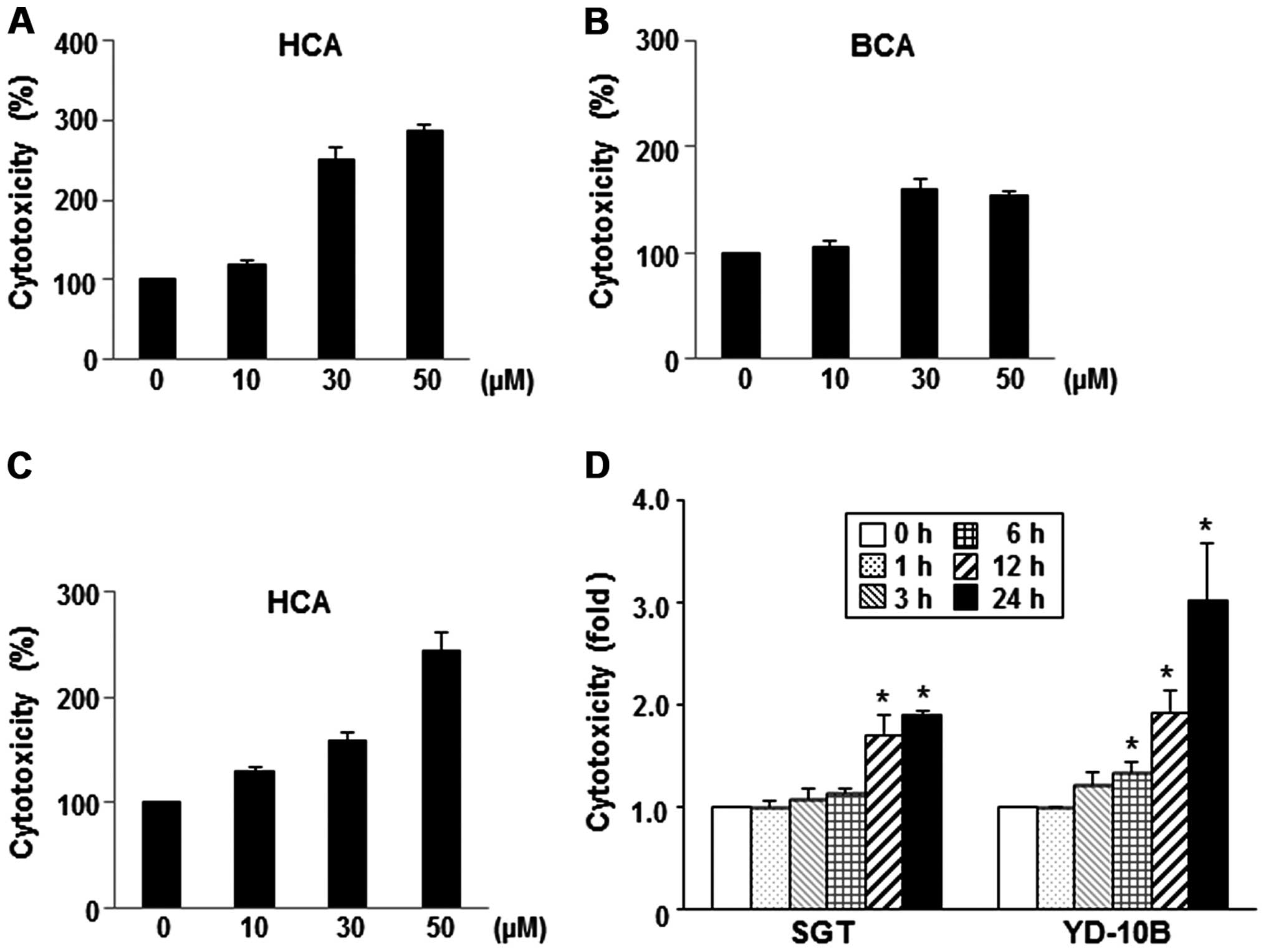
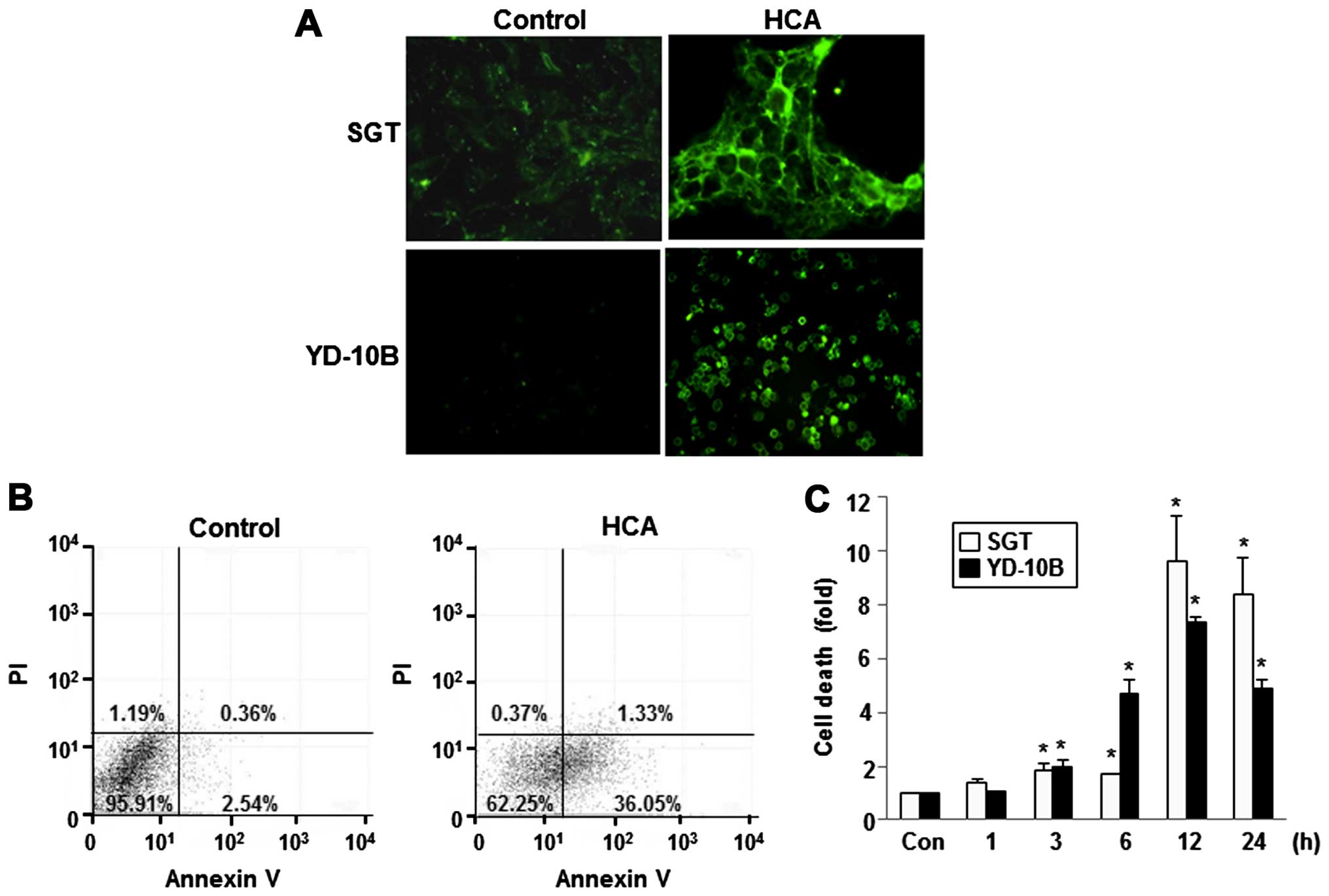
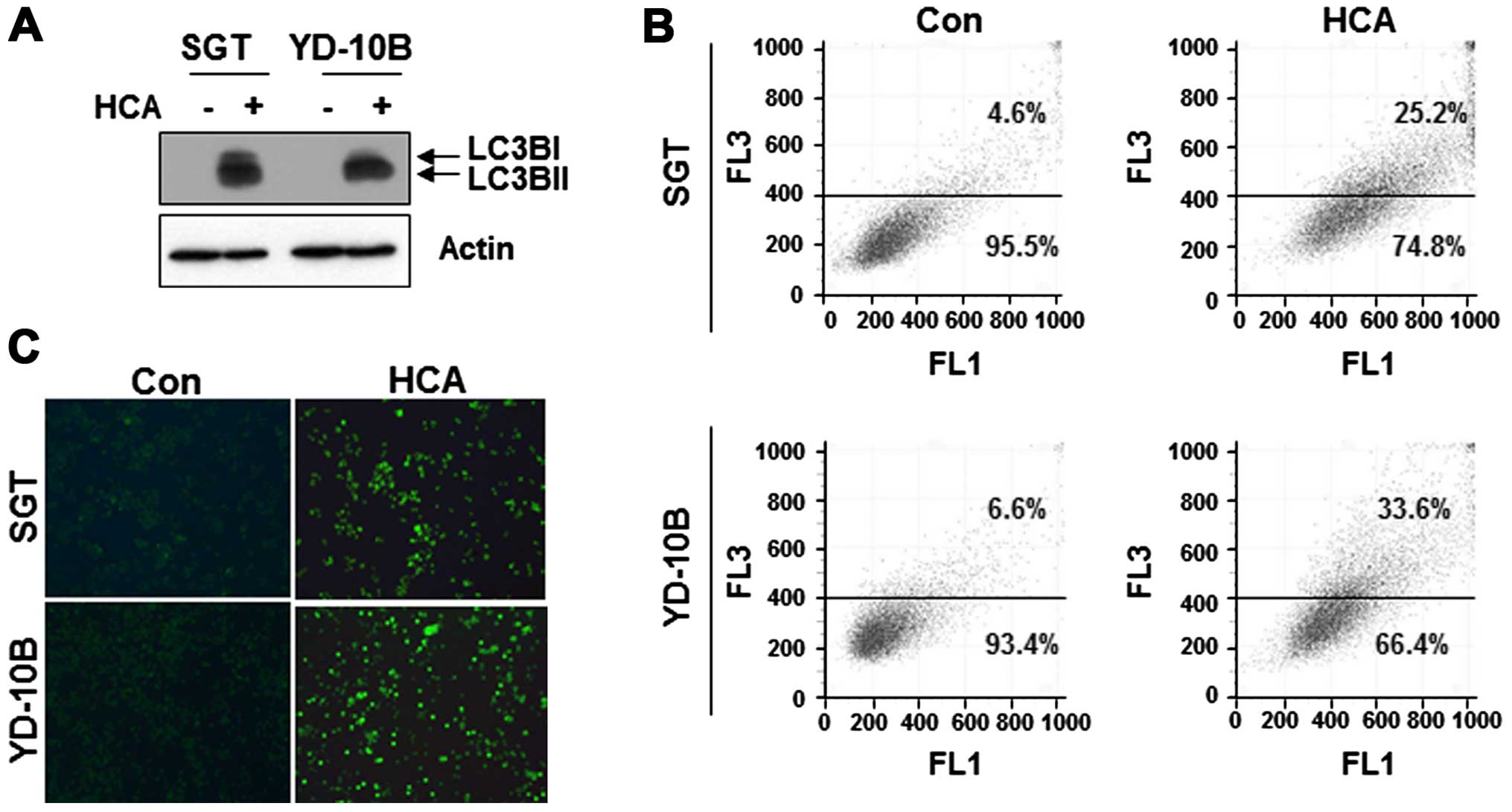
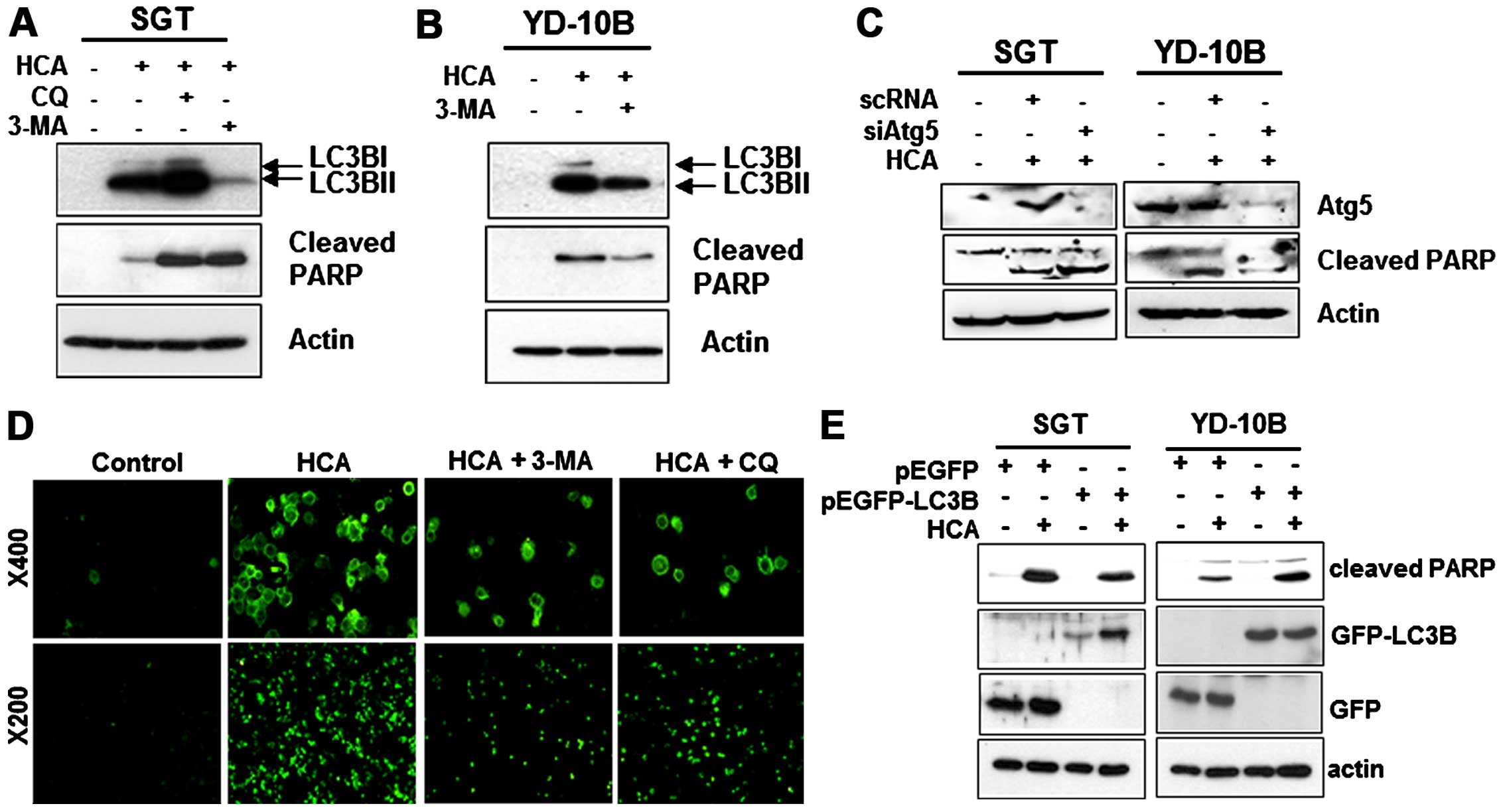
|
1
|
Jeong HW, Han DC, Son KH, Han MY, Lim JS,
Ha JH, Lee CW, Kim HM, Kim HC and Kwon BM: Antitumor effect of the
cinnamaldehyde derivative CB403 through the arrest of cell cycle
progression in the G2/M phase. Biochem Pharmacol. 65:1343–1350.