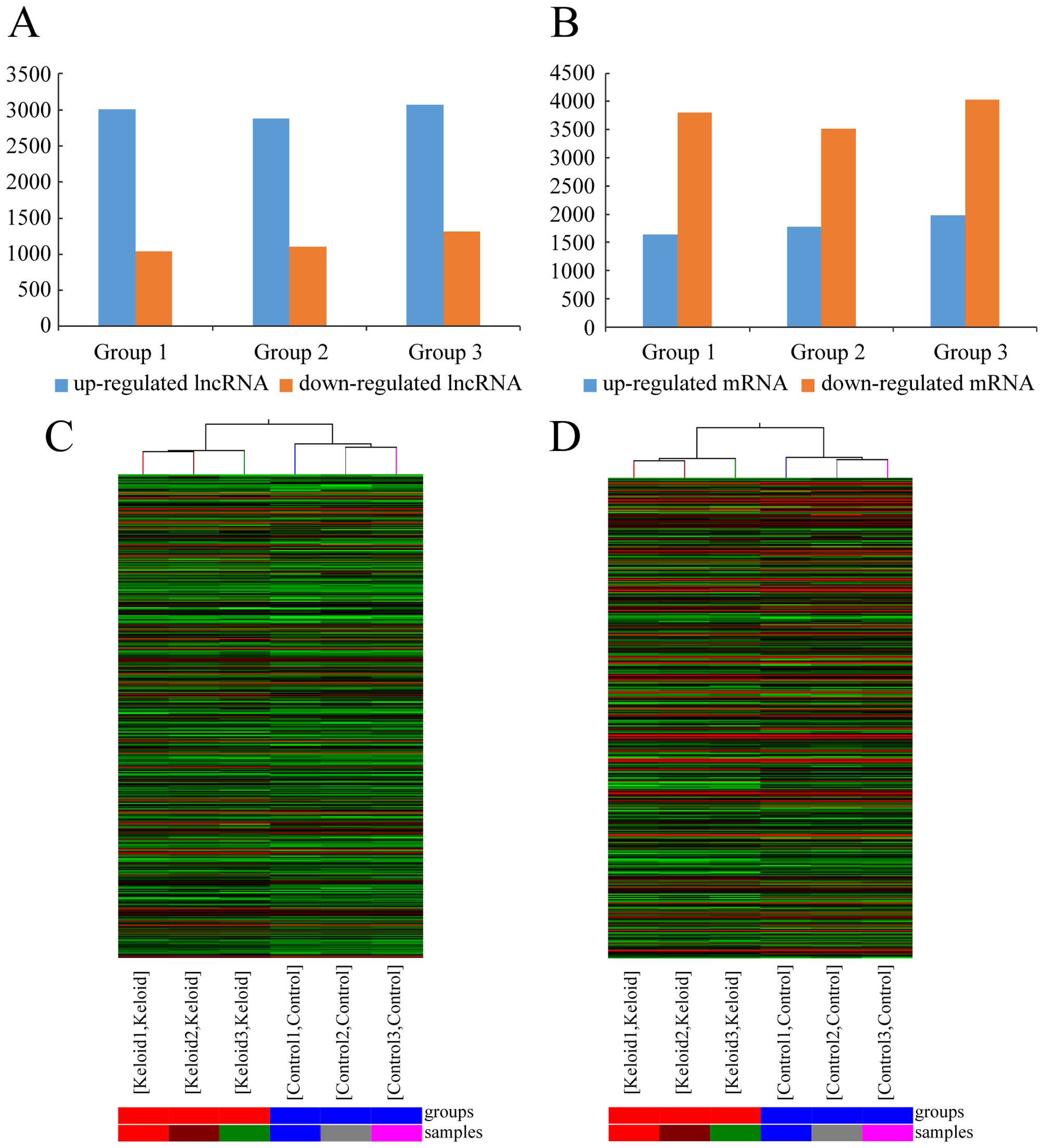
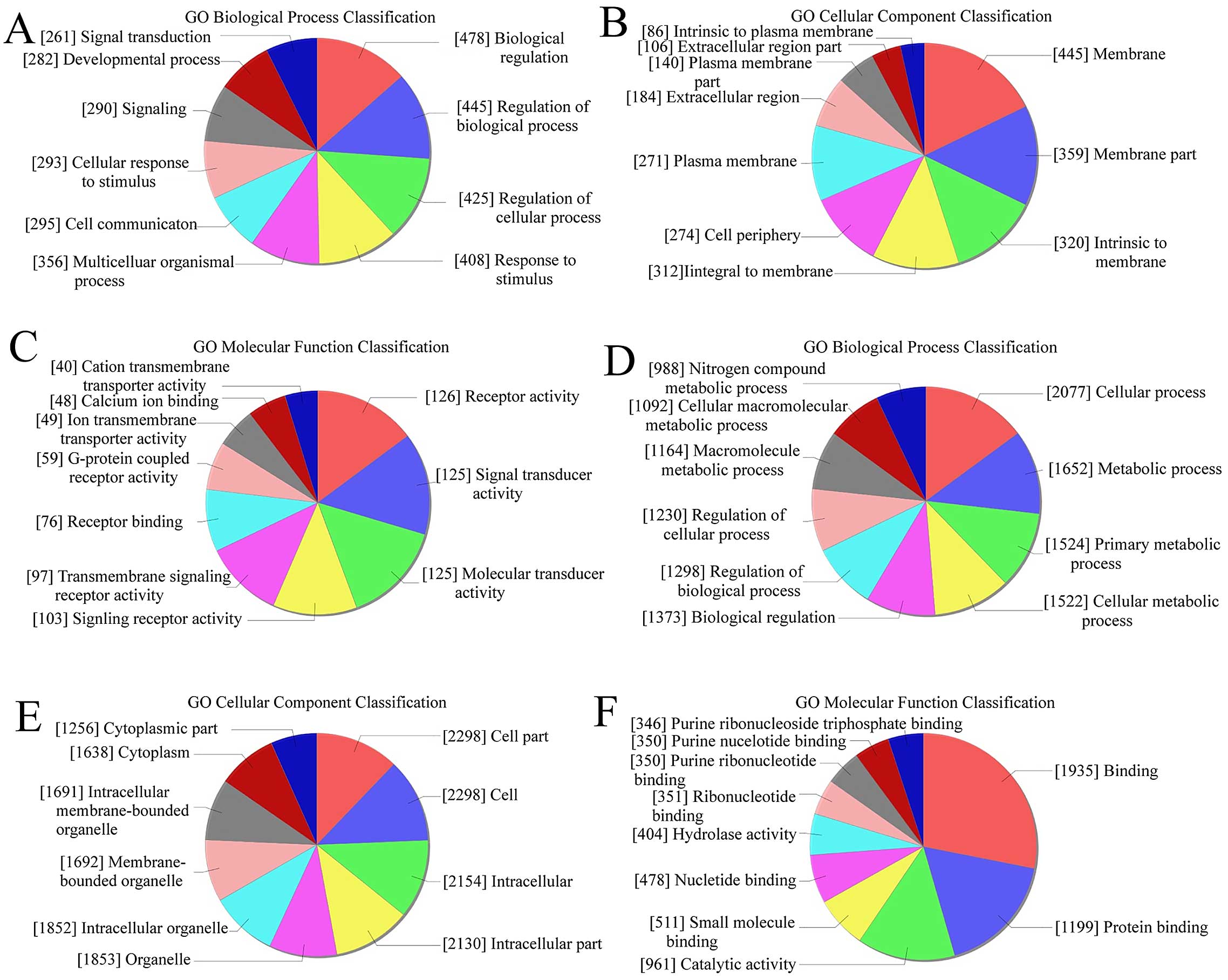
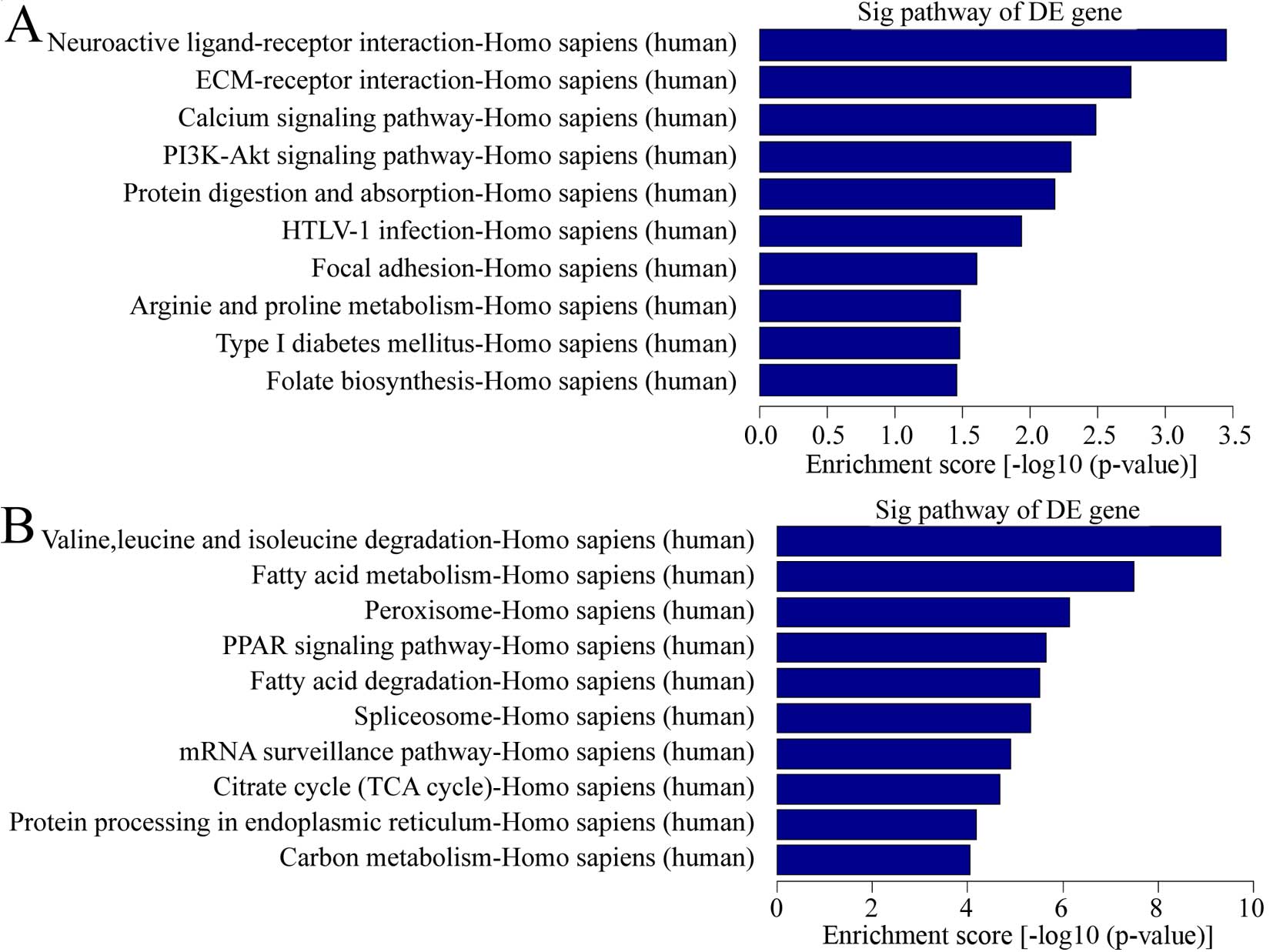
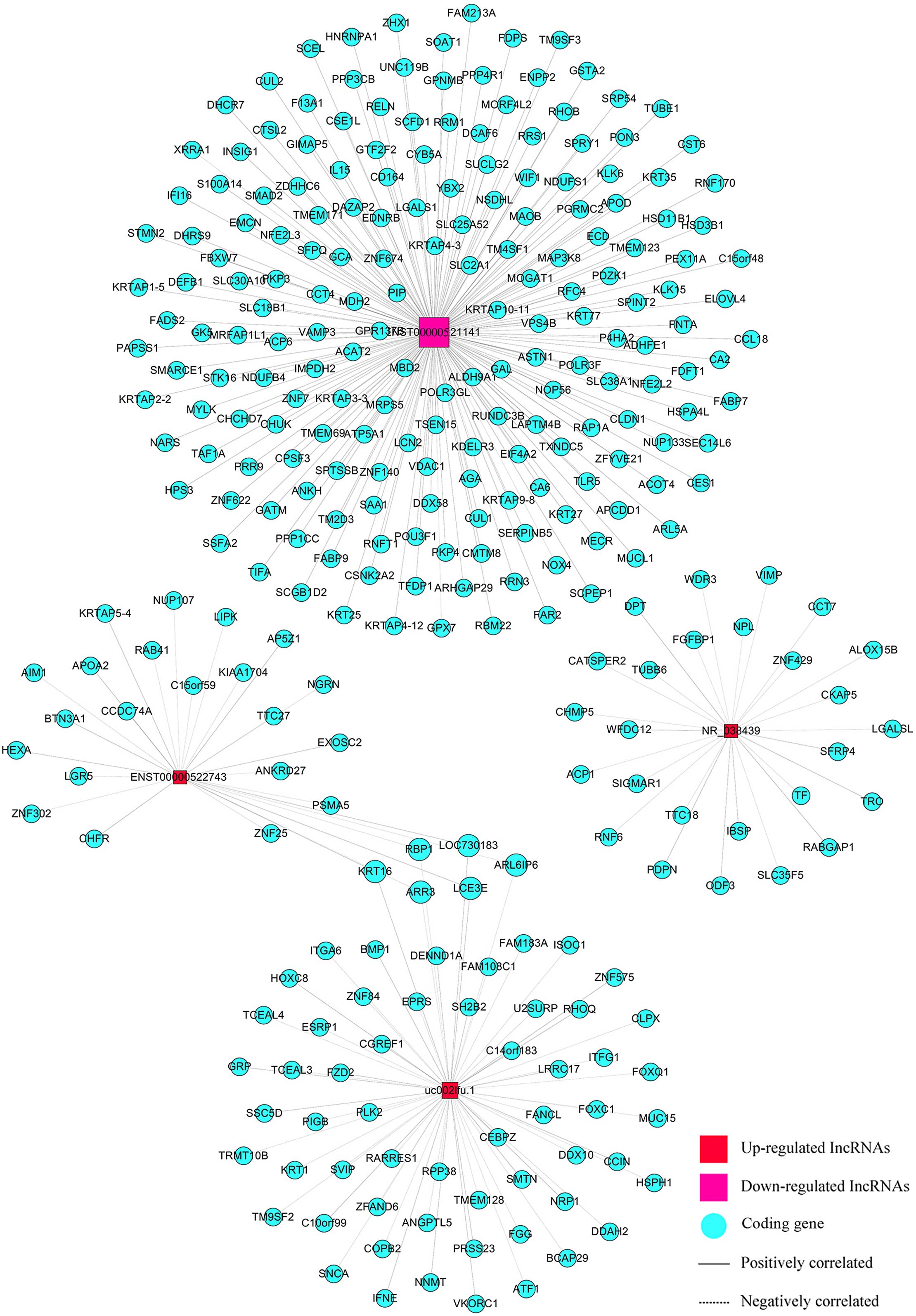
|
1
|
Halim AS, Emami A, Salahshourifar I and
Kannan TP: Keloid scarring: Understanding the genetic basis,
advances, and prospects. Arch Plast Surg. 39:184–189. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
van Leeuwen MC, van der Wal MB, Bulstra
AE, Galindo-Garre F, Molier J, van Zuijlen PP, van Leeuwen PA and
Niessen FB: Intralesional cryotherapy for treatment of keloid
scars: A prospective study. Plast Reconstr Surg. 135:580–589. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Erol OO, Gurlek A, Agaoglu G, Topcuoglu E
and Oz H: Treatment of hypertrophic scars and keloids using intense
pulsed light (IPL). Aesthetic Plast Surg. 32:902–909. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Juckett G and Hartman-Adams H: Management
of keloids and hypertrophic scars. Am Fam Physician. 80:253–260.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Mseddi M, Mesrati H, Ktaari S, Amouri M,
