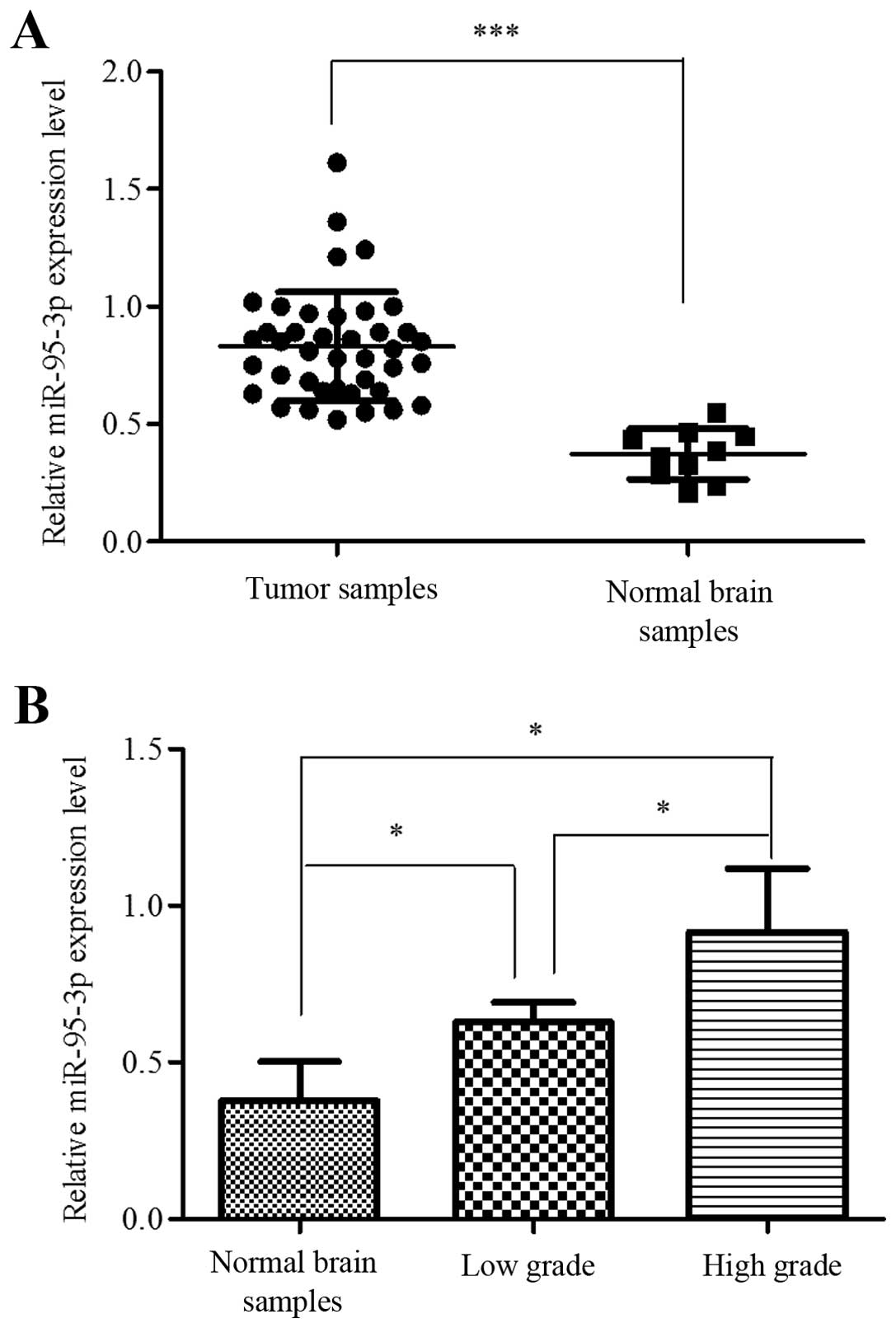
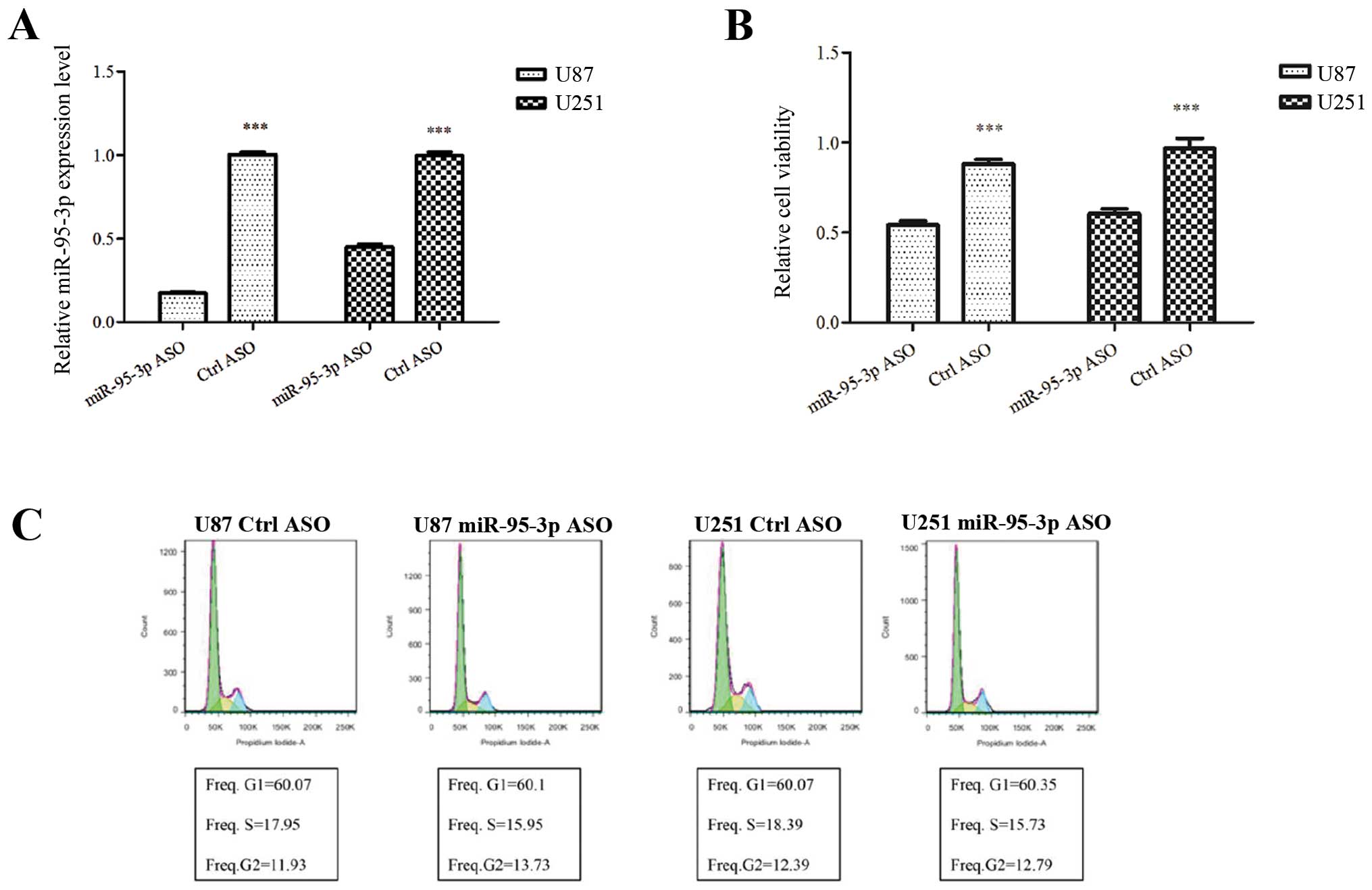
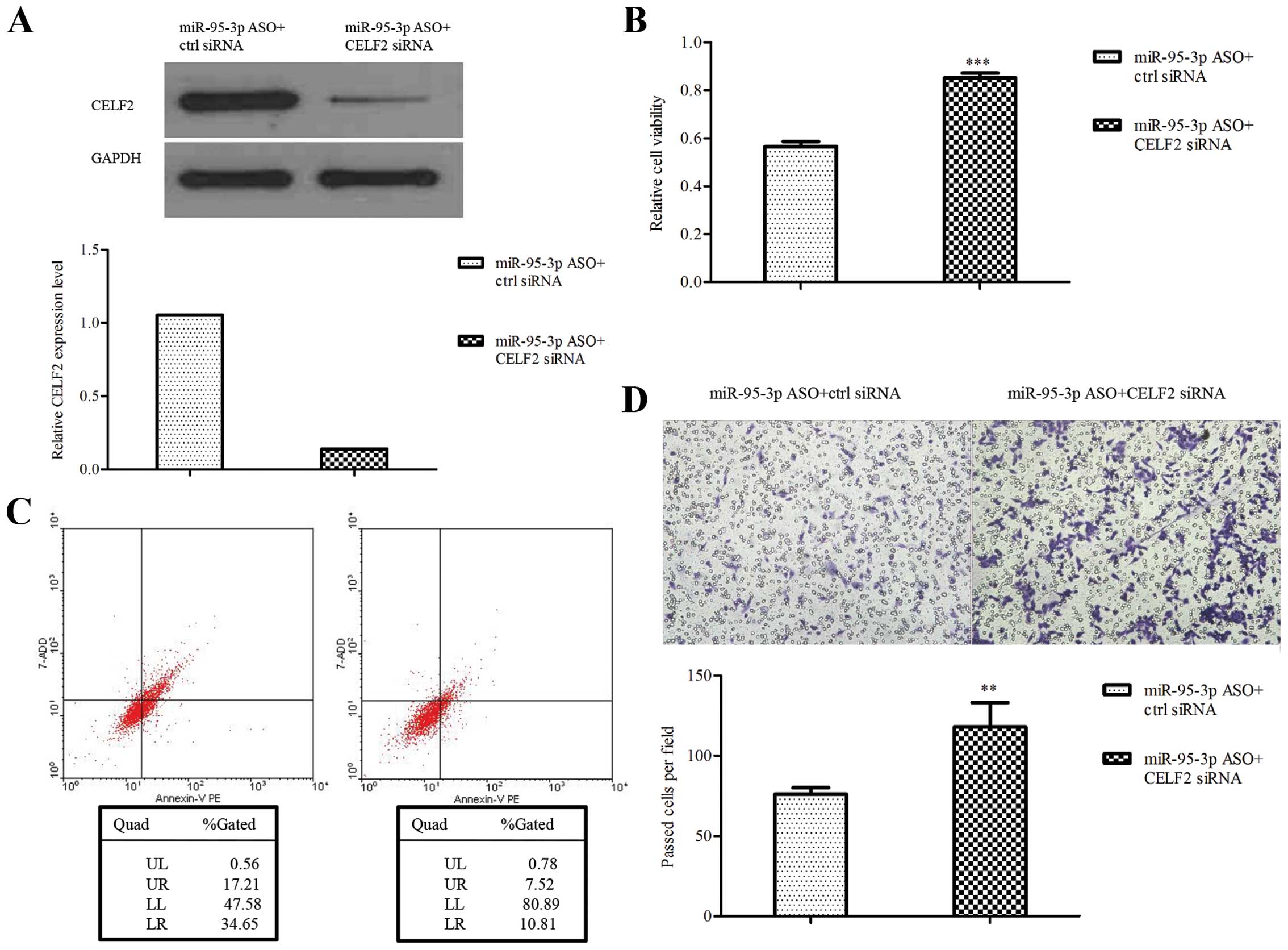
|
1
|
Giese A, Bjerkvig R, Berens ME and
Westphal M: Cost of migration: Invasion of malignant gliomas and
implications for treatment. J Clin Oncol. 21:1624–1636. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lefranc F, Brotchi J and Kiss R: Possible
future issues in the treatment of glioblastomas: Special emphasis
on cell migration and the resistance of migrating glioblastoma
cells to apoptosis. J Clin Oncol. 23:2411–2422. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Singh SK, Clarke ID, Hide T and Dirks PB:
Cancer stem cells in nervous system tumors. Oncogene. 23:7267–7273.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Furnari FB, Fenton T, Bachoo RM, Mukasa A,
Stommel JM, Stegh A, Hahn WC, Ligon KL, Louis DN, Brennan C, et al:
Malignant astrocytic glioma: Genetics, biology, and paths to
treatment. Genes Dev. 21:2683–2710. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Eulalio A, Huntzinger E and Izaurralde E:
Getting to the root of miRNA-mediated gene silencing. Cell.
