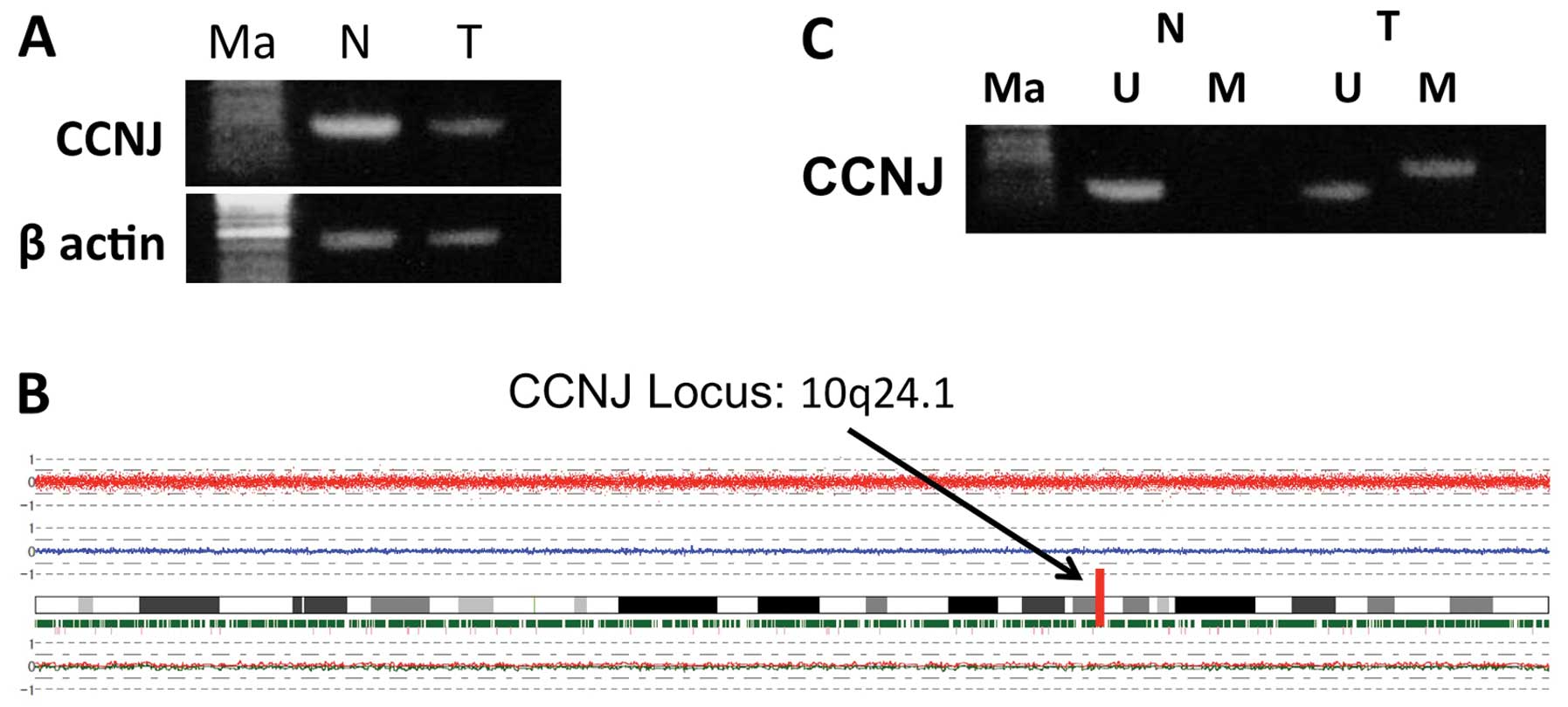
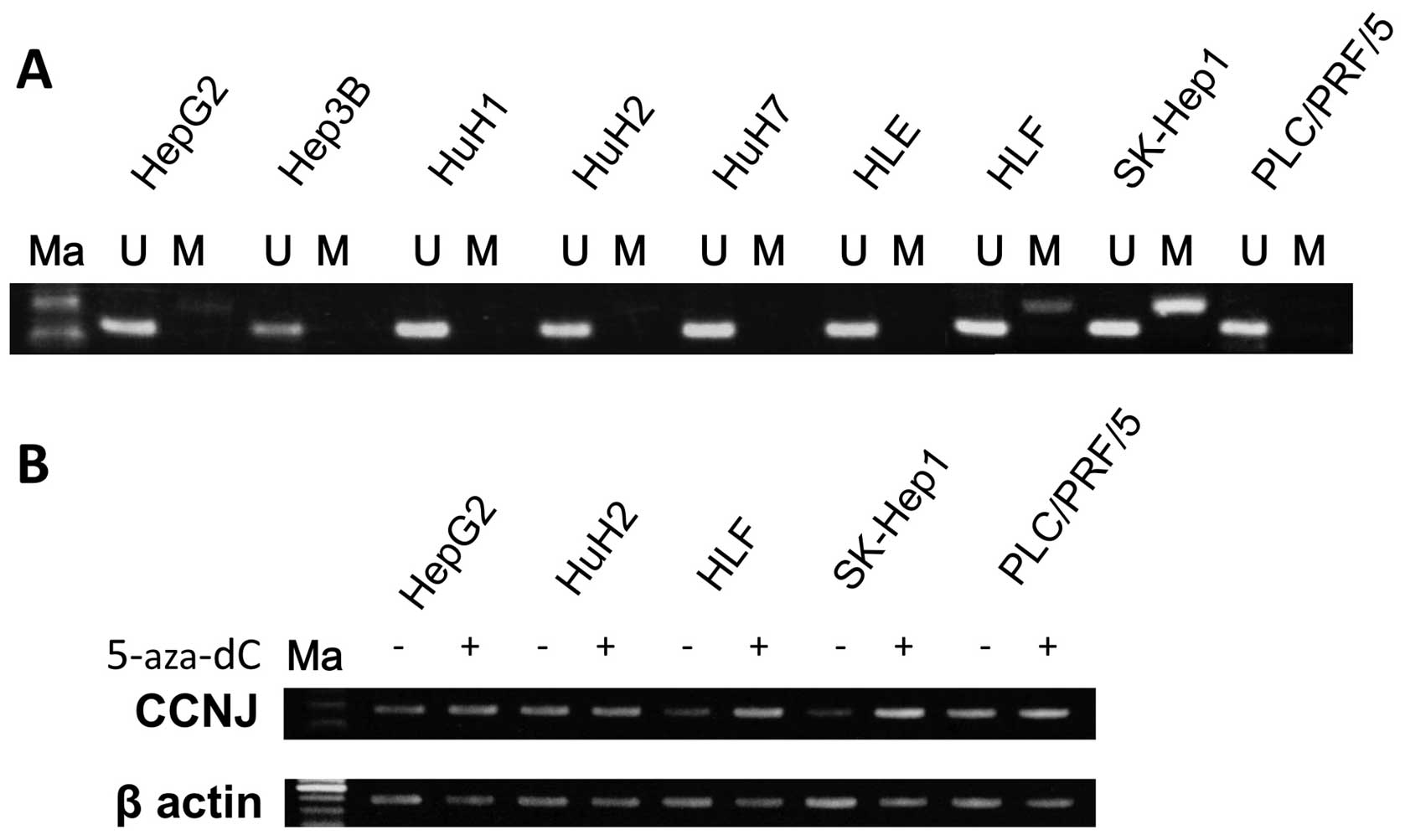
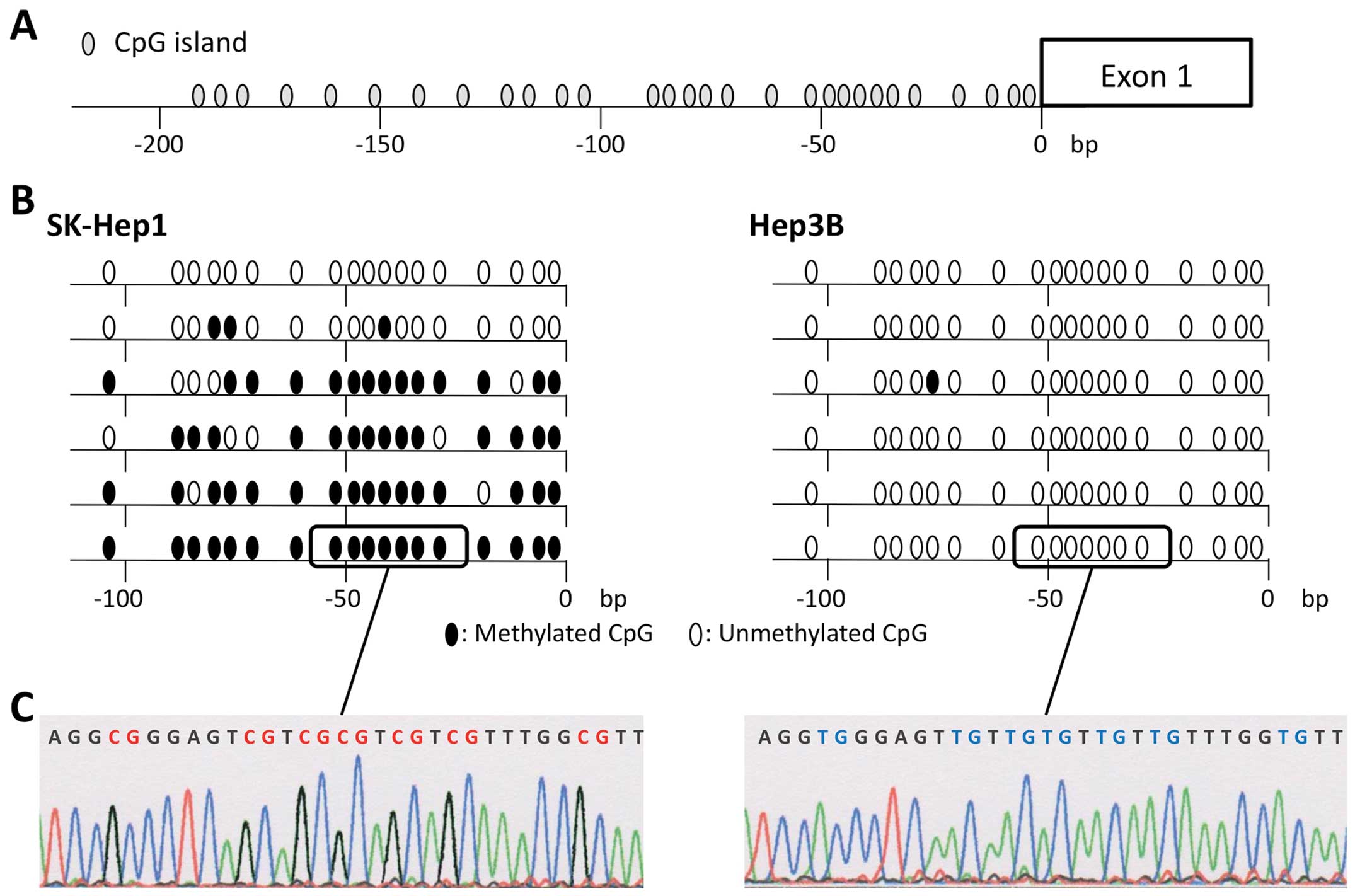
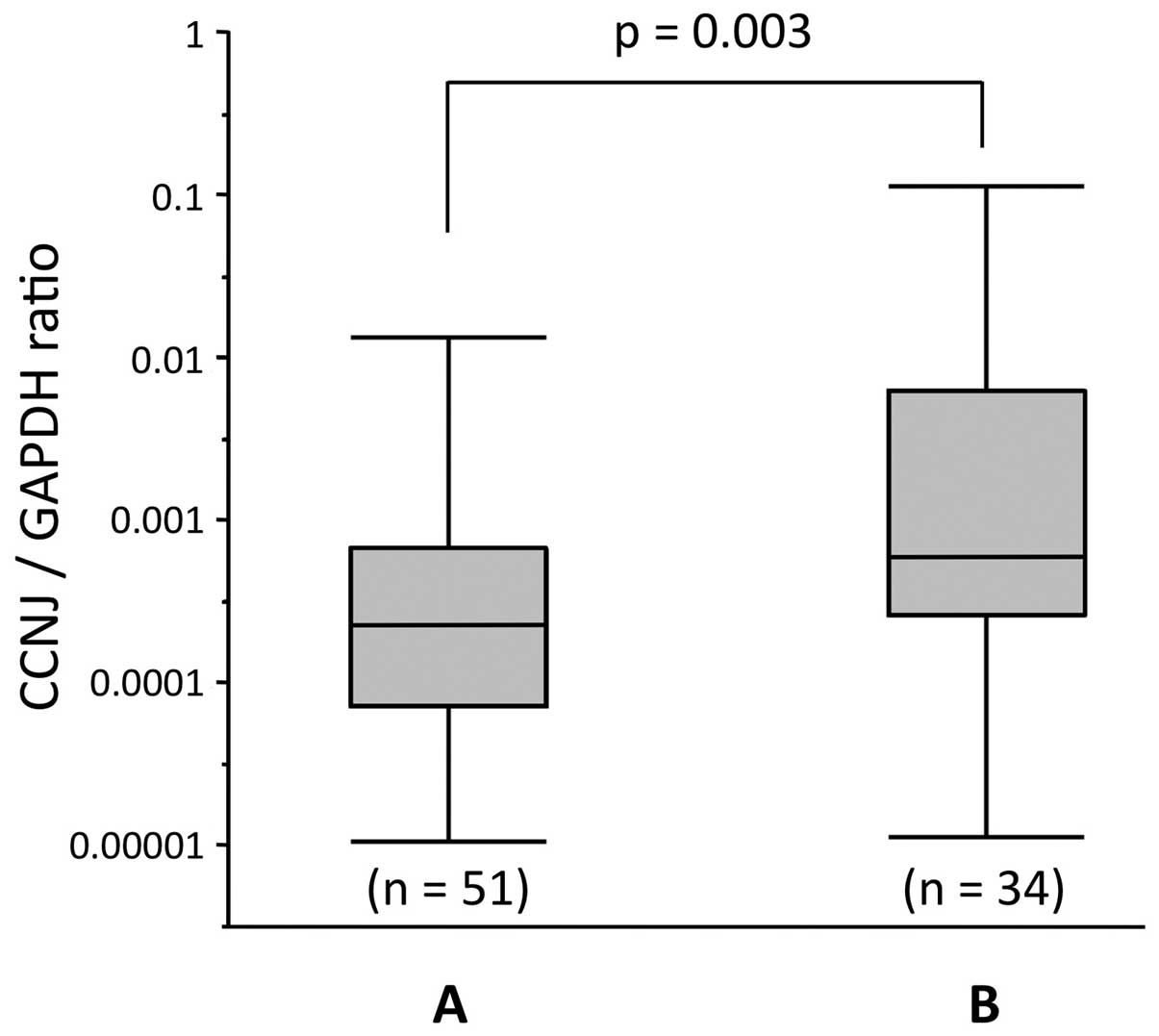
|
1
|
Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D,
Mathers C and Parkin DM: Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in
2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 127:2893–2917. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Forner A, Llovet JM and Bruix J:
Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 379:1245–1255. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Livraghi T, Goldberg SN, Lazzaroni S,
Meloni F, Solbiati L and Gazelle GS: Small hepatocellular
carcinoma: Treatment with radio-frequency ablation versus ethanol
injection. Radiology. 210:655–661. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Takayasu K, Arii S, Ikai I, et al: Liver
Cancer Study Group of Japan: Prospective cohort study of
transarterial chemo-embolization for unresectable hepatocellular
carcinoma in 8510 patients. Gastroenterology. 131:461–469. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V, et al:
SHARP Investigators Study Group: Sorafenib in advanced
hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 359:378–390. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yu MC and Yuan JM: Environmental factors
and risk for hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 127(Suppl
1): S72–S78. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Cusnir M and Patt YZ: Novel systemic
therapy options for hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer J. 10:97–103.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
El-Serag HB and Rudolph KL: Hepatocellular
carcinoma: Epidemiology and molecular carcinogenesis.
