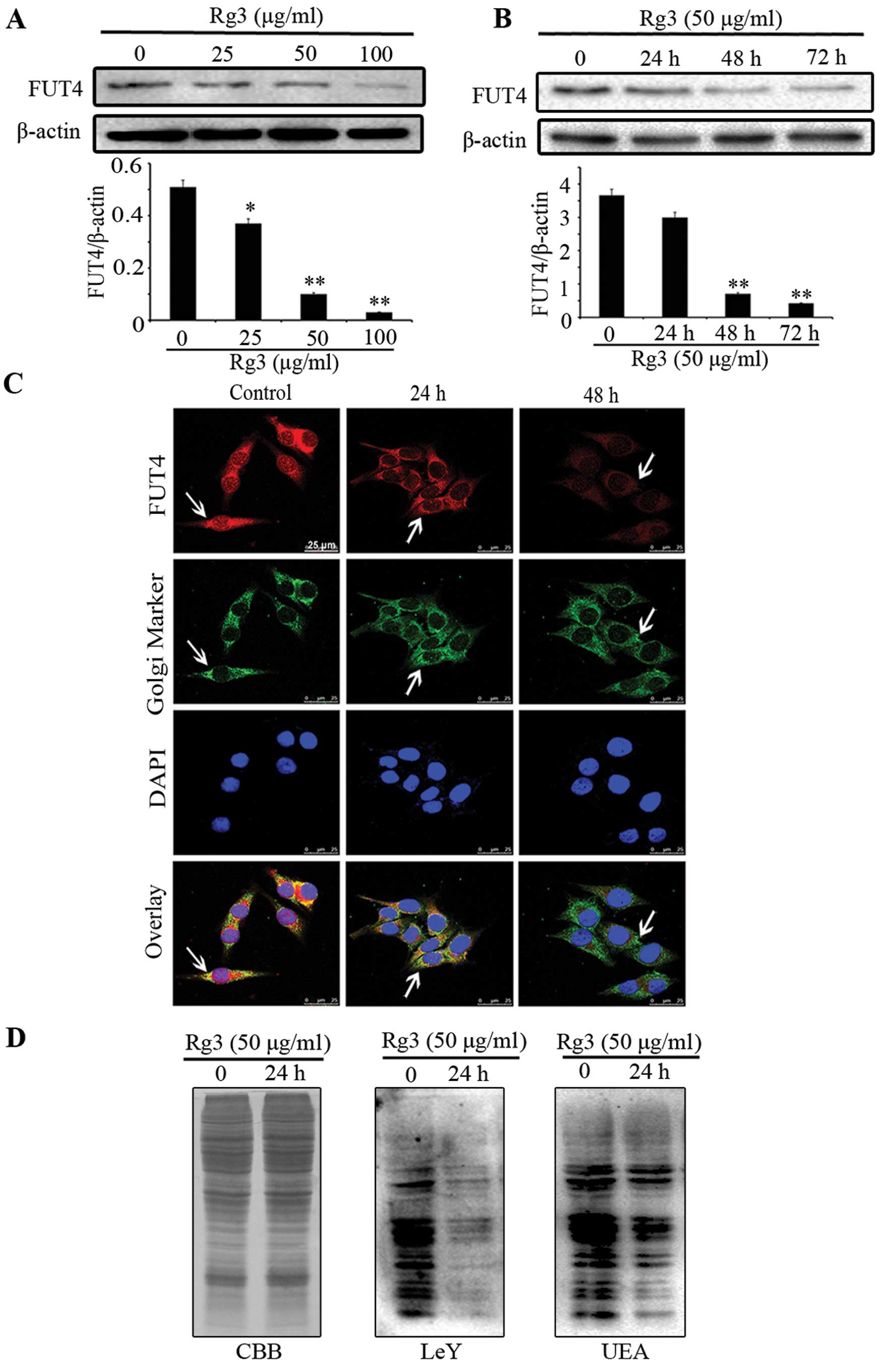
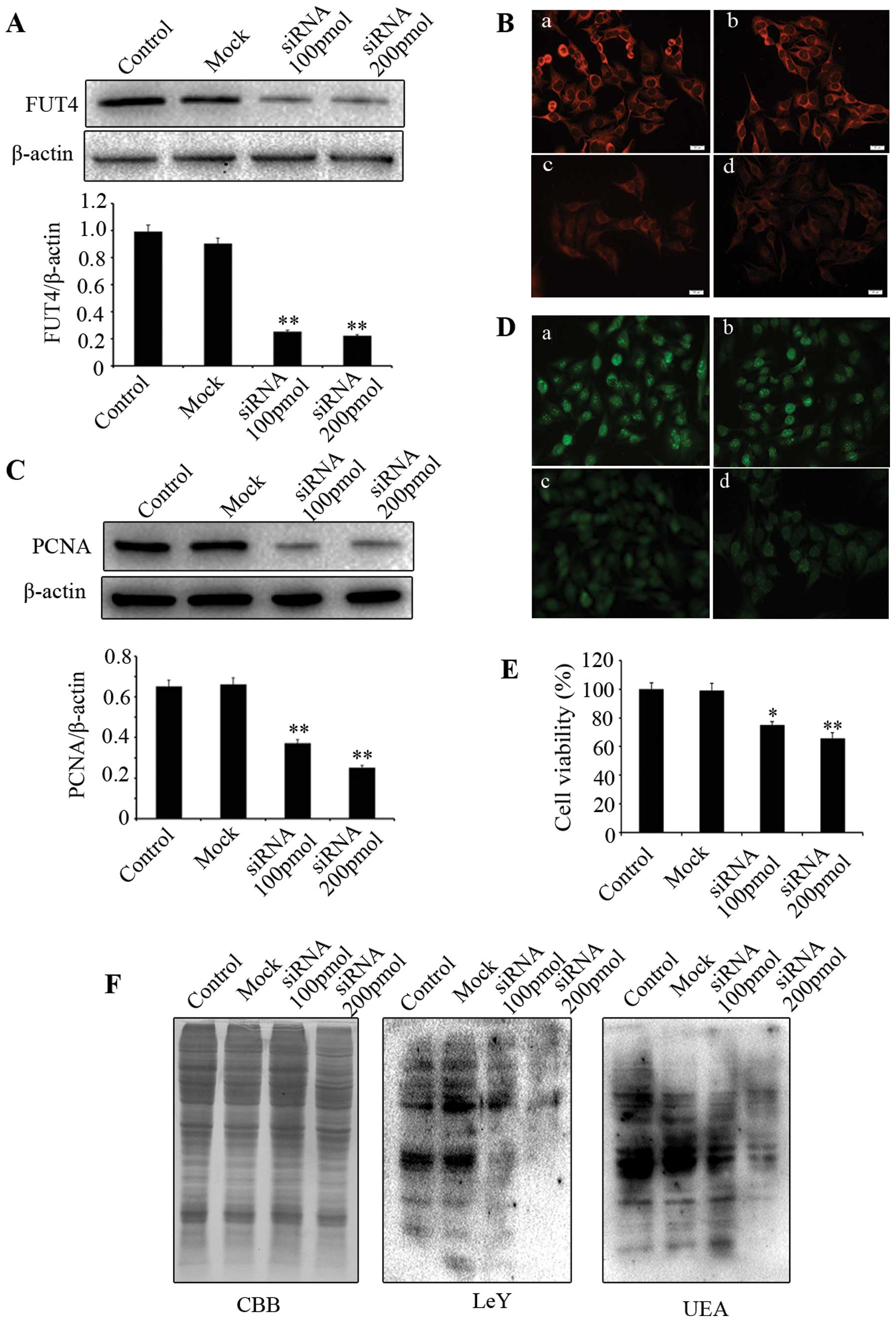
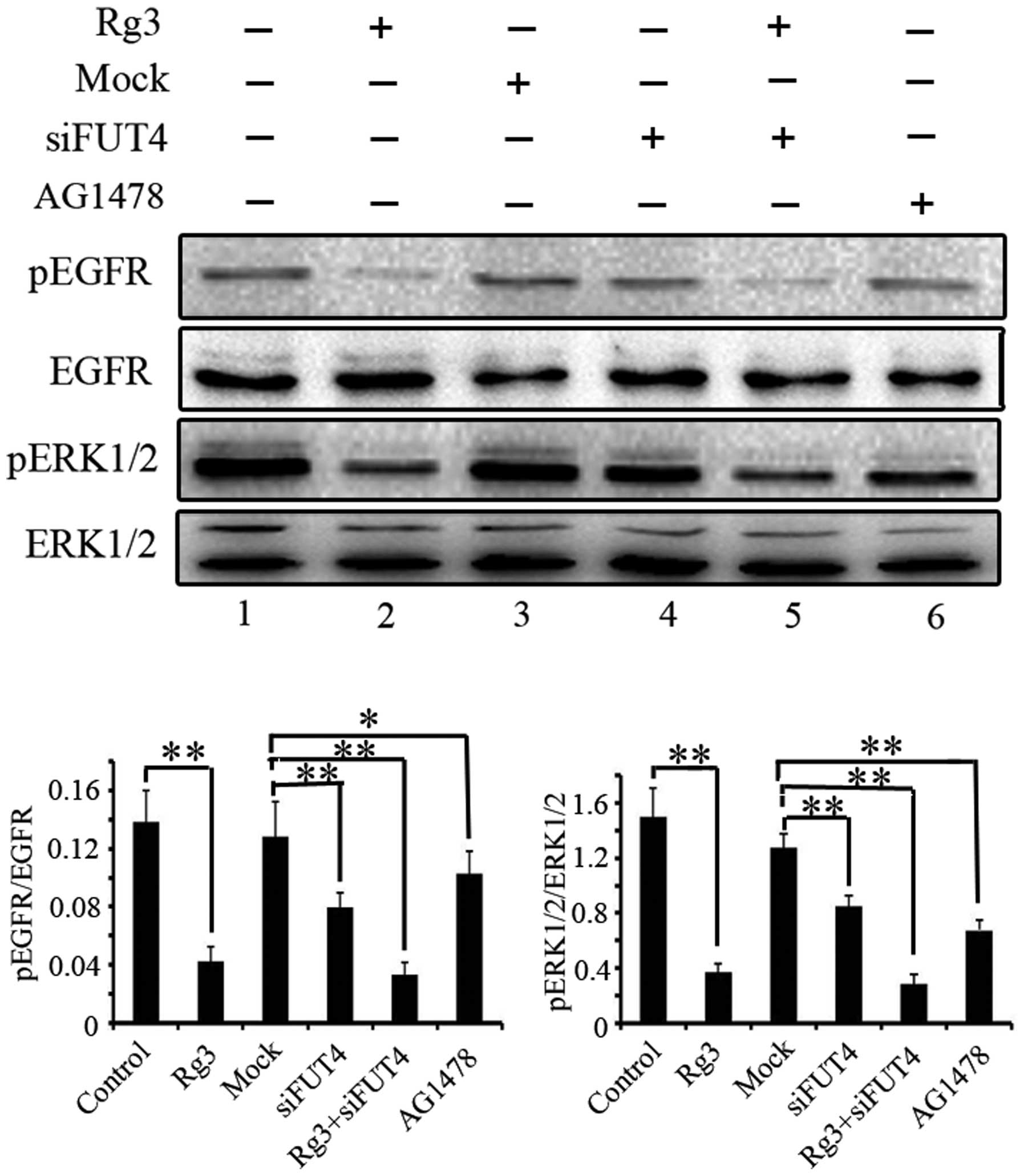
|
1
|
Ives NJ, Stowe RL, Lorigan P and Wheatley
K: Chemotherapy compared with biochemotherapy for the treatment of
metastatic melanoma: a meta-analysis of 18 trials involving 2,621
patients. J Clin Oncol. 25:5426–5434. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Balch CM, Gershenwald JE, Soong SJ, et al:
Final version of 2009 AJCC melanoma staging and classification. J
Clin Oncol. 27:6199–6206. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Menzies AM and Lon GV: Recent advances in
melanoma systemic therapy, BRAF inhibitors, CTLA4 antibodies and
beyond. Eur J Cancer. 49:3229–3241. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ma C and Armstrong AW: Severe adverse
events from the treatment of advanced melanoma: a systematic review
of severe side effects associated with ipilimumab, vemurafenib,
interferon alfa-2b, dacarbazine and interleukin-2. J Dermatolog
Treat. 25:401–408. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Menaa F: Latest approved therapies for
metastatic melanoma: what comes next? J Skin Cancer. 1:1–10. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Zhang S, Zhang HS, Cordon-Cardo C, Reuter
VE, Singhal AK, Lioyd KO and Livingston PO: Selection of tumor
antigens as targets for immune attack using immunohistochemistry:
II. Blood group-related antigens. Int J Cancer. 73:50–56. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Cao Y, Merling A, Karsten U and
