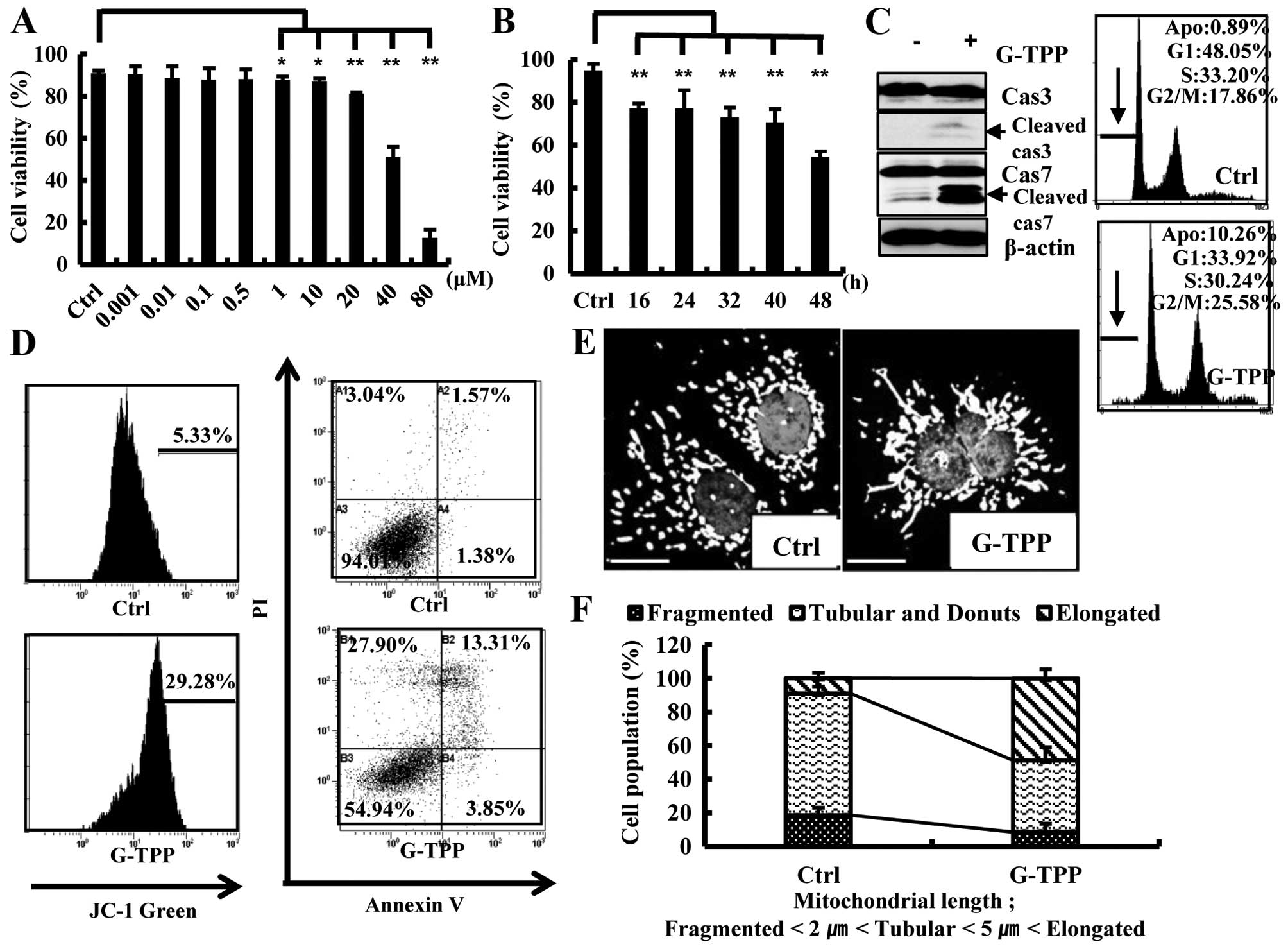
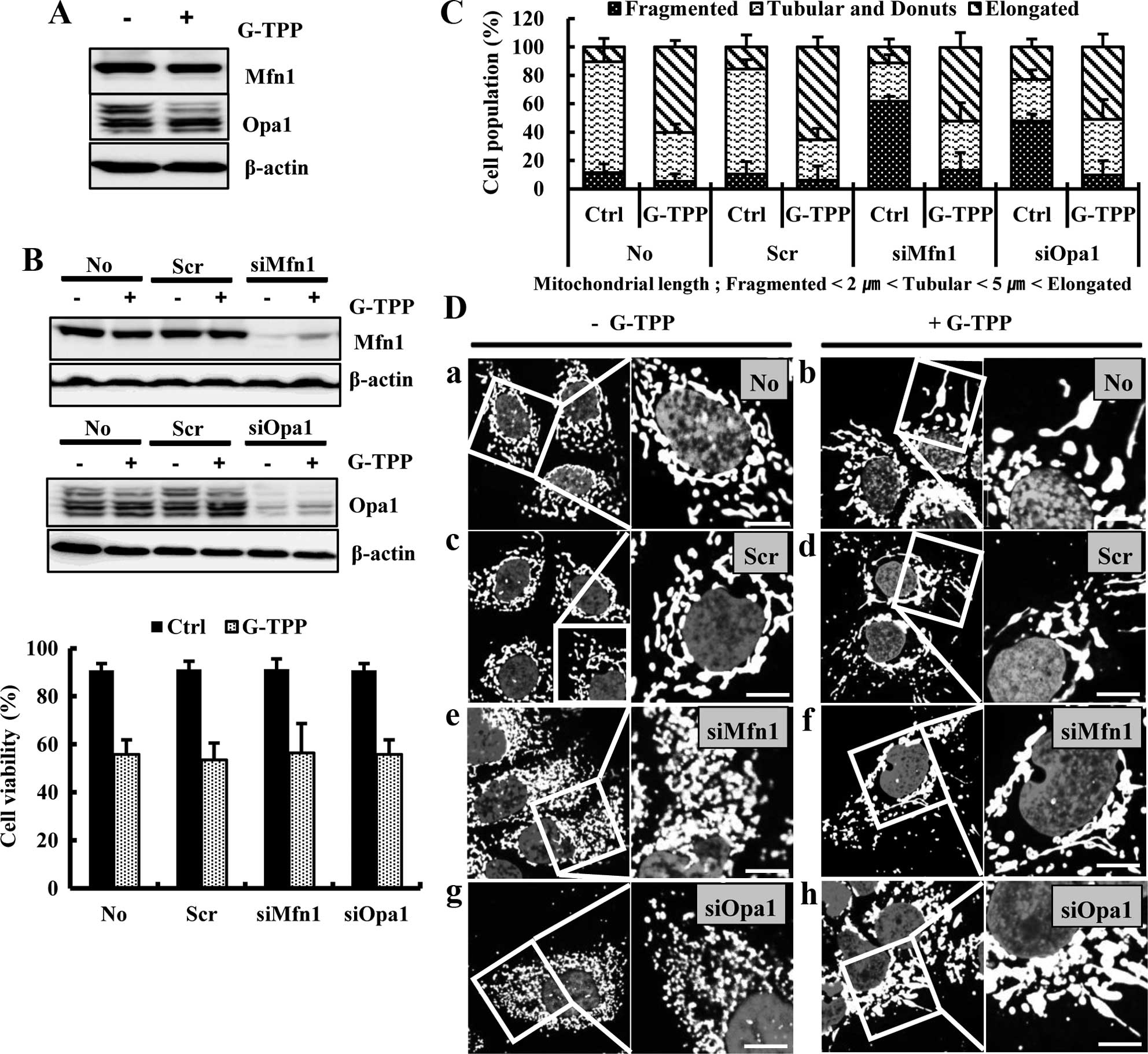
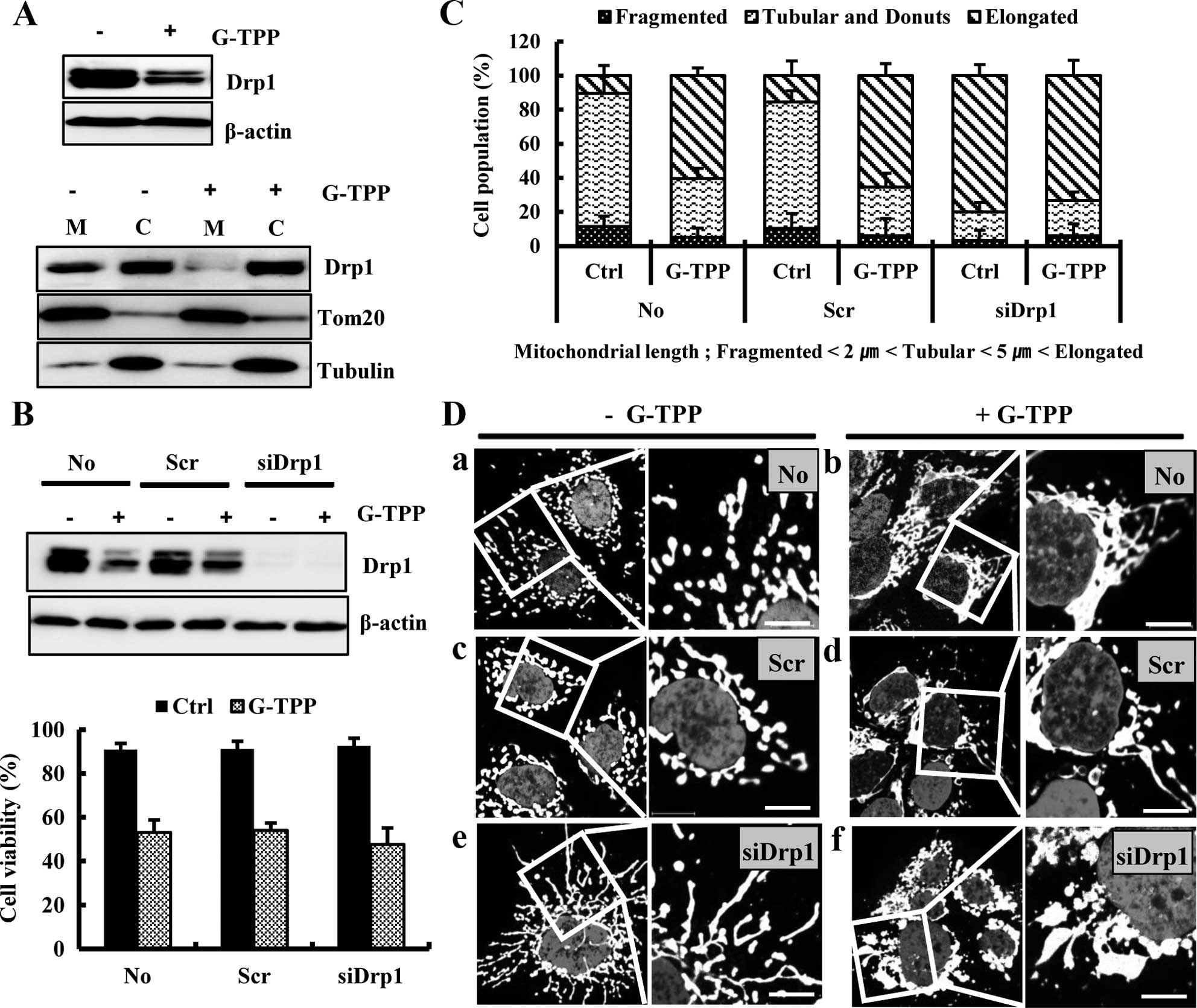
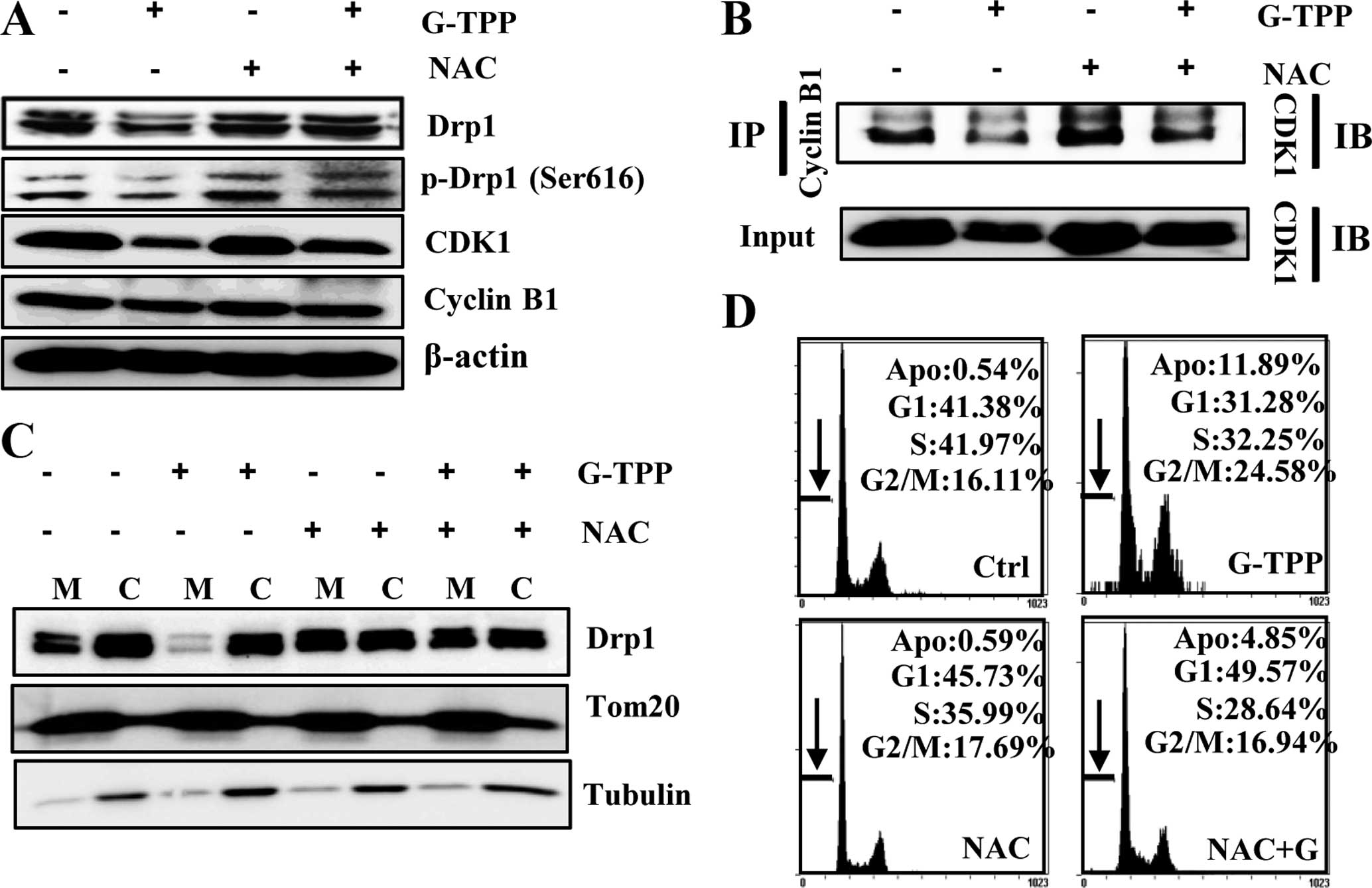
|
1
|
Campello S, Strappazzon F and Cecconi F:
Mitochondrial dismissal in mammals, from protein degradation to
mitophagy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1837:451–460. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Picard M, Shirihai OS, Gentil BJ and
Burelle Y: Mitochondrial morphology transitions and functions:
Implications for retrograde signaling? Am J Physiol Regul Integr
Comp Physiol. 304:R393–R406. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Harbauer AB, Zahedi RP, Sickmann A,
Pfanner N and Meisinger C: The protein import machinery of
mitochondria - a regulatory hub in metabolism, stress, and disease.
Cell Metab. 19:357–372. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Karbowski M and Youle RJ: Dynamics of
mitochondrial morphology in healthy cells and during apoptosis.
Cell Death Differ. 10:870–880. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Cerveny KL, Tamura Y, Zhang Z, Jensen RE
and Sesaki H: Regulation of mitochondrial fusion and division.
Trends Cell Biol. 17:563–569. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Benard G and Karbowski M: Mitochondrial
fusion and division: Regulation and role in cell viability. Semin
Cell Dev Biol. 20:365–374. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ishihara N, Fujita Y, Oka T and Mihara K:
Regulation of mitochondrial morphology through proteolytic cleavage
of OPA1. EMBO J. 25:2966–2977. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Smirnova E, Griparic L, Shurland DL and
van der Bliek AM: Dynamin-related protein Drp1 is required for
mitochondrial division in mammalian cells. Mol Biol Cell.
