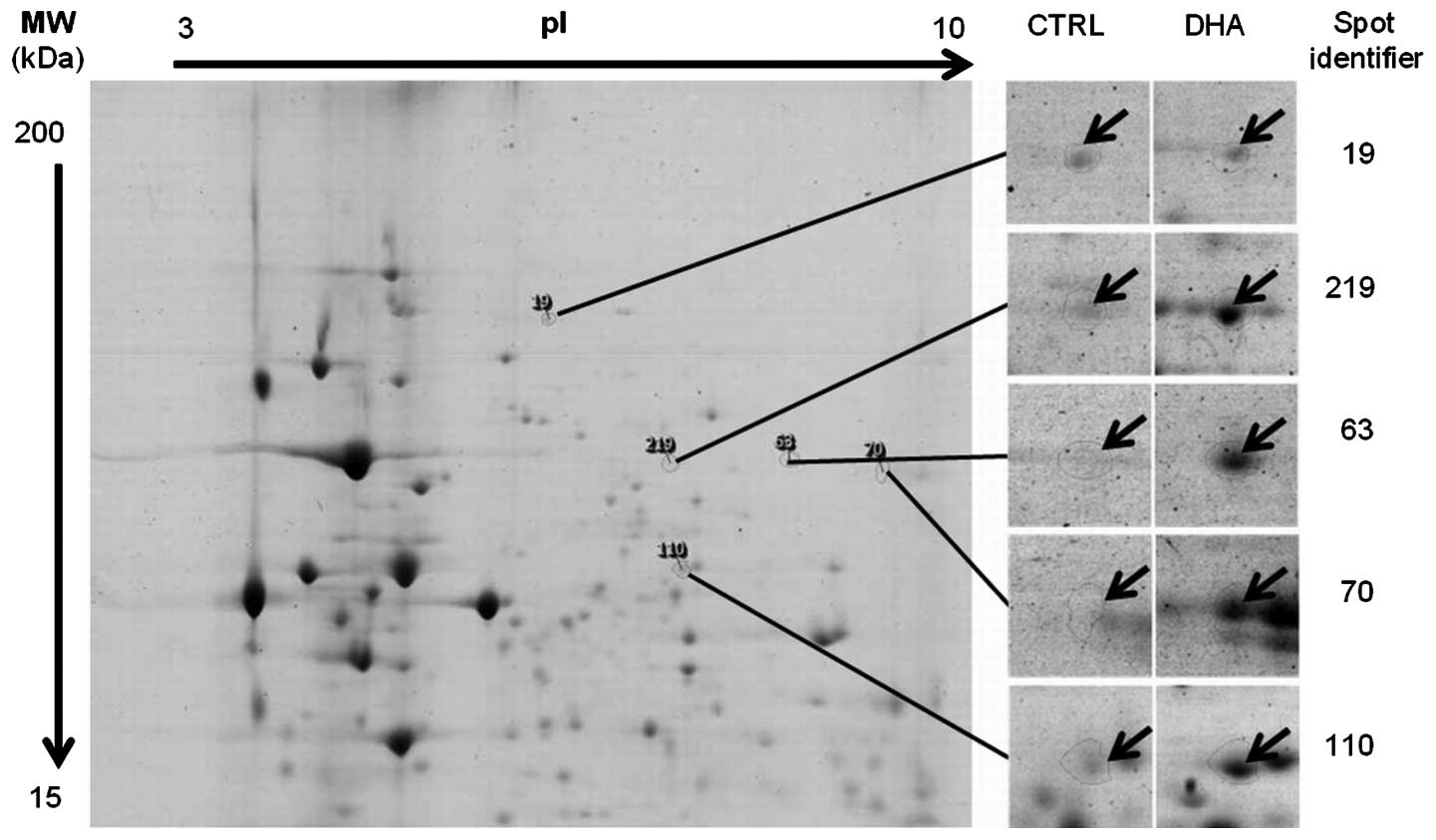
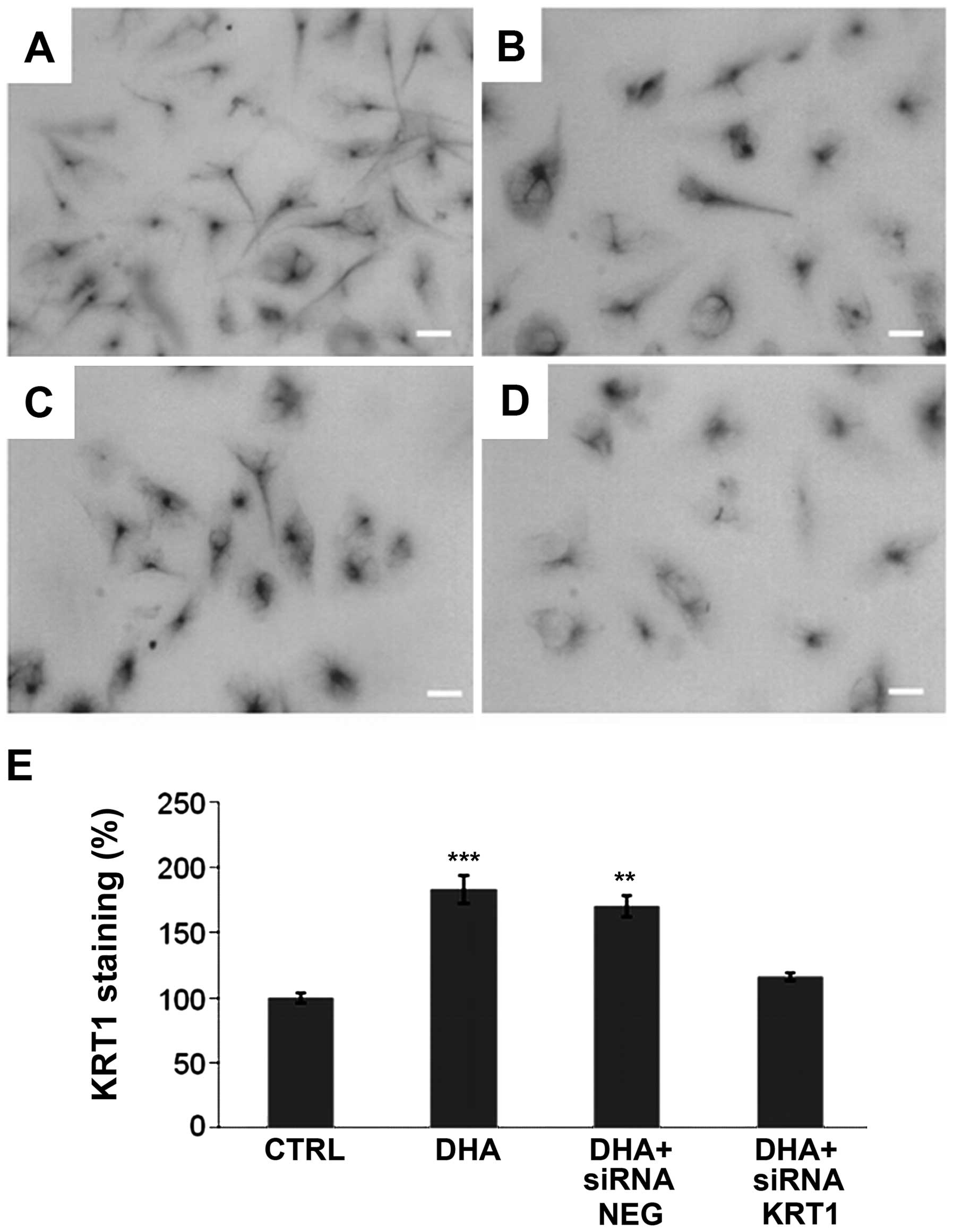
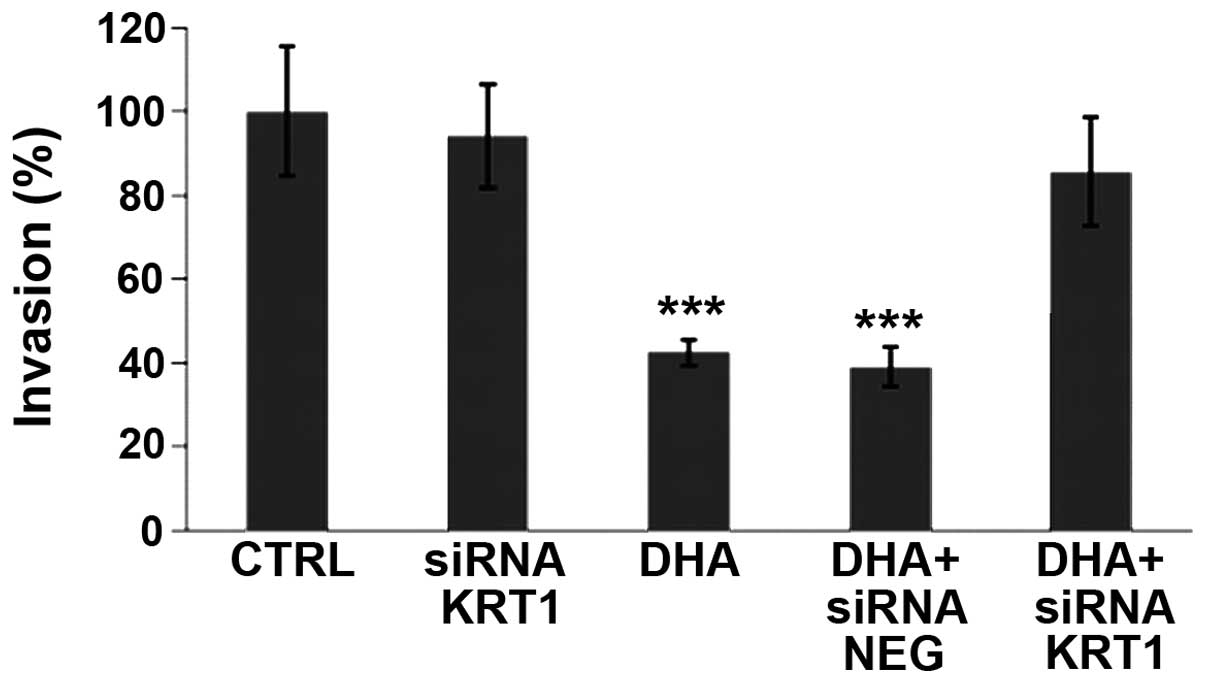
|
1
|
Larsson SC, Kumlin M, Ingelman-Sundberg M
and Wolk A: Dietary long-chain n-3 fatty acids for the prevention
of cancer: A review of potential mechanisms. Am J Clin Nutr.
79:935–945. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Doughman SD, Krupanidhi S and Sanjeevi CB:
Omega-3 fatty acids for nutrition and medicine: Considering
microalgae oil as a vegetarian source of EPA and DHA. Curr Diabetes
Rev. 3:198–203. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Poudyal H, Panchal SK, Diwan V and Brown
L: Omega-3 fatty acids and metabolic syndrome: Effects and emerging
