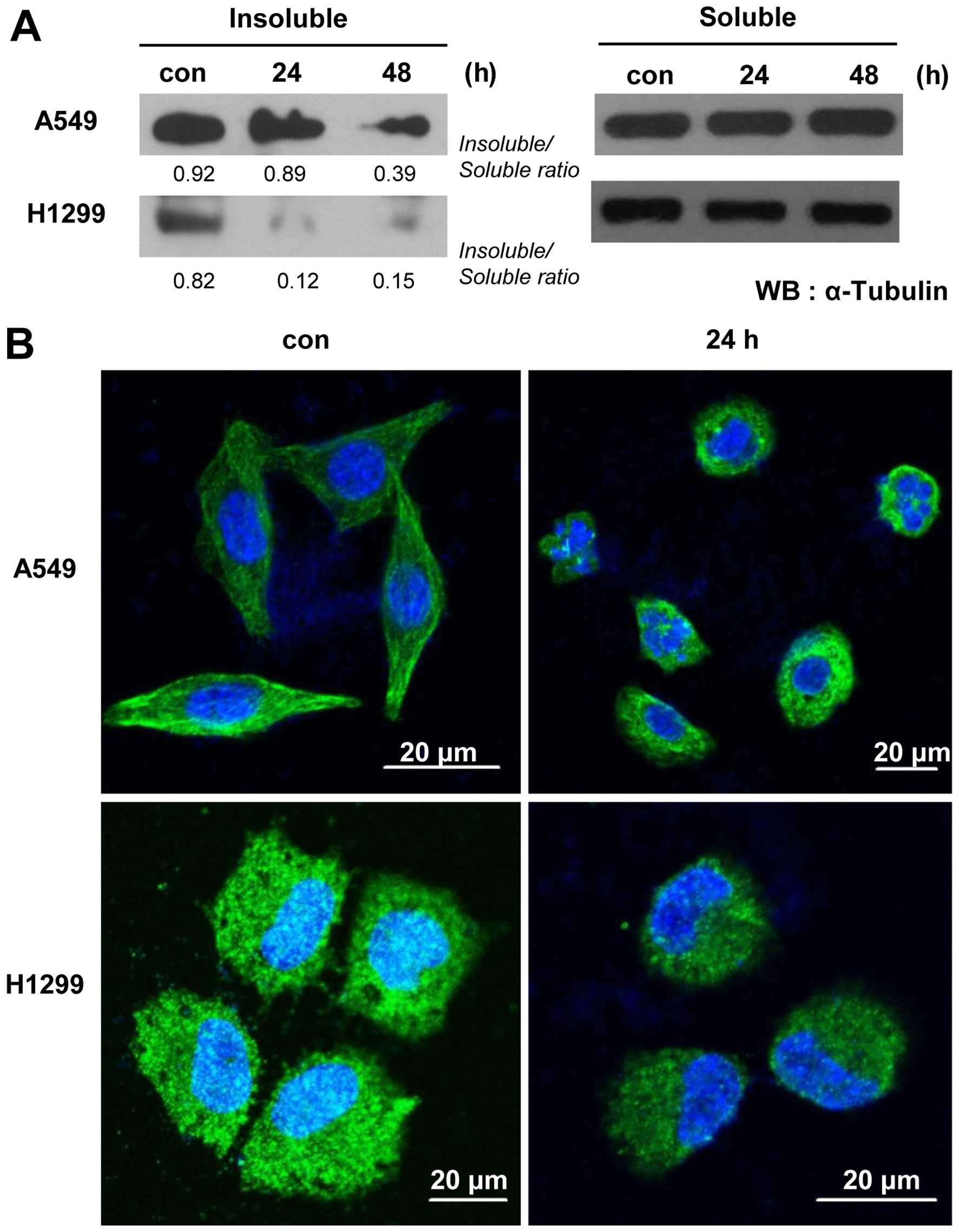
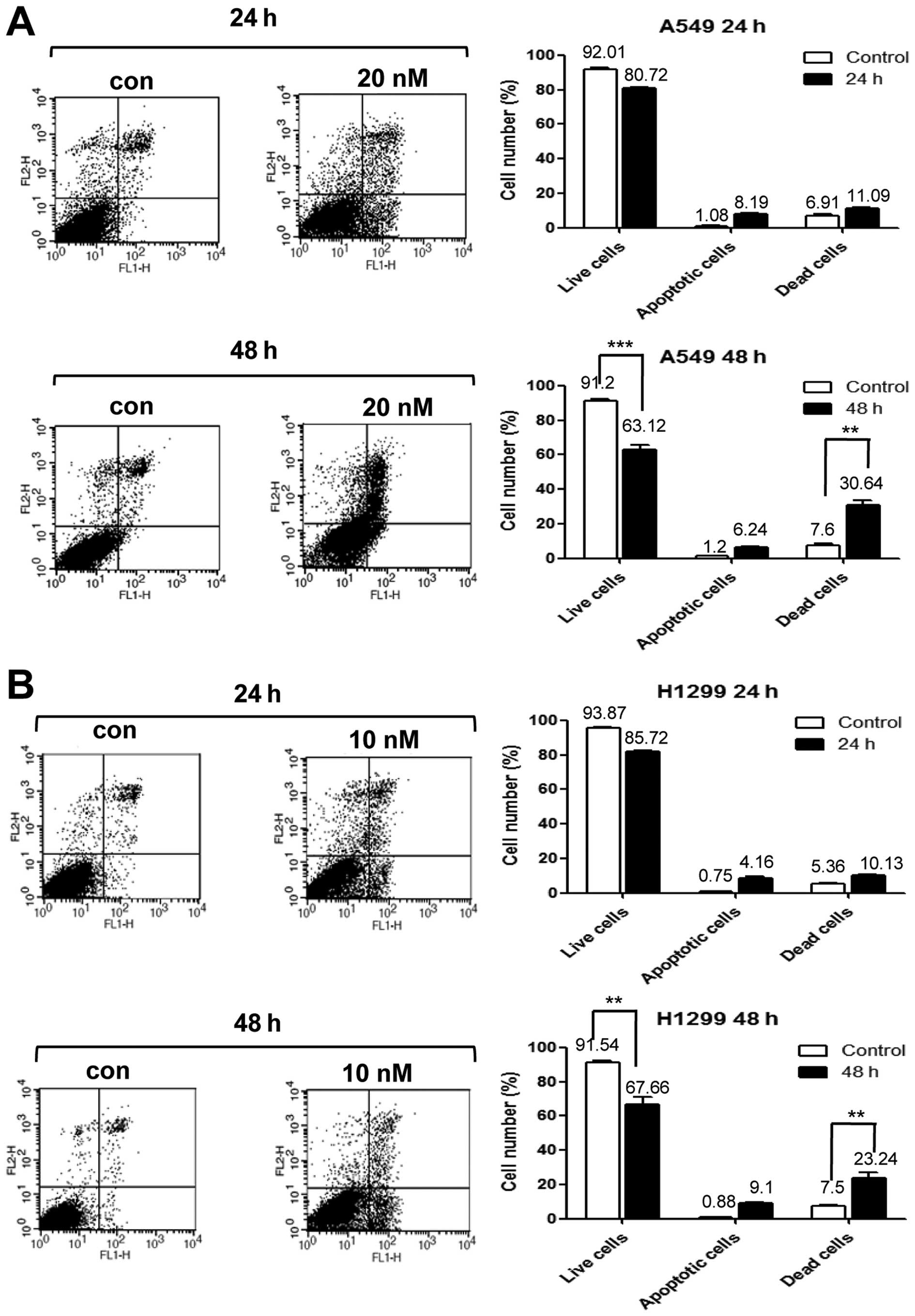
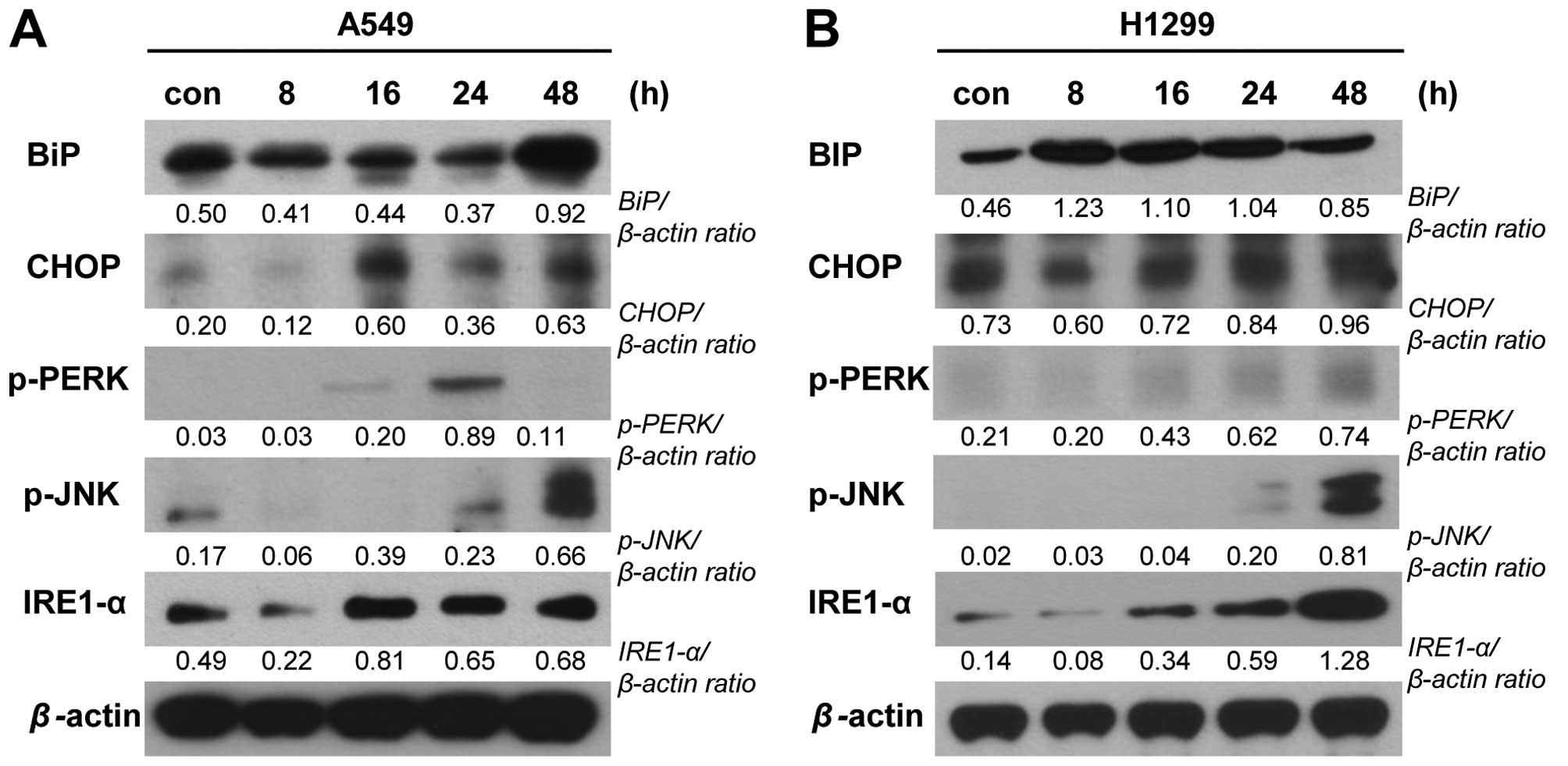
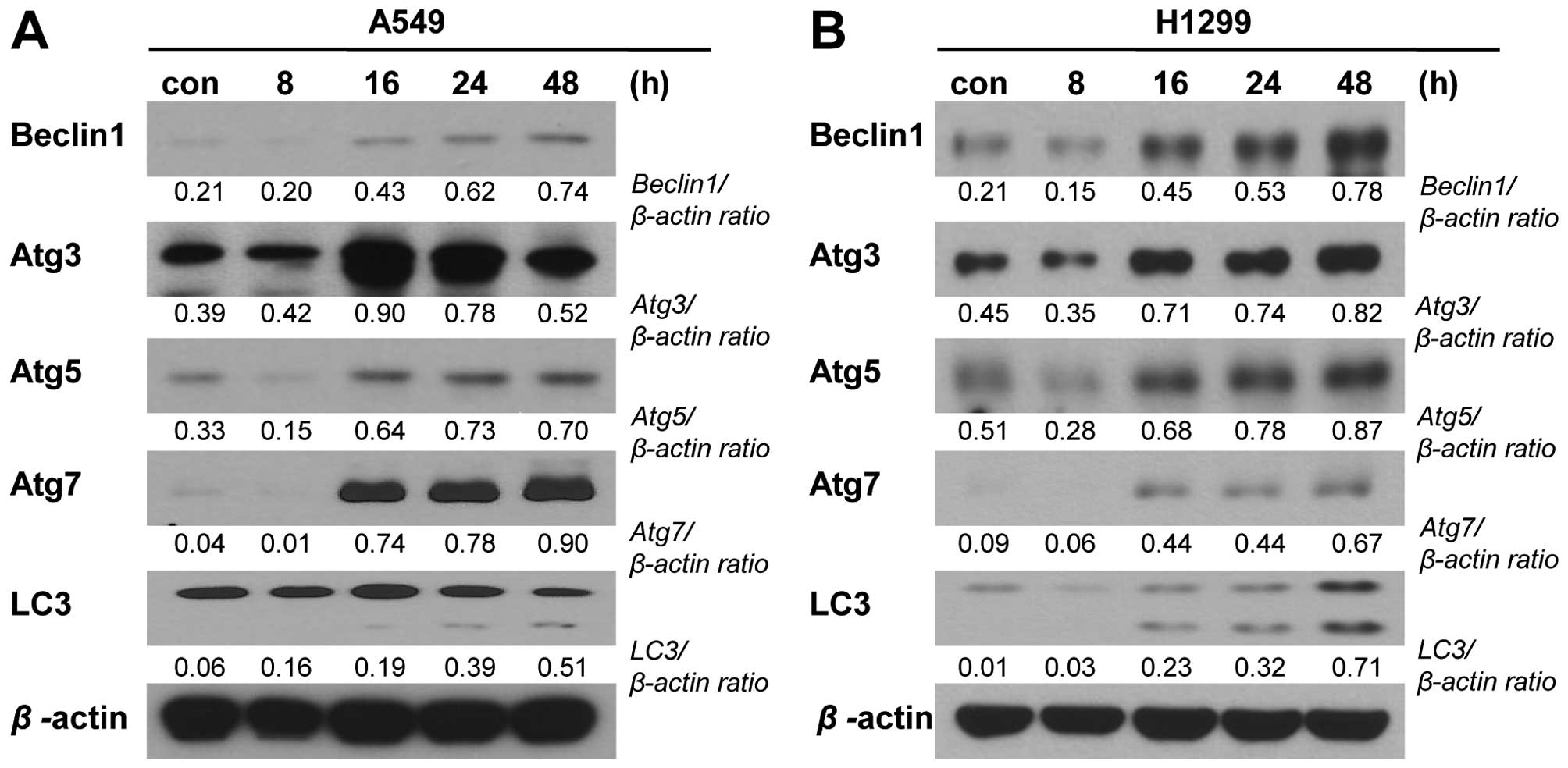
|
1
|
Cragg GM, Grothaus PG and Newman DJ:
Impact of natural products on developing new anti-cancer agents.
Chem Rev. 109:3012–3043. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Gordaliza M, García PA, del Corral JM,
Castro MA and Gómez-Zurita MA: Podophyllotoxin: Distribution,
