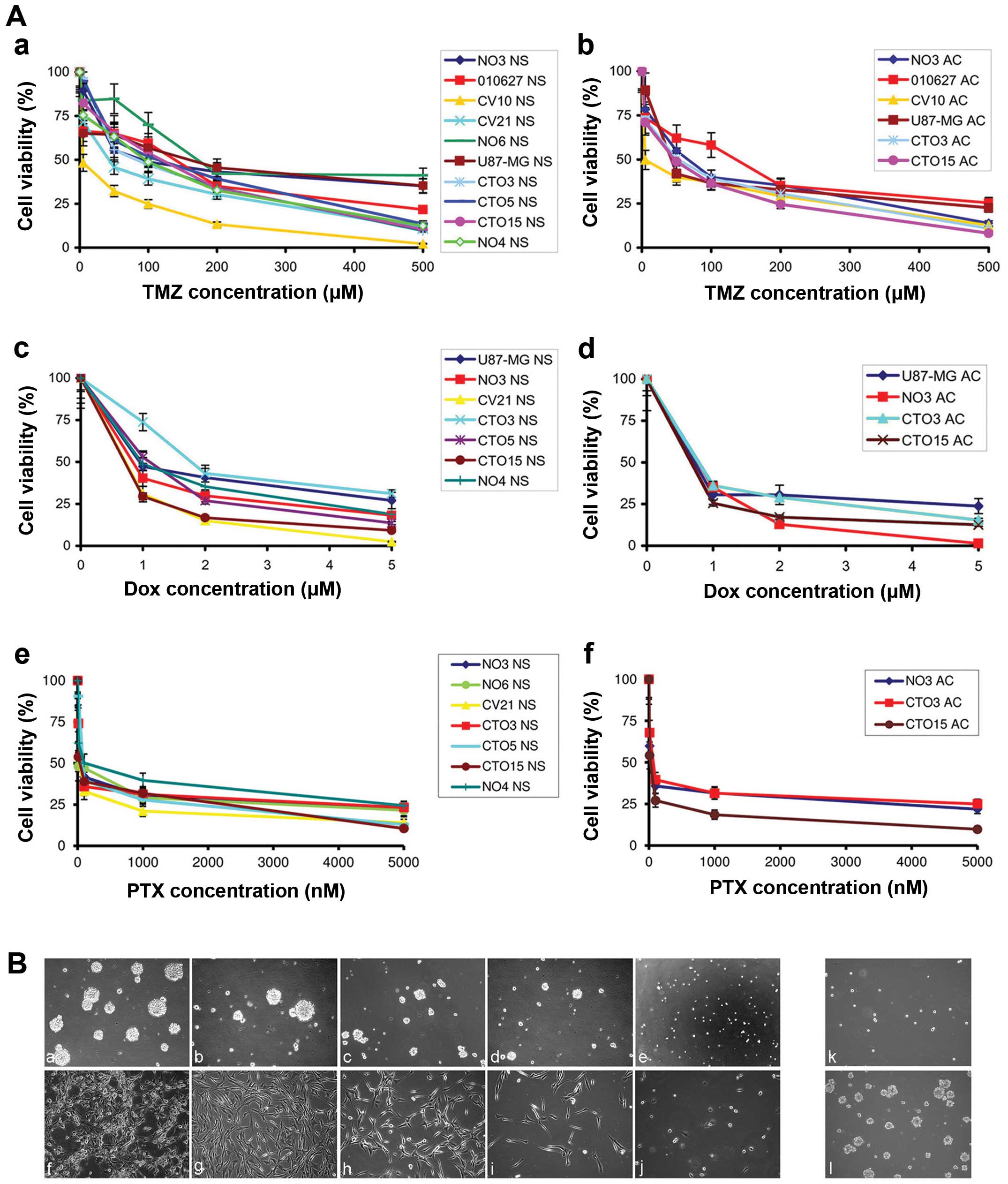
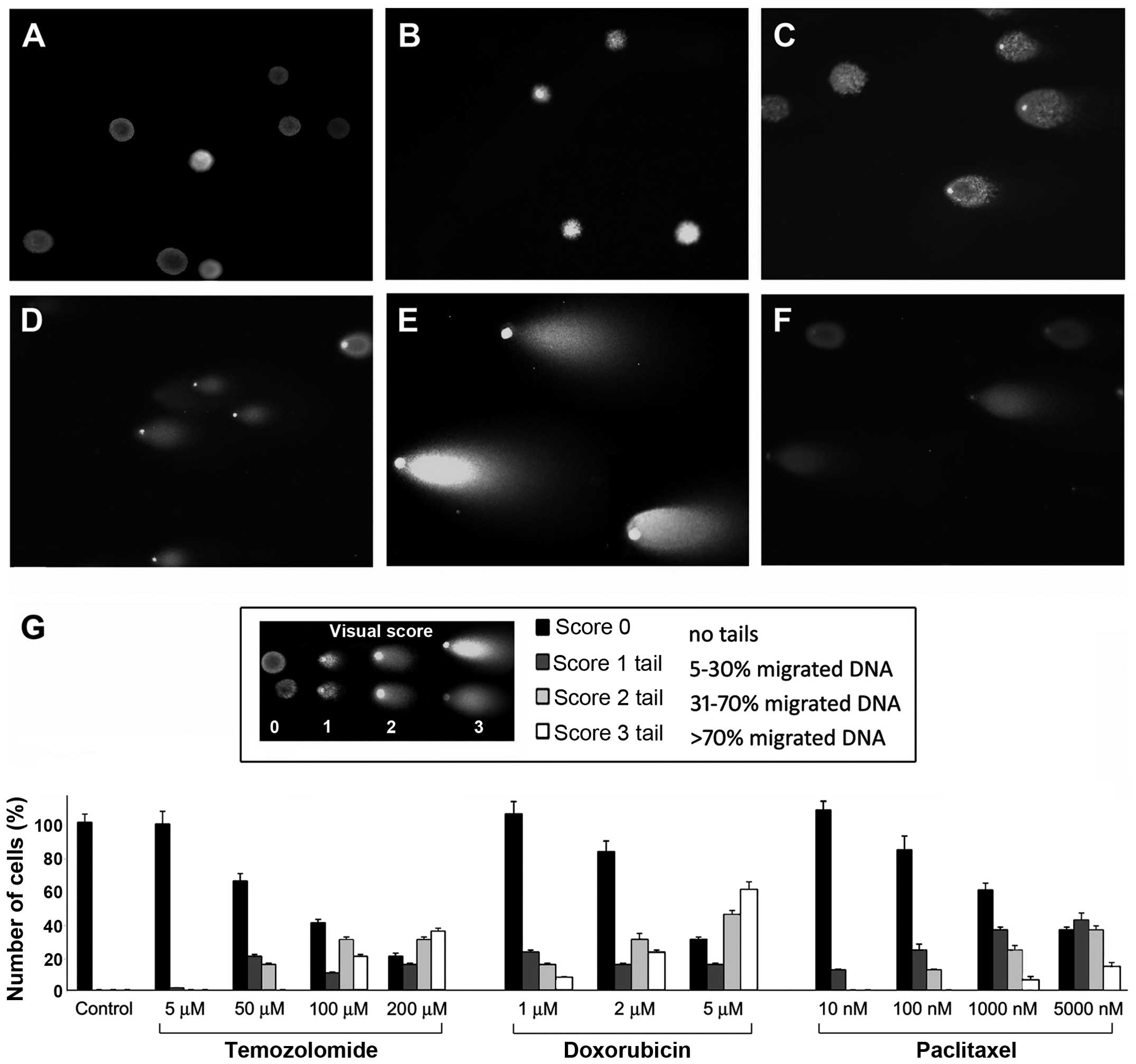
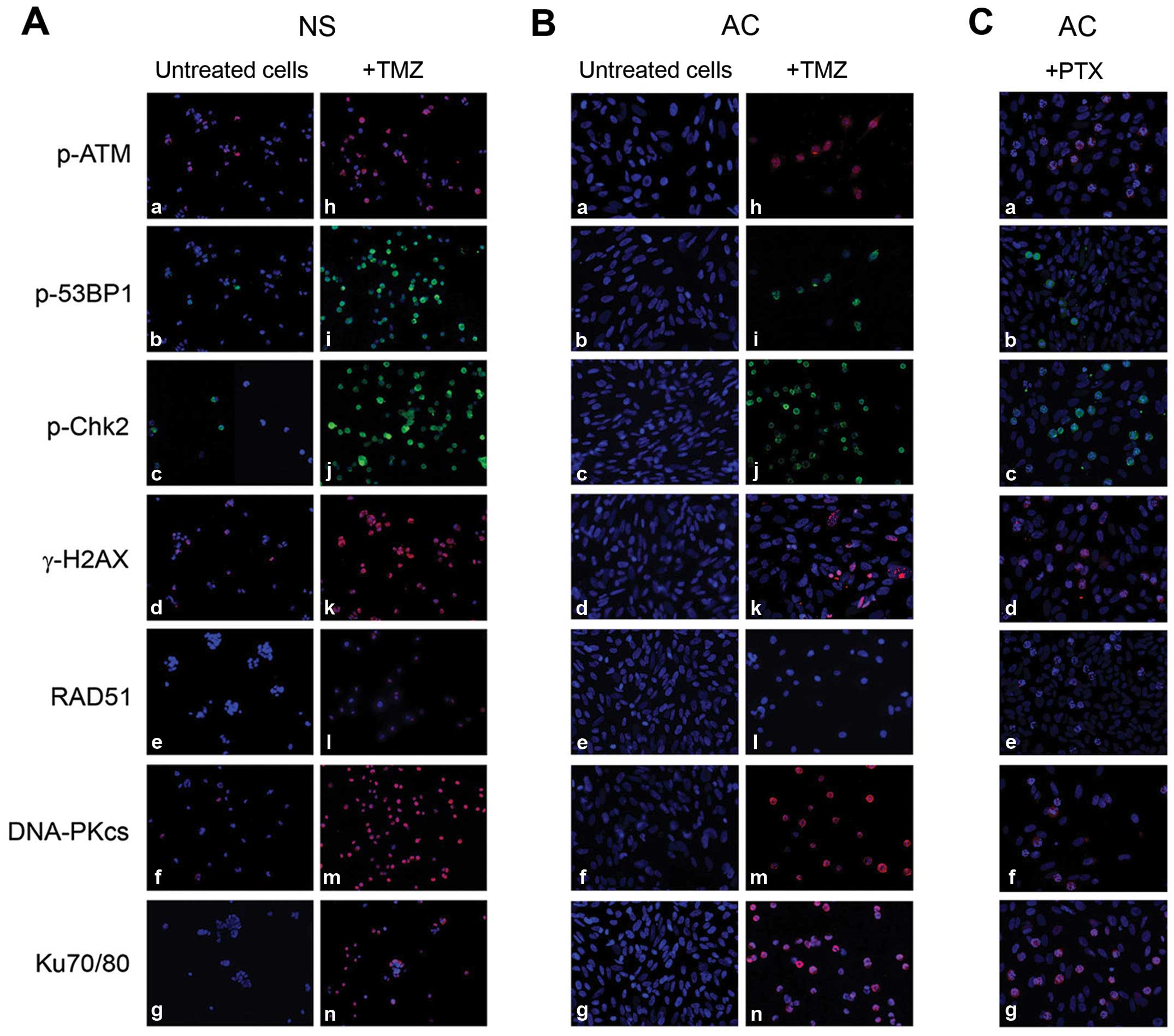
|
1
|
Caldera V, Mellai M, Annovazzi L,
Monzeglio O, Piazzi A and Schiffer D: MGMT hypermethylation and MDR
system in glioblastoma cancer stem cells. Cancer Genomics
Proteomics. 9:171–178. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Salmaggi A, Boiardi A, Gelati M, Russo A,
Calatozzolo C, Ciusani E, Sciacca FL, Ottolina A, Parati EA, La
Porta C, Alessandri G, Marras C, Croci D and De Rossi M:
Glioblastoma-derived tumorospheres identify a population of tumor
stem-like cells with angiogenic potential and enhanced multidrug
resistance phenotype. Glia. 54:850–860. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Johannessen TC and Bjerkvig R: Molecular
mechanisms of temozolomide resistance in glioblastoma multiforme.
Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 12:635–642. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Alexander BM, Pinnell N, Wen PY and
D’Andrea A: Targeting DNA repair and the cell cycle in
glioblastoma. J Neurooncol. 107:463–477. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Schmalz PG, Shen MJ and Park JK: Treatment
resistance mechanisms of malignant glioma tumor stem cells. Cancers
(Basel). 3:621–635. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Frosina G: The bright and the dark sides
of DNA repair in stem cells. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2010:8453962010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Frosina G: DNA repair and resistance of
gliomas to chemotherapy and radiotherapy. Mol Cancer Res.
7:989–999. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sarkaria JN, Kitange GJ, James CD, Plummer
R, Calvert H, Weller M and Wick W: Mechanisms of chemoresistance to
alkylating agents in malignant glioma. Clin Cancer Res.
14:2900–2908. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kastan MB and Bartek J: Cell-cycle
checkpoints and cancer. Nature. 432:316–323. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bolderson E, Richard DJ, Zhou BB and
Khanna KK: Recent advances in cancer therapy targeting proteins
involved in DNA double-strand break repair. Clin Cancer Res.
15:6314–6320. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Pardo B, Gómez-González B and Aguilera A:
DNA repair in mammalian cells: DNA double-strand break repair: how
to fix a broken relationship. Cell Mol Life Sci. 66:1039–1056.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Johannessen TC, Bjerkvig R and Tysnes BB:
DNA repair and cancer stem-like cells--potential partners in glioma
drug resistance? Cancer Treat Rev. 34:558–567. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bao S, Wu Q, McLendon RE, Hao Y, Shi Q,
Hjelmeland AB, Dewhirst MW, Bigner DD and Rich JN: Glioma stem
cells promote radioresistance by preferential activation of the DNA
damage response. Nature. 444:756–760. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Liu G, Yuan X, Zeng Z, Tunici P, Ng H,
Abdulkadir IR, Lu L, Irvin D, Black KL and Yu JS: Analysis of gene
expression and chemoresistance of CD133+ cancer stem
cells in glioblastoma. Mol Cancer. 5:672006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Hegi ME, Diserens AC, Gorlia T, Hamou MF,
de Tribolet N, Weller M, Kros JM, Hainfellner JA, Mason W, Mariani
L, et al: MGMT gene silencing and benefit from temozolomide in
glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 352:997–1003. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hirose Y, Berger MS and Pieper RO: p53
effects both the duration of G2/M arrest and the fate of
temozolomide-treated human glioblastoma cells. Cancer Res.
61:1957–1963. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Günther W, Pawlak E, Damasceno R, Arnold H
and Terzis AJ: Temozolomide induces apoptosis and senescence in
glioma cells cultured as multicellular spheroids. Br J Cancer.
88:463–469. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Roos WP, Batista LF, Naumann SC, Wick W,
Weller M, Menck CF and Kaina B: Apoptosis in malignant glioma cells
triggered by the temozolomide-induced DNA lesion O6-methylguanine.
Oncogene. 26:186–197. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Kurz EU, Douglas P and Lees-Miller SP:
Doxorubicin activates ATM-dependent phosphorylation of multiple
downstream targets in part through the generation of reactive
oxygen species. J Biol Chem. 279:53272–53281. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Branham MT, Nadin SB, Vargas-Roig LM and
Ciocca DR: DNA damage induced by paclitaxel and DNA repair
capability of peripheral blood lymphocytes as evaluated by the
alkaline comet assay. Mutat Res. 560:11–17. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Stan AC, Casares S, Radu D, Walter GF and
Brumeanu TD: Doxorubicin-induced cell death in highly invasive
human gliomas. Anticancer Res. 19(2A): 941–950. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lesniak MS, Upadhyay U, Goodwin R, Tyler B
and Brem H: Local delivery of doxorubicin for the treatment of
malignant brain tumors in rats. Anticancer Res. 25(6B): 3825–3831.
