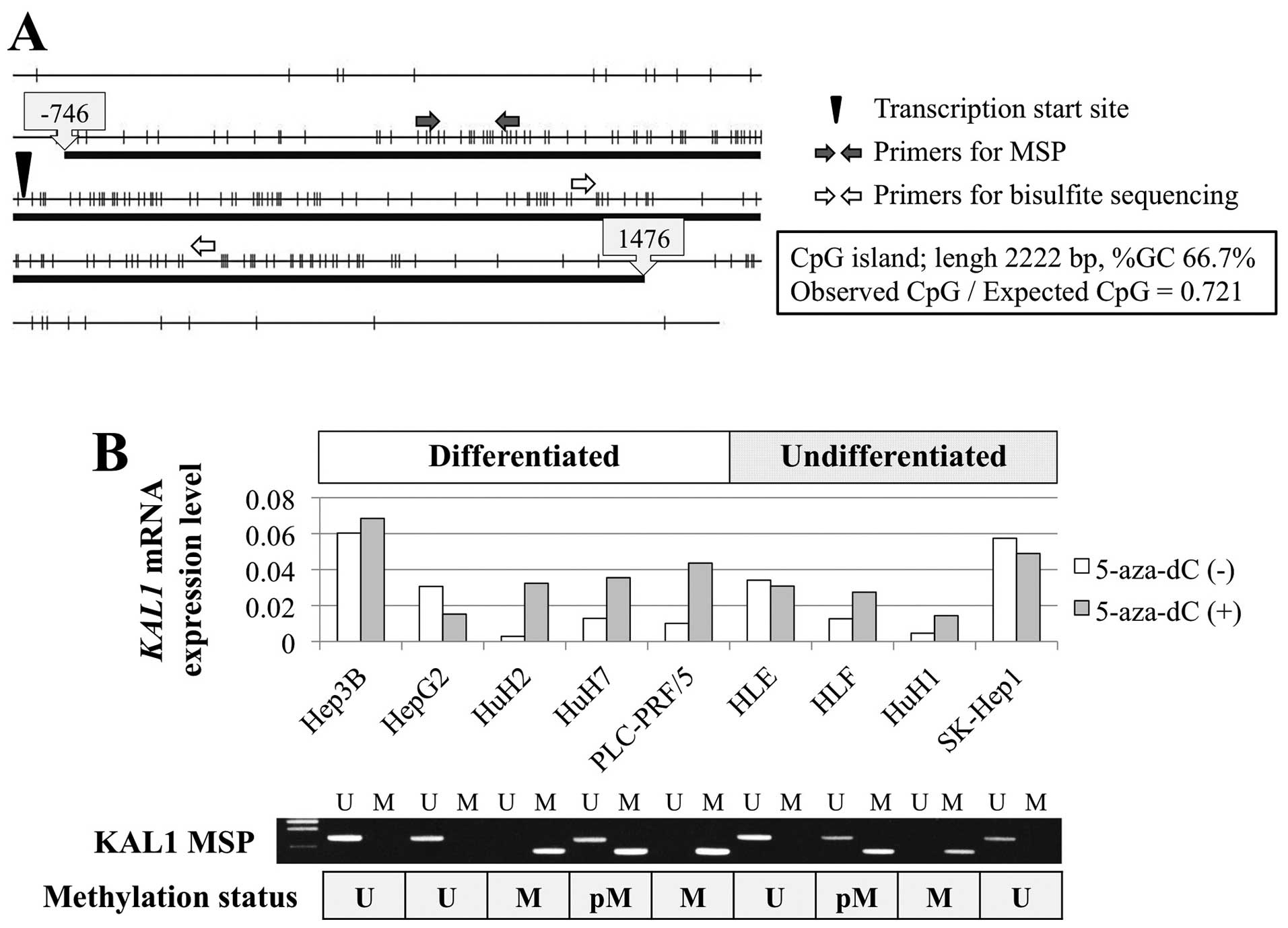
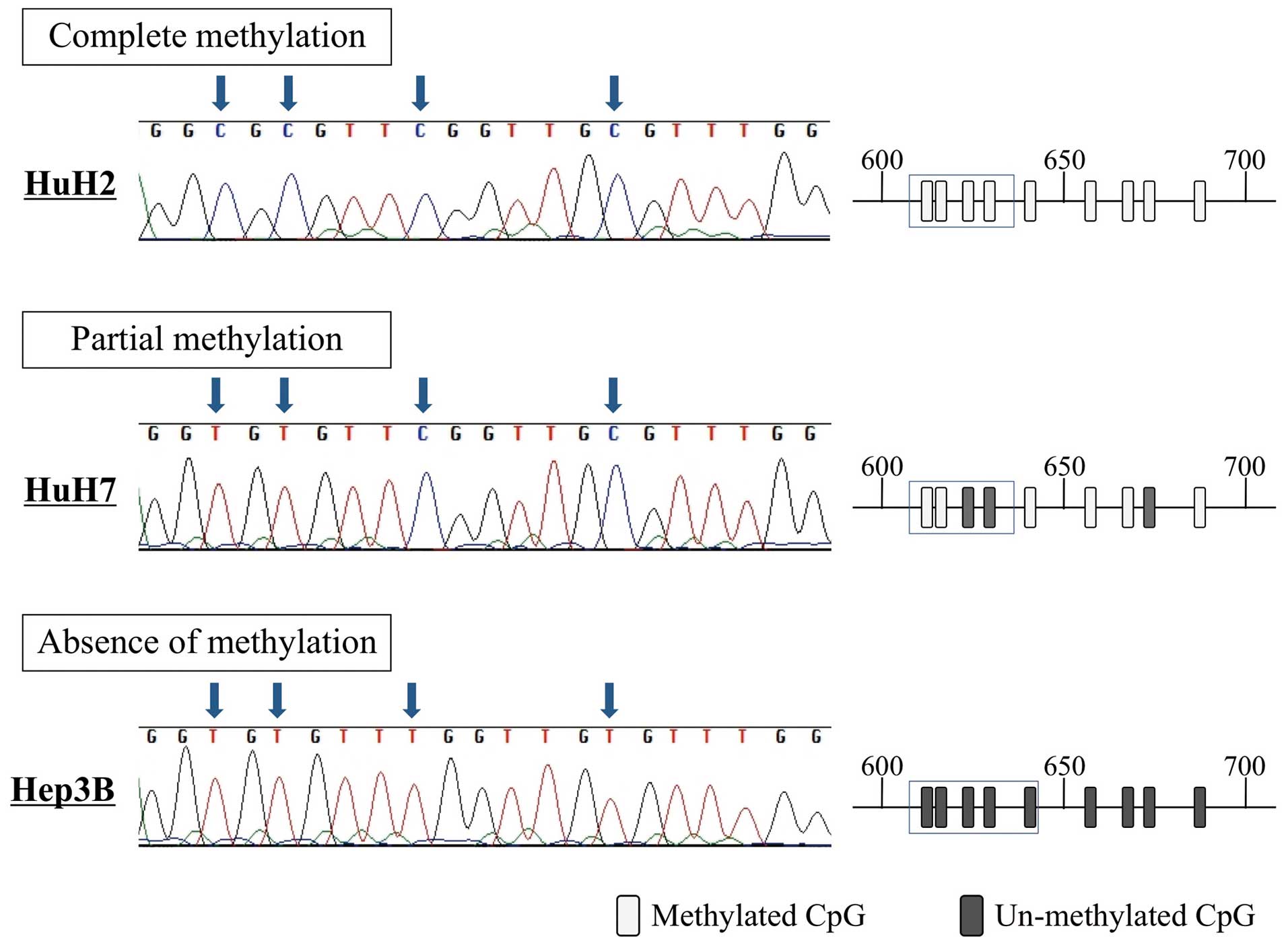
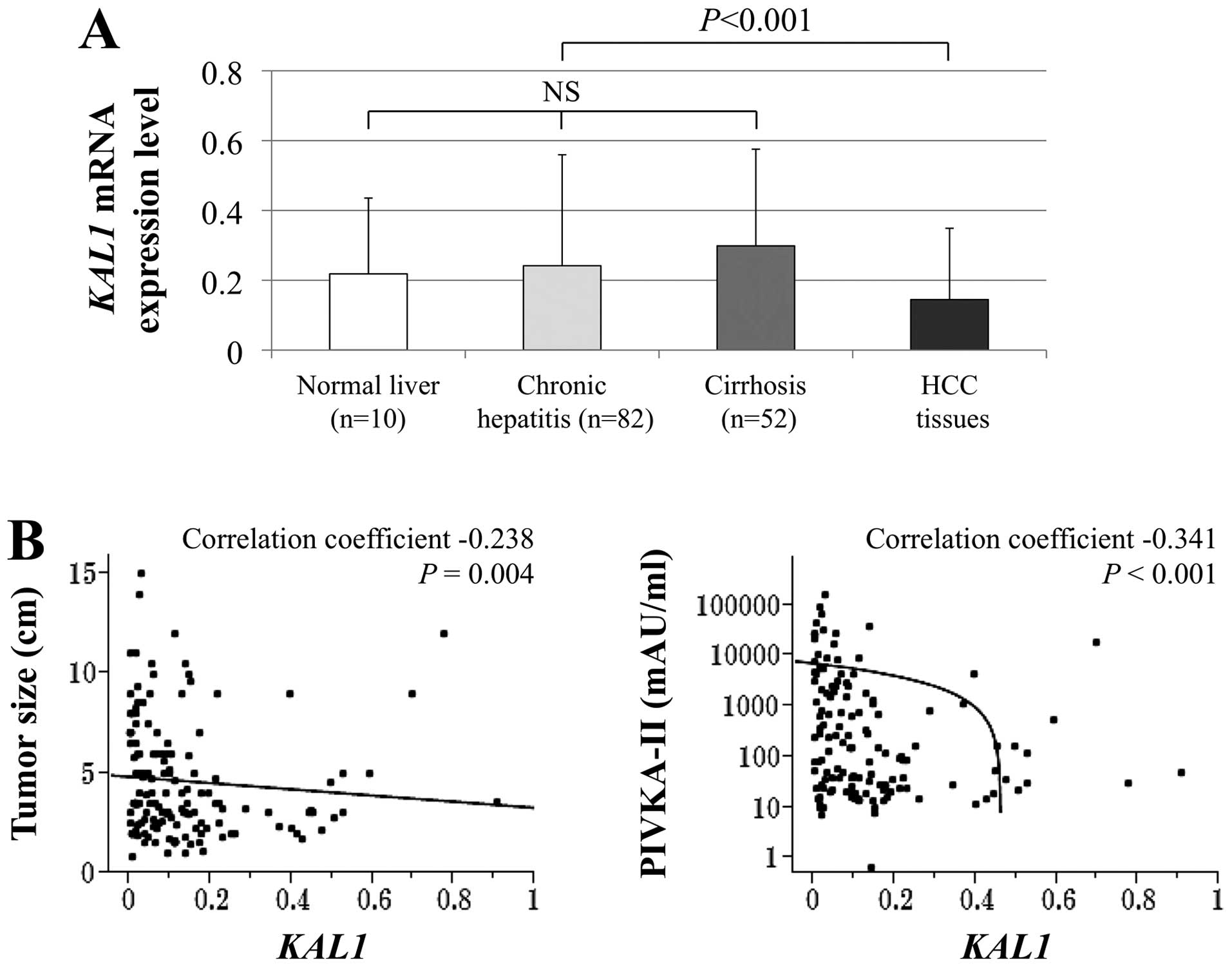
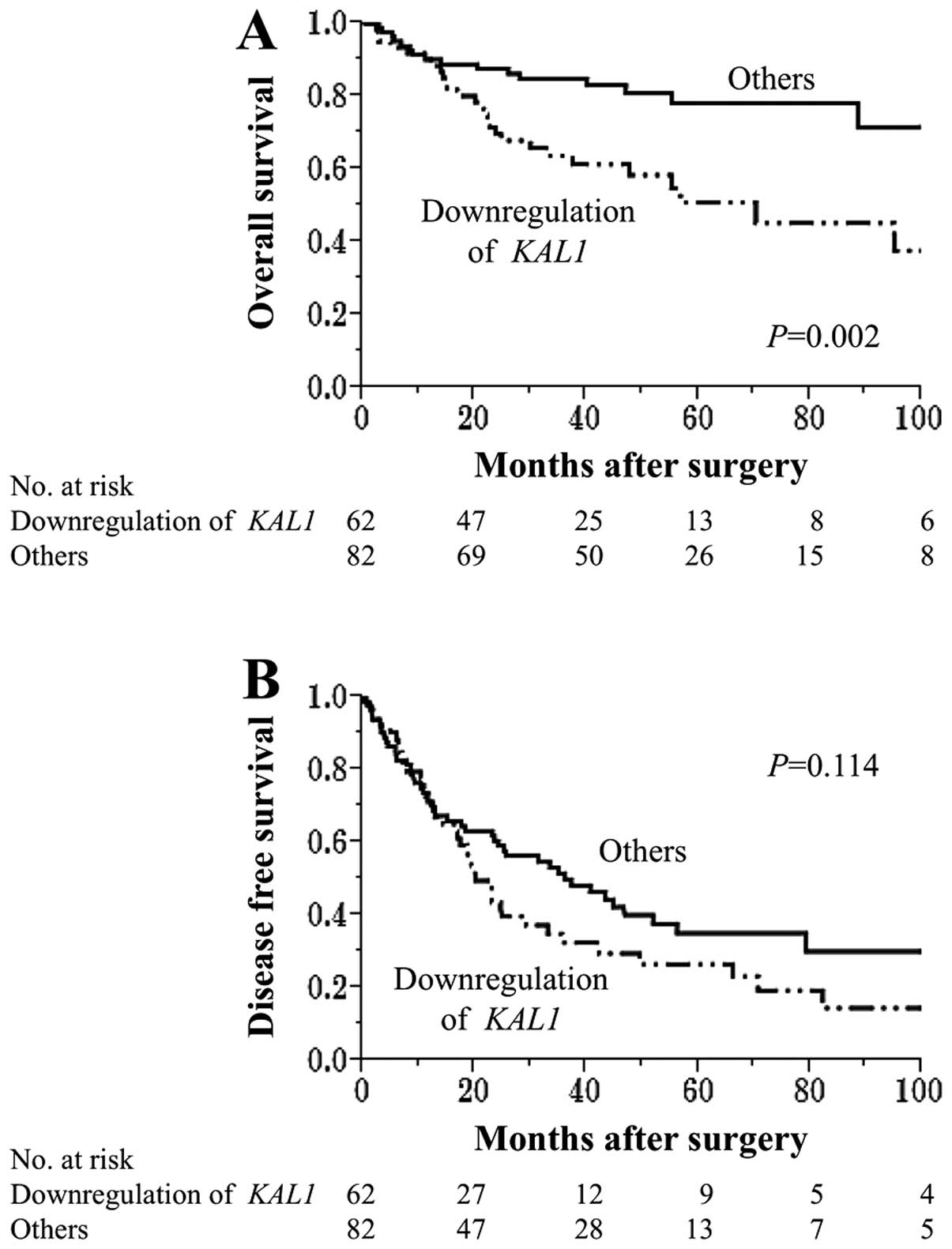
|
1
|
Siegel R, Ward E, Brawley O and Jemal A:
Cancer statistics, 2011: The impact of eliminating socioeconomic
and racial disparities on premature cancer deaths. CA Cancer J
Clin. 61:212–236. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Galuppo R, Ramaiah D, Ponte OM and Gedaly
R: Molecular therapies in hepatocellular carcinoma: What can we
target? Dig Dis Sci. 59:1688–1697. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Giannelli G, Rani B, Dituri F, Cao Y and
Palasciano G: Moving towards personalised therapy in patients with
hepatocellular carcinoma: The role of the microenvironment. Gut.