132:9–14. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Carthew RW: Gene regulation by microRNAs.
Curr Opin Genet Dev. 16:203–208. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhang B, Pan X, Cobb GP and Anderson TA:
microRNAs as oncogenes and tumor suppressors. Dev Biol. 302:1–12.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Lujambio A and Lowe SW: The microcosmos of
cancer. Nature. 482:347–355. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bagnoli M, De Cecco L, Granata A,
Nicoletti R, Marchesi E, Alberti P, Valeri B, Libra M, Barbareschi
M, Raspagliesi F, et al: Identification of a chrXq27.3 microRNA
cluster associated with early relapse in advanced stage ovarian
cancer patients. Oncotarget. 2:1265–1278. 2011.
|
|
11
|
Iorio MV and Croce CM: microRNA
involvement in human cancer. Carcinogenesis. 33:1126–1133. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Godlewski J, Nowicki MO, Bronisz A, Nuovo
G, Palatini J, De Lay M, Van Brocklyn J, Ostrowski MC, Chiocca EA
and Lawler SE: MicroRNA-451 regulates LKB1/AMPK signaling and
allows adaptation to metabolic stress in glioma cells. Mol Cell.
37:620–632. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Gabriely G, Yi M, Narayan RS, Niers JM,
Wurdinger T, Imitola J, Ligon KL, Kesari S, Esau C, Stephens RM, et
al: Human glioma growth is controlled by microRNA-10b. Cancer Res.
71:3563–3572. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Li Y, Guessous F, Zhang Y, Dipierro C,
Kefas B, Johnson E, Marcinkiewicz L, Jiang J, Yang Y, Schmittgen
TD, et al: MicroRNA-34a inhibits glioblastoma growth by targeting
multiple oncogenes. Cancer Res. 69:7569–7576. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chan JA, Krichevsky AM and Kosik KS:
MicroRNA-21 is an antiapoptotic factor in human glioblastoma cells.
Cancer Res. 65:6029–6033. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ciafrè SA, Galardi S, Mangiola A, Ferracin
M, Liu CG, Sabatino G, Negrini M, Maira G, Croce CM and Farace MG:
Extensive modulation of a set of microRNAs in primary glioblastoma.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 334:1351–1358. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhou J, Wang W, Gao Z, Peng X, Chen X,
Chen W, Xu W, Xu H, Lin MC and Jiang S: MicroRNA-155 promotes
glioma cell proliferation via the regulation of MXI1. PLoS One.
8:e830552013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
18
|
Godlewski J, Nowicki MO, Bronisz A,
Williams S, Otsuki A, Nuovo G, Raychaudhury A, Newton HB, Chiocca
EA and Lawler S: Targeting of the Bmi-1 oncogene/stem cell renewal
factor by microRNA-128 inhibits glioma proliferation and
self-renewal. Cancer Res. 68:9125–9130. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Silber J, Lim DA, Petritsch C, Persson AI,
Maunakea AK, Yu M, Vandenberg SR, Ginzinger DG, James CD, Costello
JF, et al: miR-124 and miR-137 inhibit proliferation of
glioblastoma multiforme cells and induce differentiation of brain
tumor stem cells. BMC Med. 6:142008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Bier A, Giladi N, Kronfeld N, Lee HK,
Cazacu S, Finniss S, Xiang C, Poisson L, deCarvalho AC, Slavin S,
et al: MicroRNA-137 is downregulated in glioblastoma and inhibits
the stemness of glioma stem cells by targeting RTVP-1. Oncotarget.
