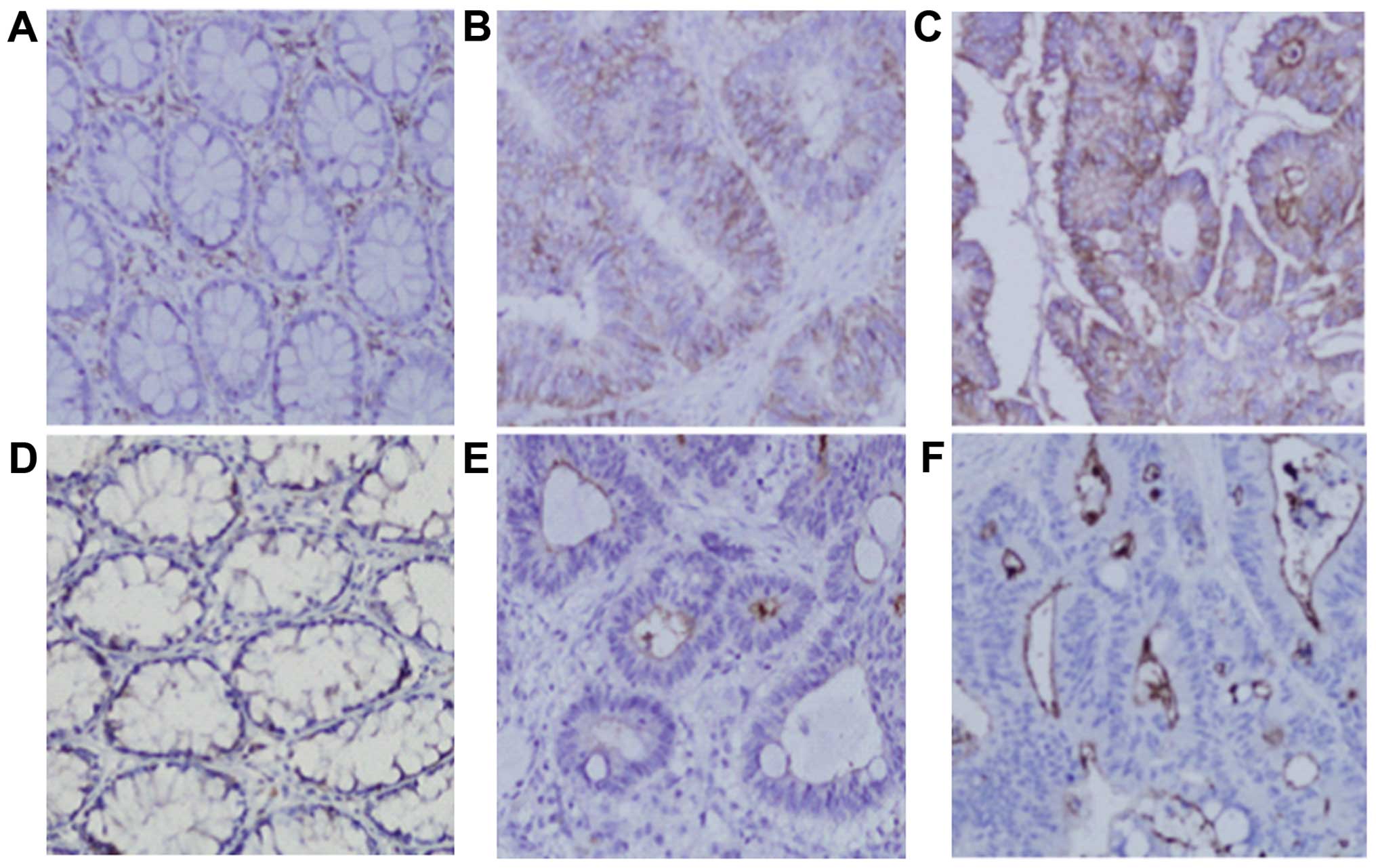
|
1
|
Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 62:10–29. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Sakai Y: Current topics in colorectal
liver metastasis. Int J Clin Oncol. 16:451. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Van Cutsem E, Lambrechts D, Prenen H, Jain
RK and Carmeliet P: Lessons from the adjuvant bevacizumab trial on
colon cancer: what next? J Clin Oncol. 29:1–4. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Huang X, Sheng Y and Guan M: Co-expression
of stem cell genes CD133 and CD44 in colorectal cancers with early
liver metastasis. Surg Oncol. 21:103–107. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Galizia G, Gemei M, Del Vecchio L, et al:
Combined CD133/CD44 expression as a prognostic indicator of
disease-free survival in patients with colorectal cancer. Arch
Surg. 147:18–24. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Anderson EC, Hessman C, Levin TG, Monroe
MM and Wong MH: The role of colorectal cancer stem cells in
metastatic disease and therapeutic response. Cancers (Basel).