mechanisms of action. Prog Lipid Res. 50:372–387. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Holub BJ: Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) and
cardiovascular disease risk factors. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent
Fatty Acids. 81:199–204. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Berquin IM, Edwards IJ and Chen YQ:
Multi-targeted therapy of cancer by omega-3 fatty acids. Cancer
Lett. 269:363–377. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bougnoux P, Hajjaji N, Maheo K, Couet C
and Chevalier S: Fatty acids and breast cancer: Sensitization to
treatments and prevention of metastatic re-growth. Prog Lipid Res.
49:76–86. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Holmes MD and Willett WC: Does diet affect
breast cancer risk? Breast Cancer Res. 6:170–178. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Barascu A, Besson P, Le Floch O, Bougnoux
P and Jourdan ML: CDK1-cyclin B1 mediates the inhibition of
proliferation induced by omega-3 fatty acids in MDA-MB-231 breast
cancer cells. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 38:196–208. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Blanckaert V, Ulmann L, Mimouni V, Antol
J, Brancquart L and Chénais B: Docosahexaenoic acid intake
decreases proliferation, increases apoptosis and decreases the
invasive potential of the human breast carcinoma cell line
MDA-MB-231. Int J Oncol. 36:737–742. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Stoll BA: Breast cancer and the western
diet: Role of fatty acids and antioxidant vitamins. Eur J Cancer.
