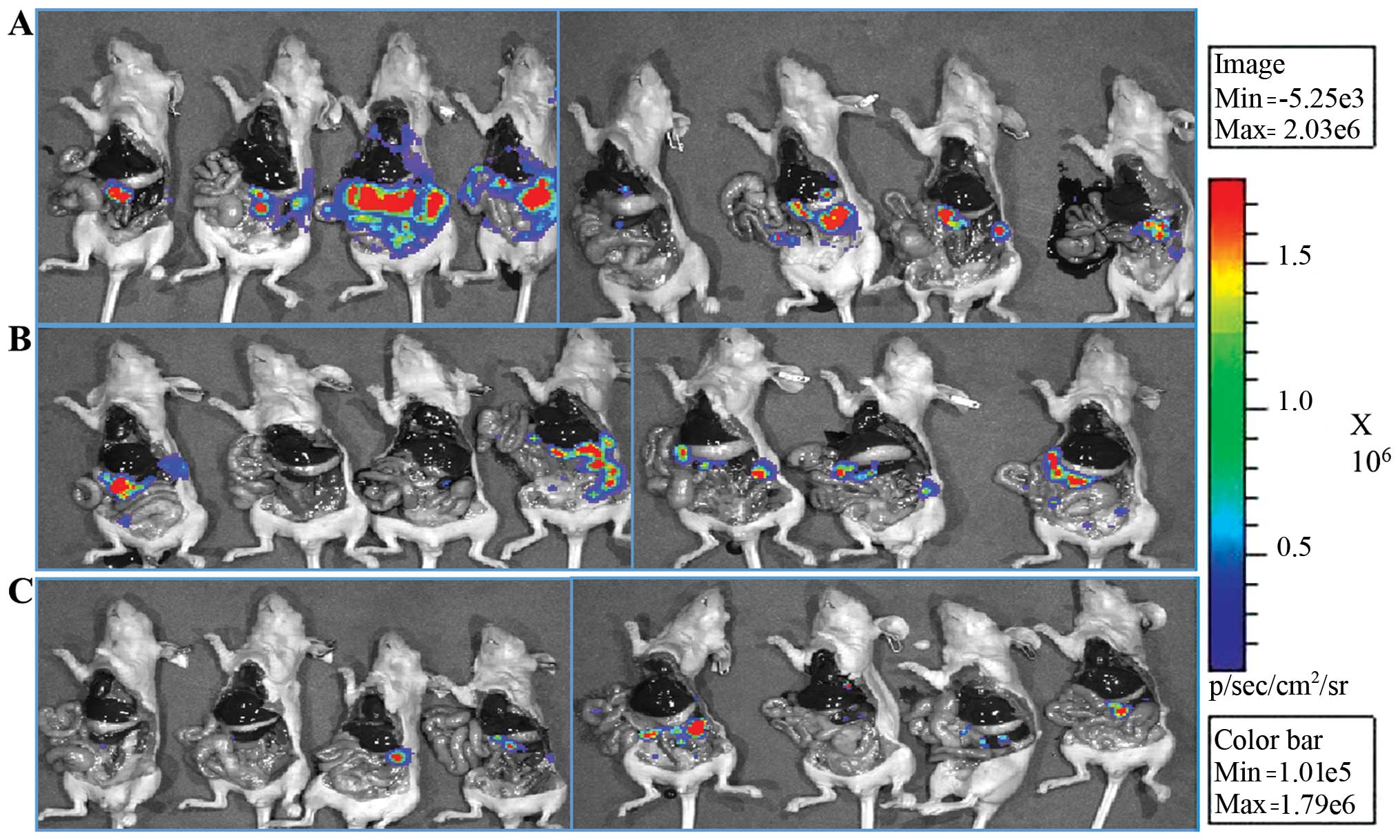
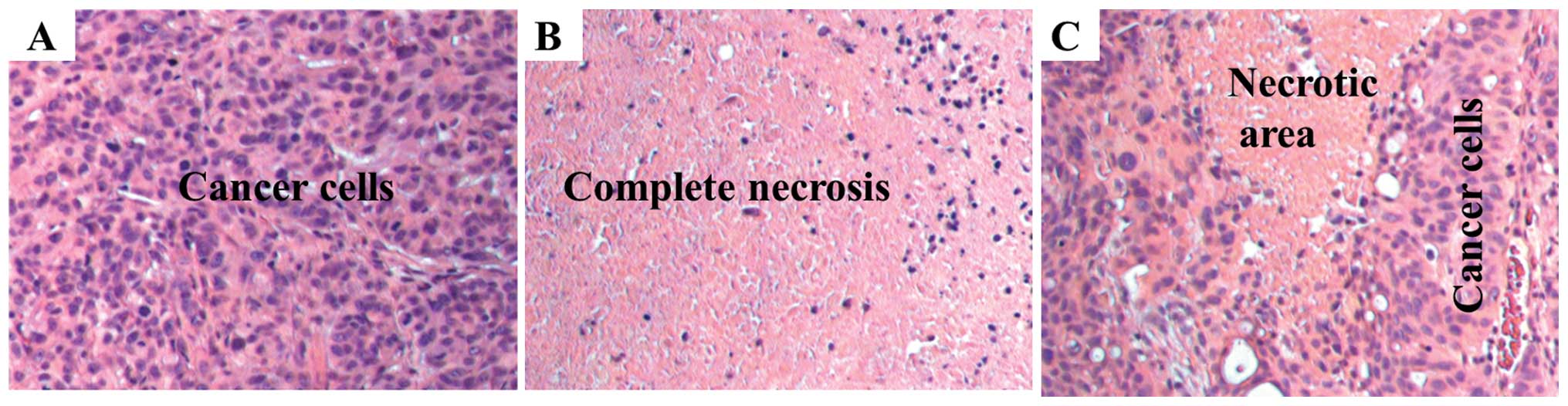
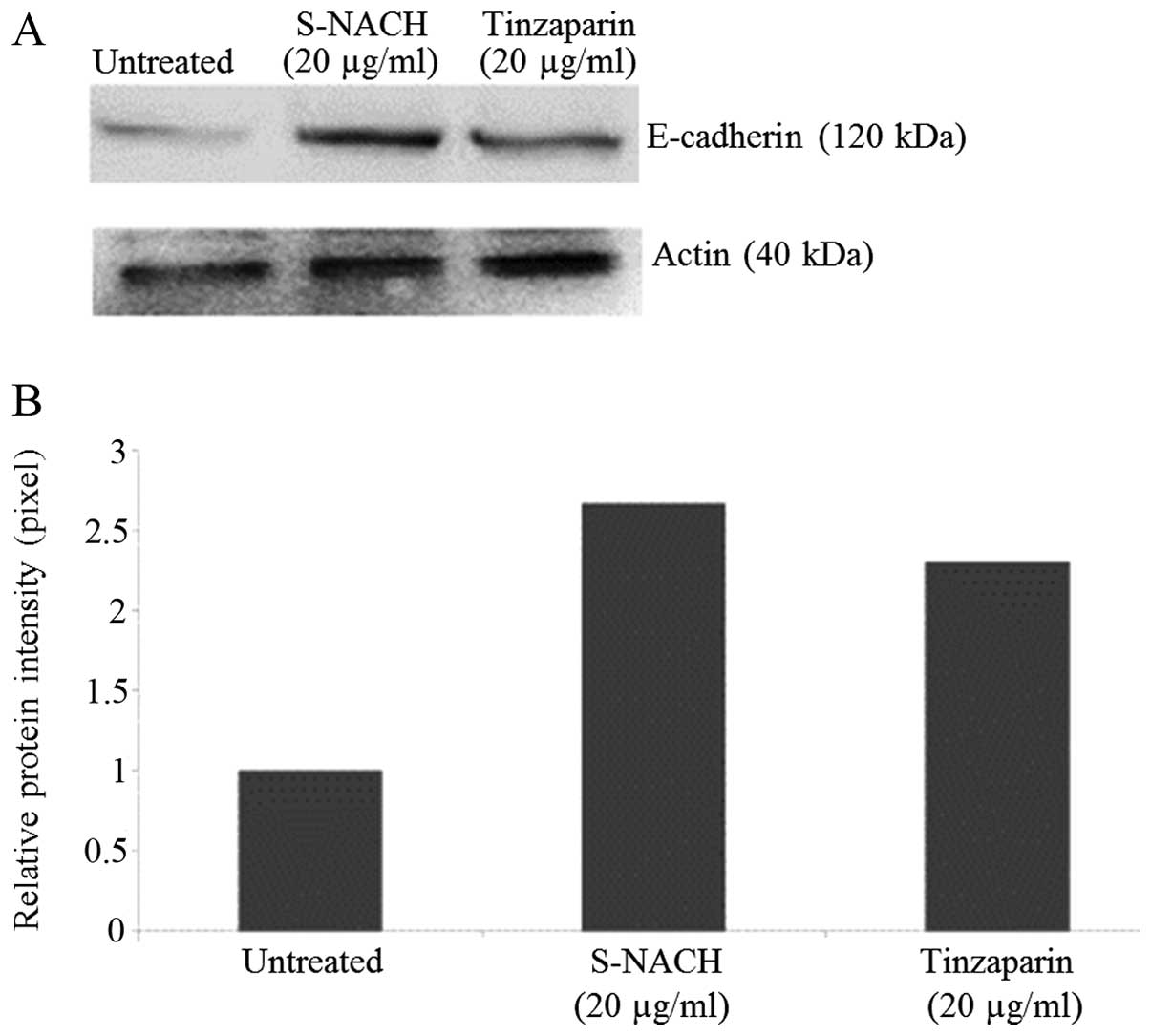
|
1
|
Siegel R, Ward E, Brawley O and Jemal A:
Cancer statistics, 2011: the impact of eliminating socioeconomic
and racial disparities on premature cancer deaths. CA Cancer J
Clin. 61:212–236. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chambers AF, Groom AC and MacDonald IC:
Dissemination and growth of cancer cells in metastatic sites. Nat
Rev Cancer. 2:563–572. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sener SF, Fremgen A, Menck HR and
Winchester DP: Pancreatic cancer: a report of treatment and
survival trends for 100,313 patients diagnosed from 1985–1995,
using the National Cancer Database. J Am Coll Surg. 189:1–7. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Borsig L, Wong R, Feramisco J, Nadeau DR,
Varki NM and Varki A: Heparin and cancer revisited: mechanistic
connections involving platelets, P-selectin, carcinoma mucins, and
tumor metastasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 98:3352–3357. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Stone JP and Wagner DD: P-selectin
mediates adhesion of platelets to neuroblastoma and small cell lung
cancer. J Clin Invest. 92:804–813. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Mannori G, Crottet P, Cecconi O, et al:
Differential colon cancer cell adhesion to E-, P-, and L-selectin:
role of mucin-type glycoproteins. Cancer Res. 55:4425–4431.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Nelson RM, Cecconi O, Roberts WG, Aruffo