Gastroenterology. 132:2557–2576. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kanda M, Nomoto S, Okamura Y, Nishikawa Y,
Sugimoto H, Kanazumi N, Takeda S and Nakao A: Detection of
metallothionein 1G as a methylated tumor suppressor gene in human
hepatocellular carcinoma using a novel method of double combination
array analysis. Int J Oncol. 35:477–483. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Nomoto S, Kanda M, Okamura Y, Nishikawa Y,
Qiyong L, Fujii T, Sugimoto H, Takeda S and Nakao A: Epidermal
growth factor-containing fibulin-like extracellular matrix protein
1, EFEMP1, a novel tumor-suppressor gene detected in hepatocellular
carcinoma using double combination array analysis. Ann Surg Oncol.
17:923–932. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Okamura Y, Nomoto S, Kanda M, Li Q,
Nishikawa Y, Sugimoto H, Kanazumi N, Takeda S and Nakao A: Leukemia
inhibitory factor receptor (LIFR) is detected as a novel suppressor
gene of hepatocellular carcinoma using double-combination array.
Cancer Lett. 289:170–177. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Okamura Y, Nomoto S, Kanda M, Hayashi M,
Nishikawa Y, Fujii T, Sugimoto H, Takeda S and Nakao A: Reduced
expression of reelin (RELN) gene is associated with high recurrence
rate of hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 18:572–579. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Kanda M, Nomoto S, Okamura Y, Hayashi M,
Hishida M, Fujii T, Nishikawa Y, Sugimoto H, Takeda S and Nakao A:
Promoter hypermethylation of fibulin 1 gene is associated with
tumor progression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Carcinog.
50:571–579. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hayashi M, Nomoto S, Kanda M, Okamura Y,
Nishikawa Y, Yamada S, Fujii T, Sugimoto H, Takeda S and Kodera Y:
Identification of the A kinase anchor protein 12 (AKAP12) gene as a
candidate tumor suppressor of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Surg
Oncol. 105:381–386. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Okamura Y, Nomoto S, Hayashi M, et al:
Identification of the bleomycin hydrolase gene as a methylated
tumor suppressor gene in hepatocellular carcinoma using a novel
triple-combination array method. Cancer Lett. 312:150–157. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hishida M, Nomoto S, Inokawa Y, et al:
Estrogen receptor 1 gene as a tumor suppressor gene in
hepatocellular carcinoma detected by triple-combination array
analysis. Int J Oncol. 43:88–94. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Inokawa Y, Nomoto S, Hishida M, et al:
Dynamin 3: A new candidate tumor suppressor gene in hepatocellular
carcinoma detected by triple combination array analysis. Onco
Targets Ther. 6:1417–1424. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Shi W, Yu KR, Wu GY and Zhang XB:
Expression of CCNG in gastric carcinoma and its relationship with
prognosis. Chin J Cell Biol. 33:994–997. 2011.
|
|
19
|
Kim Y, Shintani S, Kohno Y, Zhang R and
Wong DT: Cyclin G2 dysregulation in human oral cancer. Cancer Res.