4:665–676. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Skalsky RL and Cullen BR: Reduced
expression of brain-enriched microRNAs in glioblastomas permits
targeted regulation of a cell death gene. PLoS One. 6:e242482011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Huang Z, Huang S, Wang Q, Liang L, Ni S,
Wang L, Sheng W, He X and Du X: MicroRNA-95 promotes cell
proliferation and targets sorting Nexin 1 in human colorectal
carcinoma. Cancer Res. 71:2582–2589. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Huang X, Taeb S, Jahangiri S, Emmenegger
U, Tran E, Bruce J, Mesci A, Korpela E, Vesprini D, Wong CS, et al:
miRNA-95 mediates radioresistance in tumors by targeting the
sphingolipid phosphatase SGPP1. Cancer Res. 73:6972–6986. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhang Y, Li M, Wang H, Fisher WE, Lin PH,
Yao Q and Chen C: Profiling of 95 microRNAs in pancreatic cancer
cell lines and surgical specimens by real-time PCR analysis. World
J Surg. 33:698–709. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Xiao Z, Ching Chow S, Han Li C, Chun Tang
S, Tsui SK, Lin Z and Chen Y: Role of microRNA-95 in the anticancer
activity of Brucein D in hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur J Pharmacol.
728:141–150. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Nurul-Syakima AM, Yoke-Kqueen C, Sabariah
AR, Shiran MS, Singh A and Learn-Han L: Differential microRNA
expression and identification of putative miRNA targets and
pathways in head and neck cancers. Int J Mol Med. 28:327–336.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Barreau C, Paillard L, Méreau A and
Osborne HB: Mammalian CELF/Bruno-like RNA-binding proteins:
Molecular characteristics and biological functions. Biochimie.
88:515–525. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Keene JD: RNA recognition by autoantigens
and autoantibodies. Mol Biol Rep. 23:173–181. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ladd AN and Cooper TA: Multiple domains
control the subcellular localization and activity of ETR-3, a
regulator of nuclear and cytoplasmic RNA processing events. J Cell
Sci. 117:3519–3529. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wang GS, Kearney DL, De Biasi M, Taffet G
and Cooper TA: Elevation of RNA-binding protein CUGBP1 is an early
event in an inducible heart-specific mouse model of myotonic
dystrophy. J Clin Invest. 117:2802–2811. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Choi DK, Ito T, Mitsui Y and Sakaki Y:
Fluorescent differential display analysis of gene expression in
apoptotic neuroblastoma cells. Gene. 223:21–31. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Pershouse MA, Stubblefield E, Hadi A,
Killary AM, Yung WK and Steck PA: Analysis of the functional role
of chromosome 10 loss in human glioblastomas. Cancer Res.
53:5043–5050. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ransom DT, Ritland SR, Moertel CA, Dahl
RJ, O'Fallon JR, Scheithauer BW, Kimmel DW, Kelly PJ, Olopade OI,
Diaz MO, et al: Correlation of cytogenetic analysis and loss of
heterozygosity studies in human diffuse astrocytomas and mixed
oligo-astrocytomas. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 5:357–374. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Subramaniam D, Natarajan G, Ramalingam S,
Ramachandran I, May R, Queimado L, Houchen CW and Anant S:
Translation inhibition during cell cycle arrest and apoptosis:
Mcl-1 is a novel target for RNA binding protein CUGBP2. Am J
Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 294:G1025–G1032. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Natarajan G, Ramalingam S, Ramachandran I,
May R, Queimado L, Houchen CW and Anant S: CUGBP2 down-regulation
by prostaglandin E2 protects colon cancer cells from
radiation-induced mitotic catastrophe. Am J Physiol Gastrointest
Liver Physiol. 294:G1235–G1244. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Subramaniam D, Ramalingam S, Linehan DC,
Dieckgraefe BK, Postier RG, Houchen CW, Jensen RA and Anant S: RNA
binding protein CUGBP2/CELF2 mediates curcumin-induced mitotic
catastrophe of pancreatic cancer cells. PLoS One. 6:e169582011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|