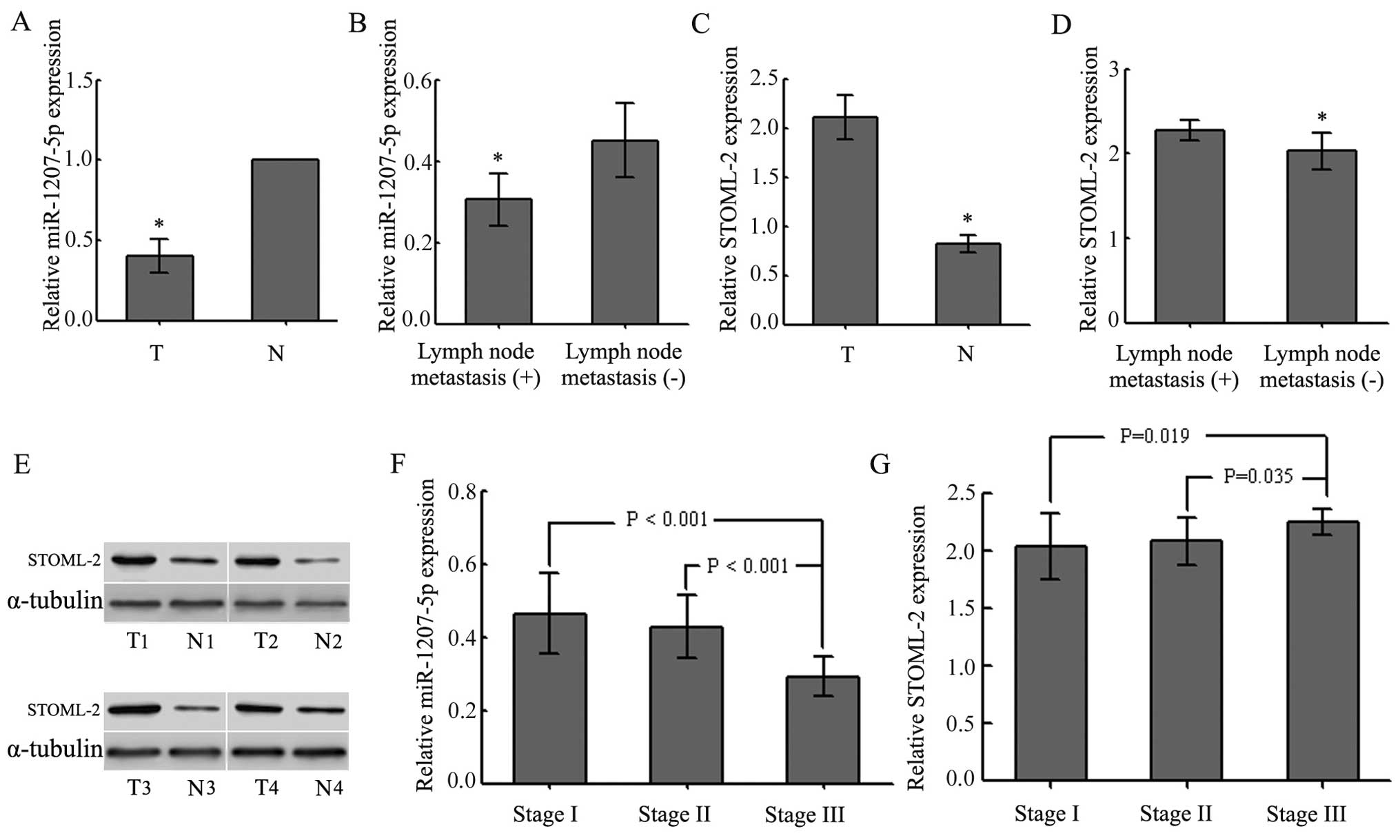
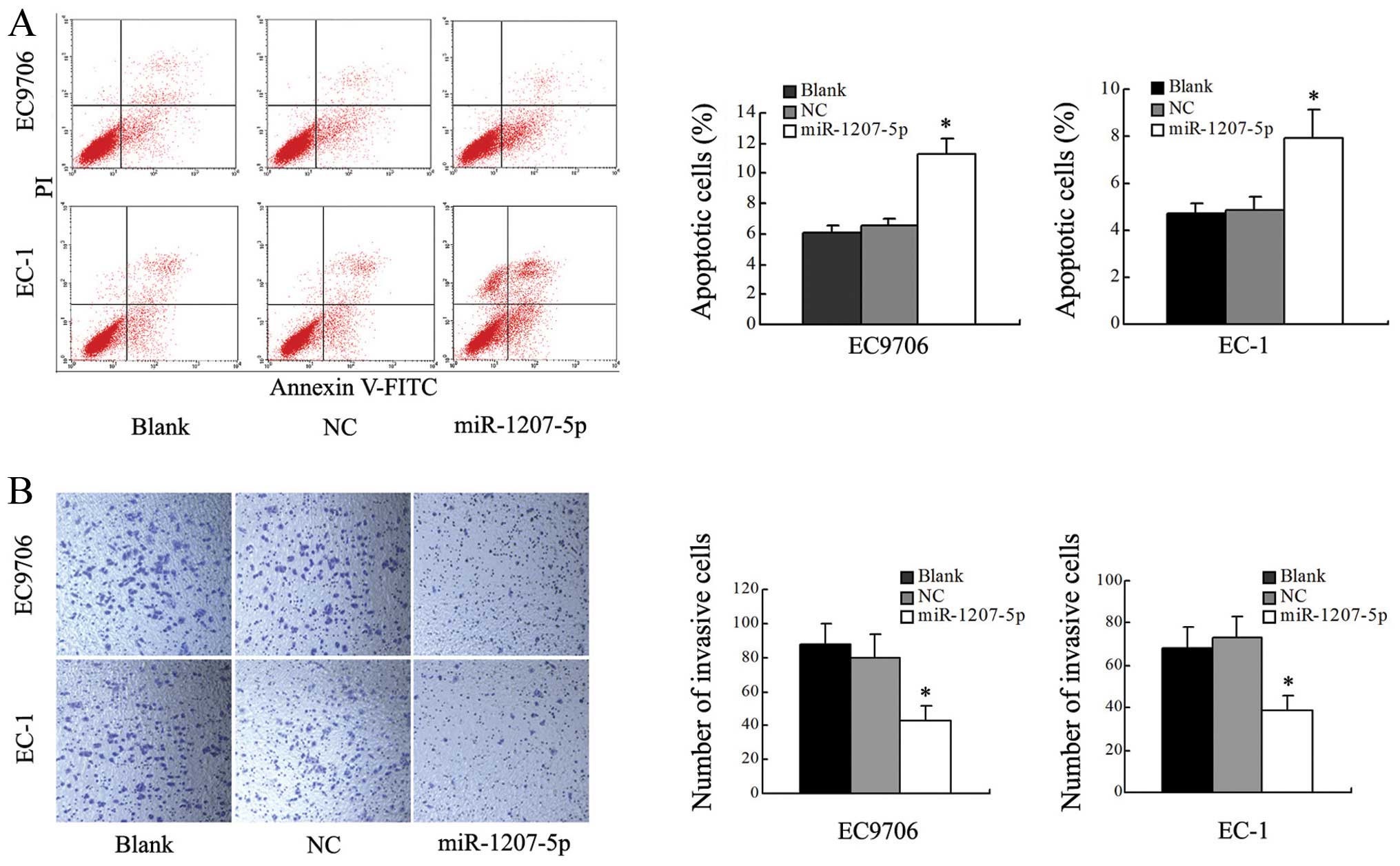
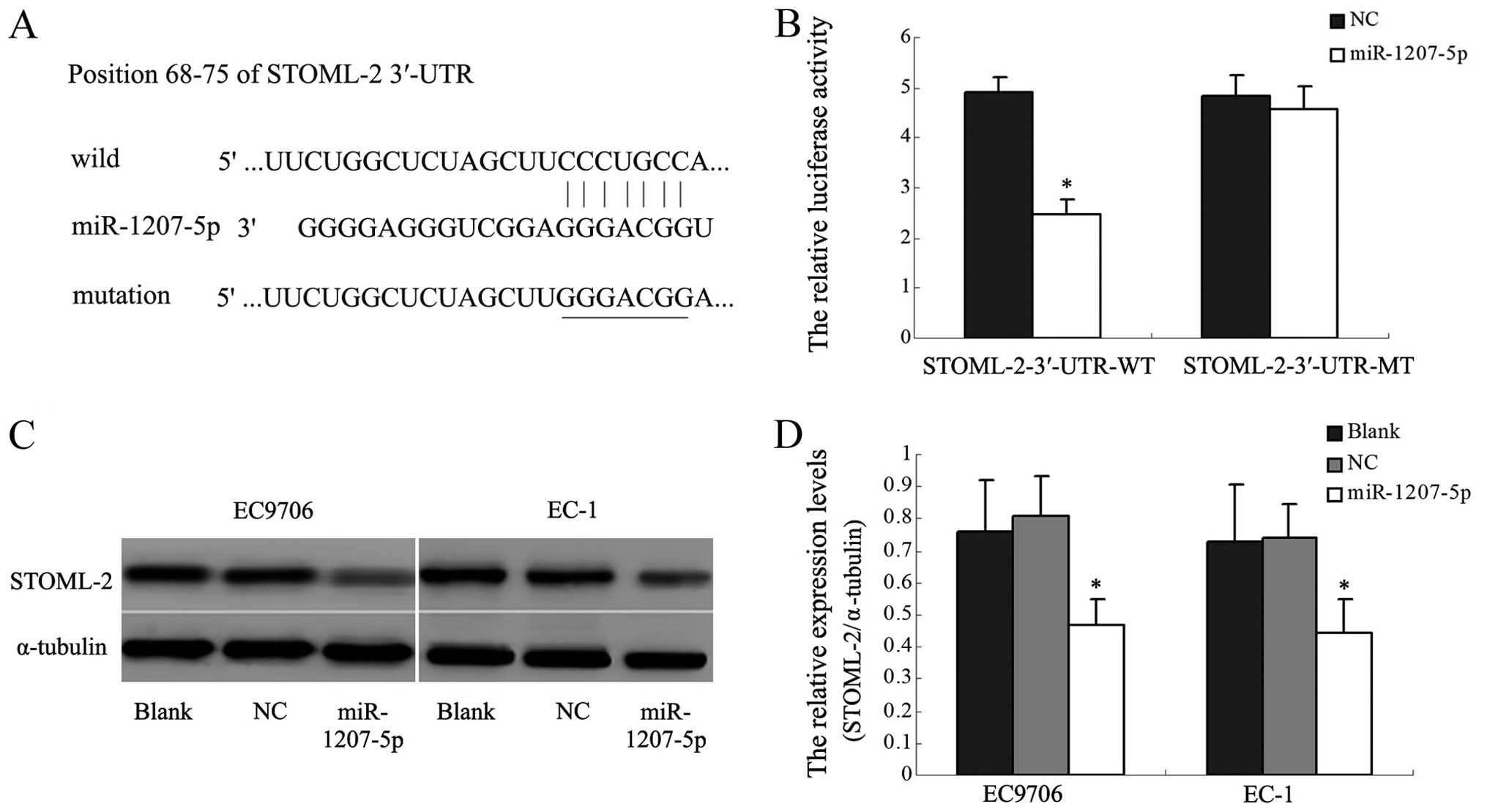
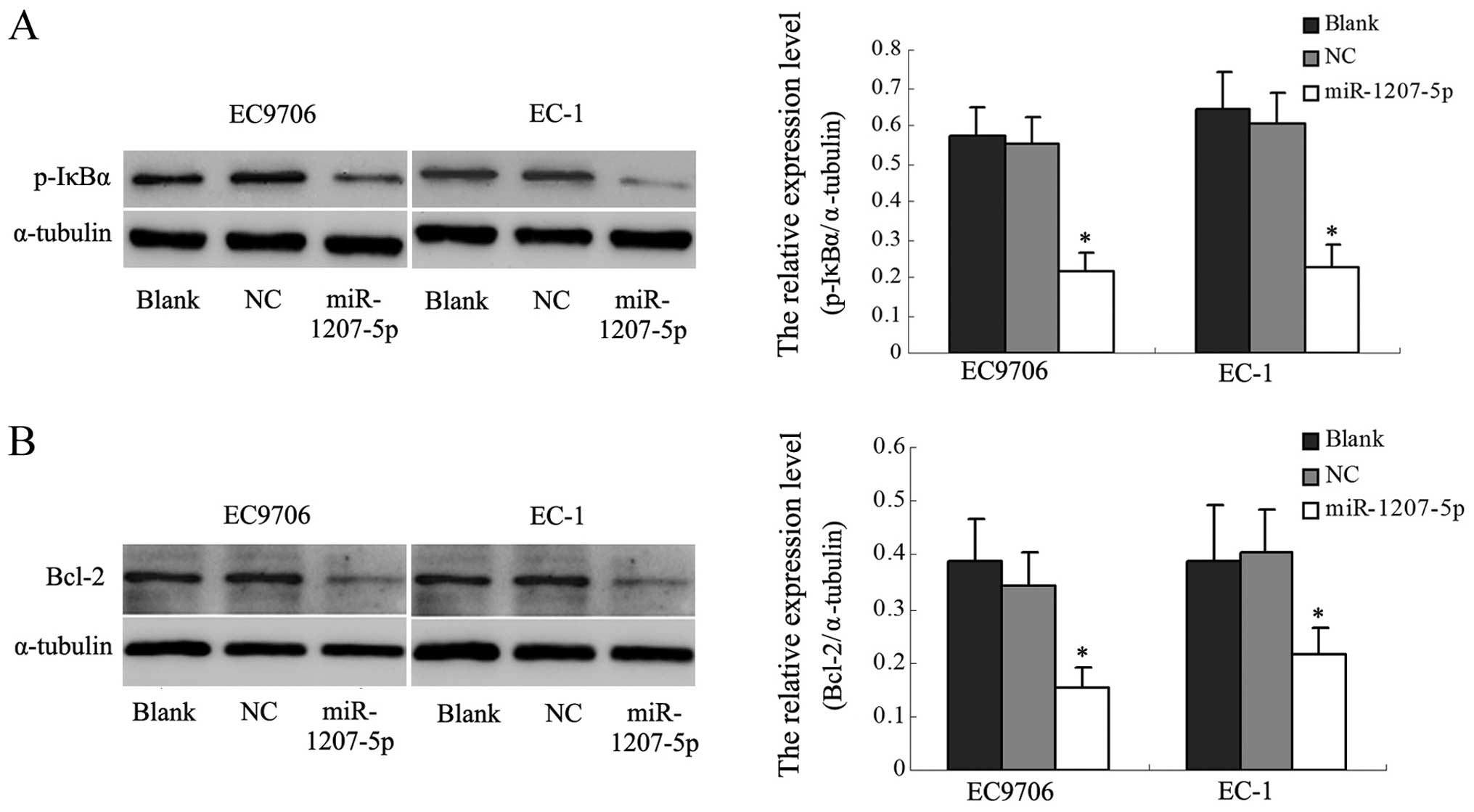
|
1
|
Lee RC and Ambros V: An extensive class of
small RNAs in Caenorhabditis elegans. Science. 294:862–864. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lau NC, Lim LP, Weinstein EG and Bartel
DP: An abundant class of tiny RNAs with probable regulatory roles
in Caenorhabditis elegans. Science. 294:858–862. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ambros V: microRNAs: Tiny regulators with
great potential. Cell. 107:823–826. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Hede K: Studies define role of microRNA in
cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 97:1114–1115. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Cheng T, Hu C, Yang H, Cao L and An J:
Transforming growth factor-β-induced miR-143 expression in
regulation of non-small cell lung cancer cell viability and
invasion capacity in vitro and in vivo. Int J Oncol. 45:1977–1988.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chiyomaru T, Seki N, Inoguchi S, et al:
Dual regulation of receptor tyrosine kinase genes EGFR and c-Met by
the tumor-suppressive microRNA-23b/27b cluster in bladder cancer.
