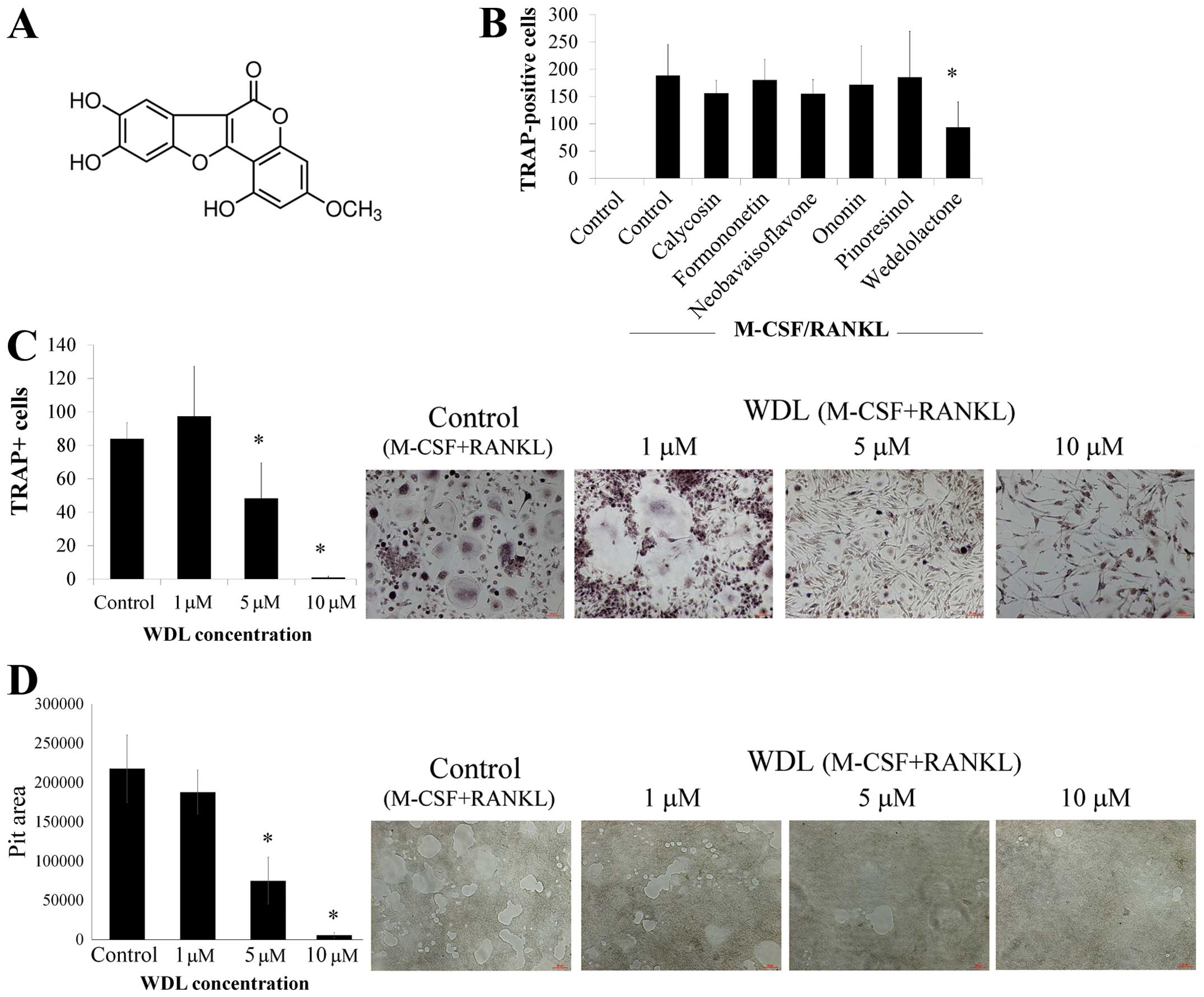
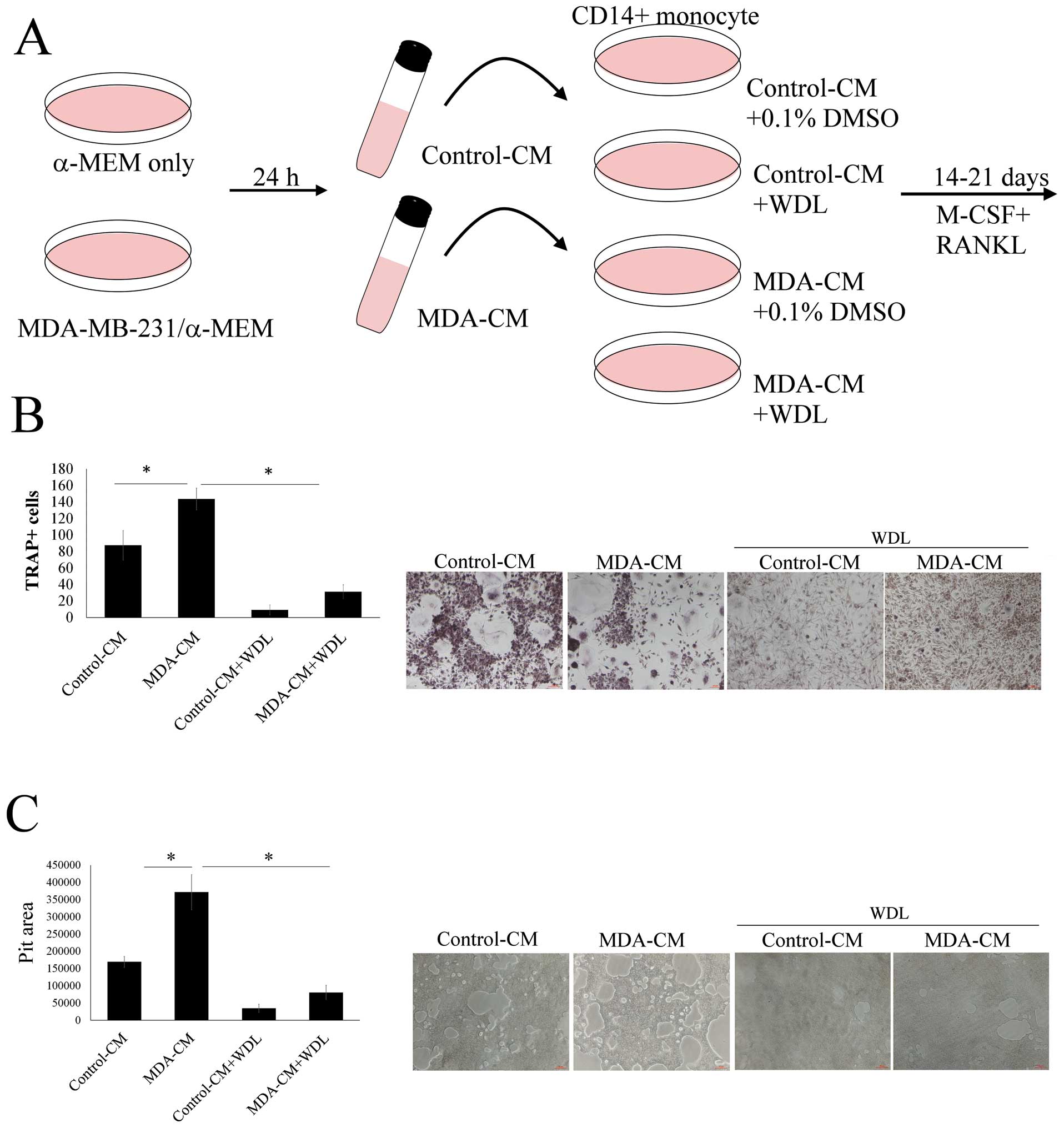
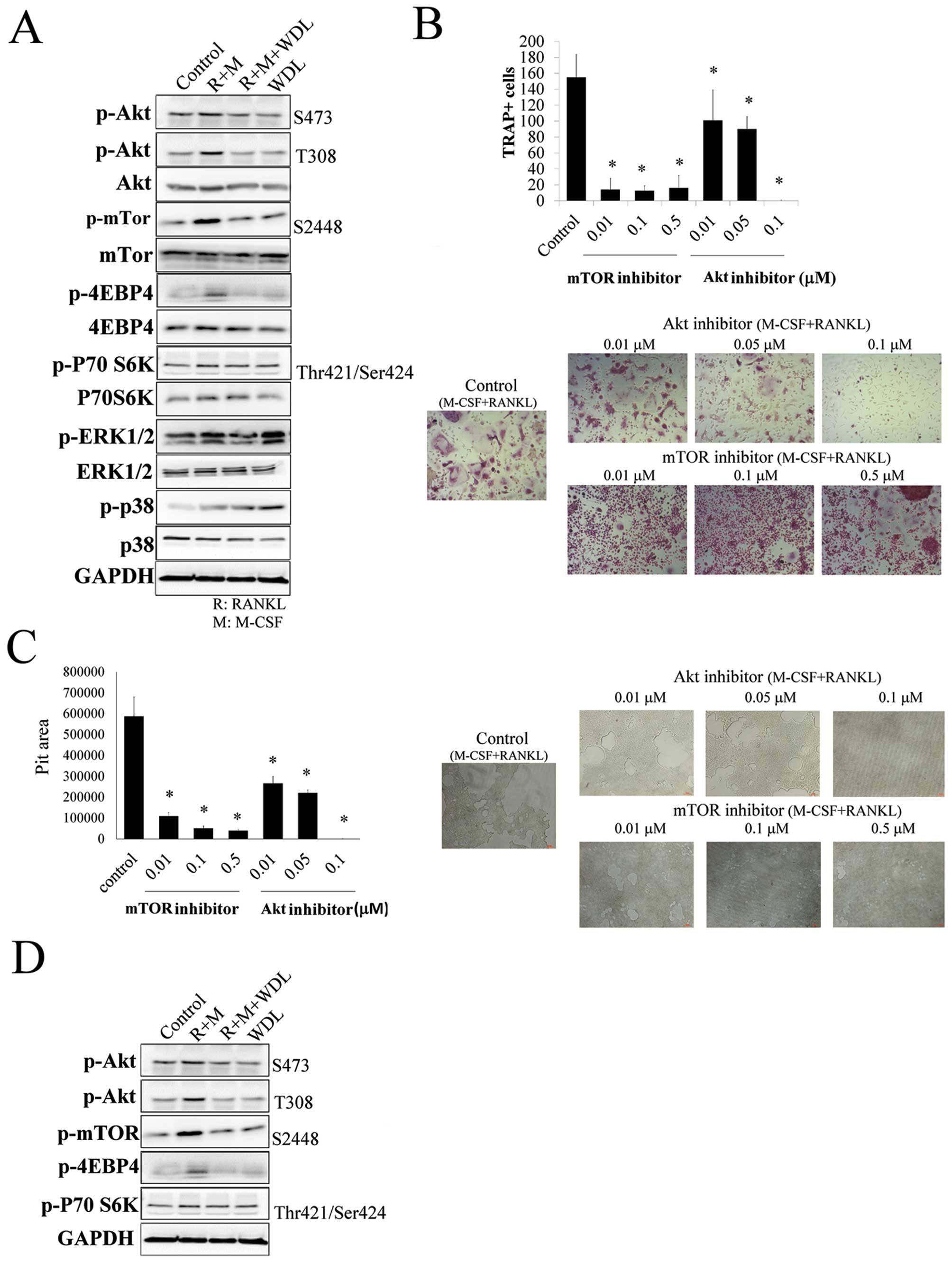
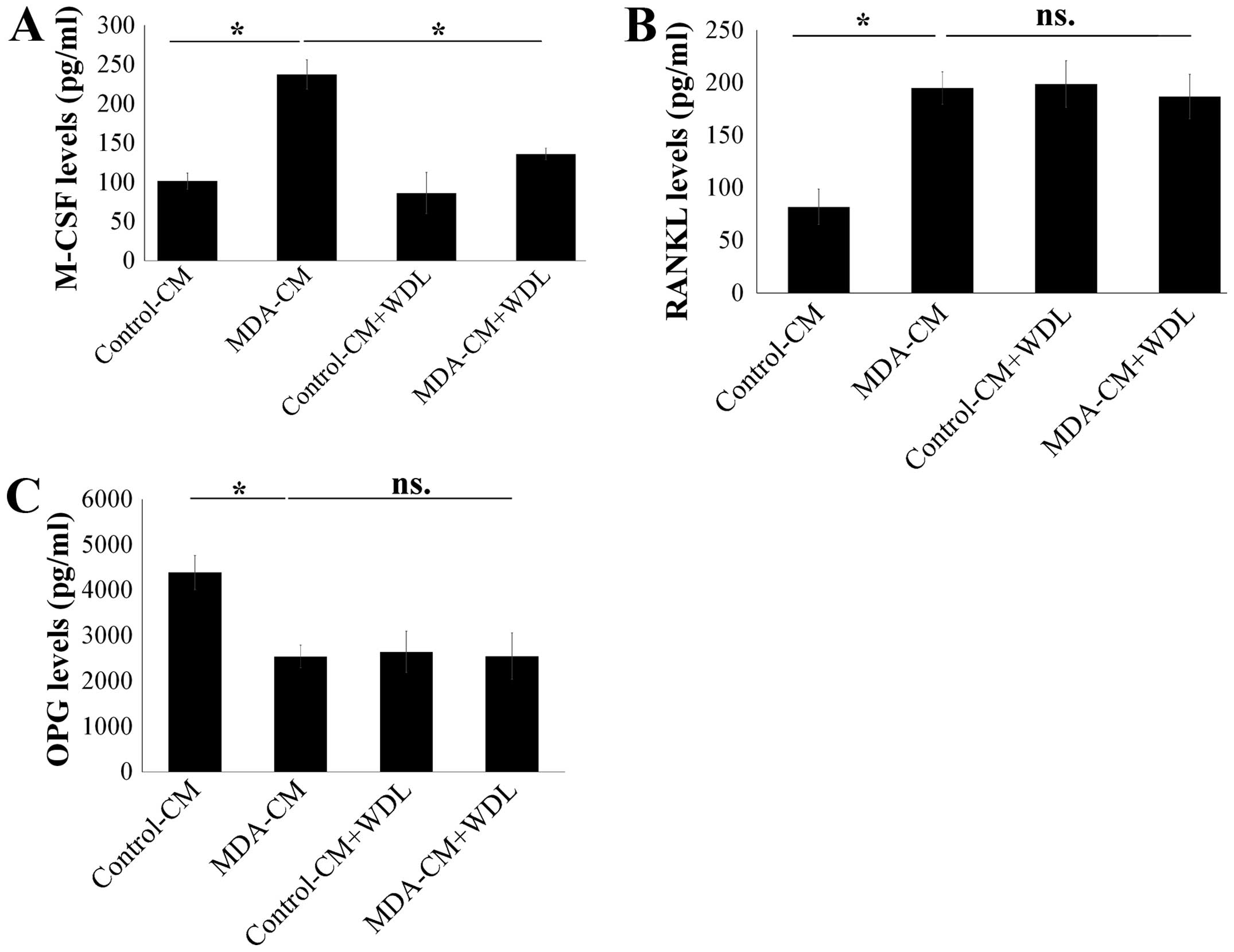
|
1
|
Akhtari M, Mansuri J, Newman KA, Guise TM
and Seth P: Biology of breast cancer bone metastasis. Cancer Biol
Ther. 7:3–9. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Rordorf T, Hassan AA, Azim H, et al: Bone
health in breast cancer patients: a comprehensive statement by