A, Linhardt RJ and Bevilacqua MP: Heparin oligosaccharides bind L-
and P-selectin and inhibit acute inflammation. Blood. 82:3253–3258.
1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Koenig A, Norgard-Sumnicht K, Linhardt R
and Varki A: Differential interactions of heparin and heparan
sulfate glycosaminoglycans with the selectins. Implications for the
use of unfractionated and low molecular weight heparins as
therapeutic agents. J Clin Invest. 101:877–889. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zacharski LR and Loynes JT: The heparins
and cancer. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 8:379–382. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kasthuri RS, Taubman MB and Mackman N:
Role of tissue factor in cancer. J Clin Oncol. 27:4834–4838. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Capila I and Linhardt RJ: Heparin-protein
interactions. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 41:391–412. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kuderer NM, Khorana AA, Lyman GH and
Francis CW: A meta-analysis and systematic review of the efficacy
and safety of anticoagulants as cancer treatment: impact on
survival and bleeding complications. Cancer. 110:1149–1161. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Mousa SA: Oxidized heparin fractions and
their use in inhibiting angiogenesis. US patent 8,071,569.
2011:December 06–2011
|
|
14
|
Lapierre F, Holme K, Lam L, et al:
Chemical modifications of heparin that diminish its anticoagulant
but preserve its heparanase-inhibitory, angiostatic, anti-tumor and
