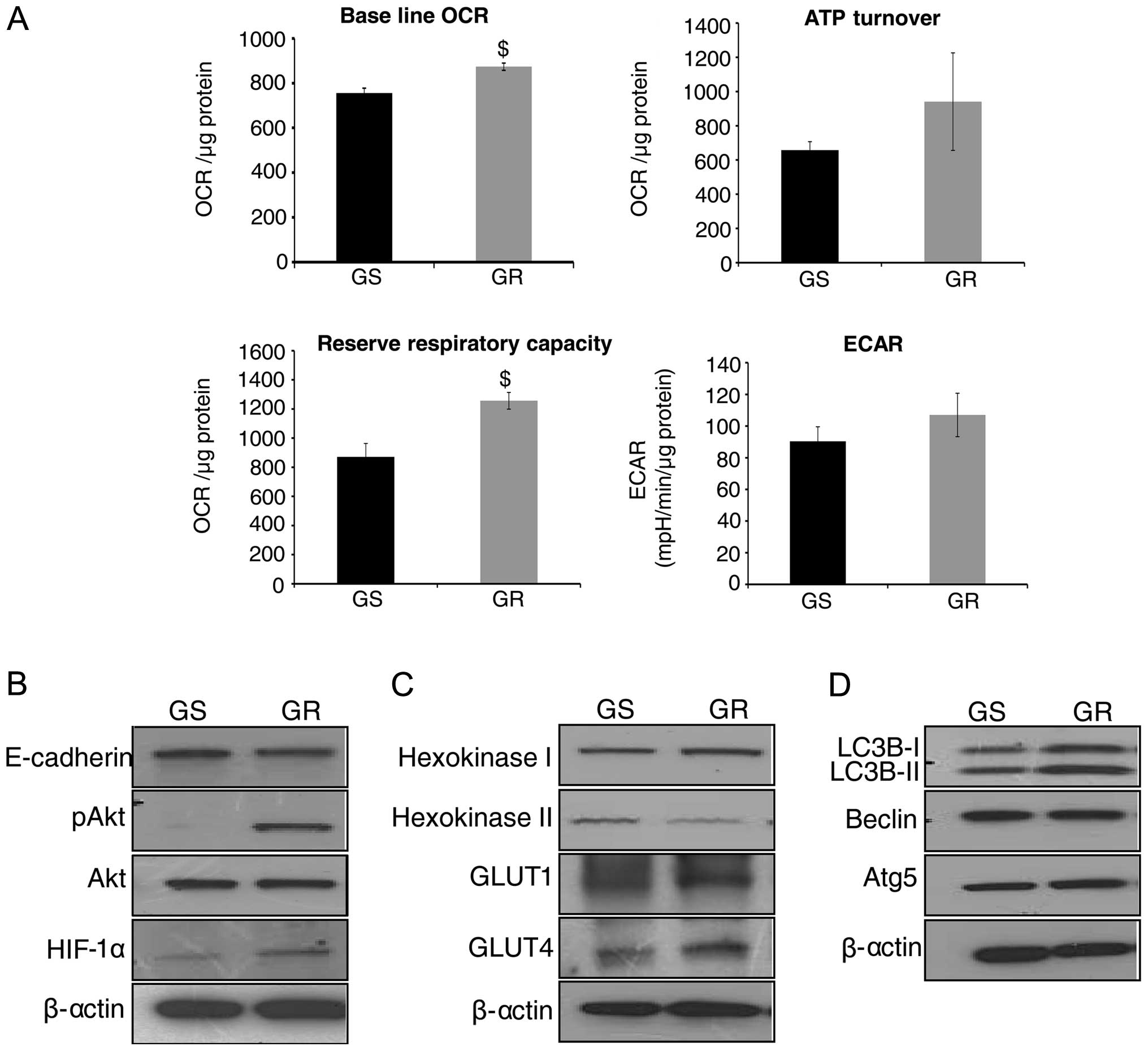
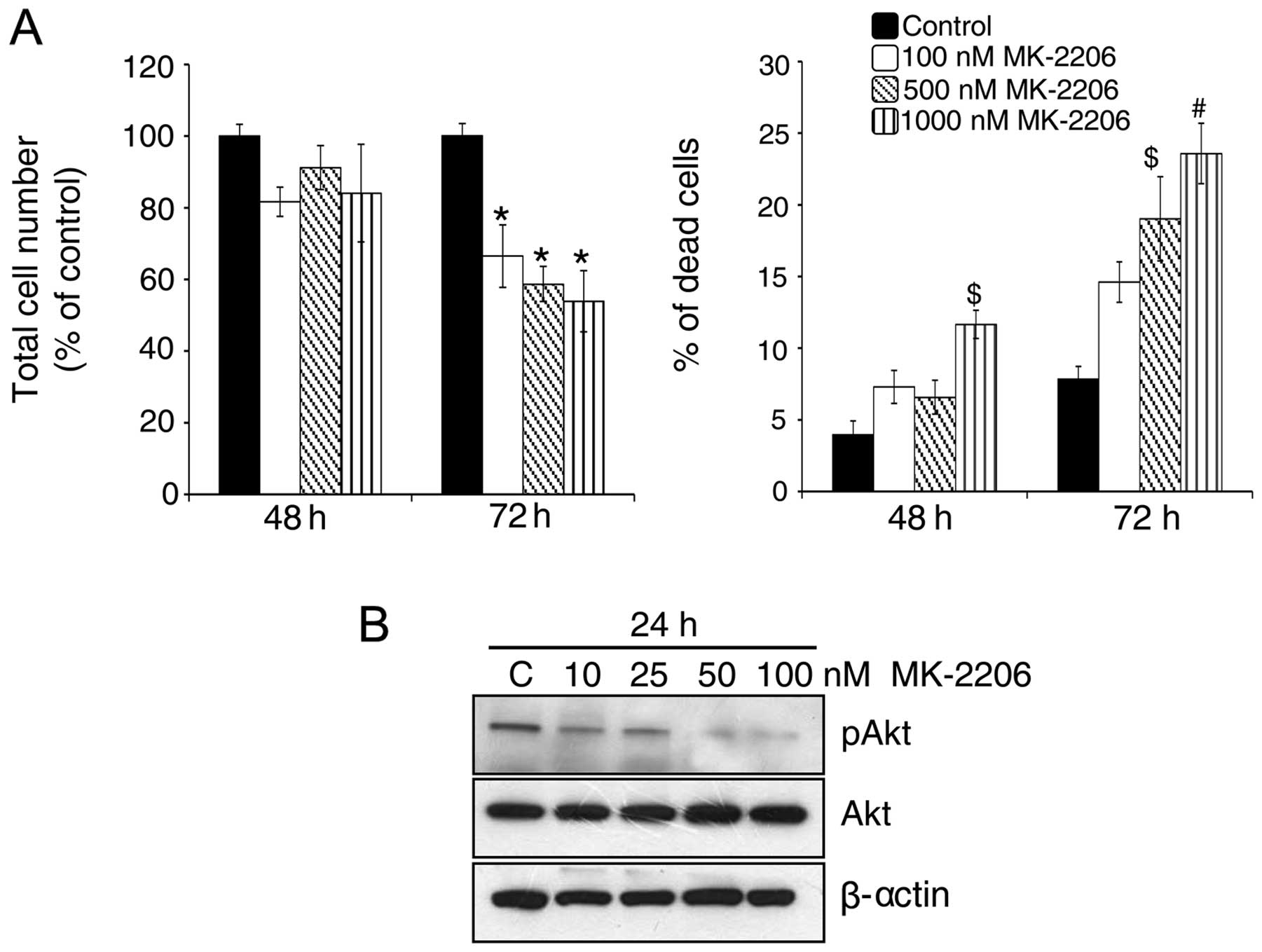
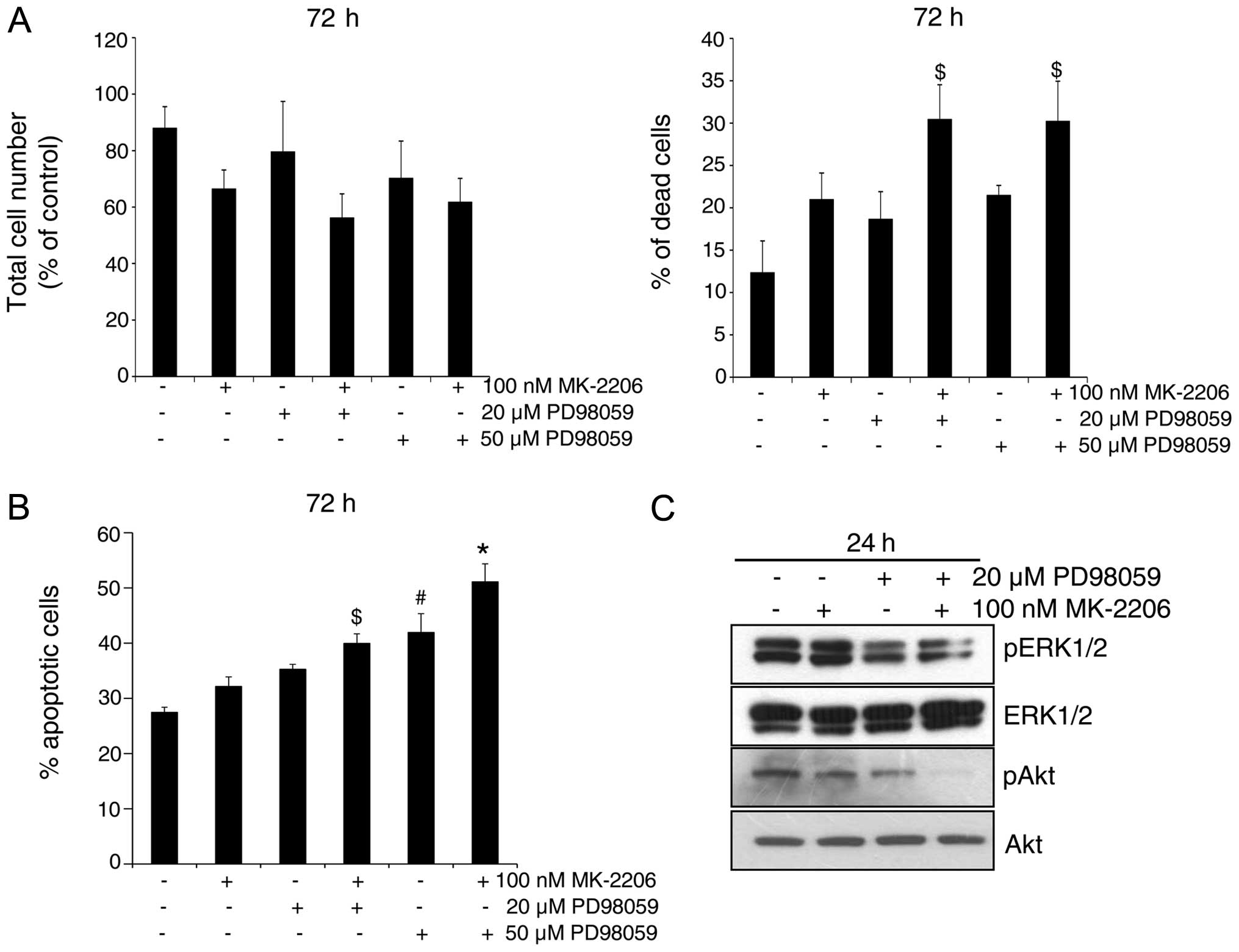
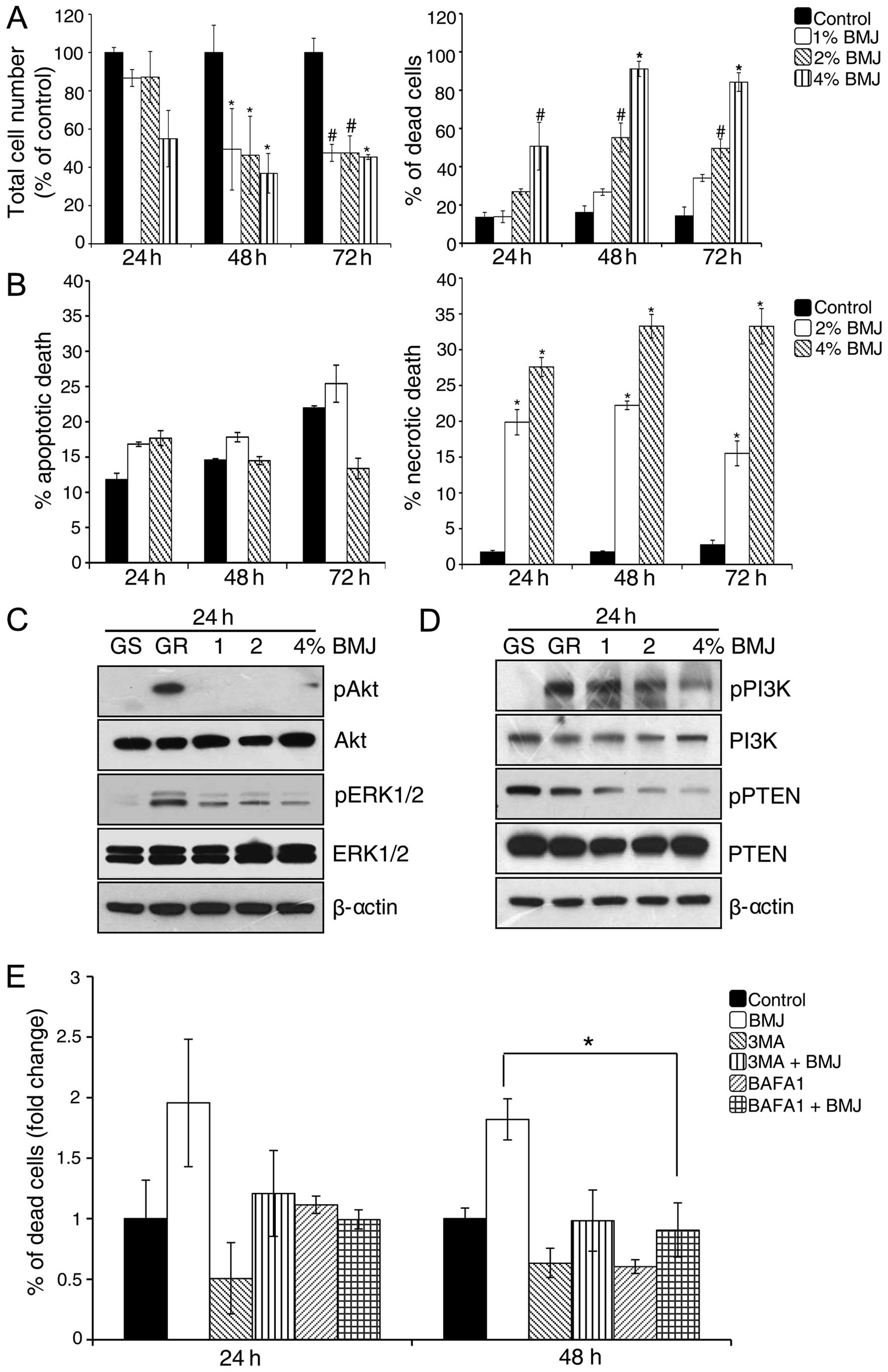
|
1
|
Guillermet-Guibert J, Davenne L,
Pchejetski D, Saint-Laurent N, Brizuela L, Guilbeau-Frugier C,
Delisle MB, Cuvillier O, Susini C and Bousquet C: Targeting the
sphingolipid metabolism to defeat pancreatic cancer cell resistance
to the chemotherapeutic gemcitabine drug. Mol Cancer Ther.
8:809–820. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Huanwen W, Zhiyong L, Xiaohua S, Xinyu R,
Kai W and Tonghua L: Intrinsic chemoresistance to gemcitabine is
associated with constitutive and laminin-induced phosphorylation of
FAK in pancreatic cancer cell lines. Mol Cancer. 8:1252009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Di Marco M, Di Cicilia R, Macchini M,
Nobili E, Vecchiarelli S, Brandi G and Biasco G: Metastatic
pancreatic cancer: Is gemcitabine still the best standard
treatment? (Review). Oncol Rep. 23:1183–1192. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kagawa S, Takano S, Yoshitomi H, et al:
Akt/mTOR signaling pathway is crucial for gemcitabine resistance
induced by Annexin II in pancreatic cancer cells. J Surg Res.
