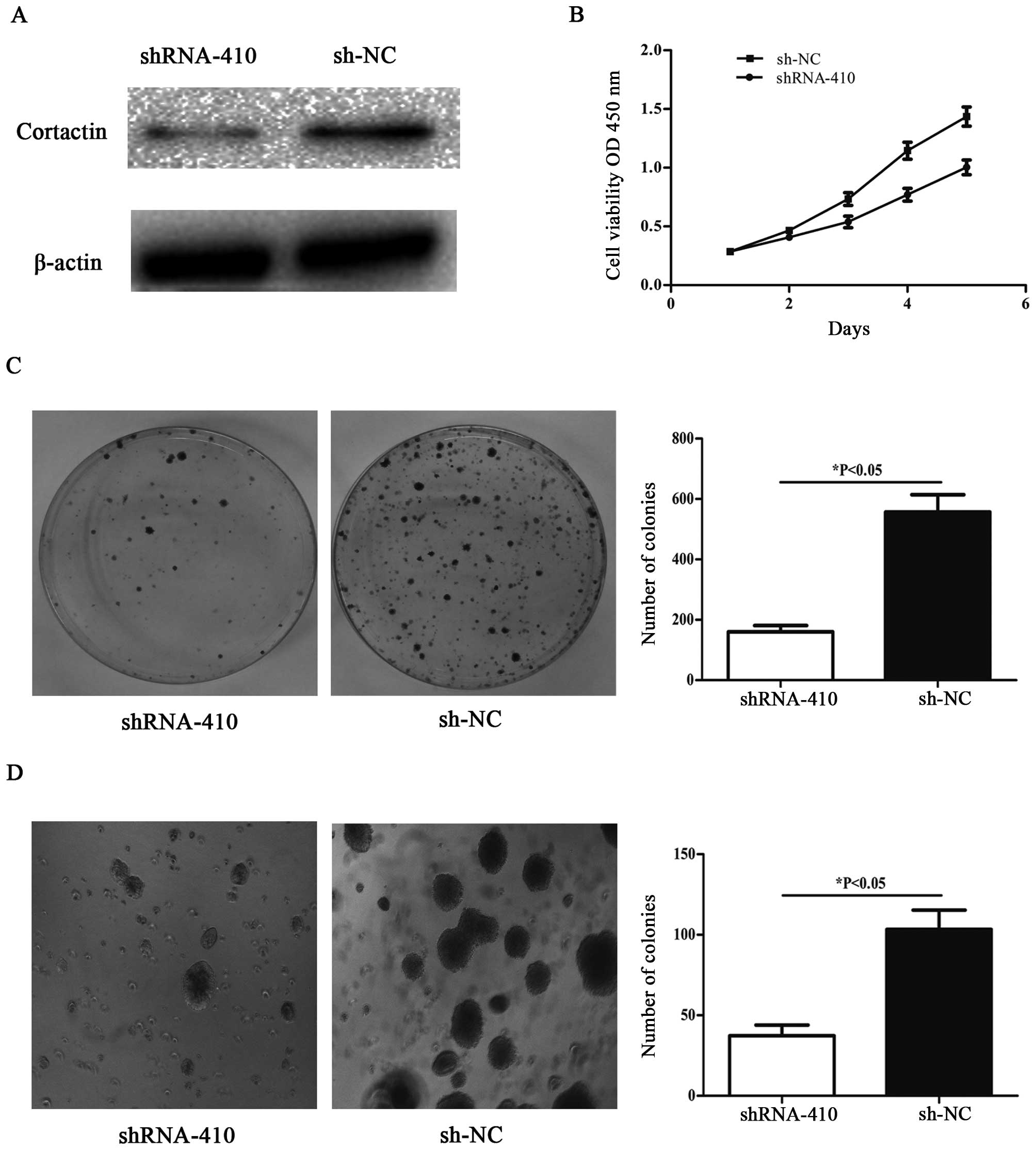
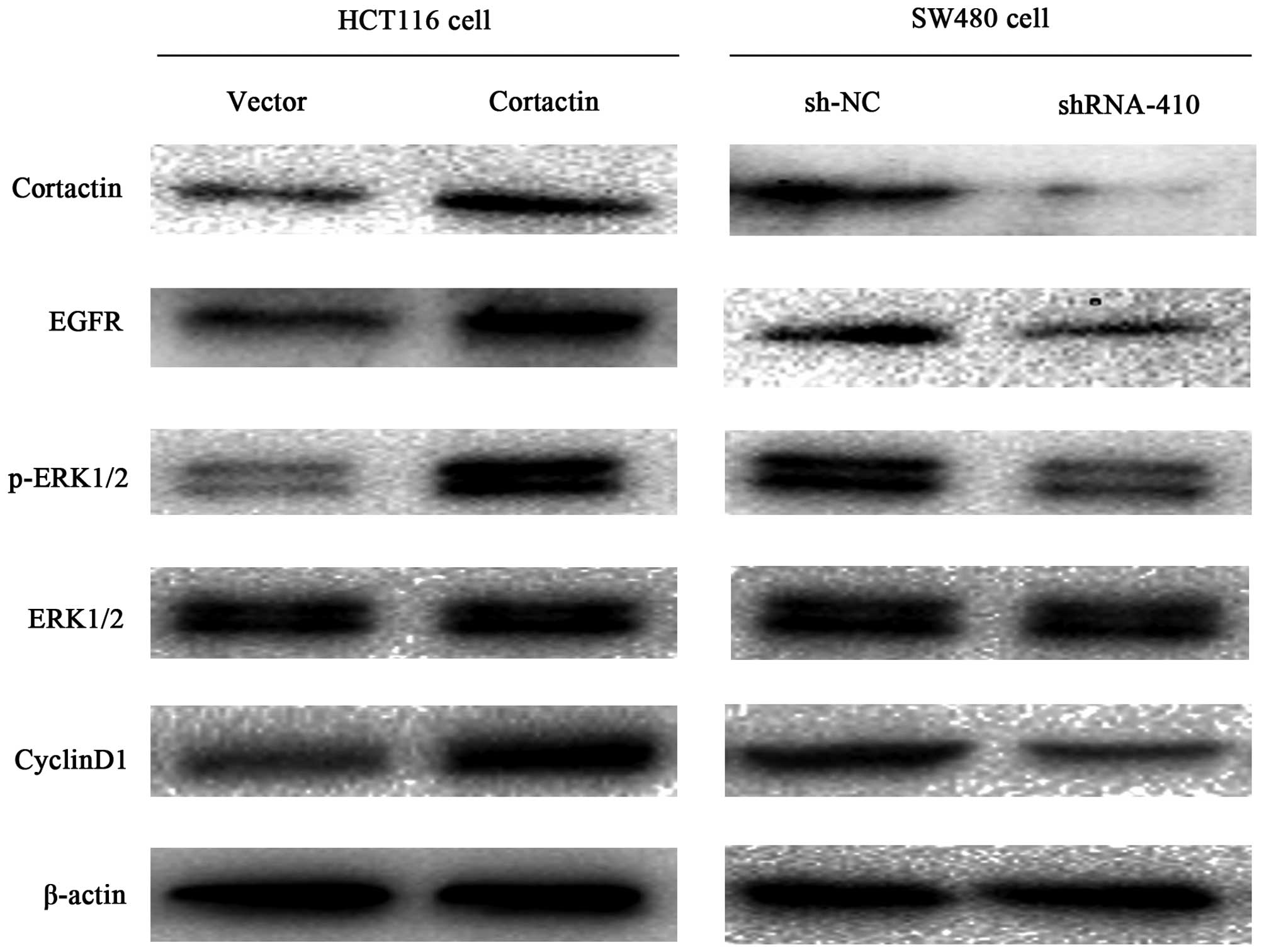
|
1
|
Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D,
Mathers C and Parkin DM: Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in
2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 127:2893–2917. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Fan NJ, Kang R, Ge XY, Li M, Liu Y, Chen
HM and Gao CF: Identification alpha-2-HS-glycoprotein precursor and
tubulin beta chain as serology diagnosis biomarker of colorectal
cancer. Diagn Pathol. 9:532014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Thomson DMP, Krupey J, Freedman SO and
Gold P: The radio-immunoassay of circulating carcinoembryonic
antigen of the human digestive system. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
64:161–167. 1969. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Duffy MJ: Role of tumor markers in
patients with solid cancers: A critical review. Eur J Intern Med.