63:1668–1676. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kanda M, Nomoto S, Nishikawa Y, Sugimoto
H, Kanazumi N, Takeda S and Nakao A: Correlations of the expression
of vascular endothelial growth factor B and its isoforms in
hepatocellular carcinoma with clinicopathological parameters. J
Surg Oncol. 98:190–196. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
El-Serag HB: Hepatocellular carcinoma. N
Engl J Med. 365:1118–1127. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sawan C, Vaissière T, Murr R and Herceg Z:
Epigenetic drivers and genetic passengers on the road to cancer.
Mutat Res. 642:1–13. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kanda M, Sugimoto H, Nomoto S, Oya H,
Hibino S, Shimizu D, Takami H, Hashimoto R, Okamura Y, Yamada S, et
al: B-cell translocation gene 1 serves as a novel prognostic
indicator of hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Oncol. 46:641–648.
2015.
|
|
8
|
Hernandez-Gea V, Toffanin S, Friedman SL
and Llovet JM: Role of the microenvironment in the pathogenesis and
treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology.
144:512–527. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Arzumanyan A, Reis HM and Feitelson MA:
Pathogenic mechanisms in HBV- and HCV-associated hepatocellular
carcinoma. Nat Rev Cancer. 13:123–135. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kanda M, Sugimoto H, Nomoto S, Oya H,
Shimizu D, Takami H, Hashimoto R, Sonohara F, Okamura Y, Yamada S,
et al: Clinical utility of PDSS2 expression to stratify patients at
risk for recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Oncol.
45:2005–2012. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Soussi-Yanicostas N, de Castro F, Julliard
AK, Perfettini I, Chédotal A and Petit C: Anosmin-1, defective in
the X-linked form of Kallmann syndrome, promotes axonal branch
formation from olfactory bulb output neurons. Cell. 109:217–228.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Di Schiavi E and Andrenacci D:
Invertebrate models of kallmann syndrome: Molecular pathogenesis
and new disease genes. Curr Genomics. 14:2–10. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Liu J, Cao W, Chen W, Xu L and Zhang C:
Decreased expression of Kallmann syndrome 1 sequence gene (KAL1)
contributes to oral squamous cell carcinoma progression and
significantly correlates with poorly differentiated grade. J Oral
Pathol Med. 44:109–114. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
González-Martínez D, Kim SH, Hu Y, Guimond
S, Schofield J, Winyard P, Vannelli GB, Turnbull J and Bouloux PM:
Anosmin-1 modulates fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 signaling
in human gonadotropin-releasing hormone olfactory neuroblasts
through a heparan sulfate-dependent mechanism. J Neurosci.
24:10384–10392. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Choy CT, Kim H, Lee JY, Williams DM,
Palethorpe D, Fellows G, Wright AJ, Laing K, Bridges LR, Howe FA,
et al: Anosmin-1 contributes to brain tumor malignancy through
integrin signal pathways. Endocr Relat Cancer. 21:85–99. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
16
|
Kanda M, Nomoto S, Okamura Y, Hayashi M,
Hishida M, Fujii T, Nishikawa Y, Sugimoto H, Takeda S and Nakao A:
Promoter hypermethylation of fibulin 1 gene is associated with
tumor progression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Carcinog.
