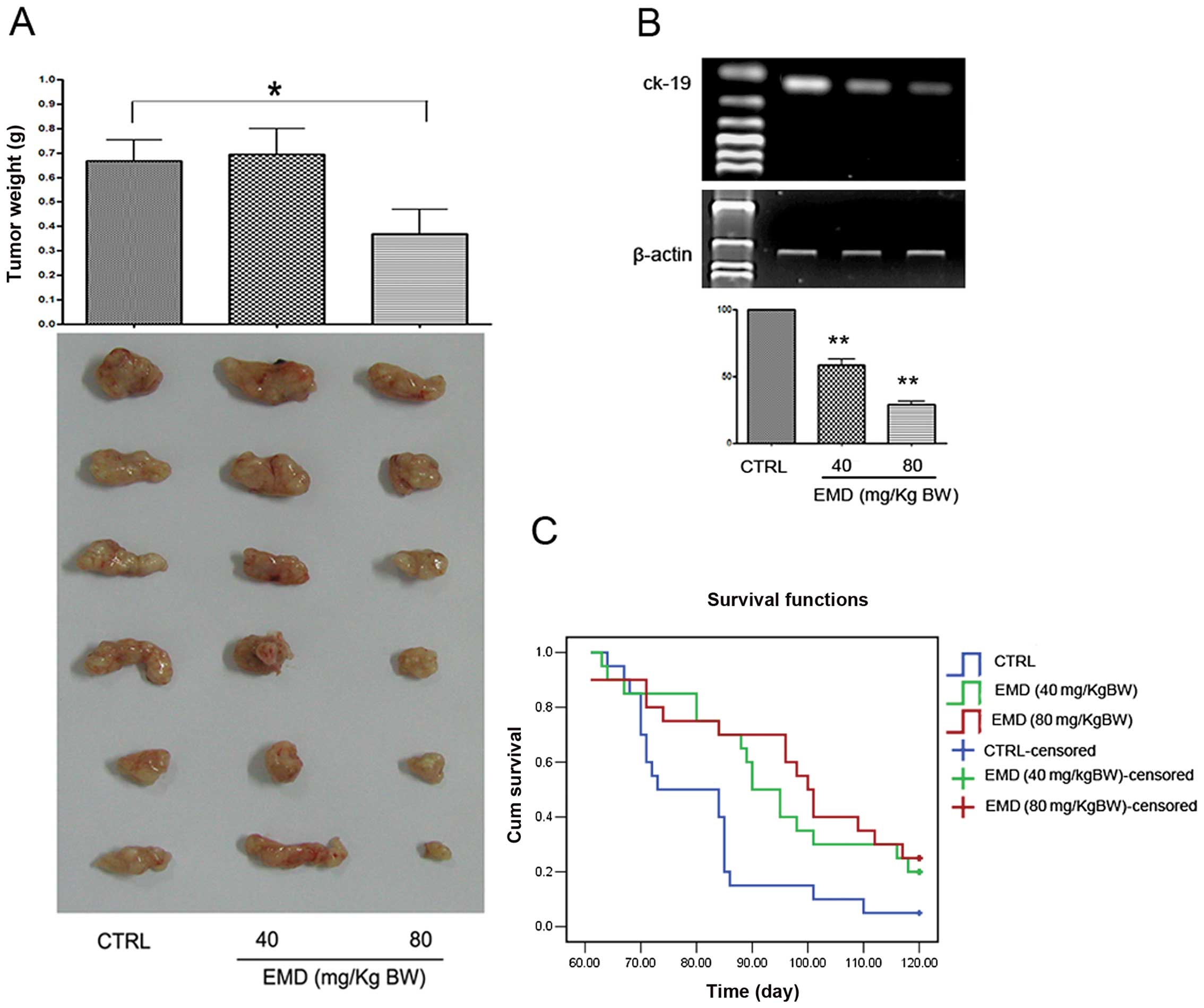
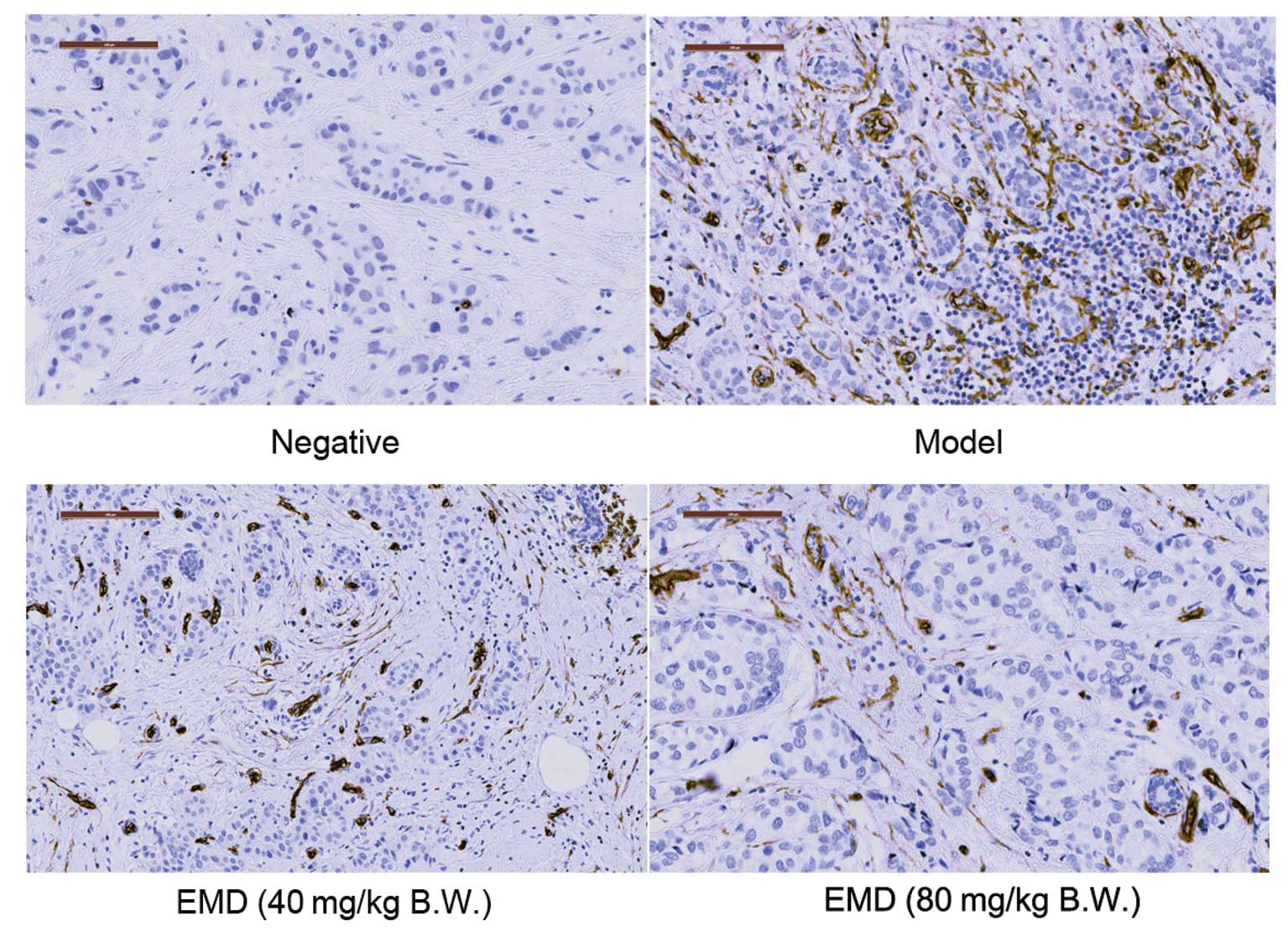
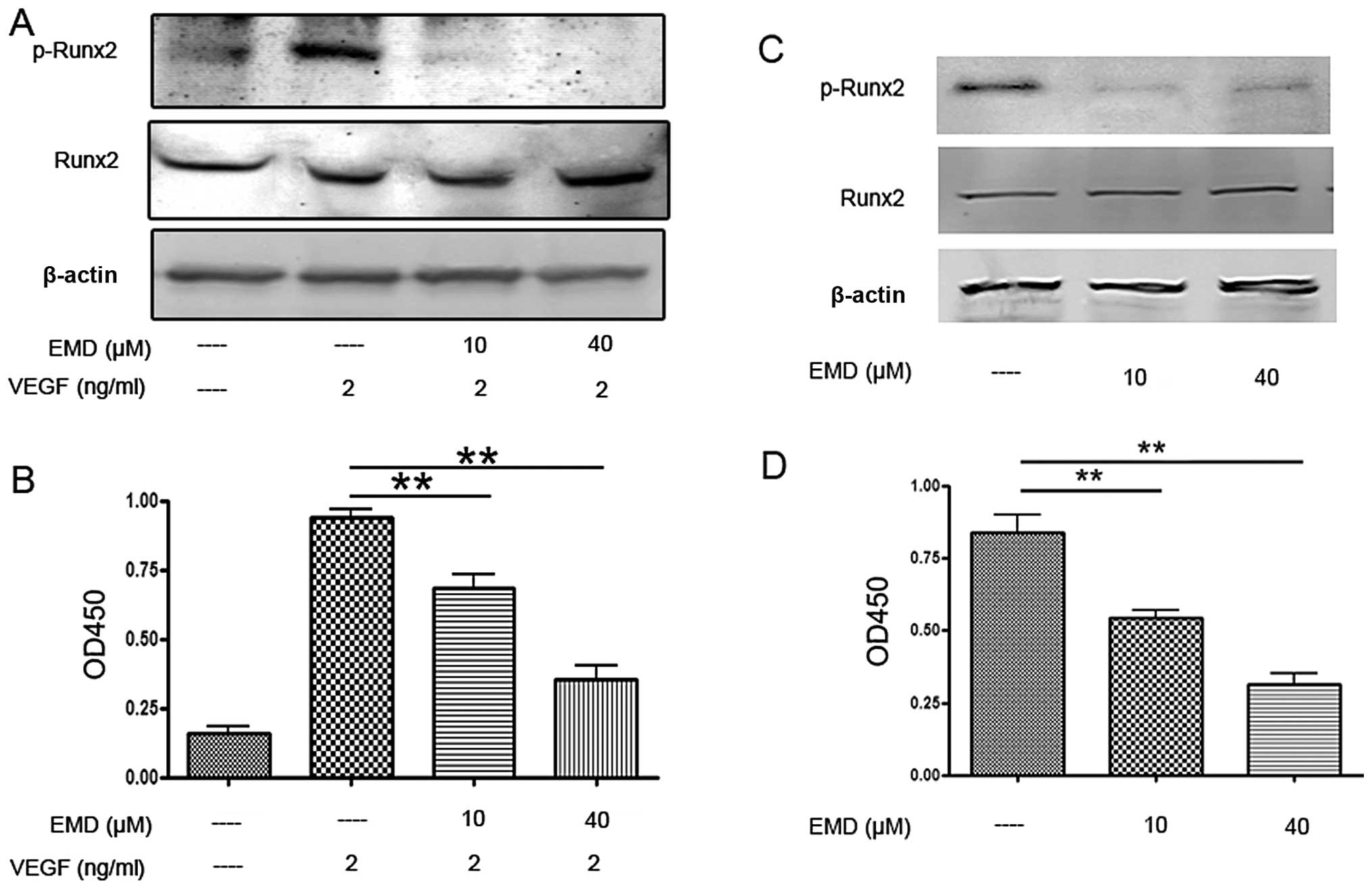
|
1
|
Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer
Statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 63:11–30. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Weigelt B, Peterse JL and van ‘t Veer LJ:
Breast cancer metastasis: markers and models. Nat Rev Cancer.
5:591–602. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Leong SP, Cady B, Jablons DM, et al:
Clinical patterns of metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 25:221–232.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Stevanovic A, Lee P and Wilcken N:
Metastatic breast cancer. Aust Fam Physician. 35:309–312.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Liu S, Goldstein RH, Scepansky EM, et al:
Inhibition of rho-associated kinase signaling prevents breast
cancer metastasis to human bone. Cancer Res. 69:8742–8751. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chiang AC and Massagué J: Molecular basis
of metastasis. N Engl J Med. 359:2814–2823. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Gupta GP and Massagué J: Cancer
metastasis: building a framework. Cell. 127:679–695. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Adams RH and Alitalo K: Molecular
regulation of angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 8:464–478. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Duffy MJ, Maguire TM, Hill A, et al:
Metalloproteinases: role in breast carcinogenesis, invasion and
metastasis. Breast Cancer Res. 2:252–257. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Roy R, Yang J and Moses MA: Matrix
metalloproteinases as novel biomarkers and potential therapeutic
targets in human cancer. J Clin Oncol. 27:5287–5297. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Radisky ES and Radisky DC: Matrix
metalloproteinase-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in
breast cancer. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 15:201–212. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lian JB, Stein JL, Stein GS, et al:
Runx2/Cbfa1 functions: diverse regulation of gene transcription by
chromatin remodeling and co-regulatory protein interactions.