Chaaben H, Boudaya S and Turki H: Treatment of keloid with phenol:
A new therapy. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 141:493–499. 2014.(In
French). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
van Leeuwen MC, Bulstra AE, van Leeuwen PA
and Niessen FB: A new argon gas-based device for the treatment of
keloid scars with the use of intralesional cryotherapy. J Plast
Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 67:1703–1710. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Nakashima M, Chung S, Takahashi A,
Kamatani N, Kawaguchi T, Tsunoda T, Hosono N, Kubo M, Nakamura Y
and Zembutsu H: A genome-wide association study identifies four
susceptibility loci for keloid in the Japanese population. Nat
Genet. 42:768–771. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chen W, Fu X, Sun X, Sun T, Zhao Z and
Sheng Z: Analysis of differentially expressed genes in keloids and
normal skin with cDNA microarray. J Surg Res. 113:208–216. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Unahabhokha T, Sucontphunt A, Nimmannit U,
Chanvorachote P, Yongsanguanchai N and Pongrakhananon V: Molecular
signalings in keloid disease and current therapeutic approaches
from natural based compounds. Pharm Biol. 53:457–463. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Murao N, Seino K, Hayashi T, Ikeda M,
Funayama E, Furukawa H, Yamamoto Y and Oyama A: Treg-enriched
CD4+ T cells attenuate collagen synthesis in keloid
fibroblasts. Exp Dermatol. 23:266–271. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kung JT, Colognori D and Lee JT: Long
noncoding RNAs: Past, present, and future. Genetics. 193:651–669.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bonasio R and Shiekhattar R: Regulation of
transcription by long noncoding RNAs. Annu Rev Genet. 48:433–455.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
He Y, Meng XM, Huang C, Wu BM, Zhang L, Lv