sources, applications and new cytotoxic derivatives. Toxicon.
44:441–459. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Guerram M, Jiang Z-Z and Zhang L-Y:
Podophyllotoxin, a medicinal agent of plant origin: Past, present
and future. Chin J Nat Med. 10:161–169. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Choi JY, Cho HJ, Hwang SG, Kim WJ, Kim JI,
Um HD and Park JK: Podophyllotoxin acetate enhances γ-ionizing
radiation-induced apoptotic cell death by stimulating the
ROS/p38/caspase pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 70:111–118. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kuo CC, Hsieh HP, Pan WY, Chen CP, Liou
JP, Lee SJ, Chang YL, Chen LT, Chen CT and Chang JY: BPR0L075, a
novel synthetic indole compound with antimitotic activity in human
cancer cells, exerts effective antitumoral activity in vivo. Cancer
Res. 64:4621–4628. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Park JK, Jung HY, Park SH, Kang SY, Yi MR,
Um HD and Hong SH: Combination of PTEN and gamma-ionizing radiation
enhances cell death and G(2)/M arrest through regulation of AKT
activity and p21 induction in non-small-cell lung cancer cells. Int
J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 70:1552–1560. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J,
Murray T and Thun MJ: Cancer statistics, 2008. CA Cancer J Clin.
