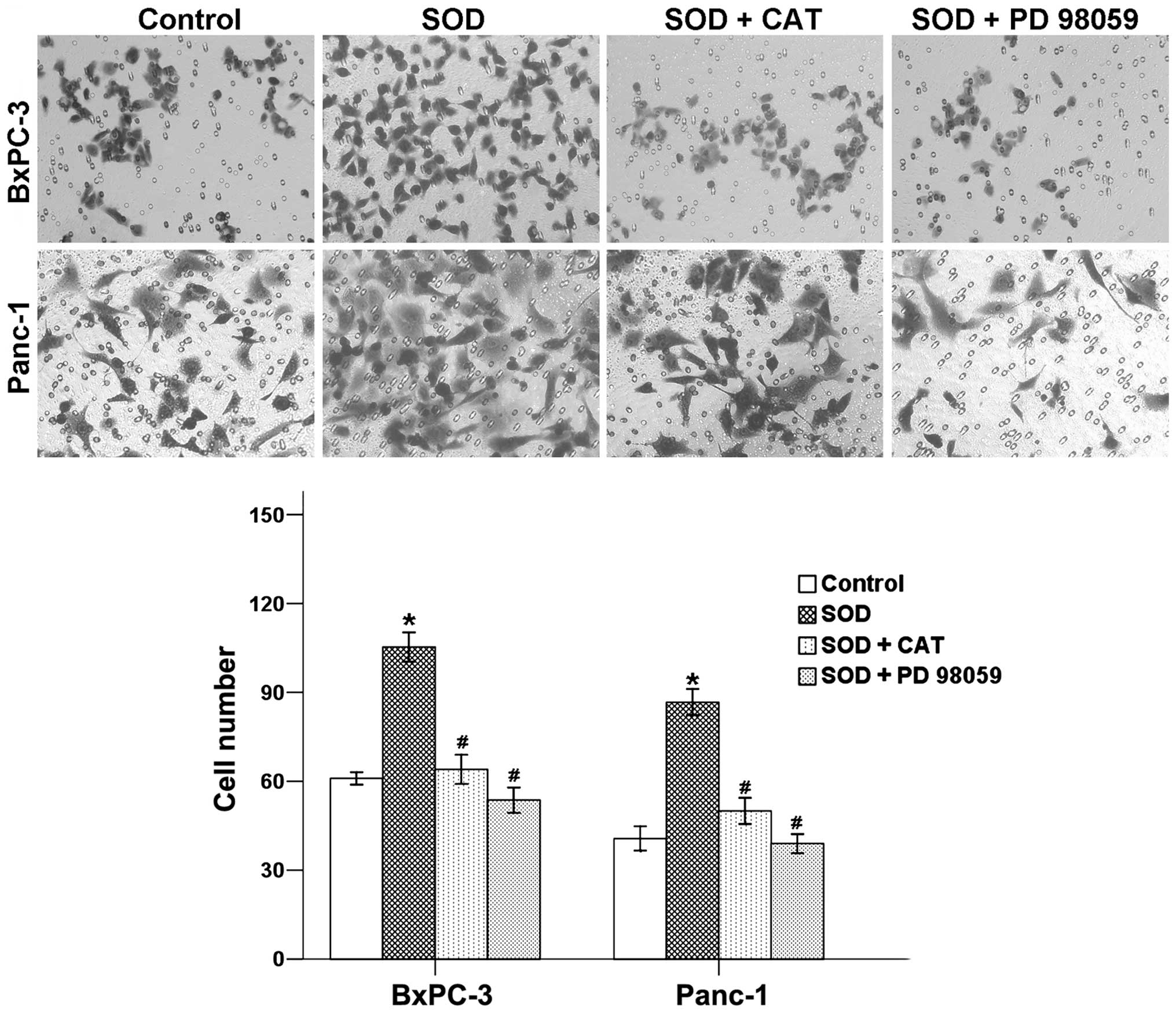
|
1
|
Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 64:9–29. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sarkar FH, Banerjee S and Li Y: Pancreatic
cancer: Pathogenesis, prevention and treatment. Toxicol Appl
Pharmacol. 224:326–336. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Castellanos EH, Cardin DB and Berlin JD:
Treatment of early-stage pancreatic cancer. Oncology (Williston
Park). 25:182–189. 2011.
|
|
4
|
Li W, Ma Q, Li J, Guo K, Liu H, Han L and
Ma G: Hyperglycemia enhances the invasive and migratory activity of
pancreatic cancer cells via hydrogen peroxide. Oncol Rep.