XW and Li J: Long noncoding RNAs: Novel insights into hepatocelluar
carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 344:20–27. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Martens-Uzunova ES, Böttcher R, Croce CM,
Jenster G, Visakorpi T and Calin GA: Long noncoding RNA in
prostate, bladder, and kidney cancer. Eur Urol. 65:1140–1151. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hombach S and Kretz M: The non-coding
skin: Exploring the roles of long non-coding RNAs in epidermal
homeostasis and disease. BioEssays. 35:1093–1100. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kretz M, Webster DE, Flockhart RJ, Lee CS,
Zehnder A, Lopez-Pajares V, Qu K, Zheng GX, Chow J, Kim GE, et al:
Suppression of progenitor differentiation requires the long
noncoding RNA ANCR. Genes Dev. 26:338–343. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Boggio RF, Freitas VM, Cassiola FM,
Urabayashi M and Machado-Santelli GM: Effect of a calcium-channel
blocker (verapamil) on the morphology, cytoskeleton and collagenase
activity of human skin fibroblasts. Burns. 37:616–625. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Kashiyama K, Mitsutake N, Matsuse M, Ogi
T, Saenko VA, Ujifuku K, Utani A, Hirano A and Yamashita S:
miR-196a down-regulation increases the expression of type I and III
collagens in keloid fibroblasts. J Invest Dermatol. 132:1597–1604.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Liu Y, Yang D, Xiao Z and Zhang M: miRNA
expression profiles in keloid tissue and corresponding normal skin
tissue. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 36:193–201. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Liu Y, Wang X, Yang D, Xiao Z and Chen X:
MicroRNA-21 affects proliferation and apoptosis by regulating
expression of PTEN in human keloid fibroblasts. Plast Reconstr
Surg. 134:561e–573e. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Di Gesualdo F, Capaccioli S and Lulli M: A
pathophysiological view of the long non-coding RNA world.