58:71–96. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Begg AC, Stewart FA and Vens C: Strategies
to improve radio-therapy with targeted drugs. Nat Rev Cancer.
11:239–253. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tsai CM, Chang KT, Perng RP, Mitsudomi T,
Chen MH, Kadoyama C and Gazdar AF: Correlation of intrinsic
chemoresistance of non-small-cell lung cancer cell lines with
HER-2/neu gene expression but not with ras gene mutations. J Natl
Cancer Inst. 85:897–901. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Xin Y, Yin F, Qi S, Shen L, Xu Y, Luo L,
Lan L and Yin Z: Parthenolide reverses doxorubicin resistance in
human lung carcinoma A549 cells by attenuating NF-κB activation and
HSP70 up-regulation. Toxicol Lett. 221:73–82. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Breen L, Heenan M, Amberger-Murphy V and
Clynes M: Investigation of the role of p53 in chemotherapy
resistance of lung cancer cell lines. Anticancer Res.
27A:1361–1364. 2007.
|
|
12
|
Jung IL, Kang HJ, Kim KC and Kim IG:
PTEN/pAkt/p53 signaling pathway correlates with the radioresponse
of non-small cell lung cancer. Int J Mol Med. 25:517–523.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Jordan MA and Wilson L: Microtubules as a
target for anticancer drugs. Nat Rev Cancer. 4:253–265. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Montecucco A and Biamonti G: Cellular
response to etoposide treatment. Cancer Lett. 252:9–18. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Kaufmann SH: Cell death induced by
topoisomerase-targeted drugs: More questions than answers. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1400:195–211. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Elmore S: Apoptosis: A review of
programmed cell death. Toxicol Pathol. 35:495–516. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bicknell AA, Babour A, Federovitch CM and
Niwa M: A novel role in cytokinesis reveals a housekeeping function
for the unfolded protein response. J Cell Biol. 177:1017–1027.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chen JY, Tang YA, Li WS, Chiou YC, Shieh
JM and Wang YC: A synthetic podophyllotoxin derivative exerts
anti-cancer effects by inducing mitotic arrest and pro-apoptotic ER
stress in lung cancer preclinical models. PLoS One. 8:e620822013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Schröder M and Kaufman RJ: ER stress and
the unfolded protein response. Mutat Res. 569:29–63. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Gills JJ, Lopiccolo J and Dennis PA:
Nelfinavir, a new anti-cancer drug with pleiotropic effects and
many paths to autophagy. Autophagy. 4:107–109. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Terés S, Lladó V, Higuera M,
Barceló-Coblijn G, Martin ML, Noguera-Salvà MA, Marcilla-Etxenike
A, García-Verdugo JM, Soriano-Navarro M, Saus C, et al:
2-Hydroxyoleate, a nontoxic membrane binding anticancer drug,
induces glioma cell differentiation and autophagy. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 109:8489–8494. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Galluzzi L, Pietrocola F, Levine B and
Kroemer G: Metabolic control of autophagy. Cell. 159:1263–1276.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yang ZJ, Chee CE, Huang S and Sinicrope
FA: The role of autophagy in cancer: Therapeutic implications. Mol
Cancer Ther. 10:1533–1541. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Klionsky DJ, Abdalla FC, Abeliovich H,
Abraham RT, Acevedo-Arozena A, Adeli K, Agholme L, Agnello M,
Agostinis P, Aguirre-Ghiso JA, et al: Guidelines for the use and
interpretation of assays for monitoring autophagy. Autophagy.
8:445–544. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yan CH, Yang YP, Qin ZH, Gu ZL, Reid P and
Liang ZQ: Autophagy is involved in cytotoxic effects of crotoxin in
human breast cancer cell line MCF-7 cells. Acta Pharmacol Sin.
28:540–548. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Abedin MJ, Wang D, McDonnell MA, Lehmann U
and Kelekar A: Autophagy delays apoptotic death in breast cancer
cells following DNA damage. Cell Death Differ. 14:500–510. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|