34:1852–1856. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Chénais B and Blanckaert V: The janus face
of lipids in human breast cancer: How polyunsaturated fatty acids
affect tumor cell hallmarks. Int J Breast Cancer. 2012:7125362012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Stillwell W and Wassall SR:
Docosahexaenoic acid: Membrane properties of a unique fatty acid.
Chem Phys Lipids. 126:1–27. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Conn EM, Botkjaer KA, Kupriyanova TA,
Andreasen PA, Deryugina EI and Quigley JP: Comparative analysis of
metastasis variants derived from human prostate carcinoma cells:
Roles in intravasation of VEGF-mediated angiogenesis and
uPA-mediated invasion. Am J Pathol. 175:1638–1652. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Brooks SA, Lomax-Browne HJ, Carter TM,
Kinch CE and Hall DM: Molecular interactions in cancer cell
metastasis. Acta Histochem. 112:3–25. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Buxton IL, Yokdang N and Matz RM:
Purinergic mechanisms in breast cancer support intravasation,
extravasation and angio-genesis. Cancer Lett. 291:131–141. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
16
|
Schley PD, Brindley DN and Field CJ: (n-3)
PUFA alter raft lipid composition and decrease epidermal growth
factor receptor levels in lipid rafts of human breast cancer cells.
J Nutr. 137:548–553. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Raghu H, Sodadasu PK, Malla RR, Gondi CS,
Estes N and Rao JS: Localization of uPAR and MMP-9 in lipid rafts
is critical for migration, invasion and angiogenesis in human
breast cancer cells. BMC Cancer. 10:647–664. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Isbilen B, Fraser SP and Djamgoz MB:
Docosahexaenoic acid (omega-3) blocks voltage-gated sodium channel
activity and migration of MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells. Int
J Biochem Cell Biol. 38:2173–2182. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Gillet L, Roger S, Bougnoux P, Le Guennec
JY and Besson P: Beneficial effects of omega-3 long-chain fatty
acids in breast cancer and cardiovascular diseases: Voltage-gated
sodium channels as a common feature? Biochimie. 93:4–6. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Maguy A, Hebert TE and Nattel S:
Involvement of lipid rafts and caveolae in cardiac ion channel
function. Cardiovasc Res. 69:798–807. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sánchez-Bailón MP, Calcabrini A,
Gómez-Domínguez D, Morte B, Martín-Forero E, Gómez-López G,
Molinari A, Wagner KU and Martín-Pérez J: Src kinases catalytic
activity regulates proliferation, migration and invasiveness of
MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. Cell Signal. 24:1276–1286. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Planas-Silva MD, Bruggeman RD, Grenko RT
and Smith JS: Role of c-Src and focal adhesion kinase in
progression and metastasis of estrogen receptor-positive breast
cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 341:73–81. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chuang NN and Huang CC: Interaction of
integrin beta1 with cytokeratin 1 in neuroblastoma NMB7 cells.
Biochem Soc Trans. 35:1292–1294. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Andavan B, Shankar G and Lemmens-Gruber R:
Modulation of Nav 1.5 variants by src tyrosine kinase.
Biophys J. 98:310a2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Venkateswaran S, Blanckaert V and
Schelling M: Membrane fragments from cultured endothelial cells for
use in screening anti-FGF receptor antibodies. Methods Cell Sci.
14:159–162. 1992.
|
|
26
|
Wilmet JP, Tastet C, Desruelles E,
Ziental-Gelus N, Blanckaert V, Hondermarck H and Le Bourhis X:
Proteome changes induced by overexpression of the p75 neurotrophin
receptor (p75NTR) in breast cancer cells. Int J Dev Biol.
55:801–809. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
D’Eliseo D, Manzi L, Merendino N and
Velotti F: Docosahexaenoic acid inhibits invasion of human RT112
urinary bladder and PT45 pancreatic carcinoma cells via
down-modulation of granzyme B expression. J Nutr Biochem.
