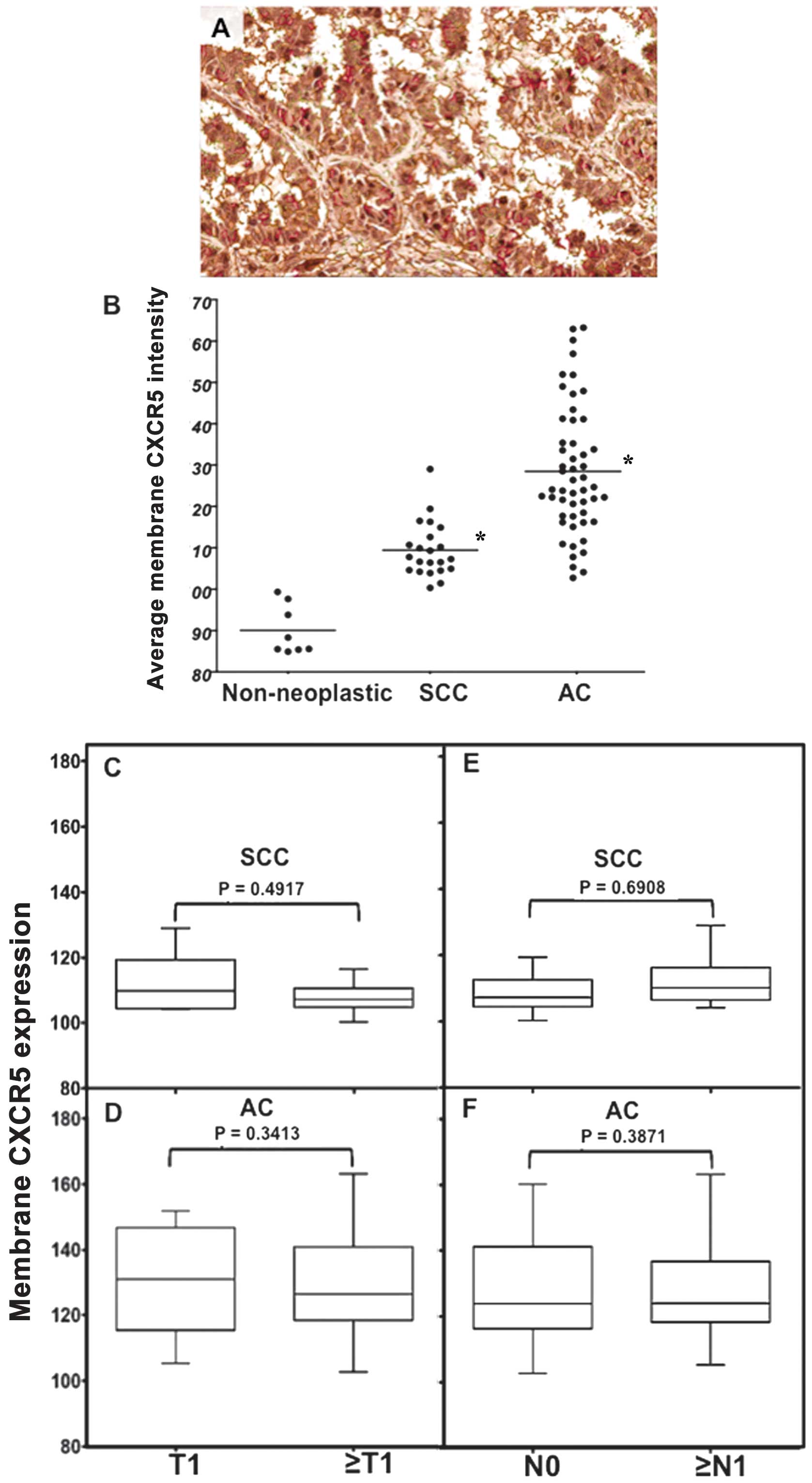
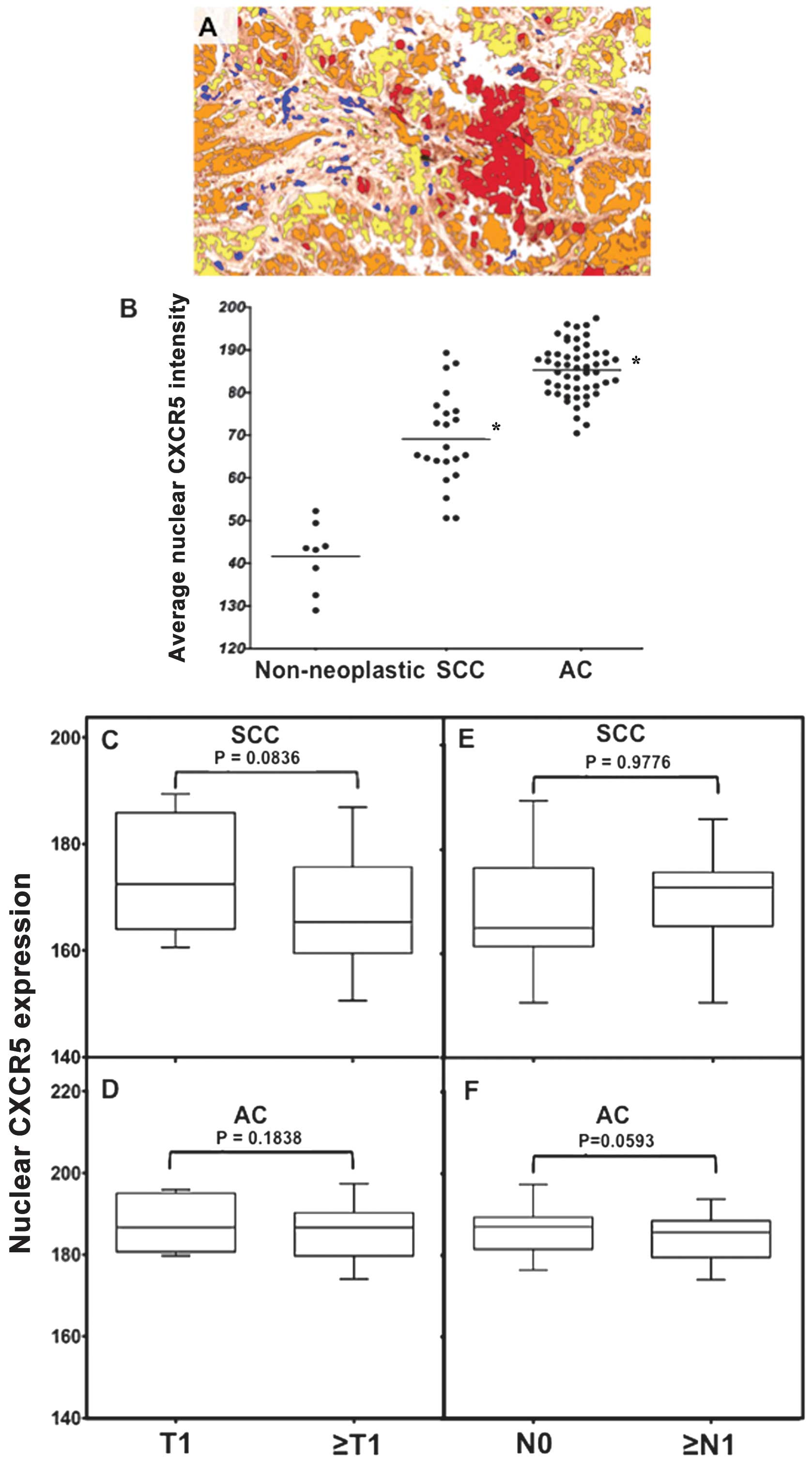
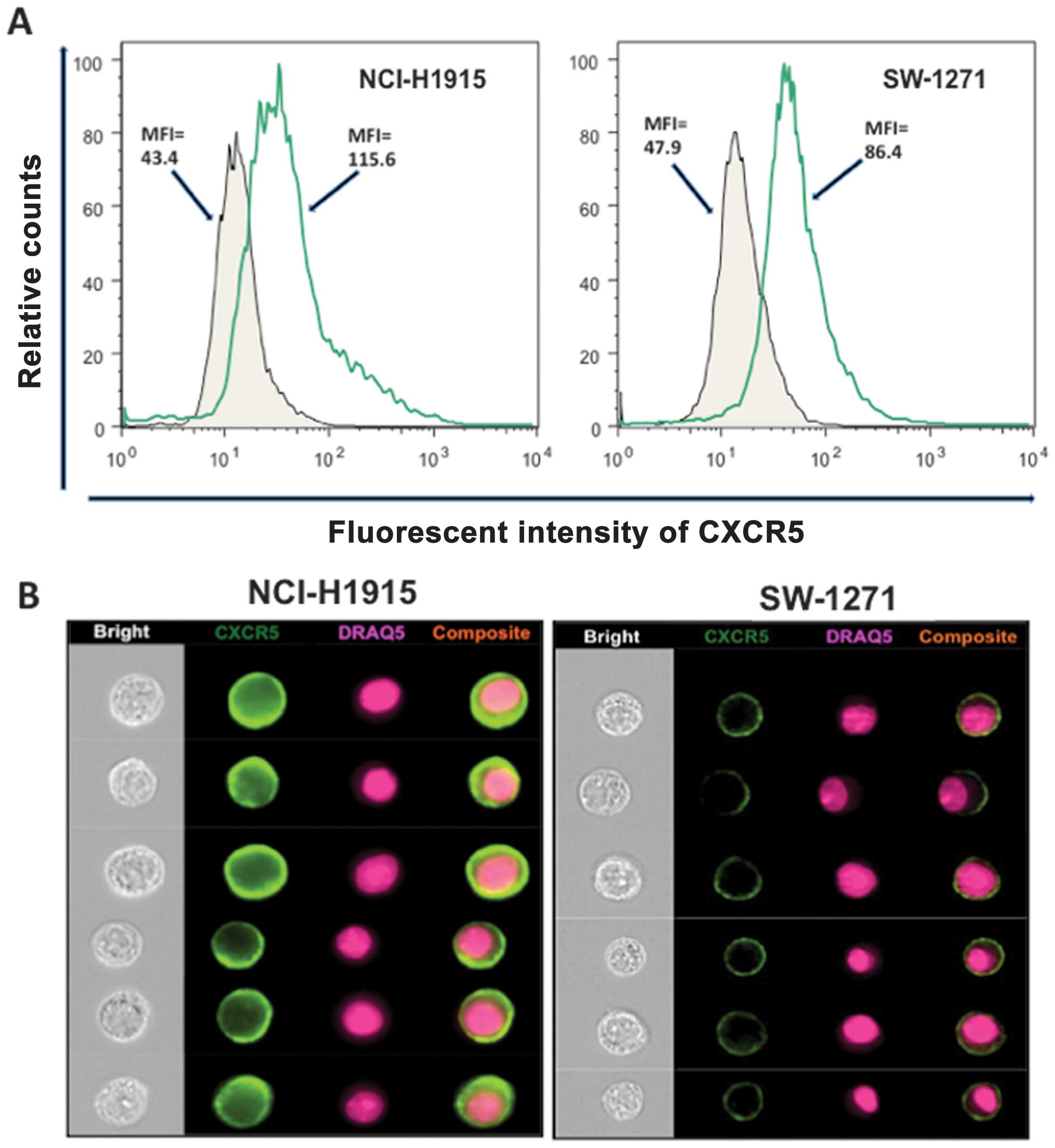
|
1
|
Esposito L, Conti D, Ailavajhala R, Khalil
N and Giordano A: Lung cancer: are we up to the challenge? Curr
Genomics. 11:513–518. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Molina JR, Yang P, Cassivi SD, Schild SE
and Adjei AA: Non-small cell lung cancer: epidemiology, risk
factors, treatment, and survivorship. Mayo Clin Proc. 83:584–594.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Baird AM, Gray SG and O’Byrne KJ:
Epigenetics underpinning the regulation of the CXC (ELR+)
chemokines in non-small cell lung cancer. PLoS One. 6:e145932011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lazennec G and Richmond A: Chemokines and
chemokine receptors: new insights into cancer-related inflammation.
Trends Mol Med. 16:133–144. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Su L, Zhang J, Xu H, Wang Y, Chu Y, Liu R
