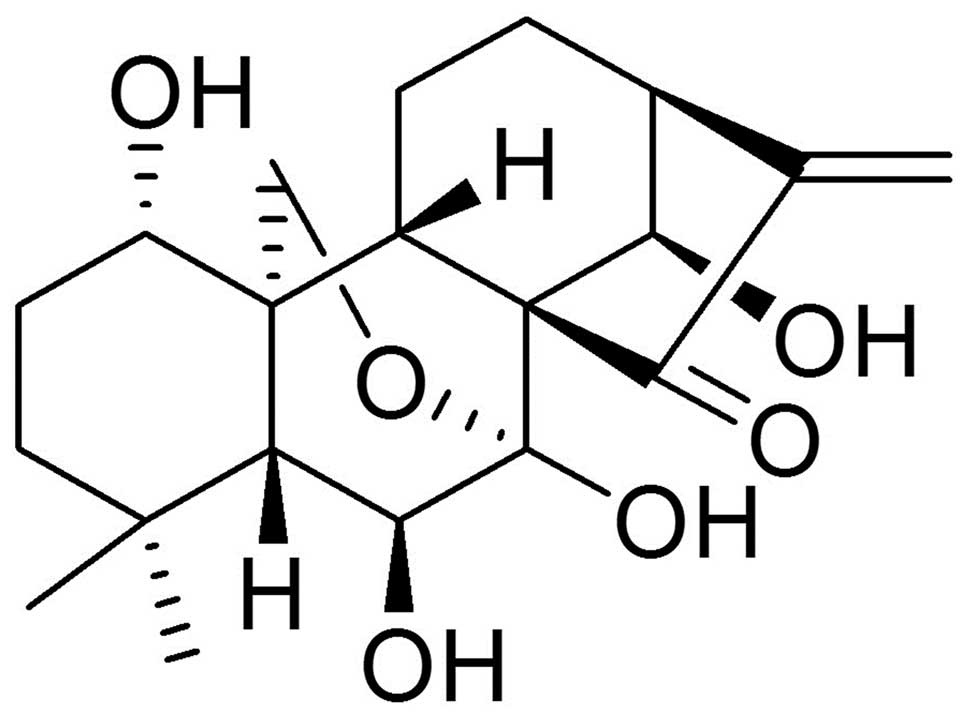
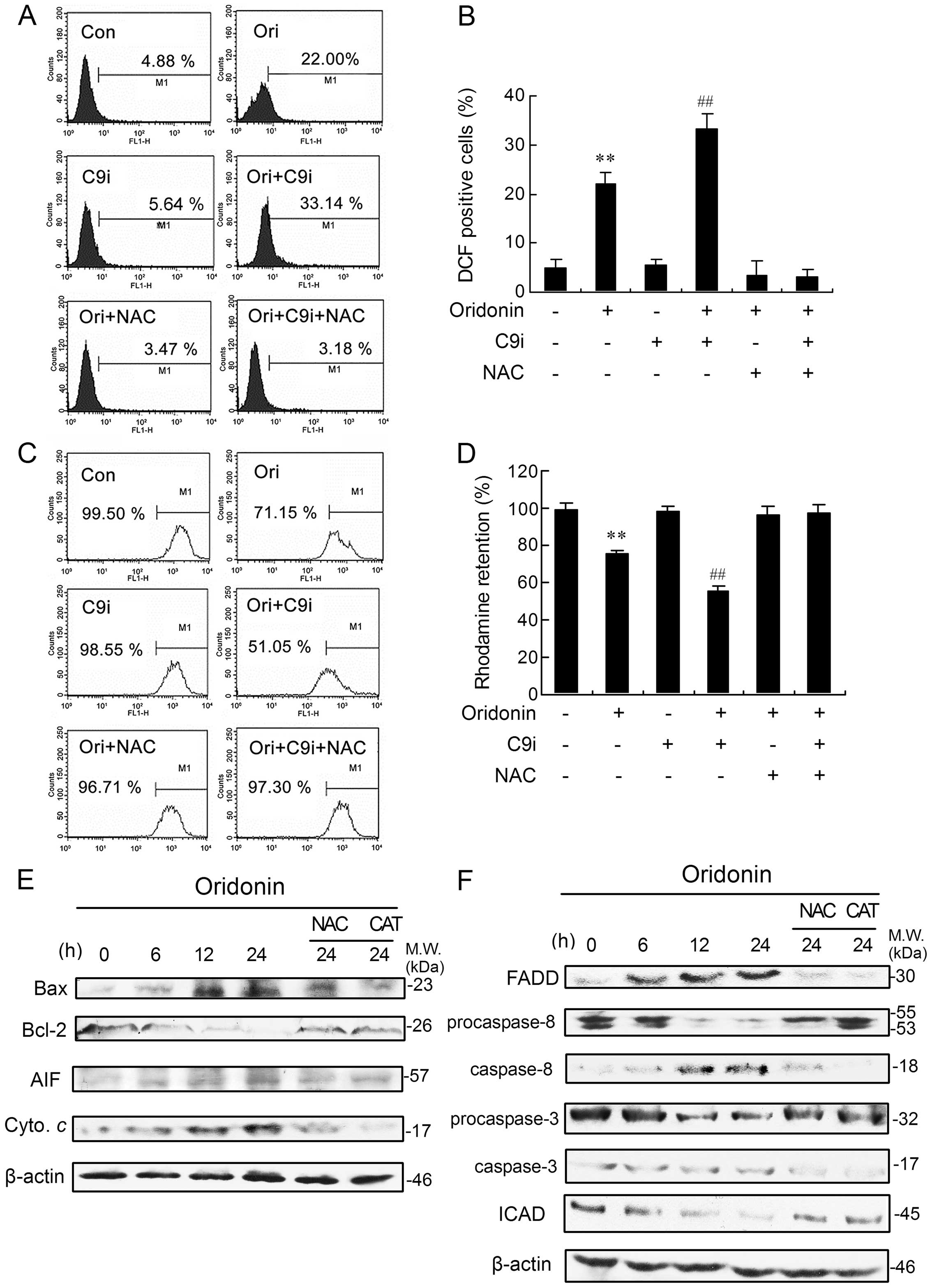
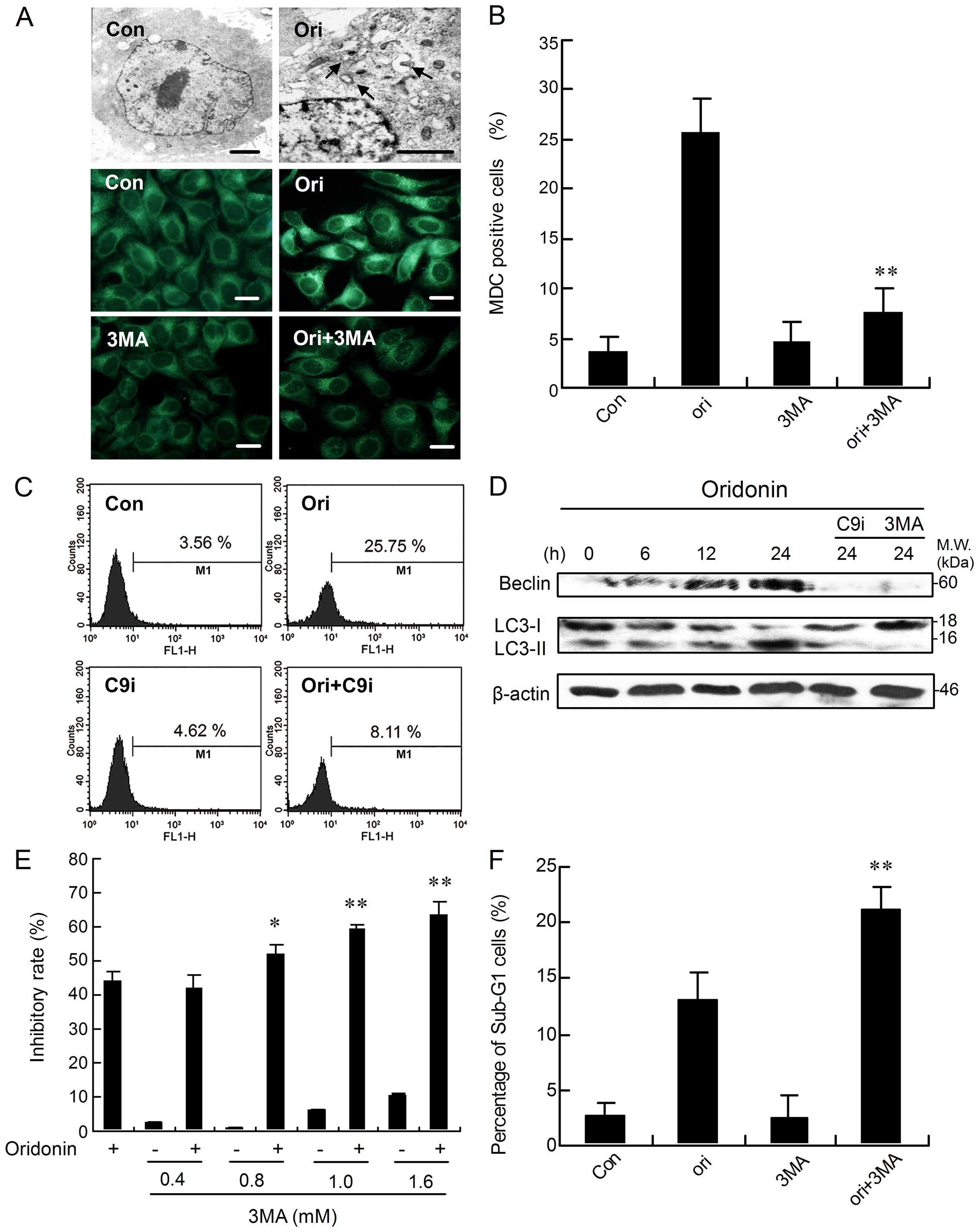
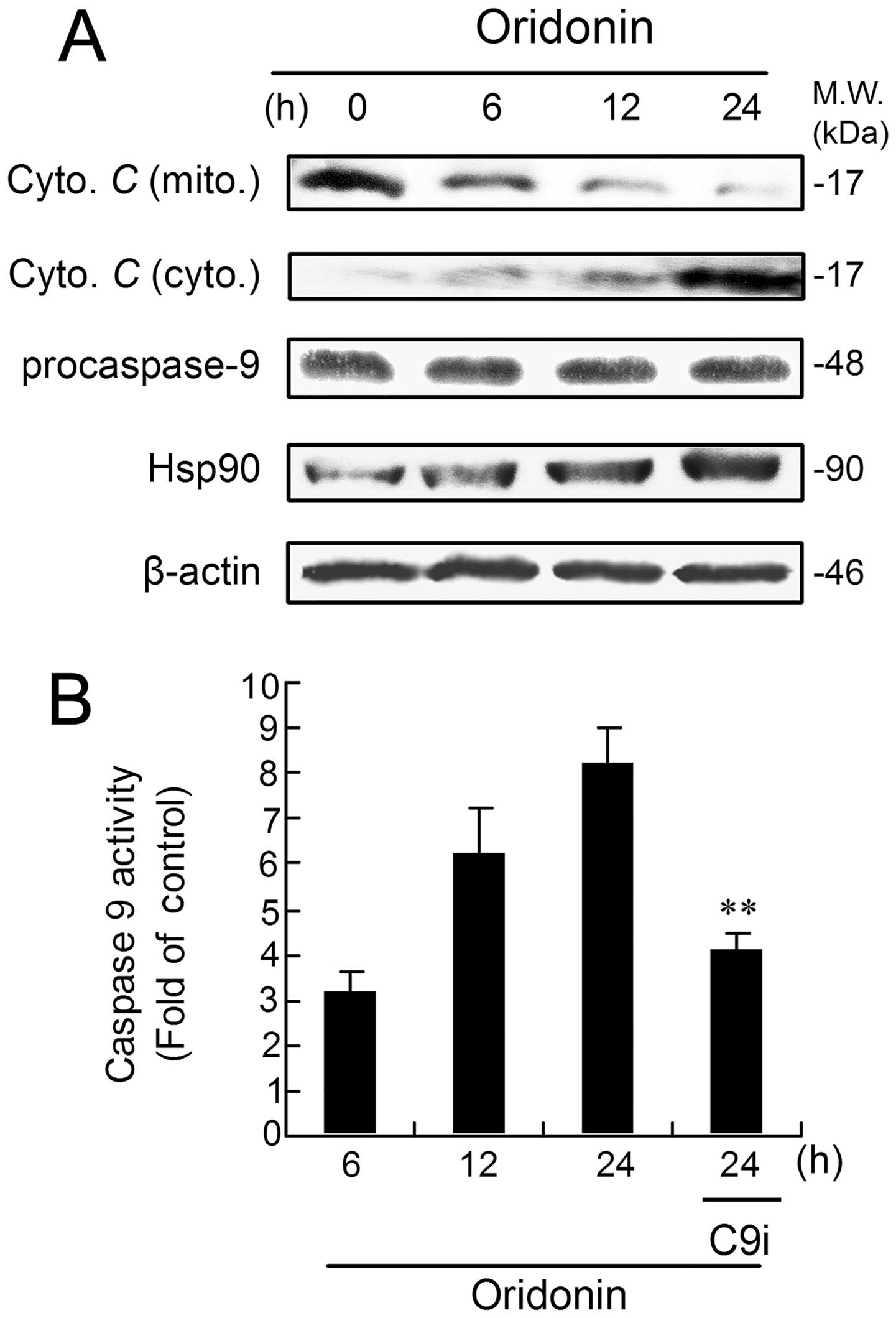
|
1
|
Danial NN and Korsmeyer SJ: Cell death:
Critical control points. Cell. 116:205–219. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Yuan J and Yankner BA: Apoptosis in the
nervous system. Nature. 407:802–809. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: The hallmarks
of cancer. Cell. 100:57–70. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Nathan C: Specificity of a third kind:
Reactive oxygen and nitrogen intermediates in cell signaling. J
Clin Invest. 111:769–778. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ohsawa I, Ishikawa M, Takahashi K,
Watanabe M, Nishimaki K, Yamagata K, Katsura K, Katayama Y, Asoh S