anti-metastatic properties. Glycobiology. 6:355–366. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sudha T, Phillips P, Kanaan C, Linhardt
RJ, Borsig L and Mousa SA: Inhibitory effect of non-anticoagulant
heparin (S-NACH) on pancreatic cancer cell adhesion and metastasis
in human umbilical cord vessel segment and in mouse model. Clin Exp
Metastasis. 29:431–439. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
van der Bij GJ, Oosterling SJ, Beelen RH,
Meijer S, Coffey JC and van Egmond M: The perioperative period is
an underutilized window of therapeutic opportunity in patients with
colorectal cancer. Ann Surg. 249:727–734. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kakkar A, Hedges R, Williamson R and
Kakkar V: Perioperative heparin-therapy inhibits late death from
metastatic cancer. Int J Oncol. 6:885–888. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
von Tempelhoff GF, Harenberg J, Niemann F,
Hommel G, Kirkpatrick CJ and Heilmann L: Effect of low molecular
weight heparin (Certoparin) versus unfractionated heparin on cancer
survival following breast and pelvic cancer surgery: a prospective
randomized double-blind trial. Int J Oncol. 16:815–824.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lim E, Modi KD and Kim J: In vivo
bioluminescent imaging of mammary tumors using IVIS spectrum. J Vis
Exp. 26:12102009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Dejana E, Callioni A, Quintana A and de
Gaetano G: Bleeding time in laboratory animals. II - A comparison
of different assay conditions in rats. Thromb Res. 15:191–197.