and Xiong S: Differential expression of CXCR4 is associated with
the meta-static potential of human non-small cell lung cancer
cells. Clin Cancer Res. 11:8273–8280. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Burger JA and Kipps TJ: CXCR4: a key
receptor in the crosstalk between tumor cells and their
microenvironment. Blood. 107:1761–1767. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bürkle A, Niedermeier M, Schmitt-Gräff A,
Wierda WG, Keating MJ and Burger JA: Overexpression of the CXCR5
chemokine receptor, and its ligand, CXCL13 in B-cell chronic
lymphocytic leukemia. Blood. 110:3316–3325. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hussain SK, Zhu W, Chang SC, et al: Serum
levels of the chemokine CXCL13, genetic variation in CXCL13 and its
receptor CXCR5, and HIV-associated non-Hodgkin B-Cell lymphoma
risk. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 22:295–307. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kurtova AV, Tamayo AT, Ford RJ and Burger
JA: Mantle cell lymphoma cells express high levels of CXCR4, CXCR5,
and VLA-4 (CD49d): importance for interactions with the stromal
microenvironment and specific targeting. Blood. 113:4604–4613.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chan CC, Shen D, Hackett JJ, Buggage RR
and Tuaillon N: Expression of chemokine receptors, CXCR4 and CXCR5,
and chemokines, BLC and SDF-1, in the eyes of patients with primary
intraocular lymphoma. Ophthalmology. 110:421–426. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Singh S, Singh R, Singh UP, et al:
Clinical and biological significance of CXCR5 expressed by prostate
cancer specimens and cell lines. Int J Cancer. 125:2288–2295. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Singh S, Singh R, Sharma PK, et al: Serum
CXCL13 positively correlates with prostatic disease,
prostate-specific antigen and mediates prostate cancer cell
invasion, integrin clustering and cell adhesion. Cancer Lett.
