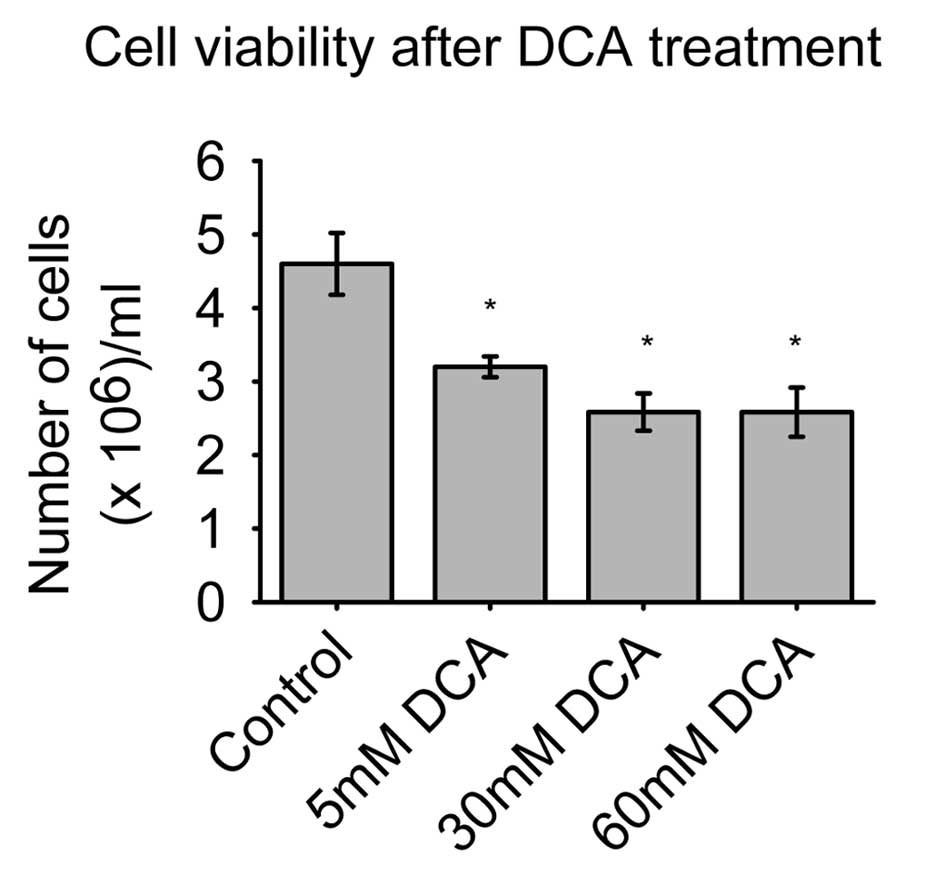
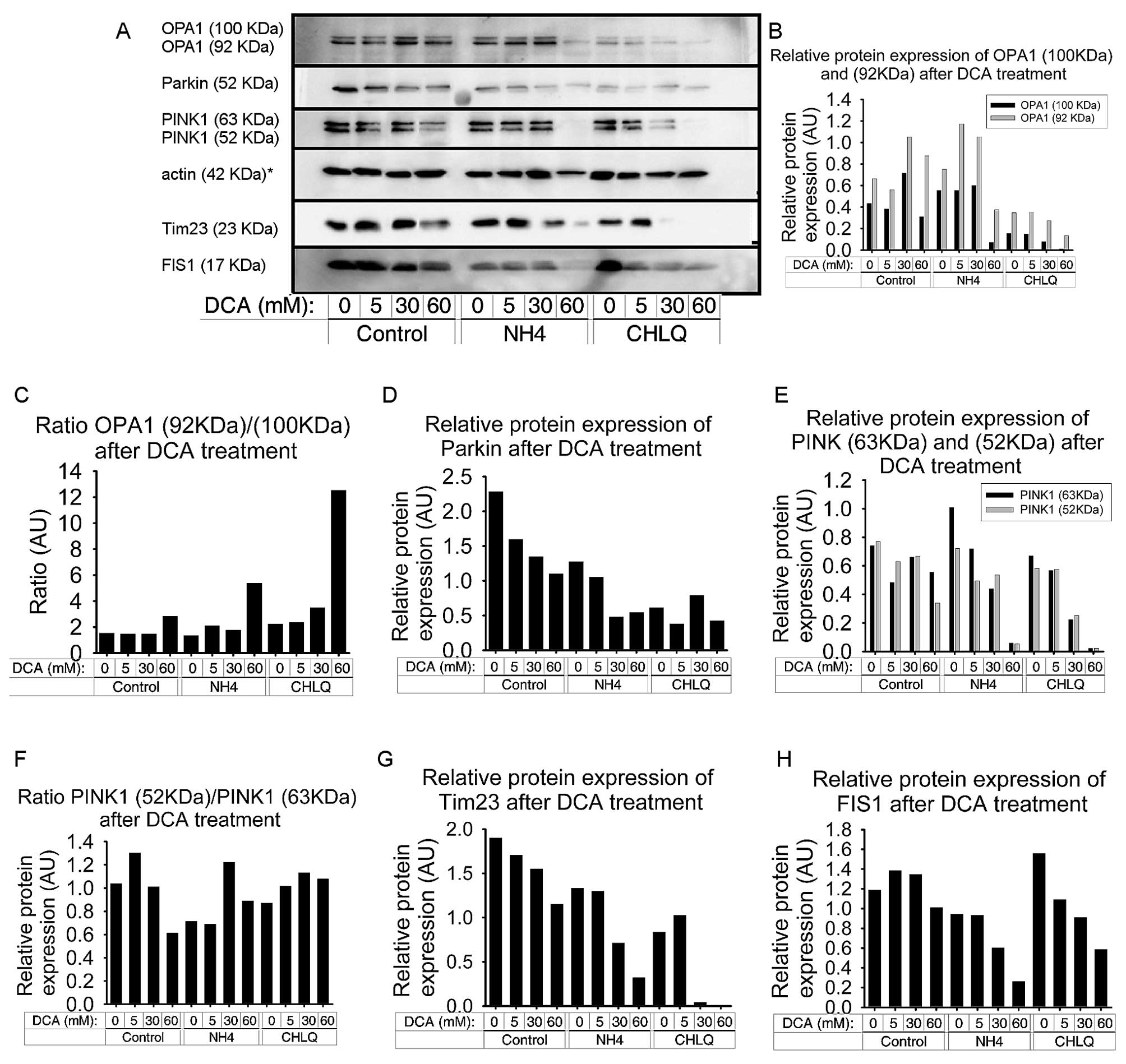
|
1
|
Bonnet S, Archer SL, Allalunis-Turner J,
Haromy A, Beaulieu C, Thompson R, Lee CT, Lopaschuk GD, Puttagunta
L, Bonnet S, et al: A mitochondria-K+ channel axis is
suppressed in cancer and its normalization promotes apoptosis and
inhibits cancer growth. Cancer Cell. 11:37–51. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lin G, Hill DK, Andrejeva G, Boult JK,
Troy H, Fong AC, Orton MR, Panek R, Parkes HG, Jafar M, et al:
Dichloroacetate induces autophagy in colorectal cancer cells and
tumours. Br J Cancer. 111:375–385. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Stacpoole PW: The pharmacology of
dichloroacetate. Metabolism. 38:1124–1144. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sun RC, Fadia M, Dahlstrom JE, Parish CR,
Board PG and Blackburn AC: Reversal of the glycolytic phenotype by
dichloroacetate inhibits metastatic breast cancer cell growth in
vitro and in vivo. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 120:253–260. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Madhok BM, Yeluri S, Perry SL, Hughes TA
and Jayne DG: Dichloroacetate induces apoptosis and cell-cycle
arrest in colorectal cancer cells. Br J Cancer. 102:1746–1752.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cao W, Yacoub S, Shiverick KT, Namiki K,
Sakai Y, Porvasnik S, Urbanek C and Rosser CJ: Dichloroacetate
(DCA) sensitizes both wild-type and over expressing Bcl-2 prostate
