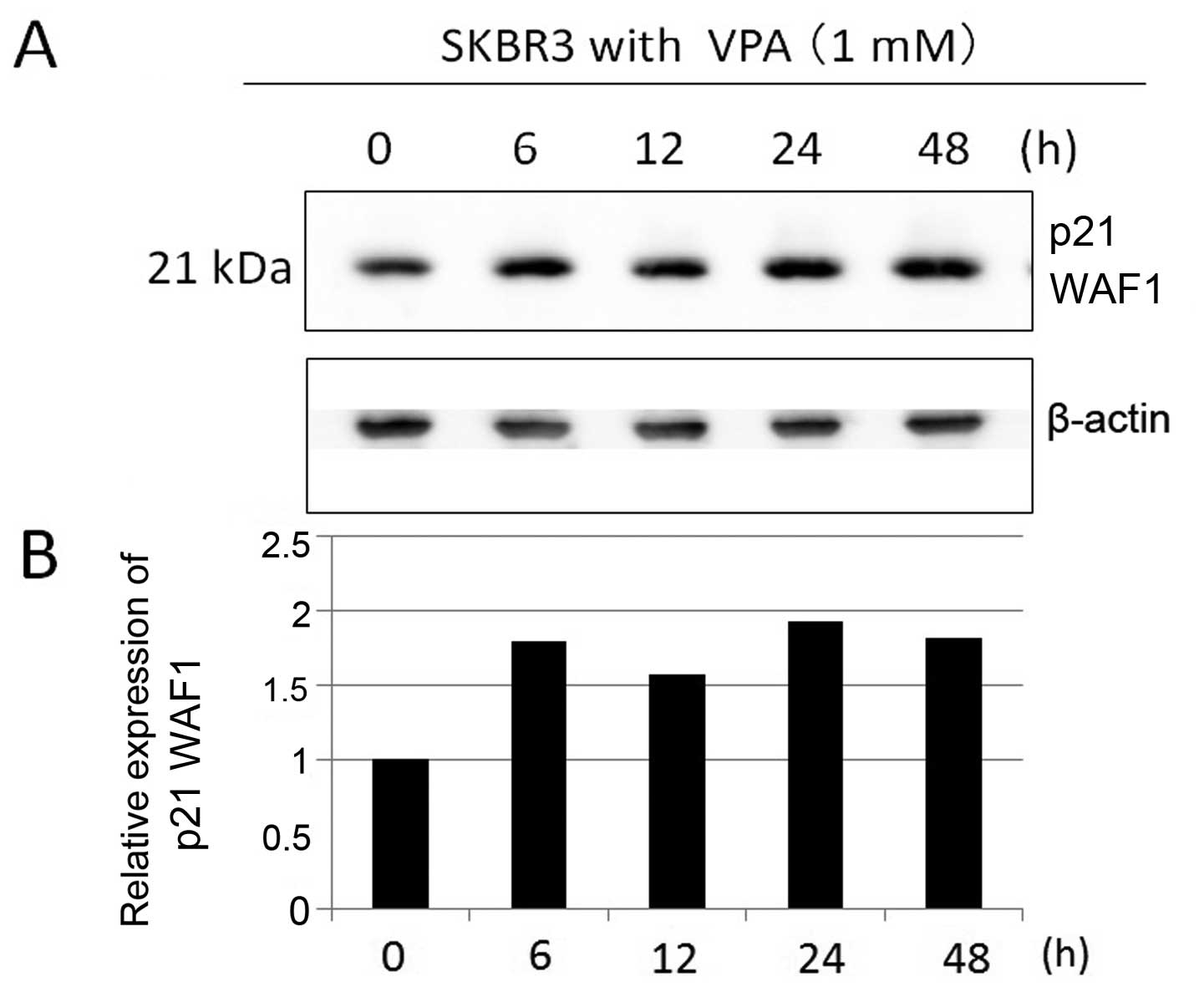
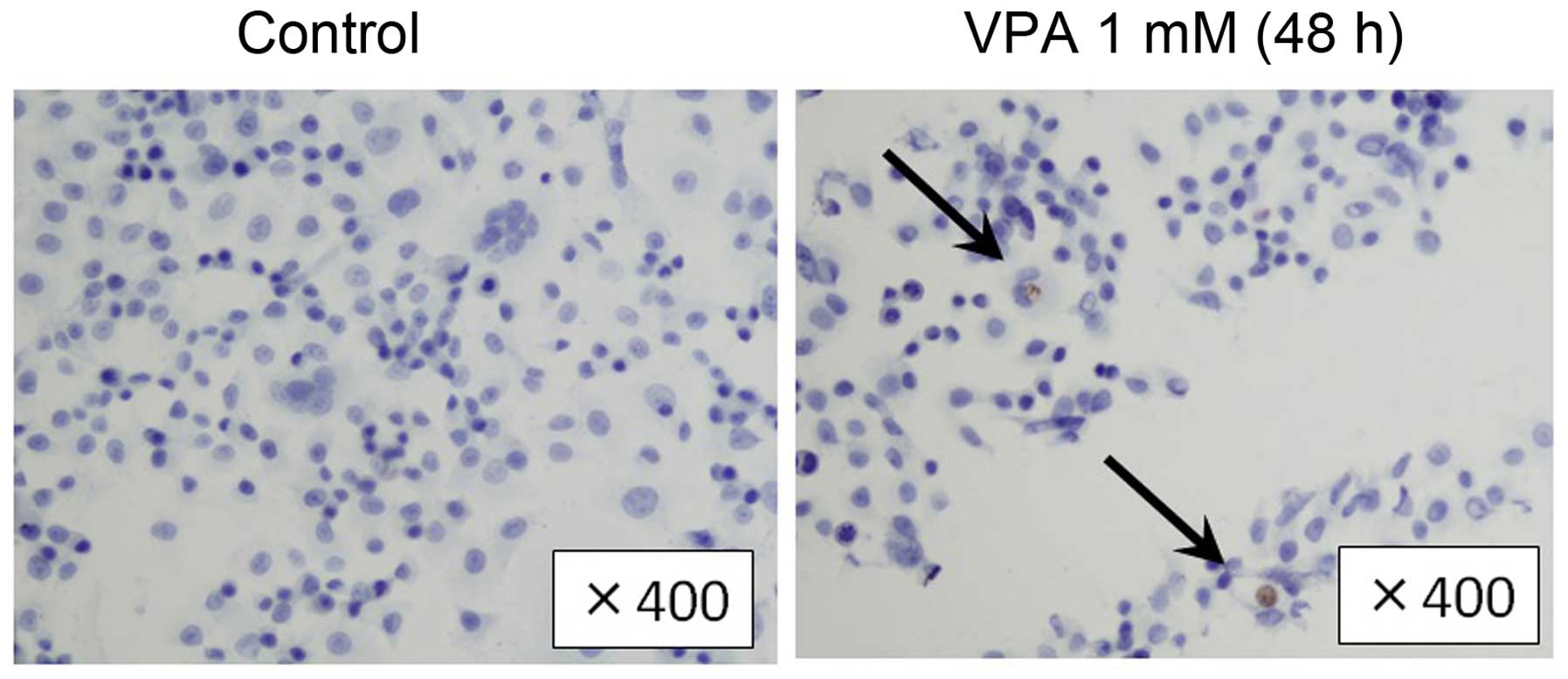