178:758–767. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Szakács G, Paterson JK, Ludwig JA,
Booth-Genthe C and Gottesman MM: Targeting multidrug resistance in
cancer. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 5:219–234. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Fanciulli M, Bruno T, Giovannelli A,
Gentile FP, Di Padova M, Rubiu O and Floridi A: Energy metabolism
of human LoVo colon carcinoma cells: correlation to drug resistance
and influence of lonidamine. Clin Cancer Res. 6:1590–1597.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhou M, Zhao Y, Ding Y, et al: Warburg
effect in chemosensitivity: Targeting lactate dehydrogenase-A
re-sensitizes taxol-resistant cancer cells to taxol. Mol Cancer.
9:332010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Vivanco I and Sawyers CL: The
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase AKT pathway in human cancer. Nat Rev
Cancer. 2:489–501. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tokunaga E, Oki E, Egashira A, Sadanaga N,
Morita M, Kakeji Y and Maehara Y: Deregulation of the Akt pathway
in human cancer. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 8:27–36. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
McCubrey JA, Steelman LS, Chappell WH, et
al: Roles of the Raf/MEK/ERK pathway in cell growth, malignant
transformation and drug resistance. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1773:1263–1284. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Elstrom RL, Bauer DE, Buzzai M, et al: Akt
stimulates aerobic glycolysis in cancer cells. Cancer Res.
64:3892–3899. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gottlob K, Majewski N, Kennedy S, Kandel
E, Robey RB and Hay N: Inhibition of early apoptotic events by
Akt/PKB is dependent on the first committed step of glycolysis and
mitochondrial hexokinase. Genes Dev. 15:1406–1418. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Plas DR, Talapatra S, Edinger AL, Rathmell
JC and Thompson CB: Akt and Bcl-xL promote growth
factor-independent survival through distinct effects on
mitochondrial physiology. J Biol Chem. 276:12041–12048. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Majewski N, Nogueira V, Bhaskar P, Coy PE,
Skeen JE, Gottlob K, Chandel NS, Thompson CB, Robey RB and Hay N:
Hexokinase-mitochondria interaction mediated by Akt is required to
inhibit apoptosis in the presence or absence of Bax and Bak. Mol
Cell. 16:819–830. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Huang WC and Hung MC: Induction of Akt
activity by chemotherapy confers acquired resistance. J Formos Med
Assoc. 108:180–194. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Duxbury MS, Ito H, Zinner MJ, Ashley SW
and Whang EE: siRNA directed against c-Src enhances pancreatic
adenocarcinoma cell gemcitabine chemosensitivity. J Am Coll Surg.
198:953–959. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yibchok-anun S, Adisakwattana S, Yao CY,
Sangvanich P, Roengsumran S and Hsu WH: Slow acting protein extract
from fruit pulp of Momordica charantia with insulin secretagogue
and insulinomimetic activities. Biol Pharm Bull. 29:1126–1131.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ganguly C, De S and Das S: Prevention of
carcinogen-induced mouse skin papilloma by whole fruit aqueous
extract of Momordica charantia. Eur J Cancer Prev. 9:283–288. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Claflin AJ, Vesely DL, Hudson JL, Bagwell
CB, Lehotay DC, Lo TM, Fletcher MA, Block NL and Levey GS:
Inhibition of growth and guanylate cyclase activity of an
undifferentiated prostate adenocarcinoma by an extract of the
balsam pear (Momordica charantia abbreviata). Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 75:989–993. 1978. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Nagasawa H, Watanabe K and Inatomi H:
Effects of bitter melon (Momordica charantia L.) or ginger rhizome
(Zingiber offifinale rosc) on spontaneous mammary tumorigenesis in
SHN mice. Am J Chin Med. 30:195–205. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Singh A, Singh SP and Bamezai R: Momordica
charantia (Bitter Gourd) peel, pulp, seed and whole fruit extract
inhibits mouse skin papillomagenesis. Toxicol Lett. 94:37–46. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Weng JR, Bai LY, Chiu CF, Hu JL, Chiu SJ
and Wu CY: Cucurbitane triterpenoid from Momordica charantia
induces apoptosis and autophagy in breast cancer cells, in part,
through peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ activation.
Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013:9356752013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Kwatra D, Subramaniam D, Ramamoorthy P,
Standing D, Moran E, Velayutham R, Mitra A, Umar S and Anant S:
Methanolic extracts of bitter melon inhibit colon cancer stem cells
by affecting energy homeostasis and autophagy. Evid Based
Complement Alternat Med. 2013:7028692013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hsiao PC, Liaw CC, Hwang SY, Cheng HL,
Zhang LJ, Shen CC, Hsu FL and Kuo YH: Antiproliferative and
hypoglycemic cucurbitane-type glycosides from the fruits of
Momordica charantia. J Agric Food Chem. 61:2979–2986. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Limtrakul P, Khantamat O and Pintha K:
Inhibition of P-glycoprotein activity and reversal of cancer
multidrug resistance by Momordica charantia extract. Cancer
Chemother Pharmacol. 54:525–530. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kaur M, Deep G, Jain AK, Raina K, Agarwal
C, Wempe MF and Agarwal R: Bitter melon juice activates cellular
energy sensor AMP-activated protein kinase causing apoptotic death
of human pancreatic carcinoma cells. Carcinogenesis. 34:1585–1592.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Agarwal C, Tyagi A, Kaur M and Agarwal R:
Silibinin inhibits constitutive activation of Stat3, and causes
caspase activation and apoptotic death of human prostate carcinoma
DU145 cells. Carcinogenesis. 28:1463–1470. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wu M, Neilson A, Swift AL, et al:
Multiparameter metabolic analysis reveals a close link between
attenuated mitochondrial bioenergetic function and enhanced
glycolysis dependency in human tumor cells. Am J Physiol Cell
Physiol. 292:C125–C136. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Brand MD and Nicholls DG: Assessing
mitochondrial dysfunction in cells. Biochem J. 435:297–312. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Potter VR and Reif AE: Inhibition of an
electron transport component by antimycin A. J Biol Chem.
194:287–297. 1952.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kasuya K, Tsuchida A, Nagakawa Y, Suzuki
M, Abe Y, Itoi T, Serizawa H, Nagao T, Shimazu M and Aoki T:
Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α expression and gemcitabine chemotherapy
for pancreatic cancer. Oncol Rep. 26:1399–1406. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhao Y, Butler EB and Tan M: Targeting
cellular metabolism to improve cancer therapeutics. Cell Death Dis.
4:e5322013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Gao T, Furnari F and Newton AC: PHLPP: a
phosphatase that directly dephosphorylates Akt, promotes apoptosis,
and suppresses tumor growth. Mol Cell. 18:13–24. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Gao AM, Ke ZP, Shi F, Sun GC and Chen H:
Chrysin enhances sensitivity of BEL-7402/ADM cells to doxorubicin
by suppressing PI3K/Akt/Nrf2 and ERK/Nrf2 pathway. Chem Biol
Interact. 206:100–108. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 62:10–29. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Tang D, Okada H, Ruland J, Liu L,
Stambolic V, Mak TW and Ingram AJ: Akt is activated in response to
an apoptotic signal. J Biol Chem. 276:30461–30466. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Jeong EK, Lee SY, Jeon HM, Ju MK, Kim CH
and Kang HS: Role of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK)1/2
in multicellular resistance to docetaxel in MCF-7 cells. Int J
Oncol. 37:655–661. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Mirmohammadsadegh A, Mota R, Gustrau A,
Hassan M, Nambiar S, Marini A, Bojar H, Tannapfel A and Hengge UR:
ERK1/2 is highly phosphorylated in melanoma metastases and protects
melanoma cells from cisplatin-mediated apoptosis. J Invest
Dermatol. 127:2207–2215. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Song J, Qu Z, Guo X, Zhao Q, Zhao X, Gao
L, Sun K, Shen F, Wu M and Wei L: Hypoxia-induced autophagy
contributes to the chemoresistance of hepatocellular carcinoma
cells. Autophagy. 5:1131–1144. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Sui X, Chen R, Wang Z, et al: Autophagy
and chemotherapy resistance: a promising therapeutic target for
cancer treatment. Cell Death Dis. 4:e8382013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Carew JS, Nawrocki ST, Kahue CN, Zhang H,
Yang C, Chung L, Houghton JA, Huang P, Giles FJ and Cleveland JL:
Targeting autophagy augments the anticancer activity of the histone
deacetylase inhibitor SAHA to overcome Bcr-Abl-mediated drug
resistance. Blood. 110:313–322. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Yang ZJ, Chee CE, Huang S and Sinicrope
FA: The role of autophagy in cancer: therapeutic implications. Mol
Cancer Ther. 10:1533–1541. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|