1979. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Alshaiban A, Muralidharan-Chari V, Nepo A
and Mousa SA: Modulation of sickle red blood cell adhesion and its
associated changes in biomarkers by sulfated non-anticoagulant
heparin derivative. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. (In press).
|
|
22
|
Gasic GJ, Gasic TB and Stewart CC:
Antimetastatic effects associated with platelet reduction. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 61:46–52. 1968. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kim YJ, Borsig L, Varki NM and Varki A:
P-selectin deficiency attenuates tumor growth and metastasis. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 95:9325–9330. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Mousa SA, Linhardt R, Francis JL and
Amirkhosravi A: Antimetastatic effect of a non-anticoagulant
low-molecular-weight heparin versus the standard
low-molecular-weight heparin, enoxaparin. Thromb Haemost.
96:816–821. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kragh M, Binderup L, Vig Hjarnaa PJ, Bramm
E, Johansen KB and Frimundt Petersen C: Non-anti-coagulant heparin
inhibits metastasis but not primary tumor growth. Oncol Rep.
14:99–104. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Bacac M and Stamenkovic I: Metastatic
cancer cell. Annu Rev Pathol. 3:221–247. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kopfstein L and Christofori G: Metastasis:
cell-autonomous mechanisms versus contributions by the tumor
microenvironment. Cell Mol Life Sci. 63:449–468. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Achen MG, Mann GB and Stacker SA:
Targeting lymphangiogenesis to prevent tumour metastasis. Br J
Cancer. 94:1355–1360. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ito S, Nakanishi H, Hirai T, et al:
Quantitative detection of CEA expressing free tumor cells in the
peripheral blood of colorectal cancer patients during surgery with
real-time RT-PCR on a LightCycler. Cancer Lett. 183:195–203. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wang F, Sloss C, Zhang X, Lee SW and
Cusack JC: Membrane-bound heparin-binding epidermal growth factor
like growth factor regulates E-cadherin expression in pancreatic
carcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 67:8486–8493. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Phillips PG, Yalcin M, Cui H, et al:
Increased tumor uptake of chemotherapeutics and improved
chemoresponse by novel non-anticoagulant low molecular weight
heparin. Anticancer Res. 31:411–419. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lebeau B, Baud M, Masanes MJ, Febvre M,
Mokhtari T and Chouaid C: Optimization of small-cell lung cancer
chemotherapy with heparin: a comprehensive retrospective study of
239 patients treated in a single specialized center. Chemotherapy.
57:253–258. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Klerk CP, Smorenburg SM, Otten HM, et al:
The effect of low molecular weight heparin on survival in patients
with advanced malignancy. J Clin Oncol. 23:2130–2135. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lebeau B, Chastang C, Brechot JM, et al:
Subcutaneous heparin treatment increases survival in small cell
lung cancer. ‘Petites Cellules’ Group. Cancer. 74:38–45. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Mousa SA and Petersen LJ: Anti-cancer
properties of low-molecular-weight heparin: preclinical evidence.
Thromb Haemost. 102:258–267. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Mousa SA: Comparative pharmacodynamic
assessment of the antiangiogenesis activity of heparin and
low-molecular-weight heparin fractions: structure-function
relationship. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 19:48–54. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Yu CJ, Ye SJ, Feng ZH, et al: Effect of
Fraxiparine, a type of low molecular weight heparin, on the
invasion and metastasis of lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells. Oncol
Lett. 1:755–760. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ilan N, Elkin M and Vlodavsky I:
Regulation, function and clinical significance of heparanase in
cancer metastasis and angiogenesis. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
38:2018–2039. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|