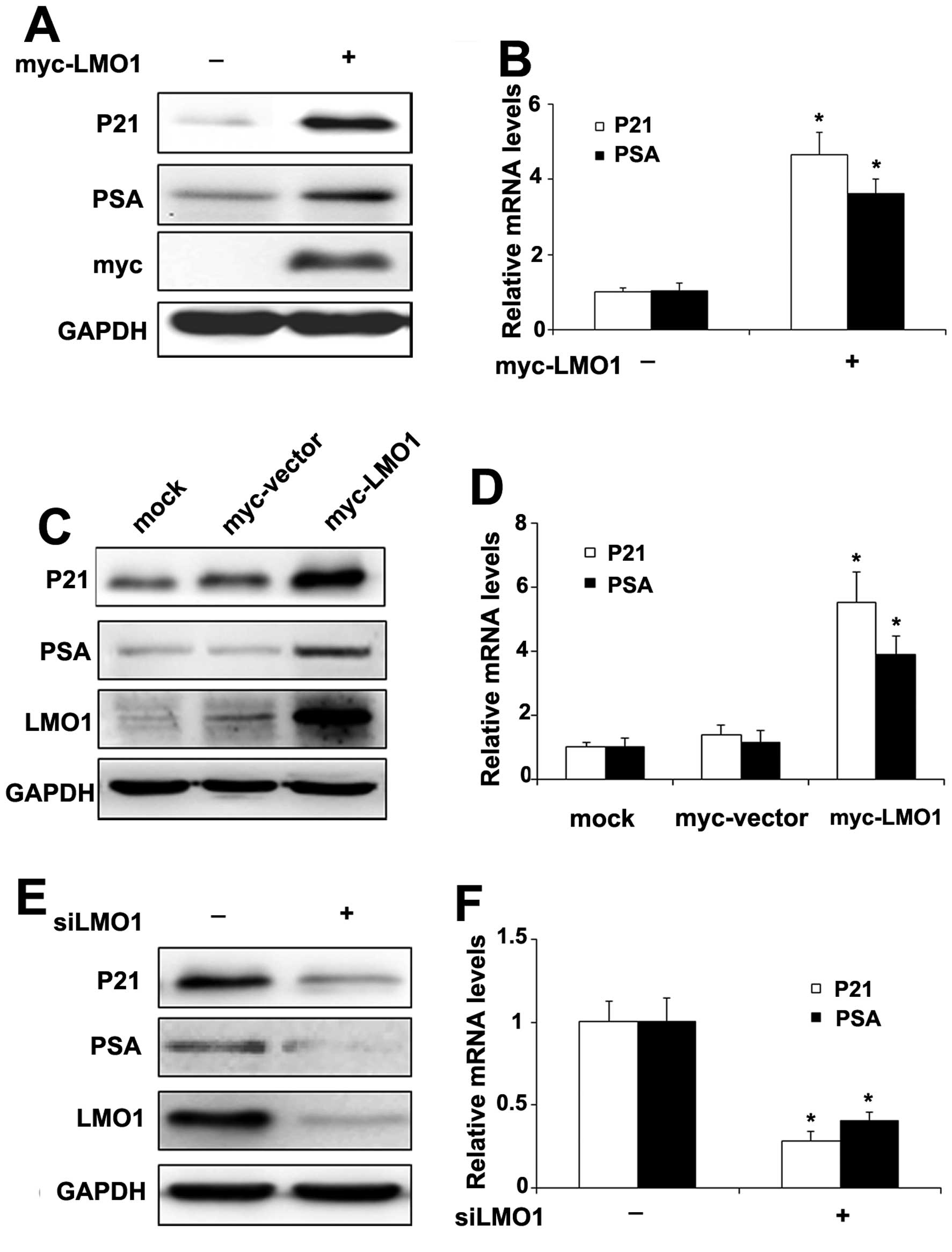
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 65:5–29. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Yap TA, Zivi A, Omlin A and de Bono JS:
The changing therapeutic landscape of castration-resistant prostate
cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 8:597–610. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zhou Y, Bolton EC and Jones JO: Androgens
and androgen receptor signaling in prostate tumorigenesis. J Mol
Endocrinol. 54:R15–R29. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Gelmann EP: Molecular biology of the
androgen receptor. J Clin Oncol. 20:3001–3015. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Heinlein CA and Chang C: Androgen receptor
in prostate cancer. Endocr Rev. 25:276–308. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Heemers HV and Tindall DJ: Androgen
receptor (AR) coregulators: A diversity of functions converging on
and regulating the AR transcriptional complex. Endocr Rev.
