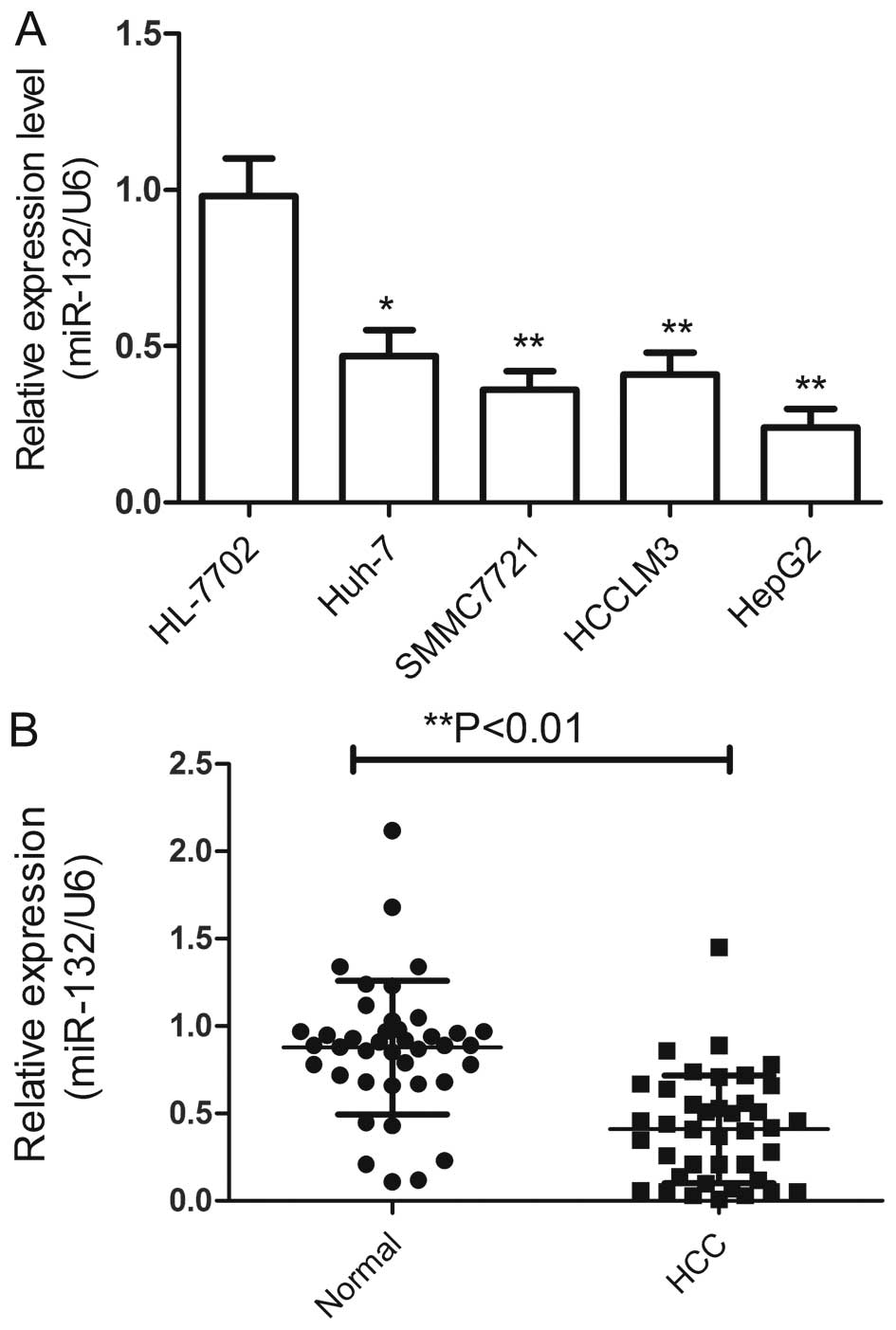
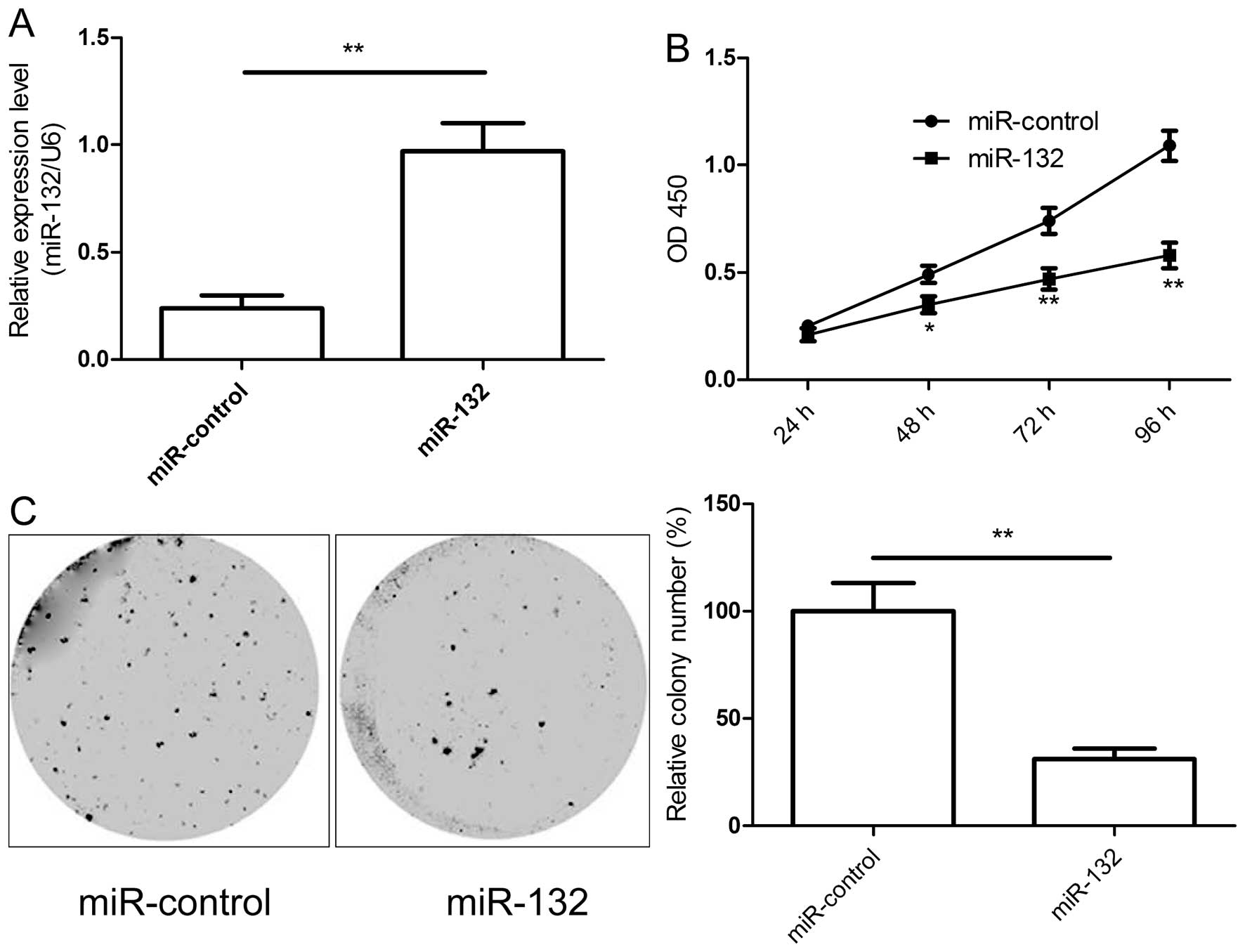
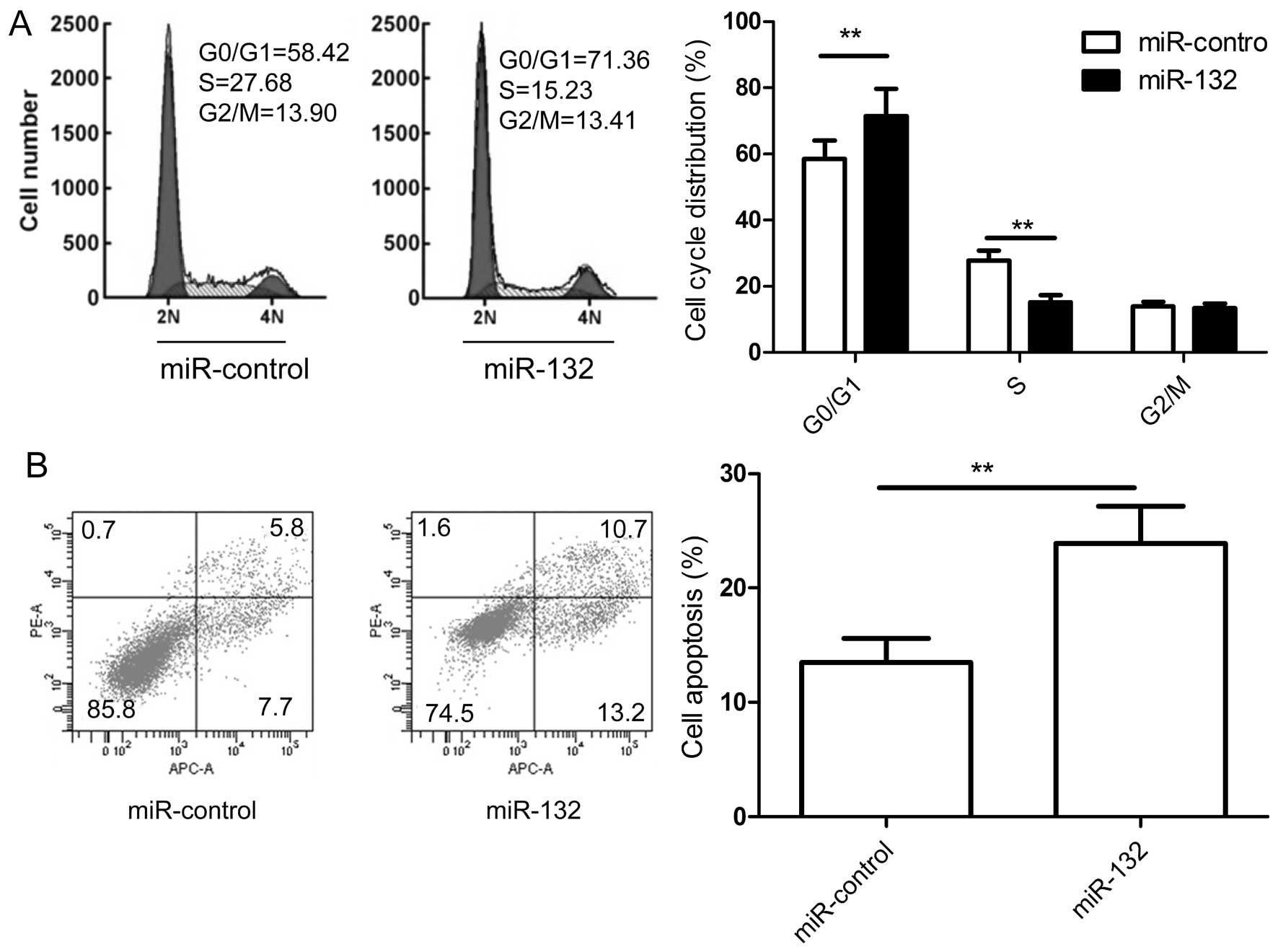
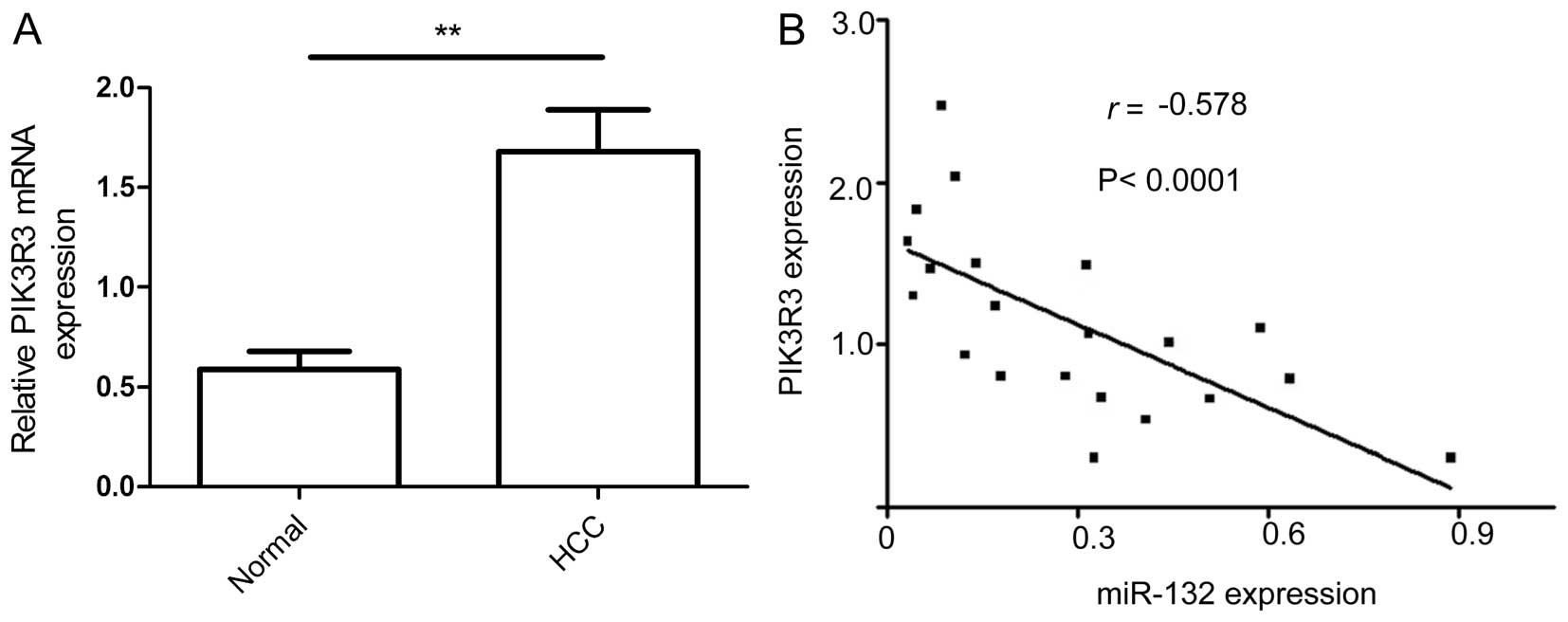
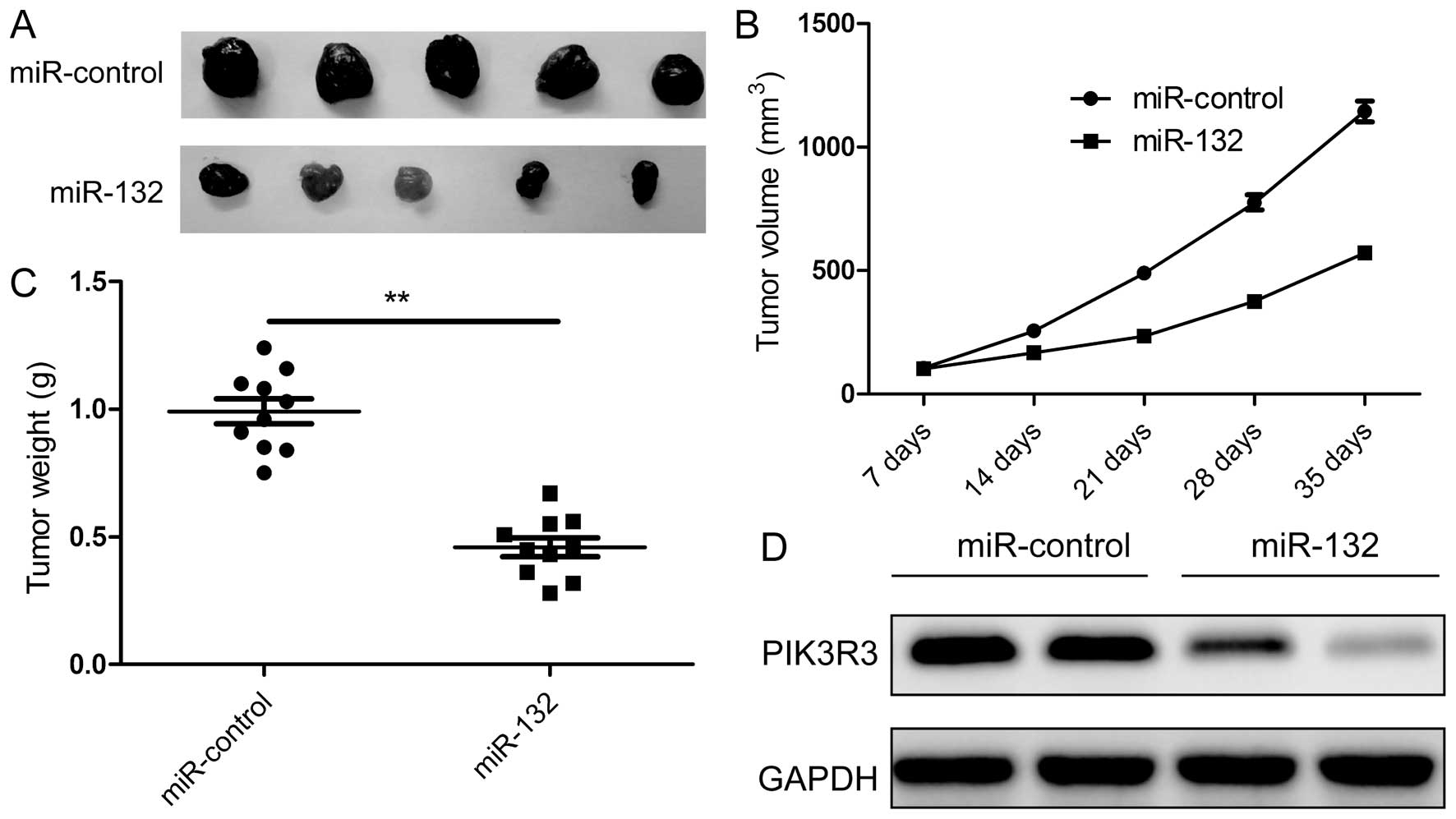
|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Livraghi T, Makisalo H and Line PD:
Treatment options in hepatocellular carcinoma today. Scand J Surg.
100:22–29. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Thorgeirsson SS and Grisham JW: Molecular
pathogenesis of human hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Genet.
31:339–346. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Malan-Müller S, Hemmings SM and Seedat S:
Big effects of small RNAs: A review of microRNAs in anxiety. Mol
Neurobiol. 47:726–739. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
6
|
Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, Alvarez-Saavedra
E, Lamb J, Peck D, Sweet-Cordero A, Ebert BL, Mak RH, Ferrando AA,
et al: MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature.