3:319–339. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
7
|
Hu Y and Fu L: Targeting cancer stem
cells: a new therapy to cure cancer patients. Am J Cancer Res.
2:340–356. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yu ZR, Pestell TG, Lisanti MP and Pestell
RG: Cancer stem cells. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 44:2144–2151. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Soltanian S and Matin MM: Cancer stem
cells and cancer therapy. Tumour Biol. 32:425–440. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wakamatsu Y, Sakamoto N, Oo HZ, Naito Y,
Uraoka N, Anami K, Sentani K, Oue N and Yasui W: Expression of
cancer stem cell markers ALDH1, CD44 and CD133 in primary tumor and
lymph node metastasis of gastric cancer. Pathol Int. 62:112–119.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bendardaf R, Algars A, Elzagheid A,
Korkeila E, Ristamaki R, Lamlum H, Collan Y, Syrjanen K and
Pyrhonen S: Comparison of CD44 expression in primary tumours and
metastases of colorectal cancer. Oncol Rep. 16:741–746.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bird NC, Mangnall D and Majeed AW: Biology
of colorectal liver metastases: a review. J Surg Oncol. 94:68–80.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Jaggupilli A and Elkord E: Significance of
CD44 and CD24 as cancer stem cell markers: an enduring ambiguity.
Clin Dev Immunol. May 30–2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Dalerba P, Dylla SJ, Park IK, et al:
Phenotypic characterization of human colorectal cancer stem cells.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 104:10158–10163. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Su YJ, Lai HM, Chang YW, Chen GY and Lee
JL: Direct reprogramming of stem cell properties in colon cancer
cells by CD44. EMBO J. 30:3186–3199. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ricci-Vitiani L, Lombardi DG, Pilozzi E,
Biffoni M, Todaro M, Peschle C and De Maria R: Identification and
expansion of human colon cancer-initiating cells. Nature.
445:111–115. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Haraguchi N, Ohkuma M, Sakashita H,
Matsuzaki S, Tanaka F, Mimori K, Kamohara Y, Inoue H and Mori M:
CD133+CD44+ population efficiently enriches
colon cancer initiating cells. Ann Surg Oncol. 15:2927–2933. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
O’Brien CA, Pollett A, Gallinger S and
Dick JE: A human colon cancer cell capable of initiating tumour
growth in immunodeficient mice. Nature. 445:106–110. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Bao SD, Wu QL, McLendon RE, Hao YL, Shi Q,
Hjelmeland AB, Dewhirst MW, Bigner DD and Rich JN: Glioma stem
cells promote radioresistance by preferential activation of the DNA
damage response. Nature. 444:756–760. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Frank NY, Pendse SS, Lapchak PH, Margaryan
A, Shlain D, Doeing C, Sayegh MH and Frank MH: Regulation of
progenitor cellfusionbyABCB5P-glycoprotein, a novel human
ATP-binding cassette transporter. J Biol Chem. 278:47156–47165.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Frank NY, Margaryan A, Huang Y, Schatton
T, Waaga-Gasser AM, Gasser M, Sayegh MH, Sadee W and Frank MH:
ABCB5-mediated doxorubicin transport and chemoresistance in human
malignant melanoma. Cancer Res. 65:4320–4333. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Horst D, Kriegl L, Engel J, Kirchner T and
Jung A: Prognostic significance of the cancer stem cell markers
CD133, CD44, and CD166 in colorectal cancer. Cancer Invest.
27:844–850. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Saigusa S, Tanaka K, Toiyama Y, Yokoe T,
Okugawa Y, Ioue Y, Miki C and Kusunoki M: Correlation of CD133,
OCT4, and SOX2 in rectal cancer and their association with distant
recurrence after chemoradiotherapy. Ann Surg Oncol. 16:3488–3498.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Botchkina IL, Rowehl RA, Rivadeneira DE,
Karpeh MS Jr, Crawford H, Dufour A, Ju J, Wang Y, Leyfman Y and
Botchkina GI: Phenotypic subpopulations of metastatic colon cancer
stem cells: genomic analysis. Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 6:19–29.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Botchkina GI, Zuniga ES, Das M, et al:
New-generation taxoid SB-T-1214 inhibits stem cell-related gene
expression in 3D cancer spheroids induced by purified colon
tumor-initiating cells. Mol Cancer. 9:1922010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chen KL, Pan F, Jiang H, Chen JF, Pei L,
Xie FW and Liang HJ: Highly enriched CD133(+)CD44(+) stem-like
cells with CD133(+) CD44(high) metastatic subset in HCT116 colon
cancer cells. Clin Exp Metastasis. 28:751–763. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Nagata T, Sakakura C, Komiyama S, et al:
Expression of cancer stem cell markers CD133 and CD44 in
locoregional recurrence of rectal cancer. Anticancer Res.
31:495–500. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hou Y, Zou QF, Ge RL, Shen F and Wang YZ:
The critical role of CD133+CD44+/high tumor
cells in hematogenous metastasis of liver cancers. Cell Res.