Oncotarget. 5:10976–10996. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kretz M: TINCR, staufen1, and cellular
differentiation. RNA Biol. 10:1597–1601. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bikle DD: The vitamin D receptor: A tumor
suppressor in skin. Discov Med. 11:7–17. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Jiang YJ and Bikle DD: LncRNA profiling
reveals new mechanism for VDR protection against skin cancer
formation. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 144pa:87–90. 2014.
|
|
25
|
Wan DC and Wang KC: Long noncoding RNA:
Significance and potential in skin biology. Cold Spring Harb
Perspect Med. 4:1–10. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Mazar J, Zhao W, Khalil AM, Lee B, Shelley
J, Govindarajan SS, Yamamoto F, Ratnam M, Aftab MN, Collins S, et
al: The functional characterization of long noncoding RNA SPRY4-IT1
in human melanoma cells. Oncotarget. 5:8959–8969. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wang KC and Chang HY: Molecular mechanisms
of long noncoding RNAs. Mol Cell. 43:904–914. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Fukunaga K: Cognitive Function and
Calcium. Cognitive improvement through T type calcium channel
stimulation. Clin Calcium. 25:247–254. 2015.(In Japanese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Toyota M, Ho C, Ohe-Toyota M, Baylin SB
and Issa JP: Inactivation of CACNA1G, a T-type calcium channel
gene, by aberrant methylation of its 5′ CpG island in human tumors.
Cancer Res. 59:4535–4541. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ohkubo T and Yamazaki J: T-type
voltage-activated calcium channel Cav3.1, but not Cav3.2, is
involved in the inhibition of proliferation and apoptosis in MCF-7
human breast cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 41:267–275. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Villegas VE and Zaphiropoulos PG:
Neighboring gene regulation by antisense long non-coding RNAs. Int
J Mol Sci. 16:3251–3266. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhang ZZ, Shen ZY, Shen YY, Zhao EH, Wang
M, Wang CJ, Cao H and Xu J: HOTAIR long noncoding RNA promotes
gastric cancer metastasis through suppression of Poly r(C) Binding
Protein (PCBP) 1. Mol Cancer Ther. 14:1162–1170. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Xue Y, Ma G, Zhang Z, Hua Q, Chu H, Tong
N, Yuan L, Qin C, Yin C, Zhang Z, et al: A novel antisense long
noncoding RNA regulates the expression of MDC1 in bladder cancer.
Oncotarget. 6:484–493. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
34
|
Ledon JA, Savas J, Franca K, Chacon A and
Nouri K: Intralesional treatment for keloids and hypertrophic
scars: A review. Dermatol Surg. 39:1745–1757. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
D'Andrea F, Brongo S, Ferraro G and Baroni
A: Prevention and treatment of keloids with intralesional
verapamil. Dermatology. 204:60–62. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Huang C and Ogawa R: Pharmacological
treatment for keloids. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 14:2087–2100.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Giugliano G, Pasquali D, Notaro A, Brongo
S, Nicoletti G, D'Andrea F, Bellastella A and Sinisi AA: Verapamil
inhibits interleukin-6 and vascular endothelial growth factor
production in primary cultures of keloid fibroblasts. Br J Plast
Surg. 56:804–809. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wu W, Okamoto O, Kato A, Matsuo N, Nomizu
M, Yoshioka H and Fujiwara S: Dermatopontin regulates fibrin
formation and its biological activity. J Invest Dermatol.
134:256–263. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Wang H, Liu J, Wang F, Chen M, Xiao Z,
Ouyang R, Fei A, Shen Y and Pan S: The role of charged
multivesicular body protein 5 in programmed cell death in leukemic
cells. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 45:383–390. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Abuharbeid S, Czubayko F and Aigner A: The
fibroblast growth factor-binding protein FGF-BP. Int J Biochem Cell
Biol. 38:1463–1468. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|