Schwartz-Albiez R: The fucosylated histoblood group antigens H type
2 (blood group O, CD173) and Lewis Y (CD174) are expressed on
CD34+ hematopoietic progenitors but absent on mature
lymphocytes. Glycobiology. 11:677–683. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Escrevente C, Machado E, Brito C, Reis CA,
Stoeck A, Runz S, Marmé A, Altevogt P and Costa J: Different
expression levels of alpha3/4 fucosyltransferases and Lewis
determinants in ovarian carcinoma tissues and cell lines. Int J
Oncol. 29:557–566. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhang Z, Sun P, Liu J, Fu L and Yan Q:
Suppression of FUT1/FUT4 expression by siRNA inhibits tumor growth.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1783:287–296. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Wang YF, Liu JJ, Lin B, Wang CZ, Li Q, Liu
S, Yan L, Zhang S and Iwamori M: Study on the expression and
clinical significances of Lewis y antigen and integrin αv, β3 in
epithelial ovarian tumors. Int J Mol Sci. 12:3409–3421. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Kuo CH, Chen PK, Chang BI, Sung MC, Shi
CS, Lee JS, Chang CF, Shi JY and Wu HL: The recombinant lectin-like
domain of thrombomodulin inhibits angiogenesis through interaction
with Lewis Y antigen. Blood. 119:1302–1313. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Gao J, Hu ZH, Liu JJ, Liu DW, Wang Y, Cai