2005.Erratum in: Anticancer Res 26: 445, 2006. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chang SM, Kuhn JG, Robins HI, Schold SC
Jr, Spence AM, Berger MS, Mehta M, Pollack IF, Rankin C and Prados
MD: A Phase II study of paclitaxel in patients with recurrent
malignant glioma using different doses depending upon the
concomitant use of anticonvulsants: A North American Brain Tumor
Consortium report. Cancer. 91:417–422. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Caldera V, Mellai M, Annovazzi L, Piazzi
A, Lanotte M, Cassoni P and Schiffer D: Antigenic and genotypic
similarity between primary glioblastomas and their derived
neurospheres. J Oncol. 2011:3149622011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Mellai M, Monzeglio O, Piazzi A, Caldera
V, Annovazzi L, Cassoni P, Valente G, Cordera S, Mocellini C and
Schiffer D: MGMT promoter hypermethylation and its associations
with genetic alterations in a series of 350 brain tumors. J
Neurooncol. 107:617–631. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Louis DN, Ohgaki H, Wiestler OD and
Cavanee WK: WHO Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous
Systems. 4th edition. International Agency for Research on Cancer
(IARC); Lyon: 2007
|
|
27
|
Singh NP, McCoy MT, Tice RR and Schneider
EL: A simple technique for quantitation of low levels of DNA damage
in individual cells. Exp Cell Res. 175:184–191. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Collins AR, Oscoz AA, Brunborg G, Gaivão
I, Giovannelli L, Kruszewski M, Smith CC and Stetina R: The comet
assay: Topical issues. Mutagenesis. 23:143–151. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Mellai M and Schiffer D: Apoptosis in
brain tumors: Prognostic and therapeutic considerations. Anticancer
Res. 27(1A): 437–448. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Beier D, Röhrl S, Pillai DR, Schwarz S,
Kunz-Schughart LA, Leukel P, Proescholdt M, Brawanski A, Bogdahn U,
Trampe-Kieslich A, et al: Temozolomide preferentially depletes
cancer stem cells in glioblastoma. Cancer Res. 68:5706–5715. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Mihaliak AM, Gilbert CA, Li L, Daou MC,
Moser RP, Reeves A, Cochran BH and Ross AH: Clinically relevant
doses of chemotherapy agents reversibly block formation of
glioblastoma neurospheres. Cancer Lett. 296:168–177. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hermisson M, Klumpp A, Wick W, Wischhusen
J, Nagel G, Roos W, Kaina B and Weller M: O6-methylguanine DNA
methyltransferase and p53 status predict temozolomide sensitivity
in human malignant glioma cells. J Neurochem. 96:766–776. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Bocangel DB, Finkelstein S, Schold SC,
Bhakat KK, Mitra S and Kokkinakis DM: Multifaceted resistance of
gliomas to temozolomide. Clin Cancer Res. 8:2725–2734.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Knizhnik AV, Roos WP, Nikolova T, Quiros
S, Tomaszowski KH, Christmann M and Kaina B: Survival and death
strategies in glioma cells: Autophagy, senescence and apoptosis
triggered by a single type of temozolomide-induced DNA damage. PLoS
One. 8:e556652013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Beier D, Schriefer B, Brawanski K, Hau P,
Weis J, Schulz JB and Beier CP: Efficacy of clinically relevant
temozolomide dosing schemes in glioblastoma cancer stem cell lines.
J Neurooncol. 109:45–52. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kase M, Vardja M, Lipping A, Asser T and
Jaal J: Impact of PARP-1 and DNA-PK expression on survival in
patients with glioblastoma multiforme. Radiother Oncol.
101:127–131. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Bartek J, Bartkova J and Lukas J: DNA
damage signalling guards against activated oncogenes and tumour
progression. Oncogene. 26:7773–7779. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Bartkova J, Hamerlik P, Stockhausen MT,
Ehrmann J, Hlobilkova A, Laursen H, Kalita O, Kolar Z, Poulsen HS,
Broholm H, et al: Replication stress and oxidative damage
contribute to aberrant constitutive activation of DNA damage
signalling in human gliomas. Oncogene. 29:5095–5102. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Battaglia L, Gallarate M, Peira E, Chirio
D, Muntoni E, Biasibetti E, Capucchio MT, Valazza A, Panciani PP,
Lanotte M, et al: Solid lipid nanoparticles for potential
doxorubicin delivery in glioblastoma treatment: Preliminary in
vitro studies. J Pharm Sci. 103:2157–2165. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Chirio D, Gallarate M, Peira E, Battaglia
L, Muntoni E, Riganti C, Biasibetti E, Capucchio MT, Valazza A,
Panciani P, et al: Positive-charged solid lipid nanoparticles as
paclitaxel drug delivery system in glioblastoma treatment. Eur J
Pharm Biopharm. 88:746–758. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|