22:259–272. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
29
|
Bellizzi A, Sebastian S, Ceglia P, et al:
Co-expression of CD133+/CD44+ in human colon
cancer and liver metastasis. J Cell Physiol. 228:408–415. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Huh JW, Kim HR, Kim YJ, Lee JH, Park YS,
Cho SH and Joo JK: Expression of standard CD44 in human colorectal
carcinoma: association with prognosis. Pathol Int. 59:241–246.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ohji Y, Yao T, Eguchi T, Yamada T,
Hirahashi M, Iida M and Tsuneyoshi M: Evaluation of risk of liver
metastasis in colorectal adenocarcinoma based on the combination of
risk factors including CD10 expression: Multivariate analysis of
clinicopathological and mmunohistochemical factors. Oncol Rep.
17:525–530. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Park JJ, Kwon JH, Oh SH, et al:
Differential expression of CD133 based on microsatellite
instability status in human colorectal cancer. Mol Carcinog.
53:E1–E10. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Jones RJ: Cancer stem cells - clinical
relevance. J Mol Med (Berl). 87:1105–1110. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Papailiou J, Bramis KJ, Gazouli M and
Theodoropoulos G: Stem cells in colon cancer. A new era in cancer
theory begins. Int J Colorectal Dis. 26:1–11. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Baumann M, Krause M and Hill R: Exploring
the role of cancer stem cells in radioresistance. Nat Rev Cancer.
8:545–554. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Eyler CE and Rich JN: Survival of the
fittest: cancer stem cells in therapeutic resistance and
angiogenesis. J Clin Oncol. 26:2839–2845. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Frank NY, Schatton T and Frank MH: The
therapeutic promise of the cancer stem cell concept. J Clin Invest.
120:41–50. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Li M, Li JY, Zhao AL and Gu J: Colorectal
cancer or colon and rectal cancer? Clinicopathological comparison
between colonic and rectal carcinomas. Oncology. 73:52–57. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Chung CK, Zaino RJ and Stryker JA:
Colorectal carcinoma: evaluation of histologic grade and factors
influencing prognosis. J Surg Oncol. 21:143–148. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Umpleby HC, Bristol JB, Rainey JB and
Williamson RC: Survival of 727 patients with single carcinomas of
the large bowel. Dis Colon Rectum. 27:803–810. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Kazama Y, Watanabe T, Kanazawa T, Tanaka
J, Tanaka T and Nagawa H: Poorly differentiated colorectal
adenocarcinomas show higher rates of microsatellite instability and
promoter methylation of p16 and hMLH1: a study matched for T
classification and tumor location. J Surg Oncol. 97:278–283. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Mulder JW, Kruyt PM, Sewnath M, Oosting J,
Seldenrijk CA, Weidema WF, Offerhaus GJ and Pals ST: Colorectal
cancer prognosis and expression of exon-v6- containing CD44
proteins. Lancet. 344:1470–1472. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Weg-Remers S, Anders M, von Lampe B,
Riecken EO, Schuder G, Feifel G, Zeitz M and Stallmach A: Decreased
expression of CD44 splicing variants in advanced colorectal
carcinomas. Eur J Cancer. 34:1607–1611. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Lugli A, Iezzi G, Hostettler I, Muraro MG,
Mele V, Tornillo L, Carafa V, Spagnoli G, Terracciano L and Zlobec
I: Prognostic impact of the expression of putative cancer stem cell
markers CD133, CD166, CD44s, EpCAM, and ALDH1 in colorectal cancer.
Br J Cancer. 103:382–390. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Horst D, Kriegl L, Engel J, Kirchner T and
Jung A: CD133 expression is an independent prognostic marker for
low survival in colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer. 99:1285–1289. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Kojima M, Ishii G, Atsumi N, Fujii S,
Saito N and Ochiai A: Imunohistochemical detection of CD133
expression in colorectal cancer: a clinicopathological study.
Cancer Sci. 99:1578–1583. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Li CY, Li BX, Liang Y, et al: Higher
percentage of CD133(+) cells is associated with poor prognosis in
colon carcinoma patients with stage IIIB. J Transl Med. 7:562009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Choi D, Lee HW, Hur KY, Kim JL, Park GS,
Jang SH, Song YS, Lang KS and Paik SS: Cancer stem cell markers
CD133 and CD24 correlate with invasiveness and differentiation in
colorectal adenocarcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. 15:2258–2264.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Huh JW, Park YS, Lee JH, Kim HR, Shin MG
and Kim YJ: CD133 mRNA expression and microsatellite instability in
colorectal carcinoma. J Surg Oncol. 102:765–770. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Zlobec I, Terracciano L, Jass JR and Lugli
A: Value of staining intensity in the interpretation of
immunohistochemistry for tumor markers in colorectal cancer.
Virchows Arch. 451:763–769. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|