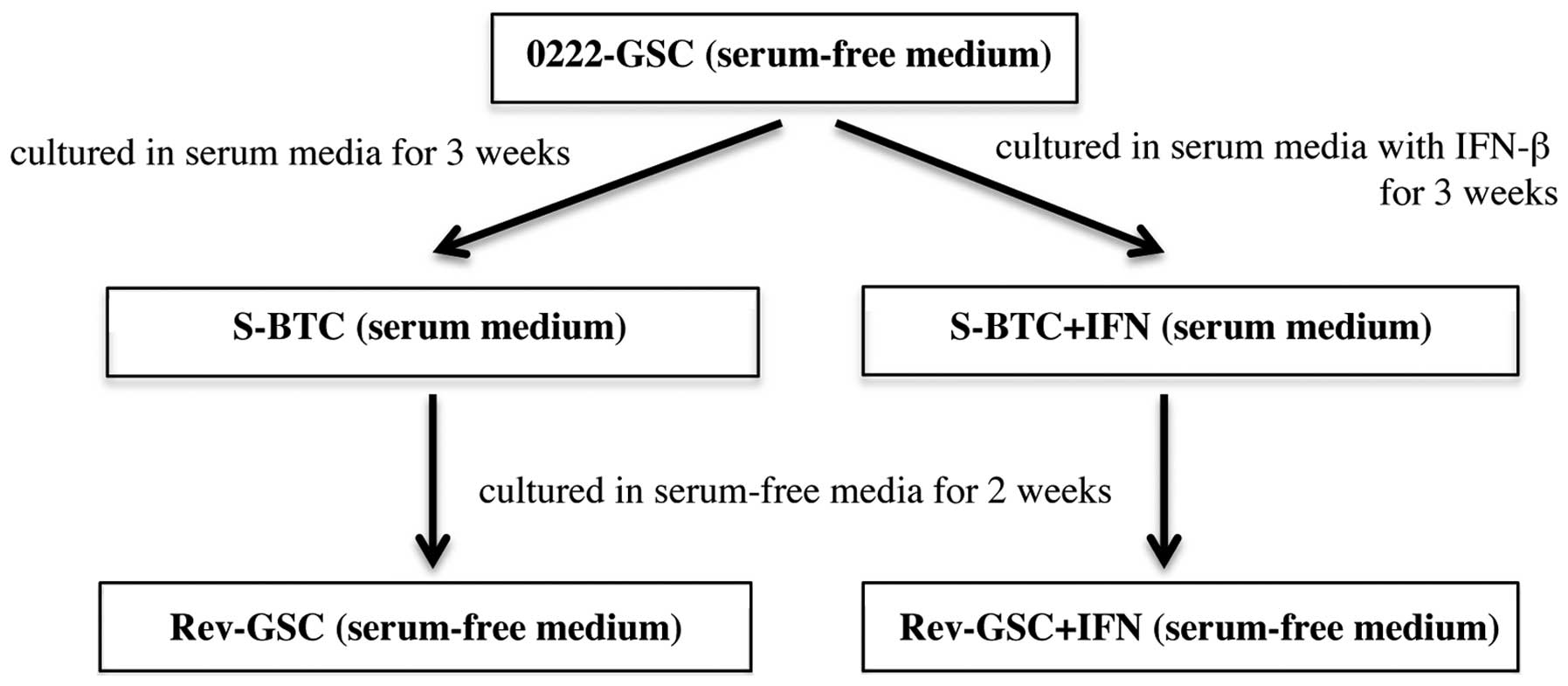
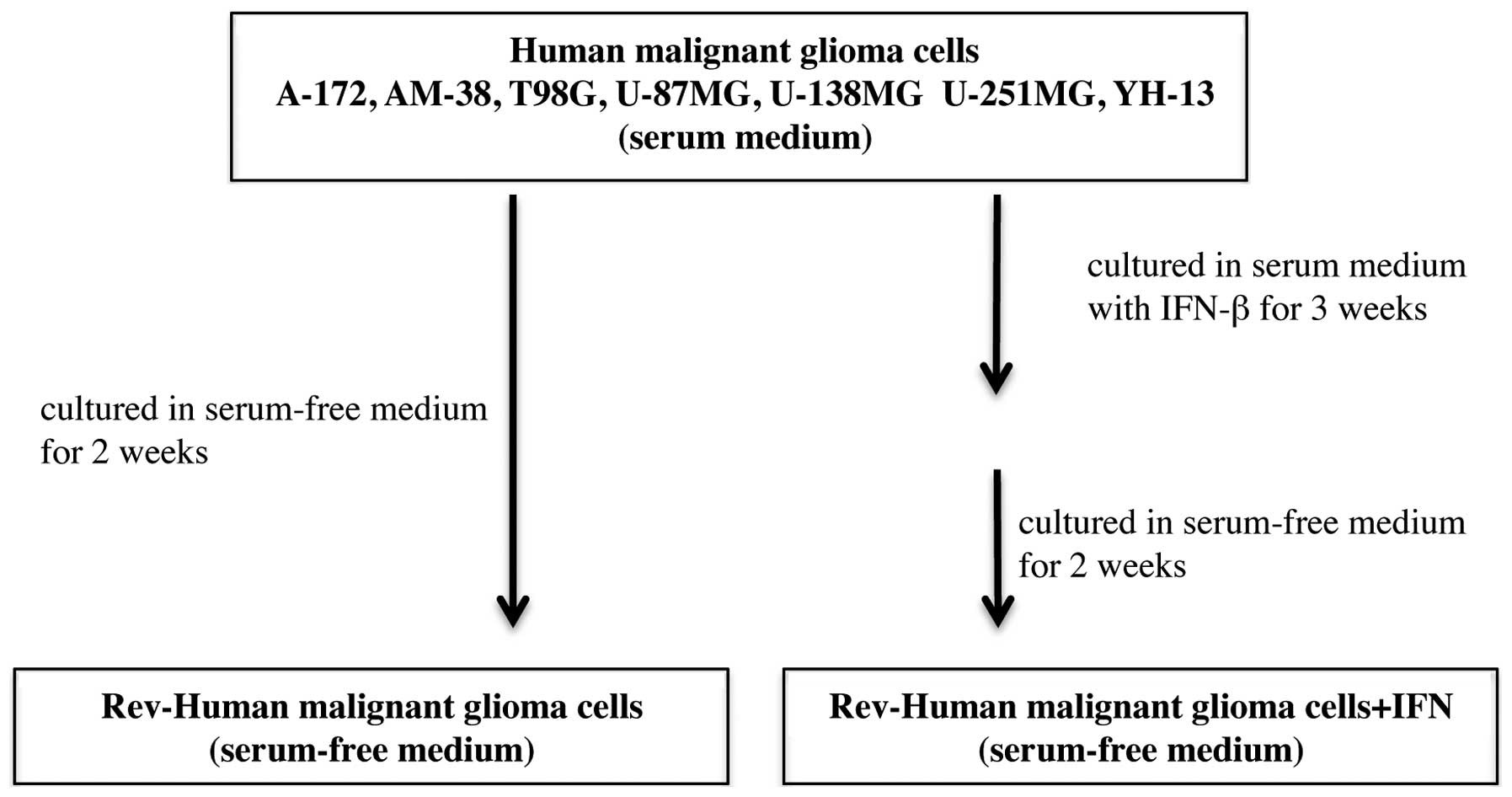
|
1
|
Lee J, Kotliarova S, Kotliarov Y, Li A, Su
Q, Donin NM, Pastorino S, Purow BW, Christopher N, Zhang W, et al:
Tumor stem cells derived from glioblastomas cultured in bFGF and
EGF more closely mirror the phenotype and genotype of primary
tumors than do serum-cultured cell lines. Cancer Cell. 9:391–403.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wilson RJ, Thomas CD, Fox R, Roy DB and
Kunin WE: Spatial patterns in species distributions reveal
biodiversity change. Nature. 432:393–396. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lee J, Son MJ, Woolard K, Donin NM, Li A,
Cheng CH, Kotliarova S, Kotliarov Y, Walling J, Ahn S, et al:
Epigenetic-mediated dysfunction of the bone morphogenetic protein
pathway inhibits differentiation of glioblastoma-initiating cells.
Cancer Cell. 13:69–80. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Peñuelas S, Anido J, Prieto-Sánchez RM,
Folch G, Barba I, Cuartas I, García-Dorado D, Poca MA, Sahuquillo
J, Baselga J, et al: TGF-beta increases glioma-initiating cell
self-renewal through the induction of LIF in human glioblastoma.