cancer cells in vitro to radiation. Prostate. 68:1223–1231. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sun RC, Board PG and Blackburn AC:
Targeting metabolism with arsenic trioxide and dichloroacetate in
breast cancer cells. Mol Cancer. 10:1422011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ayyanathan K, Kesaraju S, Dawson-Scully K
and Weissbach H: Combination of sulindac and dichloroacetate kills
cancer cells via oxidative damage. PLoS One. 7:e399492012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sanchez WY, McGee SL, Connor T, Mottram B,
Wilkinson A, Whitehead JP, Vuckovic S and Catley L: Dichloroacetate
inhibits aerobic glycolysis in multiple myeloma cells and increases
sensitivity to bortezomib. Br J Cancer. 108:1624–1633. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Fantin VR, St-Pierre J and Leder P:
Attenuation of LDH-A expression uncovers a link between glycolysis,
mitochondrial physiology, and tumor maintenance. Cancer Cell.
9:425–434. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gaude E and Frezza C: Defects in
mitochondrial metabolism and cancer. Cancer Metab. 2:102014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Weinberg F, Hamanaka R, Wheaton WW,
Weinberg S, Joseph J, Lopez M, Kalyanaraman B, Mutlu GM, Budinger
GR and Chandel NS: Mitochondrial metabolism and ROS generation are
essential for Kras-mediated tumorigenicity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
107:8788–8793. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Singleterry J, Sreedhar A and Zhao Y:
Components of cancer metabolism and therapeutic interventions.