M, Zhang D, Tan M and Lin B: Expression of CD147 and Lewis y
antigen in ovarian cancer and their relationship to drug
resistance. Med Oncol. 31:920–929. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hu ZH, Gao J, Liu B, et al: High
expression of Lewis y antigen and CD44 is correlated with
resistance to chemotherapy in epithelial ovarian cancers. PLoS One.
8:e572502013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Noble P, Spendlove I, Harding S, Parsons T
and Durrant LG: Durrant therapeutic targeting of Lewisy
and Lewisb with a novel monoclonal antibody 692/29. PLoS
One. 8:e548922013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Zandi R, Larsen AB, Anderse P, Stockhausen
MT and Poulsen HS: Mechanism for oncogenic activation of the
epidermal growth factor receptor. Cell Signal. 19:2013–2023. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Weston BW, Nair RP, Larsen RD and Lowe JB:
Isolation of a novel human alpha (1,3)-fucosyltransferase gene and
molecular comparison to the human Lewis blood group alpha (1,3/1,4)
fucosyltransferase gene. Syntenic, homologous, nonallelic genes
encoding enzymes with distinct acceptor substrate specificities. J
Biol Chem. 267:4152–4160. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Weston BW, Smith PL, Kelly RJ and Lowe JB:
Molecular cloning of a fourth member of a human alpha
(1,3)-fucosyltransferase gene family. Multiple homologous sequences
that determine expression of the Lewis x, sialyl Lewis x, and