435:834–838. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Almeida MI, Reis RM and Calin GA: MicroRNA
history: Discovery, recent applications, and next frontiers. Mutat
Res. 717:1–8. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Calin GA and Croce CM: MicroRNA-cancer
connection: The beginning of a new tale. Cancer Res. 66:7390–7394.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Manikandan J, Aarthi JJ, Kumar SD and
Pushparaj PN: Oncomirs: The potential role of non-coding microRNAs
in understanding cancer. Bioinformation. 2:330–334. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Remenyi J, Hunter CJ, Cole C, Ando H,
Impey S, Monk CE, Martin KJ, Barton GJ, Hutvagner G and Arthur JS:
Regulation of the miR-212/132 locus by MSK1 and CREB in response to
neurotrophins. Biochem J. 428:281–291. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Volinia S, Calin GA, Liu CG, Ambs S,
Cimmino A, Petrocca F, Visone R, Iorio M, Roldo C, Ferracin M, et
al: A microRNA expression signature of human solid tumors defines
cancer gene targets. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:2257–2261. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wong TS, Liu XB, Wong BY, Ng RW, Yuen AP
and Wei WI: Mature miR-184 as potential oncogenic microRNA of
squamous cell carcinoma of tongue. Clin Cancer Res. 14:2588–2592.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Anand S, Majeti BK, Acevedo LM, Murphy EA,
Mukthavaram R, Scheppke L, Huang M, Shields DJ, Lindquist JN,
Lapinski PE, et al: MicroRNA-132-mediated loss of p120RasGAP
activates the endothelium to facilitate pathological angiogenesis.
Nat Med. 16:909–914. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Schetter AJ, Leung SY, Sohn JJ, Zanetti
KA, Bowman ED, Yanaihara N, Yuen ST, Chan TL, Kwong DL, Au GK, et
al: MicroRNA expression profiles associated with prognosis and
therapeutic outcome in colon adenocarcinoma. JAMA. 299:425–436.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yang L, Belaguli N and Berger DH: MicroRNA
and colorectal cancer. World J Surg. 33:638–646. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yang J, Gao T, Tang J, Cai H, Lin L and Fu
S: Loss of microRNA-132 predicts poor prognosis in patients with
primary osteosarcoma. Mol Cell Biochem. 381:9–15. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Formosa A, Lena AM, Markert EK, Cortelli
S, Miano R, Mauriello A, Croce N, Vandesompele J, Mestdagh P,
Finazzi-Agrò E, et al: DNA methylation silences miR-132 in prostate
cancer. Oncogene. 32:127–134. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
You J, Li Y, Fang N, Liu B, Zu L, Chang R,
Li X and Zhou Q: MiR-132 suppresses the migration and invasion of
lung cancer cells via targeting the EMT regulator ZEB2. PLoS One.
9:e918272014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chung YW, Bae HS, Song JY, Lee JK, Lee NW,
Kim T and Lee KW: Detection of microRNA as novel biomarkers of
epithelial ovarian cancer from the serum of ovarian cancer
patients. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 23:673–679. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Liu HB, Hua Y and Jin ZX: Effects of
MicroRNA-132 transfection on the proliferation and apoptosis of
human liver cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke
Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 37:30–36. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wei X, Tan C, Tang C, Ren G, Xiang T, Qiu
Z, Liu R and Wu Z: Epigenetic repression of miR-132 expression by
the hepatitis B virus x protein in hepatitis B virus-related
hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Signal. 25:1037–1043. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yu T, Li J, Yan M, Liu L, Lin H, Zhao F,
Sun L, Zhang Y, Cui Y, Zhang F, et al: MicroRNA-193a-3p and -5p
suppress the metastasis of human non-small-cell lung cancer by
downregulating the ERBB4/PIK3R3/mTOR/S6K2 signaling pathway.
Oncogene. 34:413–423. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Cao G, Dong W, Meng X, Liu H, Liao H and
Liu S: MiR-511 inhibits growth and metastasis of human
hepatocellular carcinoma cells by targeting PIK3R3. Tumour Biol.
Jan 22–2015.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Liu K, Liu S, Zhang W, Ji B, Wang Y and
Liu Y: miR-222 regulates sorafenib resistance and enhance
tumorigenicity in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Oncol.