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chao LK, Hua KF, Hsu HY, Cheng SS, Lin IF,
Chen CJ, Chen ST and Chang ST: Cinnamaldehyde inhibits
pro-inflammatory cytokines secretion from monocytes/macrophages
through suppression of intracellular signaling. Food Chem Toxicol.
46:220–231. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Kwon BM, Lee SH, Cho YK, Bok SH, So SH,
Youn MR and Chang SI: Synthesis and biological activity of
cinnamaldehydes as angiogenesis inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett.
7:2473–2476. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Han DC, Lee MY, Shin KD, Jeon SB, Kim JM,
Son KH, Kim HC, Kim HM and Kwon BM: 2′-benzoyloxycinnamaldehyde
induces apoptosis in human carcinoma via reactive oxygen species. J
Biol Chem. 279:6911–6920. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Lee CW, Hong DH, Han SB, Park SH, Kim HK,
Kwon BM and Kim HM: Inhibition of human tumor growth by 2′-hydroxy-
and 2′-benzoyloxycinnamaldehydes. Planta Med. 65:263–266. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Koh WS, Yoon SY, Kwon BM, Jeong TC, Nam KS
and Han MY: Cinnamaldehyde inhibits lymphocyte proliferation and
modulates T-cell differentiation. Int J Immunopharmacol.