Cancer Cell. 15:315–327. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Gupta PB, Chaffer CL and Weinberg RA:
Cancer stem cells: Mirage or reality? Nat Med. 15:1010–1012. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Gupta PB, Fillmore CM, Jiang G, Shapira
SD, Tao K, Kuperwasser C and Lander ES: Stochastic state
transitions give rise to phenotypic equilibrium in populations of
cancer cells. Cell. 146:633–644. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Natsume A, Ito M, Katsushima K, Ohka F,
Hatanaka A, Shinjo K, Sato S, Takahashi S, Ishikawa Y, Takeuchi I,
et al: Chromatin regulator PRC2 is a key regulator of epigenetic
plasticity in glioblastoma. Cancer Res. 73:4559–4570. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Weller
M, Fisher B, Taphoorn MJ, Belanger K, Brandes AA, Marosi C, Bogdahn
U, et al; European Organisation for Research and Treatment of
Cancer Brain Tumor and Radiotherapy Groups; National Cancer
Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group. Radiotherapy plus
concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J
Med. 352:987–996. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Stupp R, Hegi ME, Mason WP, van den Bent
MJ, Taphoorn MJ, Janzer RC, Ludwin SK, Allgeier A, Fisher B,
Belanger K, et al; European Organisation for Research and Treatment
of Cancer Brain Tumour and Radiation Oncology Groups; National
Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group. Effects of
radiotherapy with concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide versus
radiotherapy alone on survival in glioblastoma in a randomised
phase III study: 5-year analysis of the EORTC-NCIC trial. Lancet
Oncol. 10:459–466. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Pegg AE: Mammalian
O6-alkylguanine-DNA alkyltransferase: Regulation and
importance in response to alkylating carcinogenic and therapeutic
agents. Cancer Res. 50:6119–6129. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Saito R, Mizuno M, Hatano M, Kumabe T,
Yoshimoto T and Yoshida J: Two different mechanisms of apoptosis
resistance observed in interferon-beta induced apoptosis of human
glioma cells. J Neurooncol. 67:273–280. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Vannucchi S, Chiantore MV, Mangino G,
Percario ZA, Affabris E, Fiorucci G and Romeo G: Perspectives in
biomolecular therapeutic intervention in cancer: From the early to
the new strategies with type I interferons. Curr Med Chem.
14:667–679. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yoshino A, Katayama Y, Yokoyama T,
Watanabe T, Ogino A, Ota T, Komine C, Fukushima T and Kusama K:
Therapeutic implications of interferon regulatory factor (IRF)-1
and IRF-2 in diffusely infiltrating astrocytomas (DIA): Response to
interferon (IFN)-beta in glioblastoma cells and prognostic value
for DIA. J Neurooncol. 74:249–260. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Natsume A, Ishii D, Wakabayashi T, Tsuno
T, Hatano H, Mizuno M and Yoshida J: IFN-beta down-regulates the
expression of DNA repair gene MGMT and sensitizes resistant glioma
cells to temozolomide. Cancer Res. 65:7573–7579. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Park JA, Joe YA, Kim TG and Hong YK:
Potentiation of anti-glioma effect with combined temozolomide and
interferon-beta. Oncol Rep. 16:1253–1260. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wakabayashi T, Kayama T, Nishikawa R,
Takahashi H, Yoshimine T, Hashimoto N, Aoki T, Kurisu K, Natsume A,
Ogura M, et al: A multicenter phase I trial of interferon-beta and
temozolomide combination therapy for high-grade gliomas (INTEGRA
Study). Jpn J Clin Oncol. 38:715–718. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wakabayashi T, Kayama T, Nishikawa R,
Takahashi H, Hashimoto N, Takahashi J, Aoki T, Sugiyama K, Ogura M,
Natsume A, et al: A multicenter phase I trial of combination
therapy with interferon-β and temozolomide for high-grade gliomas
(INTEGRA study): The final report. J Neurooncol. 104:573–577. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yuki K, Natsume A, Yokoyama H, Kondo Y,
Ohno M, Kato T, Chansakul P, Ito M, Kim SU and Wakabayashi T:
Induction of oligodendrogenesis in glioblastoma-initiating cells by
IFN-mediated activation of STAT3 signaling. Cancer Lett. 284:71–79.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yoshino A, Tashiro S, Ogino A, Yachi K,
Ohta T, Fukushima T, Watanabe T, Katayama Y, Okamoto Y, Sano E, et
al: Gene expression profiles predicting the response to IFN-β and a
combination of temozolomide and IFN-β in malignant gliomas. Int J
Oncol. 39:529–542. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Griguer CE, Oliva CR, Gobin E, Marcorelles
P, Benos DJ, Lancaster JR Jr and Gillespie GY: CD133 is a marker of
bioenergetic stress in human glioma. PLoS One. 3:e36552008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Poltavtseva RA, Marey MV, Aleksandrova MA,
Revishchin AV, Korochkin LI and Sukhikh GT: Evaluation of
progenitor cell cultures from human embryos for
neurotransplantation. Brain Res Dev Brain Res. 134:149–154. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Singh SK, Clarke ID, Terasaki M, Bonn VE,
Hawkins C, Squire J and Dirks PB: Identification of a cancer stem
cell in human brain tumors. Cancer Res. 63:5821–5828.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hatano SY, Tada M, Kimura H, Yamaguchi S,
Kono T, Nakano T, Suemori H, Nakatsuji N and Tada T: Pluripotential
competence of cells associated with Nanog activity. Mech Dev.