50:571–579. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Jian B, Nagineni CN, Meleth S, Grizzle W,
Bland K, Chaudry I and Raju R: Anosmin-1 involved in neuronal cell
migration is hypoxia inducible and cancer regulated. Cell Cycle.
8:3770–3776. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Guioli S, Incerti B, Zanaria E, Bardoni B,
Franco B, Taylor K, Ballabio A and Camerino G: Kallmann syndrome
due to a translocation resulting in an X/Y fusion gene. Nat Genet.
1:337–340. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hardelin JP, Levilliers J, del Castillo I,
Cohen-Salmon M, Legouis R, Blanchard S, Compain S, Bouloux P, Kirk
J, Moraine C, et al: X chromosome-linked Kallmann syndrome: Stop
mutations validate the candidate gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
89:8190–8194. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Nomoto S, Kanda M, Okamura Y, Nishikawa Y,
Qiyong L, Fujii T, Sugimoto H, Takeda S and Nakao A: Epidermal
growth factor-containing fibulin-like extracellular matrix protein
1, EFEMP1, a novel tumor-suppressor gene detected in
hepato-cellular carcinoma using double combination array analysis.
Ann Surg Oncol. 17:923–932. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Kanda M, Nomoto S, Oya H, Takami H, Hibino
S, Hishida M, Suenaga M, Yamada S, Inokawa Y, Nishikawa Y, et al:
Downregulation of DENND2D by promoter hypermethylation is
associated with early recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J
Oncol. 44:44–52. 2014.
|
|
22
|
Shimizu D, Kanda M, Nomoto S, Oya H,
Takami H, Hibino S, Suenaga M, Inokawa Y, Hishida M, Takano N, et
al: Identification of intragenic methylation in the TUSC1 gene as a
novel prognostic marker of hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol Rep.
31:1305–1313. 2014.
|
|
23
|
Takami H, Kanda M, Oya H, Hibino S,
Sugimoto H, Suenaga M, Yamada S, Nishikawa Y, Asai M, Fujii T, et
al: Evaluation of MAGE-D4 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma in
Japanese patients. J Surg Oncol. 108:557–562. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sobin LH, Gospodarowicz MK and Wittekind
C: International Union Against Cancer, TNM Classification of
Malignant Tumors. 7th edition. Wiley-Blackwell; New York: 2009
|
|
25
|
Kanda M, Nomoto S, Oya H, Hashimoto R,
Takami H, Shimizu D, Sonohara F, Kobayashi D, Tanaka C, Yamada S,
et al: Decreased expression of prenyl diphosphate synthase subunit
2 correlates with reduced survival of patients with gastric cancer.
J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 33:882014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Takai D and Jones PA: The CpG island
searcher: A new WWW resource. In Silico Biol. 3:235–240.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kanda M, Nomoto S, Oya H, Shimizu D,
Takami H, Hibino S, Hashimoto R, Kobayashi D, Tanaka C, Yamada S,
et al: Dihydropyrimidinase-like 3 facilitates malignant behavior of
gastric cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 33:662014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kanda M, Shimizu D, Nomoto S, Hibino S,
Oya H, Takami H, Kobayashi D, Yamada S, Inokawa Y, Tanaka C, et al:
Clinical significance of expression and epigenetic profiling of
TUSC1 in gastric cancer. J Surg Oncol. 110:136–144. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kawahara T, Hotta N, Ozawa Y, Kato S, Kano
K, Yokoyama Y, Nagino M, Takahashi T and Yanagisawa K: Quantitative
proteomic profiling identifies DPYSL3 as pancreatic ductal
adenocarcinoma-associated molecule that regulates cell adhesion and
migration by stabilization of focal adhesion complex. PLoS One.