difucosylsialyl Lewis x epitopes. J Biol Chem. 267:24575–24584.
1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Petretti T, Schulze B, Schlag PM and
Kemmner W: Altered mRNA expression of glycosyltransferases in human
gastric carcinomas. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1428:209–218. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ito H, Hiraiwa N, Kannaqi R, et al:
Altered mRNA expression of specific molecular species of fucosyl-
and sialyl-transferases in human colorectal cancer tissues. Int J
Cancer. 71:556–564. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ogawa J, Inoue H and Koide S: Expression
of alpha-1, 3-fucosyltransferase type IV and VII genes is related
to poor prognosis in lung cancer. Cancer Res. 56:325–329.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Li HY, Tong SM, Liu JW, Han L, Hou H, Yan
Q and Wang XQ: Differential fucosyltransferase IV expression in
squamous carcinoma cells is regulated by promoter methylation. Cell
Mol Biol Lett. 17:206–216. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yang X, Zhang Z, Jia S, Liu Y, Wang X and
Yan Q: Overexpression of fucosyltransferase IV in A431 cell line
increases cell proliferation. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
39:1722–1730. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Park EH, Kim YJ, Kang KS, et al: Stereo
specific anticancer effects of ginsenoside Rg3 epimers isolated
from heat-processed American ginseng on human gastric cancer cell.