Mitochondrion. 17:50–55. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Astuti D, Hart-Holden N, Latif F, Lalloo
F, Black GC, Lim C, Moran A, Grossman AB, Hodgson SV, Freemont A,
et al: Genetic analysis of mitochondrial complex II subunits SDHD,
SDHB and SDHC in paraganglioma and phaeochromocytoma
susceptibility. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 59:728–733. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Wallace DC: Mitochondria and cancer. Nat
Rev Cancer. 12:685–698. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Youle RJ and Karbowski M: Mitochondrial
fission in apoptosis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 6:657–663. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chen H and Chan DC: Mitochondrial dynamics
- fusion, fission, movement, and mitophagy - in neurodegenerative
diseases. Hum Mol Genet. 18(R2): R169–R176. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Raynaud FI, Eccles S, Clarke PA, Hayes A,
Nutley B, Alix S, Henley A, Di-Stefano F, Ahmad Z, Guillard S, et
al: Pharmacologic characterization of a potent inhibitor of class I
phosphatidylinositide 3-kinases. Cancer Res. 67:5840–5850. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Klionsky DJ, Abdalla FC, Abeliovich H,
Abraham RT, Acevedo-Arozena A, Adeli K, Agholme L, Agnello M,
Agostinis P, Aguirre-Ghiso JA, et al: Guidelines for the use and
interpretation of assays for monitoring autophagy. Autophagy.
8:445–544. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Biedler JL, Roffler-Tarlov S, Schachner M
and Freedman LS: Multiple neurotransmitter synthesis by human
neuroblastoma cell lines and clones. Cancer Res. 38:3751–3757.
1978.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Matthay KK: Neuroblastoma: biology and
therapy. Oncology (Williston Park). 11:1857–66; discussion 1869–72,
1875. 1997.
|
|
22
|
Alán L, Špaček T, Zelenka J, Tauber J,
Berková Z, Zacharovová K, Saudek F and Ježek P: Assessment of
mitochondrial DNA as an indicator of islet quality: An example in
Goto Kakizaki rats. Transplant Proc. 43:3281–3284. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Karess RE, Hayward WS and Hanafusa H:
Cellular information in the genome of recovered avian sarcoma virus
directs the synthesis of transforming protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 76:3154–3158. 1979. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Morton RE and Evans TA: Modification of
the bicinchoninic acid protein assay to eliminate lipid
interference in determining lipoprotein protein content. Anal
Biochem. 204:332–334. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Paulson JR and Laemmli UK: The structure
of histone-depleted metaphase chromosomes. Cell. 12:817–828. 1977.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Schneider CA, Rasband WS and Eliceiri KW:
NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat Methods.
9:671–675. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Scaduto RC Jr and Grotyohann LW:
Measurement of mitochondrial membrane potential using fluorescent
rhodamine derivatives. Biophys J. 76:469–477. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Stockwin LH, Yu SX, Borgel S, Hancock C,
Wolfe TL, Phillips LR, Hollingshead MG and Newton DL: Sodium
dichloroacetate selectively targets cells with defects in the
mitochondrial ETC. Int J Cancer. 127:2510–2519. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Cuervo AM, Stefanis L, Fredenburg R,
Lansbury PT and Sulzer D: Impaired degradation of mutant
alpha-synuclein by chaperone-mediated autophagy. Science.
305:1292–1295. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Maclean KH, Dorsey FC, Cleveland JL and
Kastan MB: Targeting lysosomal degradation induces p53-dependent
cell death and prevents cancer in mouse models of lymphomagenesis.
J Clin Invest. 118:79–88. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Maes H, Kuchnio A, Peric A, Moens S, Nys
K, De Bock K, Quaegebeur A, Schoors S, Georgiadou M, Wouters J, et
al: Tumor vessel normalization by chloroquine independent of
autophagy. Cancer Cell. 26:190–206. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Stacpoole PW: The dichloroacetate dilemma:
Environmental hazard versus therapeutic goldmine - both or neither?
Environ Health Perspect. 119:155–158. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
33
|
Kankotia S and Stacpoole PW:
Dichloroacetate and cancer: New home for an orphan drug? Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1846:617–629. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Gong F, Peng X, Sang Y, Qiu M, Luo C, He
Z, Zhao X and Tong A: Dichloroacetate induces protective autophagy
in LoVo cells: Involvement of cathepsin D/thioredoxin-like protein
1 and Akt-mTOR-mediated signaling. Cell Death Dis. 4:e9132013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Cheng P, Ni Z, Dai X, Wang B, Ding W, Rae
Smith A, Xu L, Wu D, He F and Lian J: The novel BH-3 mimetic
apogossypolone induces Beclin-1- and ROS-mediated autophagy in
human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. [corrected]. Cell Death Dis.