8:e796542013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Oya H, Kanda M, Sugimoto H, Shimizu D,
Takami H, Hibino S, Hashimoto R, Okamura Y, Yamada S, Fujii T, et
al: Dihydropyrimidinase-like 3 is a putative hepatocellular
carcinoma tumor suppressor. J Gastroenterol. Aug 31–2014.(Epub
ahead of print). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kanda M, Shimizu D, Nomoto S, Takami H,
Hibino S, Oya H, Hashimoto R, Suenaga M, Inokawa Y, Kobayashi D, et
al: Prognostic impact of expression and methylation status of
DENN/MADD domain-containing protein 2D in gastric cancer. Gastric
Cancer. 18:288–296. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Yam JW, Tse EY and Ng IO: Role and
significance of focal adhesion proteins in hepatocellular
carcinoma. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 24:520–530. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Maunakea AK, Nagarajan RP, Bilenky M,
Ballinger TJ, D’Souza C, Fouse SD, Johnson BE, Hong C, Nielsen C,
Zhao Y, et al: Conserved role of intragenic DNA methylation in
regulating alternative promoters. Nature. 466:253–257. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Khare S, Zhang Q and Ibdah JA: Epigenetics
of hepatocellular carcinoma: Role of microRNA. World J
Gastroenterol. 19:5439–5445. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Miki D, Ochi H, Hayes CN, Aikata H and
Chayama K: Hepato-cellular carcinoma: Towards personalized
medicine. Cancer Sci. 103:846–850. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kang YK, Hong SW, Lee H and Kim WH:
Prognostic implications of ezrin expression in human hepatocellular
carcinoma. Mol Carcinog. 49:798–804. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Chen Y, Wang D, Guo Z, Zhao J, Wu B, Deng
H, Zhou T, Xiang H, Gao F, Yu X, et al: Rho kinase phosphorylation
promotes ezrin-mediated metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Cancer Res. 71:1721–1729. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ghaffari A, Hoskin V, Szeto A, Hum M,
Liaghati N, Nakatsu K, Madarnas Y, Sengupta S and Elliott BE: A
novel role for ezrin in breast cancer angio/lymphangiogenesis.
Breast Cancer Res. 16:4382014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Piao J and Liu S, Xu Y, Wang C, Lin Z, Qin
Y and Liu S: Ezrin protein overexpression predicts the poor
prognosis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas. Exp Mol Pathol.
98:1–6. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Ogasawara S, Yano H, Iemura A, Hisaka T
and Kojiro M: Expressions of basic fibroblast growth factor and its
receptors and their relationship to proliferation of human
hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines. Hepatology. 24:198–205. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Huang X, Yu C, Jin C, Kobayashi M, Bowles
CA, Wang F and McKeehan WL: Ectopic activity of fibroblast growth
factor receptor 1 in hepatocytes accelerates hepatocarcinogenesis
by driving proliferation and vascular endothelial growth
factor-induced angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 66:1481–1490. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wang J, Li J, Wang X, Zheng C and Ma W:
Downregulation of microRNA-214 and overexpression of FGFR-1
contribute to hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 439:47–53. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Zheng SS, Chen XH, Yin X and Zhang BH:
Prognostic significance of HIF-1α expression in hepatocellular
carcinoma: A meta-analysis. PLoS One. 8:e657532013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Wu L, Fu Z, Zhou S, Gong J, Liu CA, Qiao Z
and Li S: HIF-1α and HIF-2α: Siblings in promoting angiogenesis of
residual hepatocellular carcinoma after high-intensity focused
ultrasound ablation. PLoS One. 9:e889132014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Yamada S, Utsunomiya T, Morine Y, Imura S,
Ikemoto T, Arakawa Y, Kanamoto M, Iwahashi S, Saito Y, Takasu C, et
al: Expressions of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 and epithelial cell
adhesion molecule are linked with aggressive local recurrence of
hepatocellular carcinoma after radiofrequency ablation therapy. Ann
Surg Oncol. 21(Suppl 3): S436–S442. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|