45:1537–1546. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Fang F, Chang RM, Yu L, Lei X, Xiao S,
Yang H and Yang LY: MicroRNA-188-5p suppresses tumor cell
proliferation and metastasis by directly targeting FGF5 in
hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. S0168-8278 (15)00331-1. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Ma N, Chen F, Shen SL, Chen W, Chen LZ, Su
Q, Zhang LJ, Bi J, Zeng WT, Li W, et al: MicroRNA-129-5p inhibits
hepatocellular carcinoma cell metastasis and invasion via targeting
ETS1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 461:618–623. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Jiang G, Cui Y, Yu X, Wu Z, Ding G and Cao
L: miR-211 suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma by downregulating
SATB2. Oncotarget. 6:9457–9466. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Nudelman AS, DiRocco DP, Lambert TJ,
Garelick MG, Le J, Nathanson NM and Storm DR: Neuronal activity
rapidly induces transcription of the CREB-regulated microRNA-132,
in vivo. Hippocampus. 20:492–498. 2010.
|
|
29
|
Li S, Meng H, Zhou F, Zhai L, Zhang L, Gu
F, Fan Y, Lang R, Fu L, Gu L, et al: MicroRNA-132 is frequently
down-regulated in ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) of breast and
acts as a tumor suppressor by inhibiting cell proliferation. Pathol
Res Pract. 209:179–183. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Gramantieri L, Ferracin M, Fornari F,
Veronese A, Sabbioni S, Liu CG, Calin GA, Giovannini C, Ferrazzi E,
Grazi GL, et al: Cyclin G1 is a target of miR-122a, a microRNA
frequently down-regulated in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer
Res. 67:6092–6099. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Xia X, Cheng A, Akinmade D and Hamburger
AW: The N-terminal 24 amino acids of the p55 gamma regulatory
subunit of phosphoinositide 3-kinase binds Rb and induces cell
cycle arrest. Mol Cell Biol. 23:1717–1725. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wang G, Cao X, Lai S, Luo X, Feng Y, Xia
X, Yen PM, Gong J and Hu J: PI3K stimulates DNA synthesis and
cell-cycle progression via its p55PIK regulatory subunit
interaction with PCNA. Mol Cancer Ther. 12:2100–2109. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wang G, Chen C, Yang R, Cao X, Lai S, Luo
X, Feng Y, Xia X, Gong J and Hu J: p55PIK-PI3K stimulates
angiogenesis in colorectal cancer cell by activating NF-κB pathway.
Angiogenesis. 16:561–573. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhang L, Huang J, Yang N, Greshock J,
Liang S, Hasegawa K, Giannakakis A, Poulos N, O'Brien-Jenkins A,
Katsaros D, et al: Integrative genomic analysis of
phosphatidylinositol 3′-kinase family identifies PIK3R3 as a
potential therapeutic target in epithelial ovarian cancer. Clin
Cancer Res. 13:5314–5321. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Soroceanu L, Kharbanda S, Chen R, Soriano
RH, Aldape K, Misra A, Zha J, Forrest WF, Nigro JM, Modrusan Z, et
al: Identification of IGF2 signaling through
phosphoinositide-3-kinase regulatory subunit 3 as a
growth-promoting axis in glioblastoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
104:3466–3471. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Xu L, Wen Z, Zhou Y, Liu Z, Li Q, Fei G,
Luo J and Ren T: MicroRNA-7-regulated TLR9 signaling-enhanced
growth and metastatic potential of human lung cancer cells by
altering the phosphoinositide-3-kinase, regulatory subunit 3/Akt
pathway. Mol Biol Cell. 24:42–55. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
37
|
Wang G, Yang X, Li C, Cao X, Luo X and Hu
J: PIK3R3 induces epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and promotes
metastasis in colorectal cancer. Mol Cancer Ther. 13:1837–1847.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Klahan S, Wu MS, Hsi E, Huang CC, Hou MF
and Chang WC: Computational analysis of mRNA expression profiles
identifies the ITG family and PIK3R3 as crucial genes for
regulating triple negative breast cancer cell migration. BioMed Res
Int. 2014:5365912014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|