64:8980–8986. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sun GG, Zhang J and Hu WN: CCNG2
expression is down-regulated in colorectal carcinoma and its
clinical significance. Tumour Biol. 35:3339–3346. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Shan G, Shan SG and Zhang XB: Expression
of Cyclin G1 and Cyclin G2 in transitional cell carcinoma of
bladder. Chin J Histochem Cytochem. 18:267–272. 2009.
|
|
22
|
Sun GG, Hu WN, Cui DW and Zhang J:
Decreased expression of CCNG2 is significantly linked to the
malignant transformation of gastric carcinoma. Tumour Biol.
35:2631–2639. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Bates S, Rowan S and Vousden KH:
Characterisation of human cyclin G1 and G2: DNA damage inducible
genes. Oncogene. 13:1103–1109. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Harvey RC, Mullighan CG, Wang X, et al:
Identification of novel cluster groups in pediatric high-risk
B-precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia with gene expression
profiling: Correlation with genome-wide DNA copy number
alterations, clinical characteristics, and outcome. Blood.
116:4874–4884. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Feliciano A, Castellvi J, Artero-Castro A,
et al: miR-125b acts as a tumor suppressor in breast tumorigenesis
via its novel direct targets ENPEP, CK2-α, CCNJ, and MEGF9. PLoS
One. 8:e762472013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Stangegaard M: Gene expression analysis
using agilent DNA microarrays. Methods Mol Biol. 529:133–145. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kennedy GC, Matsuzaki H, Dong S, et al:
Large-scale genotyping of complex DNA. Nat Biotechnol.
21:1233–1237. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Nannya Y, Sanada M, Nakazaki K, et al: A
robust algorithm for copy number detection using high-density
oligonucleotide single nucleotide polymorphism genotyping arrays.
Cancer Res. 65:6071–6079. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Takai D and Jones PA: The CpG island
searcher: A new WWW resource. In Silico Biol. 3:235–240.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Jones PA and Baylin SB: The fundamental
role of epigenetic events in cancer. Nat Rev Genet. 3:415–428.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Morgan DO: Cyclin-dependent kinases:
Engines, clocks, and microprocessors. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol.
13:261–291. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Satyanarayana A and Kaldis P: Mammalian
cell-cycle regulation: Several Cdks, numerous cyclins and diverse
compensatory mechanisms. Oncogene. 28:2925–2939. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Finley RL Jr, Thomas BJ, Zipursky SL and
Brent R: Isolation of Drosophila cyclin D, a protein expressed in
the morphogenetic furrow before entry into S phase. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 93:3011–3015. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kolonin MG and Finley RL Jr: A role for
cyclin J in the rapid nuclear division cycles of early Drosophila
embryogenesis. Dev Biol. 227:661–672. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Nishida N, Fukuda Y, Komeda T, et al:
Amplification and overexpression of the cyclin D1 gene in
aggressive human hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res.
54:3107–3110. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Gramantieri L, Ferracin M, Fornari F, et
al: Cyclin G1 is a target of miR-122a, a microRNA frequently
down-regulated in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res.
67:6092–6099. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Fornari F, Gramantieri L, Giovannini C, et
al: MiR-122/cyclin G1 interaction modulates p53 activity and
affects doxorubicin sensitivity of human hepatocarcinoma cells.
Cancer Res. 69:5761–5767. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Bennin DA, Don AS, Brake T, McKenzie JL,
Rosenbaum H, Ortiz L, DePaoli-Roach AA and Horne MC: Cyclin G2
associates with protein phosphatase 2A catalytic and regulatory B′
subunits in active complexes and induces nuclear aberrations and a
G1/S phase cell cycle arrest. J Biol Chem. 277:27449–27467. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|