283:29–35. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Panse J, Friedrichs K, Marx A, et al:
Chemokine CXCL13 is overexpressed in the tumour tissue and in the
peripheral blood of breast cancer patients. Br J Cancer.
99:930–938. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Del Grosso F, Coco S, Scaruffi P, et al:
Role of CXCL13-CXCR5 crosstalk between malignant neuroblastoma
cells and Schwannian stromal cells in neuroblastic tumors. Mol
Cancer Res. 9:815–823. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yuvaraj S, Griffin AC, Sundaram K,
Kirkwood KL, Norris JS and Reddy SV: A novel function of CXCL13 to
stimulate RANK ligand expression in oral squamous cell carcinoma
cells. Mol Cancer Res. 7:1399–1407. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Airoldi I, Cocco C, Morandi F, Prigione I
and Pistoia V: CXCR5 may be involved in the attraction of human
metastatic neuroblastoma cells to the bone marrow. Cancer Immunol
Immunother. 57:541–548. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
El Haibi CP, Sharma PK, Singh R, Johnson
PR, Suttles J, Singh S and Lillard JW Jr: PI3Kp110-, Src-,
FAK-dependent and DOCK2-independent migration and invasion of
CXCL13-stimulated prostate cancer cells. Mol Cancer.
9:852010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
El-Haibi CP, Singh R, Sharma PK, Singh S
and Lillard JW Jr: CXCL13 mediates prostate cancer cell
proliferation through JNK signalling and invasion through ERK
activation. Cell Prolif. 44:311–319. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Iwakiri S, Mino N, Takahashi T, et al:
Higher expression of chemokine receptor CXCR7 is linked to early
and metastatic recurrence in pathological stage I nonsmall cell
lung cancer. Cancer. 115:2580–2593. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Rollins BJ: Chemokines. Blood. 90:909–928.
1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Taub DD: Chemokine-leukocyte interactions.
The voodoo that they do so well. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev.
7:355–376. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Spano JP, Andre F, Morat L, et al:
Chemokine receptor CXCR4 and early-stage non-small cell lung
cancer: pattern of expression and correlation with outcome. Ann
Oncol. 15:613–617. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhu YM, Webster SJ, Flower D and Woll PJ:
Interleukin-8/CXCL8 is a growth factor for human lung cancer cells.
Br J Cancer. 91:1970–1976. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Phillips RJ, Burdick MD, Lutz M, Belperio
JA, Keane MP and Strieter RM: The stromal derived
factor-1/CXCL12-CXC chemokine receptor 4 biological axis in
non-small cell lung cancer metastases. Am J Respir Crit Care Med.
167:1676–1686. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Saintigny P, Massarelli E, Lin S, et al:
CXCR2 expression in tumor cells is a poor prognostic factor and
promotes invasion and metastasis in lung adenocarcinoma. Cancer
Res. 73:571–582. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chen JJ, Yao PL, Yuan A, et al:
Up-regulation of tumor interleukin-8 expression by infiltrating
macrophages: its correlation with tumor angiogenesis and patient
survival in non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 9:729–737.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ichinose Y, Yano T, Asoh H, Yokoyama H,
Yoshino I and Katsuda Y: Prognostic factors obtained by a
pathologic examination in completely resected non-small-cell lung
cancer. An analysis in each pathologic stage. J Thorac Cardiovasc
Surg. 110:601–605. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Suzuki K, Nagai K, Yoshida J, Nishimura M,
Takahashi K, Yokose T and Nishiwaki Y: Conventional
clinicopathologic prognostic factors in surgically resected
nonsmall cell lung carcinoma. A comparison of prognostic factors
for each pathologic TNM stage based on multivariate analyses.
Cancer. 86:1976–1984. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|