12:2245–2256. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Landes T and Martinou JC: Mitochondrial
outer membrane permeabilization during apoptosis: The role of
mitochondrial fission. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1813:540–545. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Otera H, Wang C, Cleland MM, Setoguchi K,
Yokota S, Youle RJ and Mihara K: Mff is an essential factor for
mitochondrial recruitment of Drp1 during mitochondrial fission in
mammalian cells. J Cell Biol. 191:1141–1158. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Twig G, Elorza A, Molina AJ, Mohamed H,
Wikstrom JD, Walzer G, Stiles L, Haigh SE, Katz S, Las G, et al:
Fission and selective fusion govern mitochondrial segregation and
elimination by autophagy. EMBO J. 27:433–446. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Eisenberg-Lerner A, Bialik S, Simon HU and
Kimchi A: Life and death partners: Apoptosis, autophagy and the
cross-talk between them. Cell Death Differ. 16:966–975. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang IH, Chen HY, Wang YH, Chang KW, Chen
YC and Chang CR: Resveratrol modulates mitochondria dynamics in
replicative senescent yeast cells. PLoS One. 9:e1043452014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Pinton P, Ferrari D, Rapizzi E, Di
Virgilio F, Pozzan T and Rizzuto R: The Ca2+
concentration of the endoplasmic reticulum is a key determinant of
ceramide-induced apoptosis: Significance for the molecular
mechanism of Bcl-2 action. EMBO J. 20:2690–2701. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Breckenridge DG, Stojanovic M, Marcellus
RC and Shore GC: Caspase cleavage product of BAP31 induces
mitochondrial fission through endoplasmic reticulum calcium
signals, enhancing cytochrome c release to the cytosol. J Cell
Biol. 160:1115–1127. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bai X, Yan Y, Canfield S, Muravyeva MY,
Kikuchi C, Zaja I, Corbett JA and Bosnjak ZJ: Ketamine enhances
human neural stem cell proliferation and induces neuronal apoptosis
via reactive oxygen species-mediated mitochondrial pathway. Anesth
Analg. 116:869–880. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Atay C, Ugurlu S and Ozören N: Shock the
heat shock network. J Clin Invest. 119:445–448. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kang BH, Plescia J, Song HY, Meli M,
Colombo G, Beebe K, Scroggins B, Neckers L and Altieri DC:
Combinatorial drug design targeting multiple cancer signaling
networks controlled by mitochondrial Hsp90. J Clin Invest.
119:454–464. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Mayer MP, Prodromou C and Frydman J: The
Hsp90 mosaic: A picture emerges. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 16:2–6. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yamano K and Youle RJ: Coupling
mitochondrial and cell division. Nat Cell Biol. 13:1026–1027. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Park HK, Lee JE, Lim J and Kang BH:
Mitochondrial Hsp90s suppress calcium-mediated stress signals
propagating from mitochondria to the ER in cancer cells. Mol
Cancer. 13:1482014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Siegelin MD, Dohi T, Raskett CM, Orlowski
GM, Powers CM, Gilbert CA, Ross AH, Plescia J and Altieri DC:
Exploiting the mitochondrial unfolded protein response for cancer
therapy in mice and human cells. J Clin Invest. 121:1349–1360.
2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Frank S, Gaume B, Bergmann-Leitner ES,
Leitner WW, Robert EG, Catez F, Smith CL and Youle RJ: The role of
dynamin-related protein 1, a mediator of mitochondrial fission, in
apoptosis. Dev Cell. 1:515–525. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lee JS, Yoon YG, Yoo SH, Jeong NY, Jeong
SH, Lee SY, Jung DI, Jeong SY and Yoo YH: Histone deacetylase
inhibitors induce mitochondrial elongation. J Cell Physiol.
227:2856–2869. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Abeliovich H: Mitophagy: The life-or-death
dichotomy includes yeast. Autophagy. 3:275–277. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Narendra D, Tanaka A, Suen DF and Youle
RJ: Parkin is recruited selectively to impaired mitochondria and
promotes their autophagy. J Cell Biol. 183:795–803. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Twig G and Shirihai OS: The interplay
between mitochondrial dynamics and mitophagy. Antioxid Redox
Signal. 14:1939–1951. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
28
|
Ni HM, Williams JA and Ding WX:
Mitochondrial dynamics and mitochondrial quality control. Redox
Biol. 4:6–13. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
29
|
Arnoult D, Rismanchi N, Grodet A, Roberts
RG, Seeburg DP, Estaquier J, Sheng M and Blackstone C:
Bax/Bak-dependent release of DDP/TIMM8a promotes Drp1-mediated
mitochondrial fission and mitoptosis during programmed cell death.