20:643–660. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ka H, Park HJ, Jung HJ, Choi JW, Cho KS,
Ha J and Lee KT: Cinnamaldehyde induces apoptosis by ROS-mediated
mitochondrial permeability transition in human promyelocytic
leukemia HL-60 cells. Cancer Lett. 196:143–152. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lee CW, Lee SH, Lee JW, Ban JO, Lee SY,
Yoo HS, Jung JK, Moon DC, Oh KW and Hong JT:
2-hydroxycinnamaldehyde inhibits SW620 colon cancer cell growth
through AP-1 inactivation. J Pharmacol Sci. 104:19–28. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hong SH, Kim J, Kim JM, Lee SY, Shin DS,
Son KH, Han DC, Sung YK and Kwon BM: Apoptosis induction of
2′-hydroxycin-namaldehyde as a proteasome inhibitor is associated
with ER stress and mitochondrial perturbation in cancer cells.
Biochem Pharmacol. 74:557–565. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kim SA, Sung YK, Kwon BM, Yoon JH, Lee H,
Ahn SG and Hong SH: 2′-Hydroxycinnamaldehyde shows antitumor
activity against oral cancer in vitro and in vivo in a rat tumor
model. Anticancer Res. 30:489–494. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kang HS, Ock J, Lee HJ, Lee YJ, Kwon BM
and Hong SH: Early growth response protein 1 upregulation and
nuclear translocation by 2′-benzoyloxycinnamaldehyde induces
prostate cancer cell death. Cancer Lett. 329:217–227. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Ock J, Lee HA, Ismail IA, Lee HJ, Kwon BM,
Suk K, Lee WH and Hong SH: Differential antiproliferation effect of
2′-benzoyloxy-cinnamaldehyde in K-ras-transformed cells via
downregulation of thiol antioxidants. Cancer Sci. 102:212–218.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Kwon JY, Hong SH, Park SD, Ahn SG, Yoon
JH, Kwon BM and Kim SA: 2′-Benzoyloxycinnamaldehyde inhibits nitric
oxide production in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells
via regulation of AP-1 pathway. Eur J Pharmacol. 696:179–186. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Young MR, Levingston C and Johnson SD:
Cytokine and adipokine levels in patients with premalignant oral
lesions or in patients with oral cancer who did or did not receive
1α,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 treatment upon cancer diagnosis. Cancers
(Basel). 7:1109–1124. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Moon SM, Ahn MY, Kwon SM, Kim SA, Ahn SG
and Yoon JH: Homeobox C5 expression is associated with the
progression of 4-nitroquinoline 1-oxide-induced rat tongue
carcinogenesis. J Oral Pathol Med. 41:470–476. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
William WN Jr and El-Naggar AK: A novel
target for oral cancer chemoprevention? Notch quite, yet…. Cancer
Prev Res (Phila). 8:262–265. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Lee EJ, Kim J, Lee SA, Kim EJ, Chun YC,
Ryu MH and Yook JI: Characterization of newly established oral
cancer cell lines derived from six squamous cell carcinoma and two
mucoepidermoid carcinoma cells. Exp Mol Med. 37:379–390. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kim SA, Kim YC, Kim SW, Lee SH, Min JJ,
Ahn SG and Yoon JH: Antitumor activity of novel indirubin
derivatives in rat tumor model. Clin Cancer Res. 13:253–259. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang L, Yu J, Park BH, Kinzler KW and
Vogelstein B: Role of BAX in the apoptotic response to anticancer
agents. Science. 290:989–992. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Pietsch EC, Perchiniak E, Canutescu AA,
Wang G, Dunbrack RL and Murphy ME: Oligomerization of BAK by p53
utilizes conserved residues of the p53 DNA binding domain. J Biol
Chem. 283:21294–21304. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Oda E, Ohki R, Murasawa H, Nemoto J,
Shibue T, Yamashita T, Tokino T, Taniguchi T and Tanaka N: Noxa, a
BH3-only member of the Bcl-2 family and candidate mediator of
p53-induced apoptosis. Science. 288:1053–1058. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Soussi T and Lozano G: p53 mutation
heterogeneity in cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 331:834–842.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Vogelstein B, Lane D and Levine AJ:
Surfing the p53 network. Nature. 408:307–310. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Oren M: Decision making by p53: Life,
death and cancer. Cell Death Differ. 10:431–442. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Vaseva AV and Moll UM: The mitochondrial
p53 pathway. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1787:414–420. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Levy JM and Thorburn A: Targeting
autophagy during cancer therapy to improve clinical outcomes.
Pharmacol Ther. 131:130–141. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chen S, Rehman SK, Zhang W, Wen A, Yao L
and Zhang J: Autophagy is a therapeutic target in anticancer drug
resistance. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1806:220–229. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Choi KS: Autophagy and cancer. Exp Mol
Med. 44:109–120. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|