18:175–184. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Roulston JE: Limitations of tumour markers
in screening. Br J Surg. 77:961–962. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bagaria B, Sood S, Sharma R and Lalwani S:
Comparative study of CEA and CA19-9 in esophageal, gastric and
colon cancers individually and in combination (ROC curve analysis).
Cancer Biol Med. 10:148–157. 2013.
|
|
7
|
Tan E, Gouvas N, Nicholls RJ, Ziprin P,
Xynos E and Tekkis PP: Diagnostic precision of carcinoembryonic
antigen in the detection of recurrence of colorectal cancer. Surg
Oncol. 18:15–24. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Flamini E, Mercatali L, Nanni O, Calistri
D, Nunziatini R, Zoli W, Rosetti P, Gardini N, Lattuneddu A,
Verdecchia GM, et al: Free DNA and carcinoembryonic antigen serum
levels: An important combination for diagnosis of colorectal
cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 12:6985–6988. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wu H, Reynolds AB, Kanner SB, Vines RR and
Parsons JT: Identification and characterization of a novel
cytoskeleton-associated pp60src substrate. Mol Cell Biol.
11:5113–5124. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wu H and Parsons JT: Cortactin, an
80/85-kilodalton pp60src substrate, is a filamentous actin-binding
protein enriched in the cell cortex. J Cell Biol. 120:1417–1426.
1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Weed SA and Parsons JT: Cortactin:
Coupling membrane dynamics to cortical actin assembly. Oncogene.
20:6418–6434. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bringuier PP, Tamimi Y, Schuuring E and
Schalken J: Expression of cyclin D1 and EMS1 in bladder tumours;
relationship with chromosome 11q13 amplification. Oncogene.
12:1747–1753. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yuan BZ, Zhou X, Zimonjic DB, Durkin ME
and Popescu NC: Amplification and overexpression of the EMS 1
oncogene, a possible prognostic marker, in human hepatocellular
carcinoma. J Mol Diagn. 5:48–53. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Rothschild BL, Shim AH, Ammer AG, Kelley
LC, Irby KB, Head JA, Chen L, Varella-Garcia M, Sacks PG, Frederick
B, et al: Cortactin overexpression regulates actin-related protein
2/3 complex activity, motility, and invasion in carcinomas with
chromosome 11q13 amplification. Cancer Res. 66:8017–8025. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hofman P, Butori C, Havet K, Hofman V,
Selva E, Guevara N, Santini J and Van Obberghen-Schilling E:
Prognostic significance of cortactin levels in head and neck
squamous cell carcinoma: Comparison with epidermal growth factor
receptor status. Br J Cancer. 98:956–964. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Clark ES, Whigham AS, Yarbrough WG and
Weaver AM: Cortactin is an essential regulator of matrix
metalloproteinase secretion and extracellular matrix degradation in
invadopodia. Cancer Res. 67:4227–4235. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wei J, Zhao Z-X, Li Y, Zhou Z-Q and You
T-G: Cortactin expression confers a more malignant phenotype to
gastric cancer SGC-7901 cells. World J Gastroenterol. 20:3287–3300.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhang YY, Chen B and Ding YQ:
Metastasis-associated factors facilitating the progression of
colorectal cancer. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 13:2437–2444. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Daly RJ: Cortactin signalling and dynamic
actin networks. Biochem J. 382:13–25. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
McNiven MA, Kim L, Krueger EW, Orth JD,
Cao H and Wong TW: Regulated interactions between dynamin and the
actin-binding protein cortactin modulate cell shape. J Cell Biol.