CECOG/SAKK intergroup. Breast. 23:511–525. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Rove KO and Crawford ED: Metastatic cancer
in solid tumors and clinical outcome: skeletal-related events.
Oncology. 23:21–27. 2009.
|
|
4
|
Weilbaecher KN, Guise TA and McCauley LK:
Cancer to bone: a fatal attraction. Nat Rev Cancer. 11:411–425.
2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Gupta S, Gupta H, Mandhyan D and
Srivastava S: Bisphophonates related osteonecrosis of the jaw. Natl
J Maxillofac Surg. 4:151–158. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Verron E, Schmid-Antomarchi H,
Pascal-Mousselard H, Schmid-Alliana A, Scimeca JC and Bouler JM:
Therapeutic strategies for treating osteolytic bone metastases.
Drug Discov Today. 19:1419–1426. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Roodman GD: Mechanisms of bone metastasis.
N Engl J Med. 350:1655–1664. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Mundy GR: Metastasis to bone: causes,
consequences and therapeutic opportunities. Nat Rev Cancer.
2:584–593. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Rodan GA and Martin TJ: Therapeutic
approaches to bone diseases. Science. 289:1508–1514. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Suda T, Takahashi N, Udagawa N, Jimi E,
Gillespie MT and Martin TJ: Modulation of osteoclast
differentiation and function by the new members of the tumor
necrosis factor receptor and ligand families. Endocr Rev.