and Ohta S: Hydrogen acts as a therapeutic antioxidant by
selectively reducing cytotoxic oxygen radicals. Nat Med.
13:688–694. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Pelicano H, Carney D and Huang P: ROS
stress in cancer cells and therapeutic implications. Drug Resist
Updat. 7:97–110. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Reggiori F and Klionsky DJ: Autophagy in
the eukaryotic cell. Eukaryot Cell. 1:11–21. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Mathew R, Karantza-Wadsworth V and White
E: Role of autophagy in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 7:961–967. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Amaravadi RK and Thompson CB: The roles of
therapy-induced autophagy and necrosis in cancer treatment. Clin
Cancer Res. 13:7271–7279. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Mizushima N, Levine B, Cuervo AM and
Klionsky DJ: Autophagy fights disease through cellular
self-digestion. Nature. 451:1069–1075. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Marioni G, Marchese-Ragona R, Cartei G,
Marchese F and Staffieri A: Current opinion in diagnosis and
treatment of laryngeal carcinoma. Cancer Treat Rev. 32:504–515.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Rafferty MA, Fenton JE and Jones AS: The
history, aetiology and epidemiology of laryngeal carcinoma. Clin
Otolaryngol Allied Sci. 26:442–446. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Wang Z, Wang N, Chen J and Shen J:
Emerging glycolysis targeting and drug discovery from Chinese
medicine in cancer therapy. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.
2012:8731752012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yang YC, Wei MC and Huang TC: Optimisation
of an ultrasound-assisted extraction followed by RP-HPLC separation
for the simultaneous determination of oleanolic acid, ursolic acid
and oridonin content in Rabdosia rubescens. Phytochem Anal.
23:627–636. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Fujita T, Takeda Y, Sun HD, Minami Y,
Marunaka T, Takeda S, Yamada Y and Togo T: Cytotoxic and antitumor
activities of Rabdosia diterpenoids. Planta Med. 54:414–417. 1988.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Huang J, Wu L, Tashiro S, Onodera S and
Ikejima T: Reactive oxygen species mediate oridonin-induced HepG2
apoptosis through p53, MAPK, and mitochondrial signaling pathways.