28:778–808. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chmelar R, Buchanan G, Need EF, Tilley W
and Greenberg NM: Androgen receptor coregulators and their
involvement in the development and progression of prostate cancer.
Int J Cancer. 120:719–733. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Boehm T, Foroni L, Kennedy M and Rabbitts
TH: The rhombotin gene belongs to a class of transcriptional
regulators with a potential novel protein dimerisation motif.
Oncogene. 5:1103–1105. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Jurata LW and Gill GN: Structure and
function of LIM domains. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 228:75–113.
1998.
|
|
10
|
Dawid IB, Breen JJ and Toyama R: LIM
domains: Multiple roles as adapters and functional modifiers in
protein interactions. Trends Genet. 14:156–162. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Matthews JM, Lester K, Joseph S and Curtis
DJ: LIM-domain-only proteins in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 13:111–122.
2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Rabbitts TH: LMO T-cell translocation
oncogenes typify genes activated by chromosomal translocations that
alter transcription and developmental processes. Genes Dev.
12:2651–2657. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Liu T, Li Y, Gu H, Zhu G, Li J, Cao L and
Li F: p21-Activated kinase 6 (PAK6) inhibits prostate cancer growth
via phosphorylation of androgen receptor and tumorigenic E3 ligase
murine double minute-2 (Mdm2). J Biol Chem. 288:3359–3369. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
14
|
Chmelar R, Buchanan G, Need EF, Tilley W
and Greenberg NM: Downregulation of p21-activated kinase-1 inhibits
the growth of gastric cancer cells involving cyclin B1. Int J
Cancer. 125:2511–2519. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Berchuck A, Soisson AP, Clarke-Pearson DL,
Soper JT, Boyer CM, Kinney RB, McCarty KS Jr and Bast RC Jr:
Immunohistochemical expression of CA 125 in endometrial
adenocarcinoma: Correlation of antigen expression with metastatic
potential. Cancer Res. 49:2091–2095. 1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang C, Li Y, Zhang H, Liu F, Cheng Z,
Wang D, Wang G, Xu H, Zhao Y, Cao L, et al: Oncogenic PAK4
regulates Smad2/3 axis involving gastric tumorigenesis. Oncogene.
33:3473–3484. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Li Y, Shao Y, Tong Y, Shen T, Zhang J, Li
Y, Gu H and Li F: Nucleo-cytoplasmic shuttling of PAK4 modulates
β-catenin intracellular translocation and signaling. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1823:465–475. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Riegman PH, Vlietstra RJ, van der Korput
JA, Brinkmann AO and Trapman J: The promoter of the
prostate-specific antigen gene contains a functional androgen
responsive element. Mol Endocrinol. 5:1921–1930. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lu S, Liu M, Epner DE, Tsai SY and Tsai
MJ: Androgen regulation of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor
p21 gene through an androgen response element in the proximal
promoter. Mol Endocrinol. 13:376–384. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Cleutjens KB, van Eekelen CC, van der
Korput HA, Brinkmann AO and Trapman J: Two androgen response
regions cooperate in steroid hormone regulated activity of the
prostate-specific antigen promoter. J Biol Chem. 271:6379–6388.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Taplin ME and Balk SP: Androgen receptor:
A key molecule in the progression of prostate cancer to hormone
independence. J Cell Biochem. 91:483–490. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Debes JD and Tindall DJ: Mechanisms of
androgen-refractory prostate cancer. N Engl J Med. 351:1488–1490.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Boehm T, Baer R, Lavenir I, Forster A,
Waters JJ, Nacheva E and Rabbitts TH: The mechanism of chromosomal
translocation t(11;14) involving the T-cell receptor C delta locus
on human chromosome 14q11 and a transcribed region of chromosome
11p15. EMBO J. 7:385–394. 1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Boehm T, Foroni L, Kaneko Y, Perutz MF and
Rabbitts TH: The rhombotin family of cysteine-rich LIM-domain
oncogenes: Distinct members are involved in T-cell translocations
to human chromosomes 11p15 and 11p13. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
88:4367–4371. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Van Vlierberghe P, van Grotel M, Beverloo
HB, Lee C, Helgason T, Buijs-Gladdines J, Passier M, van Wering ER,
Veerman AJ, Kamps WA, et al: The cryptic chromosomal deletion
del(11)(p12p13) as a new activation mechanism of LMO2 in pediatric
T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood. 108:3520–3529. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ferrando AA, Neuberg DS, Staunton J, Loh
ML, Huard C, Raimondi SC, Behm FG, Pui CH, Downing JR, Gilliland
DG, et al: Gene expression signatures define novel oncogenic
pathways in T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Cancer Cell.