Int J Oncol. 46:487–496. 2015.
|
|
7
|
Pei J, Robu V, Feder M, Cheung M,
Neumann-Domer E, Talarchek J, Dulaimi E, Millenson MM and Testa JR:
Copy neutral loss of heterozygosity in 20q in chronic lymphocytic
leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma. Cancer Genet. 207:98–102.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wang Y, Li M, Zang W, Ma Y, Wang N, Li P,
Wang T and Zhao G: MiR-429 up-regulation induces apoptosis and
suppresses invasion by targeting Bcl-2 and SP-1 in esophageal
carcinoma. Cell Oncol Dordr. 36:385–394. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Huang J, Zhang SY, Gao YM, Liu YF, Liu YB,
Zhao ZG and Yang K: MicroRNAs as oncogenes or tumour suppressors in
oesophageal cancer: Potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets.
Cell Prolif. 47:277–286. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chen Z, Li J, Tian L, et al: MiRNA
expression profile reveals a prognostic signature for esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 350:34–42. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Peña-Chilet M, Martínez MT, Pérez-Fidalgo
JA, et al: MicroRNA profile in very young women with breast cancer.
BMC Cancer. 14:5292014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Mun J, Tam C, Chan G, Kim JH, Evans D and
Fleiszig S: MicroRNA-762 is upregulated in human corneal epithelial
cells in response to tear fluid and Pseudomonas aeruginosa antigens
and negatively regulates the expression of host defense genes
encoding RNase7 and ST2. PLoS One. 8:e578502013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chen L, Lü MH, Zhang D, et al: miR-1207-5p
and miR-1266 suppress gastric cancer growth and invasion by
targeting telomerase reverse transcriptase. Cell Death Dis.
5:e10342014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Papagregoriou G, Erguler K, Dweep H,
Voskarides K, Koupepidou P, Athanasiou Y, Pierides A, Gretz N,
Felekkis KN and Deltas C: A miR-1207-5p binding site polymorphism
abolishes regulation of HBEGF and is associated with disease
severity in CFHR5 nephropathy. PLoS One. 7:e310212012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Alvarez ML, Khosroheidari M, Eddy E and
Kiefer J: Role of microRNA 1207-5P and its host gene, the long
non-coding RNA Pvt1, as mediators of extracellular matrix
accumulation in the kidney: Implications for diabetic nephropathy.
PLoS One. 8:e774682013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang Y and Morrow JS: Identification and
characterization of human SLP-2, a novel homologue of stomatin
(band 7.2b) present in erythrocytes and other tissues. J Biol Chem.
275:8062–8071. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Owczarek CM, Treutlein HR, Portbury KJ,
Gulluyan LM, Kola I and Hertzog PJ: A novel member of the
STOMATIN/EPB72/mec-2 family, stomatin-like 2 (STOML2), is
ubiquitously expressed and localizes to HSA chromosome 9p13.1.
Cytogenet Cell Genet. 92:196–203. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lapatsina L, Brand J, Poole K, Daumke O
and Lewin GR: Stomatin-domain proteins. Eur J Cell Biol.
91:240–245. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Liu Z, Yang Y, Zhang Y, Ye X, Wang L and
Xu G: Stomatin-like protein 2 is associated with the
clinicopathological features of human papillary thyroid cancer and
is regulated by TGF-β in thyroid cancer cells. Oncol Rep.
31:153–160. 2014.
|
|
20
|
Cao W, Zhang B, Liu Y, et al: High-level
SLP-2 expression and HER-2/neu protein expression are associated
with decreased breast cancer patient survival. Am J Clin Pathol.