4:e4892013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Wong JYY, Huggins GS, Debidda M, Munshi NC
and De Vivo I: Dichloroacetate induces apoptosis in endometrial
cancer cells. Gynecol Oncol. 109:394–402. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Vella S, Conti M, Tasso R, Cancedda R and
Pagano A: Dichloroacetate inhibits neuroblastoma growth by
specifically acting against malignant undifferentiated cells. Int J
Cancer. 130:1484–1493. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Cai Q, Lu L, Tian J-H, Zhu Y-B, Qiao H and
Sheng Z-H: Snapin-regulated late endosomal transport is critical
for efficient autophagy-lysosomal function in neurons. Neuron.
68:73–86. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Castino R, Fiorentino I, Cagnin M, Giovia
A and Isidoro C: Chelation of lysosomal iron protects dopaminergic
SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells from hydrogen peroxide toxicity by
precluding autophagy and Akt dephosphorylation. Toxicol Sci.
123:523–541. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Michiorri S, Gelmetti V, Giarda E,
Lombardi F, Romano F, Marongiu R, Nerini-Molteni S, Sale P, Vago R,
Arena G, et al: The Parkinson-associated protein PINK1 interacts
with Beclin1 and promotes autophagy. Cell Death Differ. 17:962–974.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Youle RJ and Narendra DP: Mechanisms of
mitophagy. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 12:9–14. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Nakahara K, Ueda M, Yamada K, Koide T,
Yoshimochi G, Funayama M, Kim JH, Yamakawa S, Mori A, Misumi Y, et
al: Juvenile-onset Parkinsonism with digenic parkin and PINK1
mutations treated with subthalamic nucleus stimulation at 45 years
after disease onset. J Neurol Sci. 345:276–277. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Scarffe LA, Stevens DA, Dawson VL and
Dawson TM: Parkin and PINK1: Much more than mitophagy. Trends
Neurosci. 37:315–324. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Exner N, Treske B, Paquet D, Holmström K,
Schiesling C, Gispert S, Carballo-Carbajal I, Berg D, Hoepken HH,
Gasser T, et al: Loss-of-function of human PINK1 results in
mitochondrial pathology and can be rescued by parkin. J Neurosci.
27:12413–12418. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Dagda RK, Cherra SJ III, Kulich SM, Tandon
A, Park D and Chu CT: Loss of PINK1 function promotes mitophagy
through effects on oxidative stress and mitochondrial fission. J
Biol Chem. 284:13843–13855. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Twig G, Elorza A, Molina AJ, Mohamed H,
Wikstrom JD, Walzer G, Stiles L, Haigh SE, Katz S, Las G, et al:
Fission and selective fusion govern mitochondrial segregation and
elimination by autophagy. EMBO J. 27:433–446. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Santin G, Piccolini VM, Barni S, Veneroni
P, Giansanti V, Dal Bo V, Bernocchi G and Bottone MG: Mitochondrial
fusion: A mechanism of cisplatin-induced resistance in
neuroblastoma cells? Neurotoxicology. 34:51–60. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Cipolat S, Martins de Brito O, Dal Zilio B
and Scorrano L: OPA1 requires mitofusin 1 to promote mitochondrial
fusion. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:15927–15932. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Zorzano A, Liesa M, Sebastián D, Segalés J
and Palacín M: Mitochondrial fusion proteins: Dual regulators of
morphology and metabolism. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 21:566–574. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Bertholet AM, Millet AME, Guillermin O,
Daloyau M, Davezac N, Miquel M-C and Belenguer P: OPA1 loss of
function affects in vitro neuronal maturation. Brain.
136:1518–1533. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Duvezin-Caubet S, Jagasia R, Wagener J,
Hofmann S, Trifunovic A, Hansson A, Chomyn A, Bauer MF, Attardi G,
Larsson NG, et al: Proteolytic processing of OPA1 links
mitochondrial dysfunction to alterations in mitochondrial
morphology. J Biol Chem. 281:37972–37979. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Kopek BG, Shtengel G, Grimm JB, Clayton DA
and Hess HF: Correlative photoactivated localization and scanning
electron microscopy. PLoS One. 8:e772092013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Schaffer S, Gruber J, Ng LF, Fong S, Wong
YT, Tang SY and Halliwell B: The effect of dichloroacetate on
health- and lifespan in C. elegans. Biogerontology. 12:195–209.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Gandhi S, Muqit MMK, Stanyer L, Healy DG,
Abou-Sleiman PM, Hargreaves I, Heales S, Ganguly M, Parsons L, Lees
AJ, et al: PINK1 protein in normal human brain and Parkinson’s
disease. Brain. 129:1720–1731. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|