25:1279–1287. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lee DJ and Kang SW: Reactive oxygen
species and tumor metastasis. Mol Cells. 35:93–98. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Li W, Ma Q, Liu J, Han L, Ma G, Liu H,
Shan T, Xie K and Wu E: Hyperglycemia as a mechanism of pancreatic
cancer metastasis. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 17:1761–1774. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Costa A, Scholer-Dahirel A and
Mechta-Grigoriou F: The role of reactive oxygen species and
metabolism on cancer cells and their microenvironment. Semin Cancer
Biol. 25:23–32. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Liu Z, Li S, Cai Y, Wang A, He Q, Zheng C,
Zhao T, Ding X and Zhou X: Manganese superoxide dismutase induces
migration and invasion of tongue squamous cell carcinoma via
H2O2-dependent Snail signaling. Free Radic
Biol Med. 53:44–50. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lewis A, Du J, Liu J, Ritchie JM, Oberley
LW and Cullen JJ: Metastatic progression of pancreatic cancer:
Changes in antioxidant enzymes and cell growth. Clin Exp
Metastasis. 22:523–532. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Duan W, Li R, Ma J, Lei J, Xu Q, Jiang Z,
Nan L, Li X, Wang Z, Huo X, et al: Overexpression of Nodal induces
a metastatic phenotype in pancreatic cancer cells via the Smad2/3
pathway. Oncotarget. 6:1490–1506. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Inumaru J, Nagano O, Takahashi E, Ishimoto
T, Nakamura S, Suzuki Y, Niwa S, Umezawa K, Tanihara H and Saya H:
Molecular mechanisms regulating dissociation of cell-cell junction
of epithelial cells by oxidative stress. Genes Cells. 14:703–716.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Barnett P, Arnold RS, Mezencev R, Chung
LW, Zayzafoon M and Odero-Marah V: Snail-mediated regulation of
reactive oxygen species in ARCaP human prostate cancer cells.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 404:34–39. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
13
|
Das TP, Suman S and Damodaran C: Induction
of reactive oxygen species generation inhibits
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and promotes growth arrest in
prostate cancer cells. Mol Carcinog. 53:537–547. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Cho KH, Choi MJ, Jeong KJ, Kim JJ, Hwang
MH, Shin SC, Park CG and Lee HY: A ROS/STAT3/HIF-1α signaling
cascade mediates EGF-induced TWIST1 expression and prostate cancer
cell invasion. Prostate. 74:528–536. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wu WS, Wu JR and Hu CT: Signal cross talks
for sustained MAPK activation and cell migration: The potential
role of reactive oxygen species. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 27:303–314.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Li F, Wang H, Huang C, Lin J, Zhu G, Hu R
and Feng H: Hydrogen peroxide contributes to the manganese
superoxide dismutase promotion of migration and invasion in glioma
cells. Free Radic Res. 45:1154–1161. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hsieh HL, Wang HH, Wu WB, Chu PJ and Yang
CM: Transforming growth factor-β1 induces matrix
metalloproteinase-9 and cell migration in astrocytes: Roles of
ROS-dependent ERK- and JNK-NF-κB pathways. J Neuroinflammation.
7:882010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Wu Y and Zhou BP: New insights of
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer metastasis. Acta
Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 40:643–650. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Wray CJ, Ahmad SA, Matthews JB and Lowy
AM: Surgery for pancreatic cancer: Recent controversies and current
practice. Gastroenterology. 128:1626–1641. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Iwatsuki M, Mimori K, Yokobori T, Ishi H,
Beppu T, Nakamori S, Baba H and Mori M: Epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in cancer development and its clinical significance.
Cancer Sci. 101:293–299. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Chiu WT, Shen SC, Chow JM, Lin CW, Shia LT
and Chen YC: Contribution of reactive oxygen species to
migration/invasion of human glioblastoma cells U87 via
ERK-dependent COX-2/PGE(2) activation. Neurobiol Dis. 37:118–129.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Chaiswing L, Zhong W, Cullen JJ, Oberley
LW and Oberley TD: Extracellular redox state regulates features
associated with prostate cancer cell invasion. Cancer Res.
68:5820–5826. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hempel N, Carrico PM and Melendez JA:
Manganese super-oxide dismutase (Sod2) and redox-control of
signaling events that drive metastasis. Anticancer Agents Med Chem.
11:191–201. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chen PM, Wu TC, Wang YC, Cheng YW, Sheu
GT, Chen CY and Lee H: Activation of NF-κB by SOD2 promotes the
aggressiveness of lung adenocarcinoma by modulating NKX2-1-mediated
IKKβ expression. Carcinogenesis. 34:2655–2663. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kinnula VL and Crapo JD: Superoxide
dismutases in malignant cells and human tumors. Free Radic Biol
Med. 36:718–744. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Toh Y, Kuninaka S, Oshiro T, Ikeda Y,
Nakashima H, Baba H, Kohnoe S, Okamura T, Mori M and Sugimachi K:
Overexpression of manganese superoxide dismutase mRNA may correlate
with aggressiveness in gastric and colorectal adenocarcinomas. Int
J Oncol. 17:107–112. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang S, Wang F, Shi X, Dai J, Peng Y, Guo
X, Wang X, Shen H and Hu Z: Association between manganese
superoxide dismutase (MnSOD) Val-9Ala polymorphism and cancer risk
- A meta-analysis. Eur J Cancer. 45:2874–2881. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Tang H, Dong X, Day RS, Hassan MM and Li
D: Antioxidant genes, diabetes and dietary antioxidants in
association with risk of pancreatic cancer. Carcinogenesis.
31:607–613. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Connor KM, Hempel N, Nelson KK, Dabiri G,
Gamarra A, Belarmino J, Van De Water L, Mian BM and Melendez JA:
Manganese superoxide dismutase enhances the invasive and migratory
activity of tumor cells. Cancer Res. 67:10260–10267. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Mori K, Shibanuma M and Nose K: Invasive
potential induced under long-term oxidative stress in mammary
epithelial cells. Cancer Res. 64:7464–7472. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kim MC, Cui FJ and Kim Y: Hydrogen
peroxide promotes epithelial to mesenchymal transition and stemness
in human malignant mesothelioma cells. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev.
14:3625–3630. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lee KH, Kim SW and Kim JR: Reactive oxygen
species regulate urokinase plasminogen activator expression and
cell invasion via mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways after
treatment with hepatocyte growth factor in stomach cancer cells. J
Exp Clin Cancer Res. 28:732009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Liu J, Ben QW, Yao WY, Zhang JJ, Chen DF,
He XY, Li L and Yuan YZ: BMP2 induces PANC-1 cell invasion by MMP-2
over-expression through ROS and ERK. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed).
17:2541–2549. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Gilmore TD: Introduction to NF-kappaB:
Players, pathways, perspectives. Oncogene. 25:6680–6684. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|