J Pharmacol Sci. 107:370–379. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kang N, Zhang JH, Qiu F, Chen S, Tashiro
S, Onodera S and Ikejima T: Induction of G(2)/M phase arrest and
apoptosis by oridonin in human laryngeal carcinoma cells. J Nat
Prod. 73:1058–1063. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wu JN, Huang J, Yang J, Tashiro S, Onodera
S and Ikejima T: Caspase inhibition augmented oridonin-induced cell
death in murine fibrosarcoma l929 by enhancing reactive oxygen
species generation. J Pharmacol Sci. 108:32–39. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Shah N, Asch RJ, Lysholm AS and Lebien TW:
Enhancement of stress-induced apoptosis in B-lineage cells by
caspase-9 inhibitor. Blood. 104:2873–2878. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kang N, Zhang JH, Qiu F, Tashiro S,
Onodera S and Ikejima T: Inhibition of EGFR signaling augments
oridonin-induced apoptosis in human laryngeal cancer cells via
enhancing oxidative stress coincident with activation of both the
intrinsic and extrinsic apoptotic pathways. Cancer Lett.
294:147–158. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lu Y, Sun C and Pan Y: Isolation and
purification of oridonin from Rabdosia rubescens using upright
counter-current chromatography. J Sep Sci. 29:314–318. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yu C and Wang L, Lv B, Lu Y, Zeng L, Chen
Y, Ma D, Shi T and Wang L: TMEM74, a lysosome and autophagosome
protein, regulates autophagy. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
369:622–629. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kim RH, Coates JM, Bowles TL, McNerney GP,
Sutcliffe J, Jung JU, Gandour-Edwards R, Chuang FY, Bold RJ and
Kung HJ: Arginine deiminase as a novel therapy for prostate cancer
induces autophagy and caspase-independent apoptosis. Cancer Res.
69:700–708. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhang Y, Wu Y, Cheng Y, Zhao Z, Tashiro S,
Onodera S and Ikejima T: Fas-mediated autophagy requires JNK
activation in HeLa cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
377:1205–1210. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang HJ, Tashiro S, Onodera S and Ikejima
T: Inhibition of insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor signaling
enhanced silibinin-induced activation of death receptor and
mitochondrial apoptotic pathways in human breast cancer MCF-7
cells. J Pharmacol Sci. 107:260–269. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Schumacker PT: Reactive oxygen species in
cancer cells: Live by the sword, die by the sword. Cancer Cell.
10:175–176. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Sablina AA, Budanov AV, Ilyinskaya GV,
Agapova LS, Kravchenko JE and Chumakov PM: The antioxidant function
of the p53 tumor suppressor. Nat Med. 11:1306–1313. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wong YT, Ruan R and Tay FE: Relationship
between levels of oxidative DNA damage, lipid peroxidation and
mitochondrial membrane potential in young and old F344 rats. Free
Radic Res. 40:393–402. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Sakahira H, Enari M and Nagata S:
Functional differences of two forms of the inhibitor of
caspase-activated DNase, ICAD-L, and ICAD-S. J Biol Chem.
274:15740–15744. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Trejo-Solís C, Jimenez-Farfan D,
Rodriguez-Enriquez S, Fernandez-Valverde F, Cruz-Salgado A,
Ruiz-Azuara L and Sotelo J: Copper compound induces autophagy and
apoptosis of glioma cells by reactive oxygen species and JNK
activation. BMC Cancer. 12:1562012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Cain K, Bratton SB, Langlais C, Walker G,
Brown DG, Sun XM and Cohen GM: Apaf-1 oligomerizes into
biologically active approximately 700-kDa and inactive
approximately 1.4-MDa apoptosome complexes. J Biol Chem.
275:6067–6070. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hu Y, Benedict MA, Ding L and Núñez G:
Role of cytochrome c and dATP/ATP hydrolysis in Apaf-1-mediated
caspase-9 activation and apoptosis. EMBO J. 18:3586–3595. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Pandey P, Saleh A, Nakazawa A, Kumar S,
Srinivasula SM, Kumar V, Weichselbaum R, Nalin C, Alnemri ES, Kufe
D, et al: Negative regulation of cytochrome c-mediated
oligomerization of Apaf-1 and activation of procaspase-9 by heat
shock protein 90. EMBO J. 19:4310–4322. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Liu JR, Opipari AW, Tan L, Jiang Y, Zhang
Y, Tang H and Nuñez G: Dysfunctional apoptosome activation in
ovarian cancer: Implications for chemoresistance. Cancer Res.
