomczak P, et al:
Comparative effectiveness of axitinib versus sorafenib in advanced
renal cell carcinoma (AXIS): a randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet.
378:1931–1939. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V, et al:
Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med.
359:378–390. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hecht JR, Trarbach T, Hainsworth JD, et
al: Randomized, placebo-controlled, phase III study of first-line
oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy plus PTK787/ZK 222584, an oral
vascular endothelial growth factor receptor inhibitor, in patients
with metastatic colorectal adenocarcinoma. J Clin Oncol.
29:1997–2003. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Bergers G, Song S, Meyer-Morse N,
Bergsland E and Hanahan D: Benefits of targeting both pericytes and
endothelial cells in the tumor vasculature with kinase inhibitors.
J Clin Invest. 111:1287–1295. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wood JM, Bold G, Buchdunger E, et al:
PTK787/ZK 222584, a novel and potent inhibitor of vascular
endothelial growth factor receptor tyrosine kinases, impairs
vascular endothelial growth factor-induced responses and tumor
growth after oral administration. Cancer Res. 60:2178–2189.
2000.
|
|
21
|
Hasumi Y, Kłosowska-Wardega A, Furuhashi
M, Ostman A, Heldin CH and Hellberg C: Identification of a subset
of pericytes that respond to combination therapy targeting PDGF and
VEGF signalling. Int J Cancer. 121:2606–2614. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Erber R, Thurnher A, Katsen AD, et al:
Combined inhibition of VEGF and PDGF signalling enforces tumor
vessel regression by interfering with pericyte-mediated endothelial
cell survival mechanisms. FASEB J. 18:338–340. 2004.
|
|
23
|
De Bock K, Mazzone M and Carmeliet P:
Antiangiogenic therapy, hypoxia, and metastasis: risky liaisons, or
not? Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 8:393–404. 2011.
|
|
24
|
Drevs J, Müller-Driver R, Wittig C, et al:
PTK787/ZK 222584, a specific vascular endothelial growth
factor-receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, affects the anatomy of
the tumor vascular bed and the functional vascular properties as
detected by dynamic enhanced magnetic resonance imaging. Cancer
Res. 62:4015–4022. 2002.
|
|
25
|
Drevs J, Hofmann I, Hugenschmidt H, et al:
Effects of PTK787/ZK 222584, a specific inhibitor of vascular
endothelial growth factor receptor tyrosine kinases, on primary
tumor, metastasis, vessel density, and blood flow in a murine renal
cell carcinoma model. Cancer Res. 60:4819–4824. 2000.
|
|
26
|
Schomber T, Zumsteg A, Strittmatter K, et
al: Differential effects of the vascular endothelial growth factor
receptor inhibitor PTK787/ZK222584 on tumor angiogenesis and tumor
lymphangiogenesis. Mol Cancer Ther. 8:55–63. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Gauler TC, Besse B, Mauguen A, et al:
Phase II trial of PTK787/ZK 222584 vatalanib administered orally
once-daily or in two divided daily doses as second-line monotherapy
in relapsed or progressing patients with stage IIIB/IV
non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Ann Oncol. 23:678–687. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Van Cutsem E, Bajetta E, Valle J, et al:
Randomized, placebo-controlled, phase III study of oxaliplatin,
fluorouracil, and leucovorin with or without PTK787/ZK 222584 in
patients with previously treated metastatic colorectal
adenocarcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 29:2004–2010. 2011.
|
|
29
|
Hewett PW and Murray JC: Isolation of
microvascular endothelial cells using magnetic beads coated with
anti-PECAM-1 antibodies. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 32:4621996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Jaffe EA, Nachman RL, Becker CG and Minick
CR: Culture of human endothelial cells derived from umbilical
veins. Identification by morphologic and immunologic criteria. J
Clin Invest. 52:2745–2756. 1973. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Bauer TW, Fan F, Liu W, et al: Targeting
of insulin-like growth factor-I receptor with a monoclonal antibody
inhibits growth of hepatic metastases from human colon carcinoma in
mice. Ann Surg Oncol. 14:2838–2846. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhao X and Guan JL: Focal adhesion kinase
and its signalling pathways in cell migration and angiogenesis. Adv
Drug Deliv Rev. 63:610–615. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Deakin NO and Turner CE: Paxillin comes of
age. J Cell Sci. 121:2435–2444. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Jain RK, Duda DG, Willett CG, et al:
Biomarkers of response and resistance to antiangiogenic therapy.
Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 6:327–338. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Murakami M, Kobayashi S, Marubashi S, et
al: Tyrosine kinase inhibitor PTK/ZK enhances the antitumor effects
of interferon-α/5-fluorouracil therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma
cells. Ann Surg Oncol. 18:589–596. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Yang ZF, Poon RT, Liu Y, et al: High doses
of tyrosine kinase inhibitor PTK787 enhance the efficacy of
ischemic hypoxia for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma:
dual effects on cancer cell and angiogenesis. Mol Cancer Ther.
5:2261–2270. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Riesterer O, Oehler-Jänne C, Jochum W,
Broggini-Tenzer A, Vuong V and Pruschy M: Ionizing radiation and
inhibition of angiogenesis in a spontaneous mammary carcinoma and
in a syngenic heterotopic allograft tumor model: a comparative
study. Radiat Oncol. 6:662011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Barleon B, Sozzani S, Zhou D, Weich HA,
Mantovani A and Marmé D: Migration of human monocytes in response
to vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is mediated via the
VEGF receptor flt-1. Blood. 87:3336–3343. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|