23:452–457. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Mandal CC, Ghosh-Choudhury T, Yoneda T,
Choudhury GG and Ghosh-Choudhury N: Fish oil prevents breast cancer
cell metastasis to bone. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 402:602–607.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Siddiqui RA, Harvey KA, Walker C,
Altenburg J, Xu Z, Terry C, Camarillo I, Jones-Hall Y and Mariash
C: Characterization of synergistic anti-cancer effects of
docosahexaenoic acid and curcumin on DMBA-induced mammary
tumorigenesis in mice. BMC Cancer. 13:418–434. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Belt EJ, Fijneman RJ, van den Berg EG,
Bril H, Delis-van Diemen PM, Tijssen M, van Essen HF, De Lange-de
Klerk ES, Beliën JA, Stockmann HB, et al: Loss of lamin A/C
expression in stage II and III colon cancer is associated with
disease recurrence. Eur J Cancer. 47:1837–1845. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wazir U, Ahmed MH, Bridger JM, Harvey A,
Jiang WG, Sharma AK and Mokbel K: The clinicopathological
significance of lamin A/C, lamin B1 and lamin B receptor mRNA
expression in human breast cancer. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 18:595–611.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yu L, Wan F, Dutta S, Welsh S, Liu Z,
Freundt E, Baehrecke EH and Lenardo M: Autophagic programmed cell
death by selective catalase degradation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
103:4952–4957. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Bechtel W and Bauer G: Catalase protects
tumor cells from apoptosis induction by intercellular ROS
signaling. Anticancer Res. 29:4541–4557. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Richard D, Hollender P and Chénais B:
Butyric acid increases invasiveness of HL-60 leukemia cells: Role
of reactive oxygen species. FEBS Lett. 518:159–163. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Richard D, Hollender P and Chénais B:
Involvement of reactive oxygen species in aclarubicin-induced
differentiation and invasiveness of HL-60 leukemia cells. Int J
Oncol. 21:393–399. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Hurd TR, DeGennaro M and Lehmann R: Redox
regulation of cell migration and adhesion. Trends Cell Biol.
22:107–115. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Payne SL, Fogelgren B, Hess AR, Seftor EA,
Wiley EL, Fong SF, Csiszar K, Hendrix MJ and Kirschmann DA: Lysyl
oxidase regulates breast cancer cell migration and adhesion through
a hydrogen peroxide-mediated mechanism. Cancer Res. 65:11429–11436.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Nikitovic D, Corsini E, Kouretas D,
Tsatsakis A and Tzanakakis G: ROS-major mediators of extracellular
matrix remodeling during tumor progression. Food Chem Toxicol.
61:178–186. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Seo J, Barhoumi R, Johnson AE, Lupton JR
and Chapkin RS: Docosahexaenoic acid selectively inhibits plasma
membrane targeting of lipidated proteins. FASEB J. 20:770–772.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
DeAngelis JT, Li Y, Mitchell N, Wilson L,
Kim H and Tollefsbol TO: 2D difference gel electrophoresis analysis
of different time points during the course of neoplastic
transformation of human mammary epithelial cells. J Proteome Res.
10:447–458. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Attallah AM, El-Far M, Omran MM, Abdallah
SO, El-Desouky MA, El-Dosoky I, Abdelrazek MA, Attallah AA,
Elweresh MA, Abdel Hameed GE, et al: Circulating levels and
clinical implications of epithelial membrane antigen and
cytokeratin-1 in women with breast cancer: Can their ratio improve
the results? Tumour Biol. 35:10737–10745. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Rohl CA, Boeckman FA, Baker C, Scheuer T,
Catterall WA and Klevit RE: Solution structure of the sodium
channel inactivation gate. Biochemistry. 38:855–861. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Yang M, Kozminski DJ, Wold LA, Modak R,
Calhoun JD, Isom LL and Brackenbury WJ: Therapeutic potential for
phenytoin: Targeting Na(v)1.5 sodium channels to reduce migration
and invasion in metastatic breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat.
134:603–615. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|