62:924–931. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lee KH: Anticancer drug design based on
plant-derived natural products. J Biomed Sci. 6:236–250.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Herrera B, Alvarez AM, Sánchez A,
Fernández M, Roncero C, Benito M and Fabregat I: Reactive oxygen
species (ROS) mediates the mitochondrial-dependent apoptosis
induced by transforming growth factor (beta) in fetal hepatocytes.
FASEB J. 15:741–751. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Herrera B, Fernández M, Alvarez AM,
Roncero C, Benito M, Gil J and Fabregat I: Activation of caspases
occurs downstream from radical oxygen species production, Bcl-xL
down-regulation, and early cytochrome C release in apoptosis
induced by transforming growth factor beta in rat fetal
hepatocytes. Hepatology. 34:548–556. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Chen Q, Chai YC, Mazumder S, Jiang C,
Macklis RM, Chisolm GM and Almasan A: The late increase in
intracellular free radical oxygen species during apoptosis is
associated with cytochrome c release, caspase activation, and
mitochondrial dysfunction. Cell Death Differ. 10:323–334. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Daugas E, Nochy D, Ravagnan L, Loeffler M,
Susin SA, Zamzami N and Kroemer G: Apoptosis-inducing factor (AIF):
A ubiquitous mitochondrial oxidoreductase involved in apoptosis.
FEBS Lett. 476:118–123. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Mitsiades CS, Poulaki V, Fanourakis G,
Sozopoulos E, McMillin D, Wen Z, Voutsinas G, Tseleni-Balafouta S
and Mitsiades N: Fas signaling in thyroid carcinomas is diverted
from apoptosis to proliferation. Clin Cancer Res. 12:3705–3712.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Chandra J, Samali A and Orrenius S:
Triggering and modulation of apoptosis by oxidative stress. Free
Radic Biol Med. 29:323–333. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Jeong HS, Choi HY, Lee ER, Kim JH, Jeon K,
Lee HJ and Cho SG: Involvement of caspase-9 in autophagy-mediated
cell survival pathway. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1813.80–90. 2011.
|
|
43
|
Norman JM, Cohen GM and Bampton ET: The in
vitro cleavage of the hAtg proteins by cell death proteases.
Autophagy. 6:1042–1056. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Young MM, Takahashi Y, Khan O, Park S,
Hori T, Yun J, Sharma AK, Amin S, Hu CD, Zhang J, et al:
Autophagosomal membrane serves as platform for intracellular
death-inducing signaling complex (iDISC)-mediated caspase-8
activation and apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 287:12455–12468. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Cho DH, Jo YK, Hwang JJ, Lee YM, Roh SA
and Kim JC: Caspase-mediated cleavage of ATG6/Beclin-1 links
apoptosis to autophagy in HeLa cells. Cancer Lett. 274:95–100.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Wang ZH, Xu L, Duan ZL, Zeng LQ, Yan NH
and Peng ZL: Beclin 1-mediated macroautophagy involves regulation
of caspase-9 expression in cervical cancer HeLa cells. Gynecol
Oncol. 107:107–113. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Lum JJ, Bauer DE, Kong M, Harris MH, Li C,
Lindsten T and Thompson CB: Growth factor regulation of autophagy
and cell survival in the absence of apoptosis. Cell. 120:237–248.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Crighton D, Wilkinson S, O'Prey J, Syed N,
Smith P, Harrison PR, Gasco M, Garrone O, Crook T and Ryan KM:
DRAM, a p53-induced modulator of autophagy, is critical for
apoptosis. Cell. 126:121–134. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Rodriguez J and Lazebnik Y: Caspase-9 and
APAF-1 form an active holoenzyme. Genes Dev. 13:3179–3184. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Stennicke HR, Deveraux QL, Humke EW, Reed
JC, Dixit VM and Salvesen GS: Caspase-9 can be activated without
proteolytic processing. J Biol Chem. 274:8359–8362. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|