Curr Biol. 15:2112–2118. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Bernhardt D, Müller M, Reichert AS and
Osiewacz HD: Simultaneous impairment of mitochondrial fission and
fusion reduces mitophagy and shortens replicative lifespan. Sci
Rep. 5:78852015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Deng H, Dodson MW, Huang H and Guo M: The
Parkinson's disease genes pink1 and parkin promote mitochondrial
fission and/or inhibit fusion in Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 105:14503–14508. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Poole AC, Thomas RE, Andrews LA, McBride
HM, Whitworth AJ and Pallanck LJ: The PINK1/Parkin pathway
regulates mitochondrial morphology. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
105:1638–1643. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kageyama Y, Hoshijima M, Seo K, Bedja D,
Sysa-Shah P, Andrabi SA, Chen W, Höke A, Dawson VL, Dawson TM, et
al: Parkin-independent mitophagy requires Drp1 and maintains the
integrity of mammalian heart and brain. EMBO J. 33:2798–2813. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hirota Y, Kang D and Kanki T: The
physiological role of mitophagy: New insights into phosphorylation
events. Int J Cell Biol. 2012:3549142012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Mitra K, Wunder C, Roysam B, Lin G and
Lippincott-Schwartz J: A hyperfused mitochondrial state achieved at
G1-S regulates cyclin E buildup and entry into S phase. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 106:11960–11965. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Qian W, Choi S, Gibson GA, Watkins SC,
Bakkenist CJ and Van Houten B: Mitochondrial hyperfusion induced by
loss of the fission protein Drp1 causes ATM-dependent G2/M arrest
and aneuploidy through DNA replication stress. J Cell Sci.
125:5745–5757. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Westrate LM, Sayfie AD, Burgenske DM and
MacKeigan JP: Persistent mitochondrial hyperfusion promotes G2/M
accumulation and caspase-dependent cell death. PLoS One.
9:e919112014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Huang WW, Ko SW, Tsai HY, Chung JG, Chiang
JH, Chen KT, Chen YC, Chen HY, Chen YF and Yang JS: Cantharidin
induces G2/M phase arrest and apoptosis in human colorectal cancer
colo 205 cells through inhibition of CDK1 activity and
caspase-dependent signaling pathways. Int J Oncol. 38:1067–1073.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Cribbs JT and Strack S: Reversible
phosphorylation of Drp1 by cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase and
calcineurin regulates mitochondrial fission and cell death. EMBO
Rep. 8:939–944. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Chang CR and Blackstone C: Cyclic
AMP-dependent protein kinase phosphorylation of Drp1 regulates its
GTPase activity and mitochondrial morphology. J Biol Chem.
282:21583–21587. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Taguchi N, Ishihara N, Jofuku A, Oka T and
Mihara K: Mitotic phosphorylation of dynamin-related GTPase Drp1
participates in mitochondrial fission. J Biol Chem.
282:11521–11529. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Yang Y, Bazhin AV, Werner J and
Karakhanova S: Reactive oxygen species in the immune system. Int
Rev Immunol. 32:249–270. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Matsuzawa A and Ichijo H: Redox control of
cell fate by MAP kinase: Physiological roles of ASK1-MAP kinase
pathway in stress signaling. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1780:1325–1336.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zhang Y, Du Y, Le W, Wang K, Kieffer N and
Zhang J: Redox control of the survival of healthy and diseased
cells. Antioxid Redox Signal. 15:2867–2908. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Chandel NS: Mitochondria as signaling
organelles. BMC Biol. 12:342014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Yu T, Robotham JL and Yoon Y: Increased
production of reactive oxygen species in hyperglycemic conditions
requires dynamic change of mitochondrial morphology. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 103:2653–2658. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Yu T, Sheu SS, Robotham JL and Yoon Y:
Mitochondrial fission mediates high glucose-induced cell death
through elevated production of reactive oxygen species. Cardiovasc
Res. 79:341–351. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Kageyama Y, Zhang Z, Roda R, Fukaya M,
Wakabayashi J, Wakabayashi N, Kensler TW, Reddy PH, Iijima M and
Sesaki H: Mitochondrial division ensures the survival of
postmitotic neurons by suppressing oxidative damage. J Cell Biol.
197:535–551. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Chiche J, Rouleau M, Gounon P,
Brahimi-Horn MC, Pouysségur J and Mazure NM: Hypoxic enlarged
mitochondria protect cancer cells from apoptotic stimuli. J Cell
Physiol. 222:648–657. 2010.
|
|
50
|
Yoon YS, Yoon DS, Lim IK, Yoon SH, Chung
HY, Rojo M, Malka F, Jou MJ, Martinou JC and Yoon G: Formation of
elongated giant mitochondria in DFO-induced cellular senescence:
Involvement of enhanced fusion process through modulation of Fis1.
J Cell Physiol. 209:468–480. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|