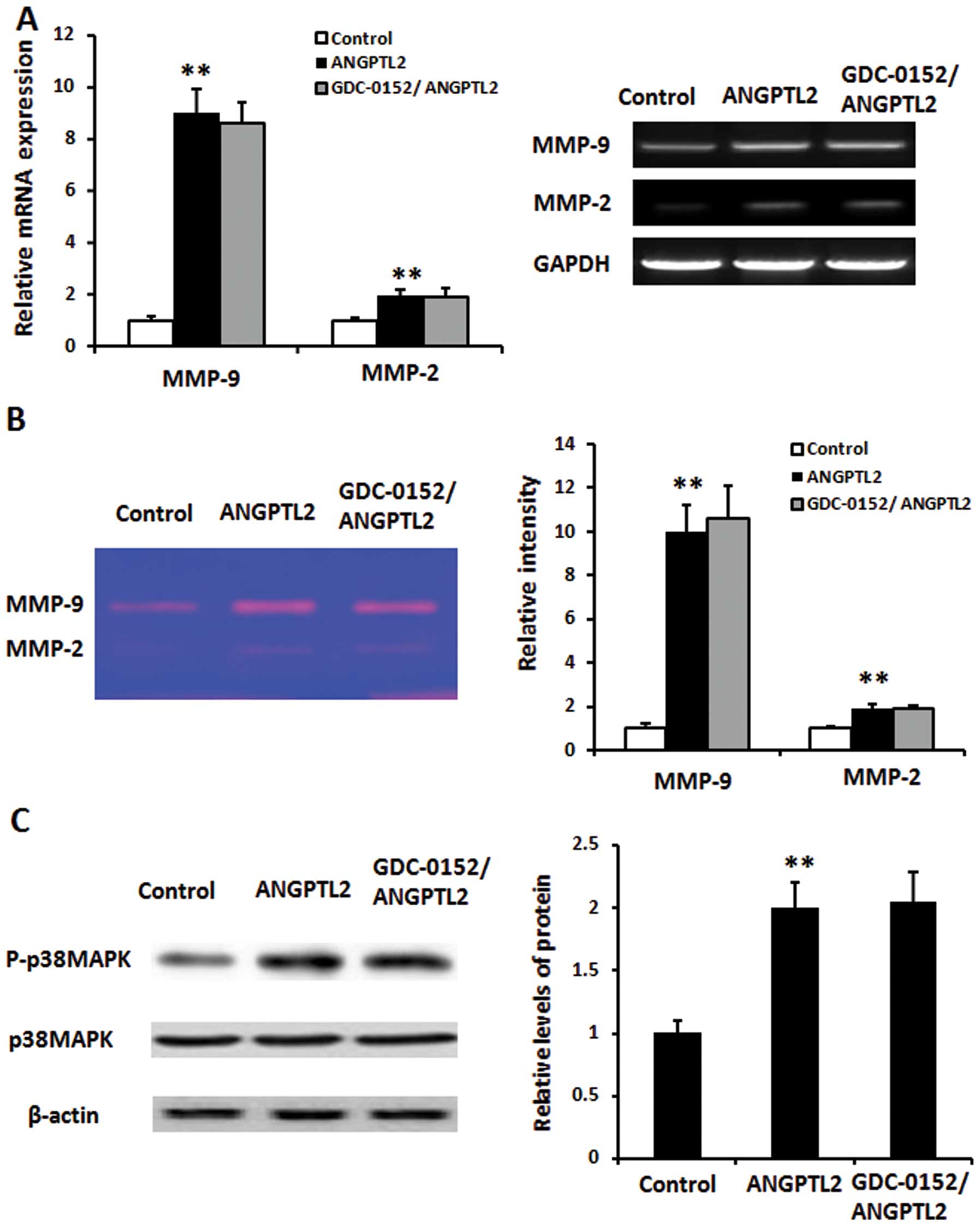
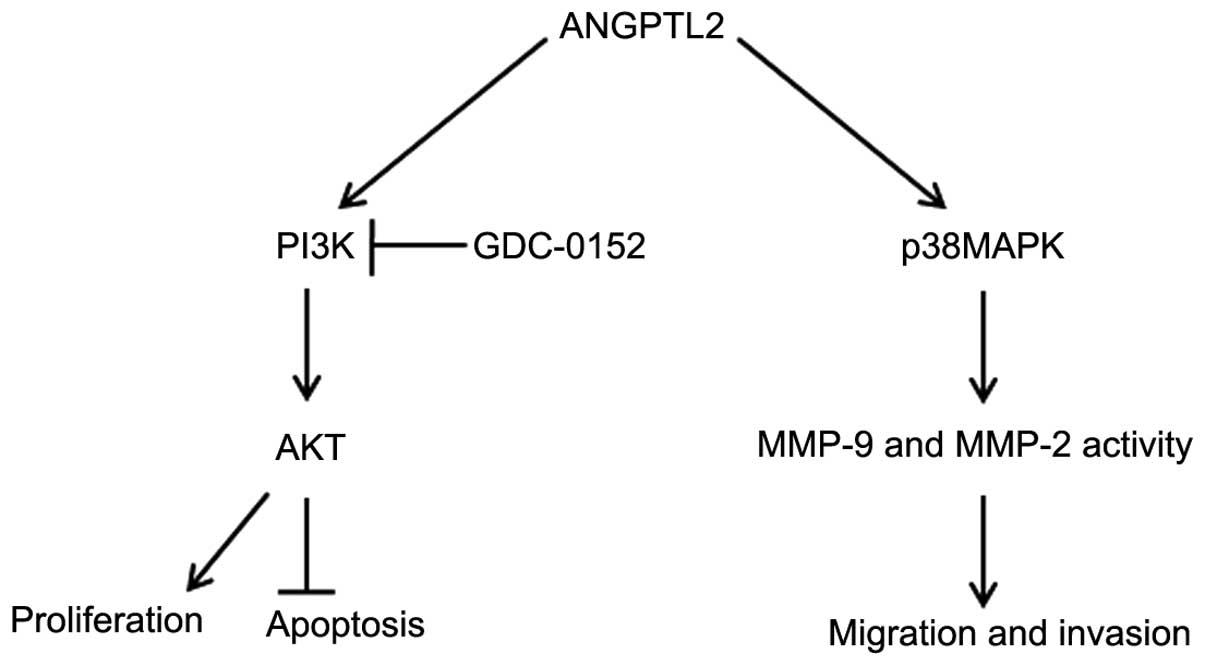
|
1
|
Tian Z, Miyata K, Tazume H, et al:
Perivascular adipose tissue-secreted angiopoietin-like protein 2
(Angptl2) accelerates neointimal hyperplasia after endovascular
injury. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 57:1–12. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Tabata M, Kadomatsu T, Fukuhara S, et al:
Angiopoietin-like protein 2 promotes chronic adipose tissue
inflammation and obesity-related systemic insulin resistance. Cell
Metab. 10:178–188. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Oike Y, Yasunaga K and Suda T:
Angiopoietin-related/angiopoietin-like proteins regulate
angiogenesis. Int J Hematol. 80:21–28. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Li Q, Gong W, Yang Z, Lu B, et al: Serum
Angptl2 levels are independently associated with albuminuria in
type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 100:385–390. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kikuchi R, Tsuda H, Kozaki K, et al:
Frequent inactivation of a putative tumor suppressor,
angiopoietin-like protein 2, in ovarian cancer. Cancer Res.
68:5067–5075. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tazume H, Miyata K, Tian Z, et al:
Macrophage-derived angiopoietin-like protein 2 accelerates
development of abdominal aortic aneurysm. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc
Biol. 32:1400–1409. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Aoi J, Endo M, Kadomatsu T, et al:
Angiopoietin-like protein 2 is an important facilitator of
inflammatory carcinogenesis and metastasis. Cancer Res.
71:7502–7512. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Endo M, Nakano M, Kadomatsu T, et al:
Tumor cell-derived angiopoietin-like protein ANGPTL2 is a critical
driver of metastasis. Cancer Res. 72:1784–1794. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zheng JY, Zou JJ, Wang WZ, et al: Tumor
necrosis factor-α increases angiopoietin-like protein 2 gene
expression by activating Foxo1 in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Mol Cell
Endocrinol. 339:120–129. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kitazawa M, Nagano M, Masumoto KH,
Shigeyoshi Y, Natsume T and Hashimoto S: Angiopoietin-like 2, a
circadian gene, improves type 2 diabetes through potentiation of
insulin sensitivity in mice adipocytes. Endocrinology.