Connect Tissue Res. 44(Suppl 1): S141–S148. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Karsenty G: Role of Cbfa1 in osteoblast
differentiation and function. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 11:343–346.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Komori T: Runx2, a multifunctional
transcription factor in skeletal development. J Cell Biochem.
87:1–8. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Stein GS, Lian JB, van Wijnen AJ, et al:
Runx2 control of organization, assembly and activity of the
regulatory machinery for skeletal gene expression. Oncogene.
23:4315–4329. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Harada S and Rodan GA: Control of
osteoblast function and regulation of bone mass. Nature.
423:349–355. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Shore P: A role for Runx2 in normal
mammary gland and breast cancer bone metastasis. J Cell Biochem.
96:484–489. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Sun L, Vitolo MI, Qiao M, et al:
Regulation of TGFbeta1-mediated growth inhibition and apoptosis by
RUNX2 isoforms in endothelial cells. Oncogene. 23:4722–4734. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Qiao M, Shapiro P, Fosbrink M, et al: Cell
cycle-dependent phosphorylation of the RUNX2 transcription factor
by cdc2 regulates endothelial cell proliferation. J Biol Chem.
281:7118–7128. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sun L, Vitolo MI and Passaniti A:
Runt-related gene 2 in endothelial cells: inducible expression and
specific regulation of cell migration and invasion. Cancer Res.
61:4994–5001. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Liu A, Chen H, Wei W, et al:
Antiproliferative and antimetastatic effects of emodin on human
pancreatic cancer. Oncol Rep. 26:81–89. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kaneshiro T, Morioka T, Inamine M, et al:
Anthraquinone derivative emodin inhibits tumor-associated
angiogenesis through inhibition of extracellular signal-regulated
kinase 1/2 phosphorylation. Eur J Pharmacol. 553:46–53. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Fu J, Ding Y, Huang D, et al: The retinoid
X receptor-selective ligand, LGD1069, inhibits tumor-induced
angiogenesis via suppression of VEGF in human non-small cell lung
cancer. Cancer Lett. 248:153–163. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Hsu S-C and Chung J-G: Anticancer
potential of emodin. BioMedicine. 2:108–116. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Lu HF, Lai KC, Hsu SC, et al: Involvement
of matrix metalloproteinases on the inhibition of cells invasion
and migration by emodin in human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells.
Neurochem Res. 34:1575–1583. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chambers AF and Matrisian LM: Changing
views of the role of matrix metalloproteinases in metastasis. J
Natl Cancer Inst. 89:1260–1270. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Fidler IJ: Angiogenesis and cancer
metastasis. Cancer J. 6(Suppl 2): S134–S141. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Inman CK, Li N and Shore P: Oct-1
counteracts autoinhibition of Runx2 DNA binding to form a novel
Runx2/Oct-1 complex on the promoter of the mammary gland-specific
gene beta-casein. Mol Cell Biol. 25:3182–3193. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Barnes GL, Javed A, Waller SM, et al:
Osteoblast-related transcription factors Runx2 (Cbfa1/AMl3) and
MSX2 mediate the expression of bone sialoprotein in human
metastatic breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 63:2631–2637.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Inman CK and Shore P: The osteoblast
transcription factor Runx2 is expressed in mammary epithelial cells
and mediates osteopontin expression. J Biol Chem. 278:48684–48689.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Jiménez MJ, Balbín M, López JM, et al:
Collagenase 3 is a target of Cbfa1, a transcription factor of the
runt gene family involved in bone formation. Mol Cell Biol.
19:4431–4442. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Selvamurugan N and Partridge NC:
Constitutive expression and regulation of collagenase-3 in human
breast cancer cells. Mol Cell Biol Res Commun. 3:218–223. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Selvamurugan N, Kwok S and Partridge NC:
Smad3 interacts with JunB and Cbfa1/Runx2 for transforming growth
factor-beta1-stimulated collagenase-3 expression in human breast
cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 279:27764–27773. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Pratap J, Javed A, Languino LR, et al: The
Runx2 osteogenic transcription factor regulates matrix
metalloproteinase 9 in bone metastatic cancer cells and controls
cell invasion. Mol Cell Biol. 25:8581–8591. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kwon TG, Zhao X, Yang Q, et al: Physical
and functional interactions between Runx2 and HIF-1α induce
vascular endothelial growth factor gene expression. J Cell Biochem.
112:3582–3593. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|