128:430–436. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Cui Z, Zhang L, Hua Z, Cao W, Feng W and
Liu Z: Stomatin-like protein 2 is overexpressed and related to cell
growth in human endometrial adenocarcinoma. Oncol Rep. 17:829–833.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhang L, Ding F, Cao W and Liu Z, Liu W,
Yu Z, Wu Y, Li W, Li Y and Liu Z: Stomatin-like protein 2 is
overexpressed in cancer and involved in regulating cell growth and
cell adhesion in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Clin
Cancer Res. 12:1639–1646. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Cao W, Zhang B, Li J, Liu Y, Liu Z and Sun
B: SLP-2 overexpression could serve as a prognostic factor in node
positive and HER2 negative breast cancer. Pathology. 43:713–718.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Cao W, Zhang B, Ding F, Zhang W, Sun B and
Liu Z: Expression of SLP-2 was associated with invasion of
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. PLoS One. 8:e638902013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Song L, Liu L, Wu Z, Lin C, Dai T, Yu C,
Wang X, Wu J, Li M and Li J: Knockdown of stomatin-like protein 2
(STOML2) reduces the invasive ability of glioma cells through
inhibition of the NF-κB/MMP-9 pathway. J Pathol. 226:534–543. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, et al: MicroRNA
expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature. 435:834–838.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Adams BD, Kasinski AL and Slack FJ:
Aberrant regulation and function of microRNAs in cancer. Curr Biol.
24:R762–R776. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Bouyssou JM, Manier S, Huynh D, Issa S,
Roccaro AM and Ghobrial IM: Regulation of microRNAs in cancer
metastasis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1845:255–265. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chang D, Ma K, Gong M, Cui Y, Liu ZH, Zhou
XG, Zhou CN and Wang TY: SLP-2 overexpression is associated with
tumour distant metastasis and poor prognosis in pulmonary squamous
cell carcinoma. Biomarkers. 15:104–110. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Gasparini C, Celeghini C, Monasta L and
Zauli G: NF-kappaB pathways in hematological malignancies. Cell Mol
Life Sci. 71:2083–2102. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Tong L, Yuan Y and Wu S: Therapeutic
microRNAs targeting the NF-kappa B signaling circuits of cancers.
Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 81:1–15. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Abdel-Latif MM, O’Riordan J, Windle HJ,
Carton E, Ravi N, Kelleher D and Reynolds JV: NF-kappaB activation
in esophageal adenocarcinoma: Relationship to Barrett’s metaplasia,
survival, and response to neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy. Ann Surg.
239:491–500. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Gong H, Song L, Lin C, Liu A, Lin X, Wu J,
Li M and Li J: Downregulation of miR-138 sustains NF-κB activation
and promotes lipid raft formation in esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 19:1083–1093. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Bhaumik D, Scott GK, Schokrpur S, Patil
CK, Campisi J and Benz CC: Expression of microRNA-146 suppresses
NF-kappaB activity with reduction of metastatic potential in breast
cancer cells. Oncogene. 27:5643–5647. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kumar V, Palermo R, Talora C, et al: Notch
and NF-κB signaling pathways regulate miR-223/FBXW7 axis in T-cell
acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia. 28:2324–2335. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Hardwick JM, Chen YB and Jonas EA:
Multipolar functions of BCL-2 proteins link energetics to
apoptosis. Trends Cell Biol. 22:318–328. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wood WG, Igbavboa U, Muller WE and Eckert
GP: Statins, Bcl-2, and apoptosis: Cell death or cell protection?
Mol Neurobiol. 48:308–314. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Sarbia M, Bittinger F, Porschen R, Verreet
P, Dutkowski P, Willers R and Gabbert HE: bcl-2 expression and
prognosis in squamous-cell carcinomas of the esophagus. Int J
Cancer. 69:324–328. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Torzewski M, Sarbia M, Heep H, Dutkowski
P, Willers R and Gabbert HE: Expression of Bcl-X(L), an
antiapoptotic member of the Bcl-2 family, in esophageal squamous
cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 4:577–583. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|