122:67–79. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Mitsui K, Tokuzawa Y, Itoh H, Segawa K,
Murakami M, Takahashi K, Maruyama M, Maeda M and Yamanaka S: The
homeoprotein Nanog is required for maintenance of pluripotency in
mouse epiblast and ES cells. Cell. 113:631–642. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Clevers H: The cancer stem cell: Premises,
promises and challenges. Nat Med. 17:313–319. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Bao S, Wu Q, McLendon RE, Hao Y, Shi Q,
Hjelmeland AB, Dewhirst MW, Bigner DD and Rich JN: Glioma stem
cells promote radioresistance by preferential activation of the DNA
damage response. Nature. 444:756–760. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Qiang L, Yang Y, Ma YJ, Chen FH, Zhang LB,
Liu W, Qi Q, Lu N, Tao L, Wang XT, et al: Isolation and
characterization of cancer stem like cells in human glioblastoma
cell lines. Cancer Lett. 279:13–21. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Smith TJ: The art of oncology: When the
tumor is not the target. Tell it like it is. J Clin Oncol.
18:3441–3445. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kondo Y, Shen L, Cheng AS, Ahmed S,
Boumber Y, Charo C, Yamochi T, Urano T, Furukawa K, Kwabi-Addo B,
et al: Gene silencing in cancer by histone H3 lysine 27
trimethylation independent of promoter DNA methylation. Nat Genet.
40:741–750. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sparmann A and van Lohuizen M: Polycomb
silencers control cell fate, development and cancer. Nat Rev
Cancer. 6:846–856. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chi P, Allis CD and Wang GG: Covalent
histone modifications--miswritten, misinterpreted and mis-erased in
human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 10:457–469. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ougolkov AV, Bilim VN and Billadeau DD:
Regulation of pancreatic tumor cell proliferation and
chemoresistance by the histone methyltransferase enhancer of zeste
homologue 2. Clin Cancer Res. 14:6790–6796. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Raaphorst FM, Meijer CJ, Fieret E,
Blokzijl T, Mommers E, Buerger H, Packeisen J, Sewalt RA, Otte AP
and van Diest PJ: Poorly differentiated breast carcinoma is
associated with increased expression of the human polycomb group
EZH2 gene. Neoplasia. 5:481–488. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Sauvageau M and Sauvageau G: Polycomb
group proteins: Multifaceted regulators of somatic stem cells and
cancer. Cell Stem Cell. 7:299–313. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Schwartz YB and Pirrotta V: Polycomb
silencing mechanisms and the management of genomic programmes. Nat
Rev Genet. 8:9–22. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Bracken AP and Helin K: Polycomb group
proteins: Navigators of lineage pathways led astray in cancer. Nat
Rev Cancer. 9:773–784. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kleer CG, Cao Q, Varambally S, Shen R, Ota
I, Tomlins SA, Ghosh D, Sewalt RG, Otte AP, Hayes DF, et al: EZH2
is a marker of aggressive breast cancer and promotes neoplastic
transformation of breast epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
100:11606–11611. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Cebrià F, Kobayashi C, Umesono Y, Nakazawa
M, Mineta K, Ikeo K, Gojobori T, Itoh M, Taira M, Sánchez Alvarado
A, et al: FGFR-related gene nou-darake restricts brain tissues to
the head region of planarians. Nature. 419:620–624. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Fiskus W, Wang Y, Sreekumar A, Buckley KM,
Shi H, Jillella A, Ustun C, Rao R, Fernandez P, Chen J, et al:
Combined epigenetic therapy with the histone methyltransferase EZH2
inhibitor 3-deazaneplanocin A and the histone deacetylase inhibitor
panobinostat against human AML cells. Blood. 114:2733–2743. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Tan J, Yang X, Zhuang L, Jiang X, Chen W,
Lee PL, Karuturi RK, Tan PB, Liu ET and Yu Q: Pharmacologic
disruption of Polycomb-repressive complex 2-mediated gene
repression selectively induces apoptosis in cancer cells. Genes
Dev. 21:1050–1063. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Ernst T, Chase AJ, Score J, Hidalgo-Curtis
CE, Bryant C, Jones AV, Waghorn K, Zoi K, Ross FM, Reiter A, et al:
Inactivating mutations of the histone methyltransferase gene EZH2
in myeloid disorders. Nat Genet. 42:722–726. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|