J Ginseng Res. 38:22–27. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chen XP, Qian LL, Hong JH and Chen JH:
Ginsenoside Rg3 inhibits CXCR4 expression and related migrations in
a breast cancer cell line. Int J Clin Oncol. 16:519–523. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lee SY, Kim GT, Roh SH, Song JS, Kim HJ,
Hong SS, Kwon SW and Park JH: Proteomic analysis of the anti-cancer
effect of 20S-Ginsenoside Rg3 in human colon cancer cell lines.
Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 73:811–816. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhang C, Liu LJ, Yu Y, Chen B, Tang C and
Li X: Antitumor effects of ginsenoside Rg3 on human hepatocellular
carcinoma cells. Mol Med Rep. 5:1295–1298. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kim JW, Jung SY, Kwon YH, Lee JH, Lee YM,
Lee BY and Kwon SM: Ginsenoside Rg3 attenuates tumor angiogenesis
via inhibiting bioactivities of endothelial progenitor cells.
Cancer Biol Ther. 13:504–515. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kim YJ, Choi WI, Ko H, et al: Stereo
specific effects of ginsenoside 20-Rg3 inhibits TGF1-induced
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and suppresses lung cancer
migration, invasion and anoikis resistance. Toxicology. 322:23–33.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kim DG, Jung KH, Kim YS, et al: 20
(S)-Ginsenoside Rg3 is a novel inhibitor of autophagy and
sensitizes hepatocellular carcinoma to doxorubicin. Oncotarget.
5:4438–4451. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
He BC, Gao JL, Zhou BQ, et al: Ginsenoside
Rg3 inhibits colorectal tumor growth through the down-regulation of
Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Int J Oncol. 38:437–445. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Kim SM, Lee SY, Yuk DY, Moon DC, Choi SS,
Kim Y, Han SB, Oh KW and Hong JT: Inhibition of NF-κB by
ginsenoside Rg3 enhances the susceptibility of colon cancer cells
to docetaxel. Arch Pharm Res. 32:755–765. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yang XS, Liu S, Liu YJ, Liu JW, Liu TJ,
Wang XQ and Yan Q: Overexpression of fucosyltransferase IV promotes
A431 cell proliferation through activating MAPK and PI3K/Akt
signaling pathways. J Cell Physiol. 225:612–619. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yang XS, Liu YJ, Liu JW, Wang XQ and Yan
Q: Cyclophosphamide-induced apoptosis in A431 cells is inhibited by
fucosyltransferase IV. J Cell Biochem. 112:1376–1383. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ciolczyk-Wierzbicka D, Bodzioch M, Gil D,
Zmudzinska D, Dembinska-Kiec A and Laidler P: Expression of
fucosyltransferases contributes to melanoma invasive phenotype. Med
Chem. 3:418–424. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Azuma Y, Ito M, Taniguchi A and Matsumoto
K: Expression of cell surface Lewis X and Y antigens and FUT4 mRNA
is increased in Jurkat cells undergoing apoptosis. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1672:157–163. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Madjd Z, Parsons T, Watson N, Spendlove I,
Ellis I and Durrant LG: High expression of Lewisy/b antigens is
associated with decreased survival in lymph node negative breast
carcinomas. Breast Cancer Res. 7:780–787. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Hu ZH, Gao S, Lin B, et al: Elevated
levels of Lewis Y and integrin α5β1 correlate with chemotherapeutic
drug resistance in epithelial ovarian carcinoma. Int J Mol Sci.
13:15588–15600. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Farhan H, Schuster C, Kircheis R, et al:
Inhibition of xenograft tumor growth and down-regulation of ErbB
receptors by an antibody directed against Lewis Y antigen. J
Pharmacology Exp Ther. 319:1459–1466. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|