20:345–357. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lee ZH and Kim HH: Signal transduction by
receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa B in osteoclasts.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 305:211–214. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chen YC, Sosnoski DM and Mastro AM: Breast
cancer metastasis to the bone: mechanisms of bone loss. Breast
Cancer Res. 12:2152010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Mountzios G, Dimopoulos MA, Bamias A, et
al: Abnormal bone remodeling process is due to an imbalance in the
receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappaB ligand
(RANKL)/osteoprotegerin (OPG) axis in patients with solid tumors
metastatic to the skeleton. Acta Oncol. 46:221–229. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
McGrath EE: OPG/RANKL/RANK pathway as a
therapeutic target in cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 6:1468–1473. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Azim HA, Kamal NS and Azim HA Jr: Bone
metastasis in breast cancer: the story of RANK-ligand. J Egypt Nat
Cancer Inst. 24:107–114. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Patel M, Kadakia V and Mishra S:
Simultaneous estimation of andrographolide and wedelolactone in
herbal formulations. Indian J Pharm Sci. 70:6892008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Roy RK, Thakur M and Dixit VK: Hair growth
promoting activity of Eclipta alba in male albino rats. Arch
Dermatol Res. 300:357–364. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Singh B, Saxena AK, Chandan BK, Agarwal SG
and Anand KK: In vivo hepatoprotective activity of active fraction
from ethanolic extract of Eclipta alba leaves. Indian J Physiol
Pharmacol. 45:435–441. 2001.
|
|
19
|
Wagner H, Geyer B, Kiso Y, Hikino H and
Rao GS: Coumestans as the main active principles of the liver drugs
Eclipta alba and Wedelia calendulacea. Planta Med. 370–374. 1986.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lin FM, Chen LR, Lin EH, et al: Compounds
from Wedelia chinensis synergistically suppress androgen activity
and growth in prostate cancer cells. Carcinogenesis. 28:2521–2529.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tewtrakul S, Subhadhirasakul S,
Cheenpracha S and Karalai C: HIV-1 protease and HIV-1 integrase
inhibitory substances from Eclipta prostrata. Phytother Res.
21:1092–1095. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tsai CH, Lin FM, Yang YC, et al: Herbal
extract of Wedelia chinensis attenuates androgen receptor activity
and orthotopic growth of prostate cancer in nude mice. Clin Cancer
Res. 15:5435–5444. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Vender JR, Laird MD and Dhandapani KM:
Inhibition of NFkappaB reduces cellular viability in GH3 pituitary
adenoma cells. Neurosurgery. 62:1122–1128. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Idris AI, Libouban H, Nyangoga H,
Landao-Bassonga E, Chappard D and Ralston SH: Pharmacologic
inhibitors of IkappaB kinase suppress growth and migration of
mammary carcinosarcoma cells in vitro and prevent osteolytic bone
metastasis in vivo. Mol Cancer Ther. 8:2339–2347. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sarveswaran S, Gautam SC and Ghosh J:
Wedelolactone, a medicinal plant-derived coumestan, induces
caspase-dependent apoptosis in prostate cancer cells via
downregulation of PKCɛ without inhibiting Akt. Int J Oncol.
41:2191–2199. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sterling JA, Edwards JR, Martin TJ and
Mundy GR: Advances in the biology of bone metastasis: how the
skeleton affects tumor behavior. Bone. 48:6–15. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Furugaki K, Moriya Y, Iwai T, et al:
Erlotinib inhibits osteolytic bone invasion of human non-small-cell
lung cancer cell line NCI-H292. Clin Exp Metastasis. 28:649–659.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hsu YL, Huang MS, Yang CJ, Hung JY, Wu LY
and Kuo PL: Lung tumor-associated osteoblast-derived bone
morphogenetic protein-2 increased epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transition of cancer by Runx2/Snail signaling pathway. J Biol Chem.
286:37335–37346. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Takayanagi H: New immune connections in
osteoclast formation. Ann NY Acad Sci. 192:117–123. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Yoneda T, Tanaka S and Hata K: Role of
RANKL/RANK in primary and secondary breast cancer. World J Orthop.
4:178–185. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Skeen JE, Bhaskar PT, Chen CC, et al: Akt
deficiency impairs normal cell proliferation and suppresses
oncogenesis in a p53-independent and mTORC1-dependent manner.
Cancer Cell. 10:269–280. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Moon JB, Kim JH, Kim K, et al: Akt induces
osteoclast differentiation through regulating the GSK3β/NFATc1
signaling cascade. J Immunol. 188:163–169. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Cao H, Zhu K, Qiu L, et al: Critical role
of AKT protein in myeloma-induced osteoclast formation and
osteolysis. J Biol Chem. 288:30399–30410. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Sugatani T and Hruska KA: Akt1/Akt2 and
mammalian target of rapamycin/Bim play critical roles in osteoclast
differentiation and survival, respectively, whereas Akt is
dispensable for cell survival in isolated osteoclast precursors. J
Biol Chem. 280:3583–3589. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Sanchez CP and He YZ: Bone growth during
rapamycin therapy in young rats. BMC Pediatr. 9:32009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|