152:2558–2567. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kubota Y, Oike Y, Satoh S, et al:
Cooperative interaction of Angiopoietin-like proteins 1 and 2 in
zebrafish vascular development. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
102:13502–13507. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Odagiri H, Kadomatsu T, Endo M, et al: The
secreted protein ANGPTL2 promotes metastasis of osteosarcoma cells
through integrin α5β1, p38 MAPK, and matrix metalloproteinases. Sci
Signal. 7:ra72014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Erickson RI, Tarrant J, Cain G, et al:
Toxicity profile of small-molecule IAP antagonist GDC-0152 is
linked to TNF-α pharmacology. Toxicol Sci. 131:247–258. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Yue Q, Mulder T, Rudewicz PJ, et al:
Evaluation of metabolism and disposition of GDC-0152 in rats using
14C labeling strategy at two different positions: a novel formation
of hippuric acid from 4-phenyl-5-amino-1,2,3-thiadiazole. Drug
Metab Dispos. 41:508–517. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Wong H, Budha NR, West K, et al: Dogs are
more sensitive to antagonists of inhibitor of apoptosis proteins
than rats and humans: a translational toxicokinetic/toxicodynamic
analysis. Toxicol Sci. 130:205–213. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Flygare JA, Beresini M, Budha N, et al:
Discovery of a potent small-molecule antagonist of inhibitor of
apoptosis (IAP) proteins and clinical candidate for the treatment
of cancer (GDC-0152). J Med Chem. 55:4101–4113. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Terzyan SS, Peracaula R, de Llorens R, et
al: The three-dimensional structure of human RNase 4, unliganded
and complexed with d(Up), reveals the basis for its uridine
selectivity. J Mol Biol. 285:205–214. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Xie P, Fujii I, Zhao J, Shinohara M and
Matsukura M: A novel polysaccharide compound derived from algae
extracts protects retinal pigment epithelial cells from high
glucose-induced oxidative damage in vitro. Biol Pharm Bull.
35:1447–1453. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Falk W, Goodwin RH Jr and Leonard EJ: A
48-well micro chemotaxis assembly for rapid and accurate
measurement of leukocyte migration. J Immunol Methods. 33:239–247.
1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Laemmli UK: Cleavage of structural
proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4.
Nature. 227:680–685. 1970. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kyhse-Andersen J: Electroblotting of
multiple gels: a simple apparatus without buffer tank for rapid
transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide to nitrocellulose. J
Biochem Biophys Methods. 10:203–209. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hosogai N, Fukuhara A, Oshima K, et al:
Adipose tissue hypoxia in obesity and its impact on adipocytokine
dysregulation. Diabetes. 56:901–911. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Aoi J, Endo M, Kadomatsu T, et al:
Angiopoietin-like protein 2 accelerates carcinogenesis by
activating chronic inflammation and oxidative stress. Mol Cancer
Res. 12:239–249. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Kim I, Kim HG, Kim H, et al: Hepatic
expression, synthesis and secretion of a novel
fibrinogen/angiopoietin-related protein that prevents
endothelial-cell apoptosis. Biochem J. 3:603–610. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Vucic D and Fairbrother WJ: The inhibitor
of apoptosis proteins as therapeutic targets in cancer. Clin Cancer
Res. 13:5995–6000. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Varfolomeev E and Vucic D: Inhibitor of
apoptosis proteins: fascinating biology leads to attractive tumor
therapeutic targets. Future Oncol. 7:633–648. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Cantley LC: The phosphoinositide 3-kinase
pathway. Science. 296:1655–1657. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Vivanco I and Sawyers CL: The
phosphatidylonositol 3-kinase-AKT pathway in human cancer. Nat Rev
Cancer. 2:489–501. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kessenbrock K, Plaks V and Werb Z: Matrix
metalloproteinases: regulators of the tumor microenvironment. Cell.
141:52–67. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|