151:187–198. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Cao H, Orth JD, Chen J, Weller SG, Heuser
JE and McNiven MA: Cortactin is a component of clathrin-coated pits
and participates in receptor-mediated endocytosis. Mol Cell Biol.
23:2162–2170. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Engqvist-Goldstein AE, Zhang CX, Carreno
S, Barroso C, Heuser JE and Drubin DG: RNAi-mediated Hip1R
silencing results in stable association between the endocytic
machinery and the actin assembly machinery. Mol Biol Cell.
15:1666–1679. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hui R, Campbell DH, Lee CS, McCaul K,
Horsfall DJ, Musgrove EA, Daly RJ, Seshadri R and Sutherland RL:
EMS1 amplification can occur independently of CCND1 or INT-2
amplification at 11q13 and may identify different phenotypes in
primary breast cancer. Oncogene. 15:1617–1623. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Rodrigo JP, García LA, Ramos S, Lazo PS
and Suárez C: EMS1 gene amplification correlates with poor
prognosis in squamous cell carcinomas of the head and neck. Clin
Cancer Res. 6:3177–3182. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Patel AS, Schechter GL, Wasilenko WJ and
Somers KD: Overexpression of EMS1/cortactin in NIH3T3 fibroblasts
causes increased cell motility and invasion in vitro. Oncogene.
16:3227–3232. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Huang C, Liu J, Haudenschild CC and Zhan
X: The role of tyrosine phosphorylation of cortactin in the
locomotion of endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 273:25770–25776.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Li Y, Tondravi M, Liu J, Smith E,
Haudenschild CC, Kaczmarek M and Zhan X: Cortactin potentiates bone
metastasis of breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 61:6906–6911.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Clauditz TS, Gontarewicz A, Lebok P,
Tsourlakis MC, Grob TJ, Münscher A, Sauter G, Bokemeyer C, Knecht R
and Wilczak W: Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) in salivary
gland carcinomas: Potentials as therapeutic target. Oral Oncol.
48:991–996. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Gazdar AF: Epidermal growth factor
receptor inhibition in lung cancer: The evolving role of
individualized therapy. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 29:37–48. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Pirker R, Pereira JR, von Pawel J,
Krzakowski M, Ramlau R, Park K, de Marinis F, Eberhardt WE,
Paz-Ares L, Störkel S, et al: EGFR expression as a predictor of
survival for first-line chemotherapy plus cetuximab in patients
with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: Analysis of data from the
phase 3 FLEX study. Lancet Oncol. 13:33–42. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Harder J, Waiz O, Otto F, Geissler M,
Olschewski M, Weinhold B, Blum HE, Schmitt-Graeff A and Opitz OG:
EGFR and HER2 expression in advanced biliary tract cancer. World J
Gastroenterol. 15:4511–4517. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Galizia G, Lieto E, Orditura M, Castellano
P, Mura AL, Imperatore V, Pinto M, Zamboli A, De Vita F and
Ferraraccio F: Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) expression
is associated with a worse prognosis in gastric cancer patients
undergoing curative surgery. World J Surg. 31:1458–1468. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Sebolt-Leopold JS and Herrera R: Targeting
the mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade to treat cancer. Nat
Rev Cancer. 4:937–947. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hoshino R, Chatani Y, Yamori T, Tsuruo T,
Oka H, Yoshida O, Shimada Y, Ari-i S, Wada H, Fujimoto J, et al:
Constitutive activation of the 41-/43-kDa mitogen-activated protein
kinase signaling pathway in human tumors. Oncogene. 18:813–822.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Amundadottir LT and Leder P: Signal
transduction pathways activated and required for mammary
carcinogenesis in response to specific oncogenes. Oncogene.
16:737–746. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Alessi DR, Cuenda A, Cohen P, Dudley DT
and Saltiel AR: PD 098059 is a specific inhibitor of the activation
of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase in vitro and in vivo. J
Biol Chem. 270:27489–27494. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|