1:75–87. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Tremblay M, Tremblay CS, Herblot S, Aplan
PD, Hébert J, Perreault C and Hoang T: Modeling T-cell acute
lymphoblastic leukemia induced by the SCL and LMO1 oncogenes. Genes
Dev. 24:1093–1105. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Neale GA, Rehg JE and Goorha RM:
Disruption of T-cell differentiation precedes T-cell tumor
formation in LMO-2 (rhombotin-2) transgenic mice. Leukemia.
11(Suppl 3): 289–290. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wang K, Diskin SJ, Zhang H, Attiyeh EF,
Winter C, Hou C, Schnepp RW, Diamond M, Bosse K, Mayes PA, et al:
Integrative genomics identifies LMO1 as a neuroblastoma oncogene.
Nature. 469:216–220. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Aoyama M, Ozaki T, Inuzuka H, Tomotsune D,
Hirato J, Okamoto Y, Tokita H, Ohira M and Nakagawara A: LMO3
interacts with neuronal transcription factor, HEN2, and acts as an
oncogene in neuroblastoma. Cancer Res. 65:4587–4597. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Montañez-Wiscovich ME, Seachrist DD,
Landis MD, Visvader J, Andersen B and Keri RA: LMO4 is an essential
mediator of ErbB2/HER2/Neu-induced breast cancer cell cycle
progression. Oncogene. 28:3608–3618. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wang N, Lin KK, Lu Z, Lam KS, Newton R, Xu
X, Yu Z, Gill GN and Andersen B: The LIM-only factor LMO4 regulates
expression of the BMP7 gene through an HDAC2-dependent mechanism,
and controls cell proliferation and apoptosis of mammary epithelial
cells. Oncogene. 26:6431–6441. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ma S, Guan XY, Beh PS, Wong KY, Chan YP,
Yuen HF, Vielkind J and Chan KW: The significance of LMO2
expression in the progression of prostate cancer. J Pathol.
211:278–285. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Levine AJ: p53, the cellular gatekeeper
for growth and division. Cell. 88:323–331. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wang J and Walsh K: Resistance to
apoptosis conferred by Cdk inhibitors during myocyte
differentiation. Science. 273:359–361. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Lu S, Tsai SY and Tsai MJ: Molecular
mechanisms of androgen-independent growth of human prostate cancer
LNCaP-AI cells. Endocrinology. 140:5054–5059. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Omar EA, Behlouli H, Chevalier S and
Aprikian AG: Relationship of p21(WAF-I) protein expression with
prognosis in advanced prostate cancer treated by androgen ablation.
Prostate. 49:191–199. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Fizazi K, Martinez LA, Sikes CR, Johnston
DA, Stephens LC, McDonnell TJ, Logothetis CJ, Trapman J, Pisters L,
et al: The association of p21(WAF-1/CIP1) with
progression to androgen-independent prostate cancer. Clin Cancer
Res. 8:775–781. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Gorospe M, Cirielli C, Wang X, Seth P,
Capogrossi MC and Holbrook NJ: p21Waf1/Cip1 protects
against p53-mediated apoptosis of human melanoma cells. Oncogene.
14:929–935. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Gittes RF: Carcinoma of the prostate. N
Engl J Med. 324:236–245. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|