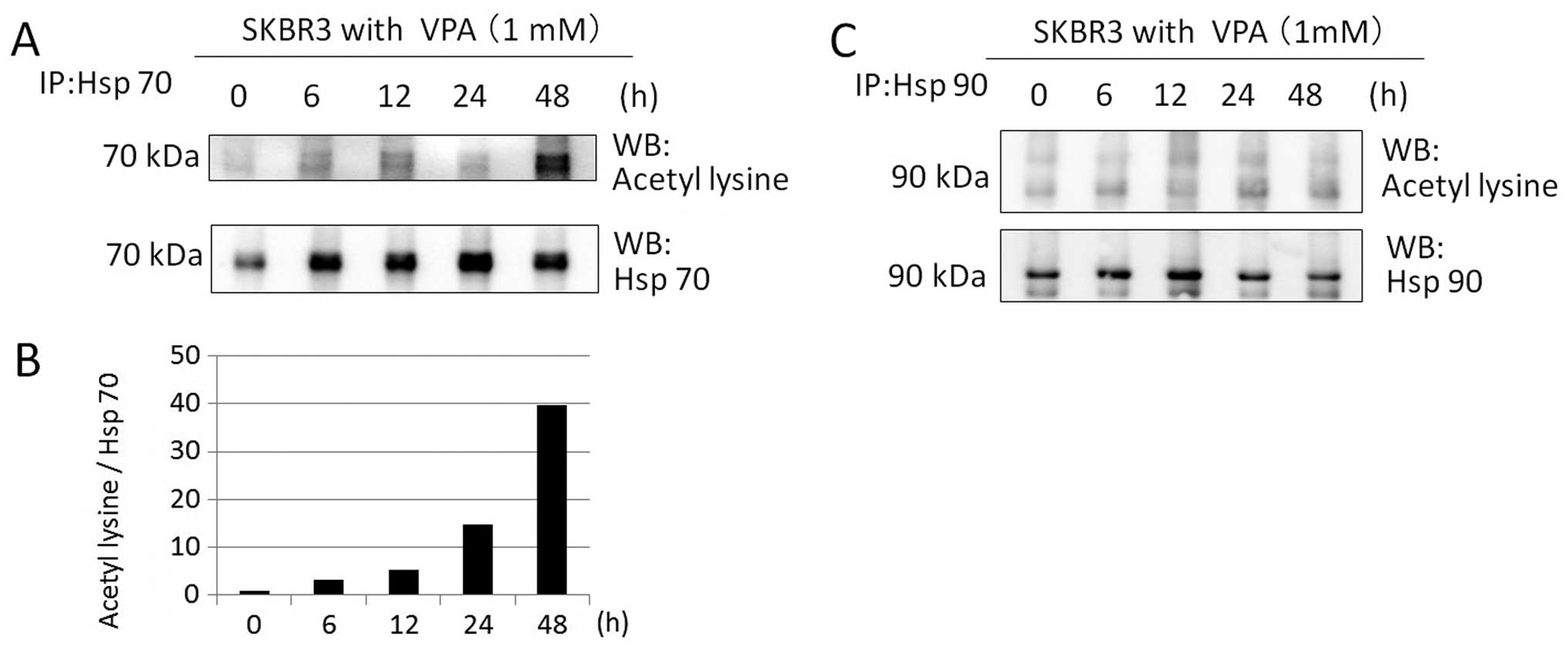
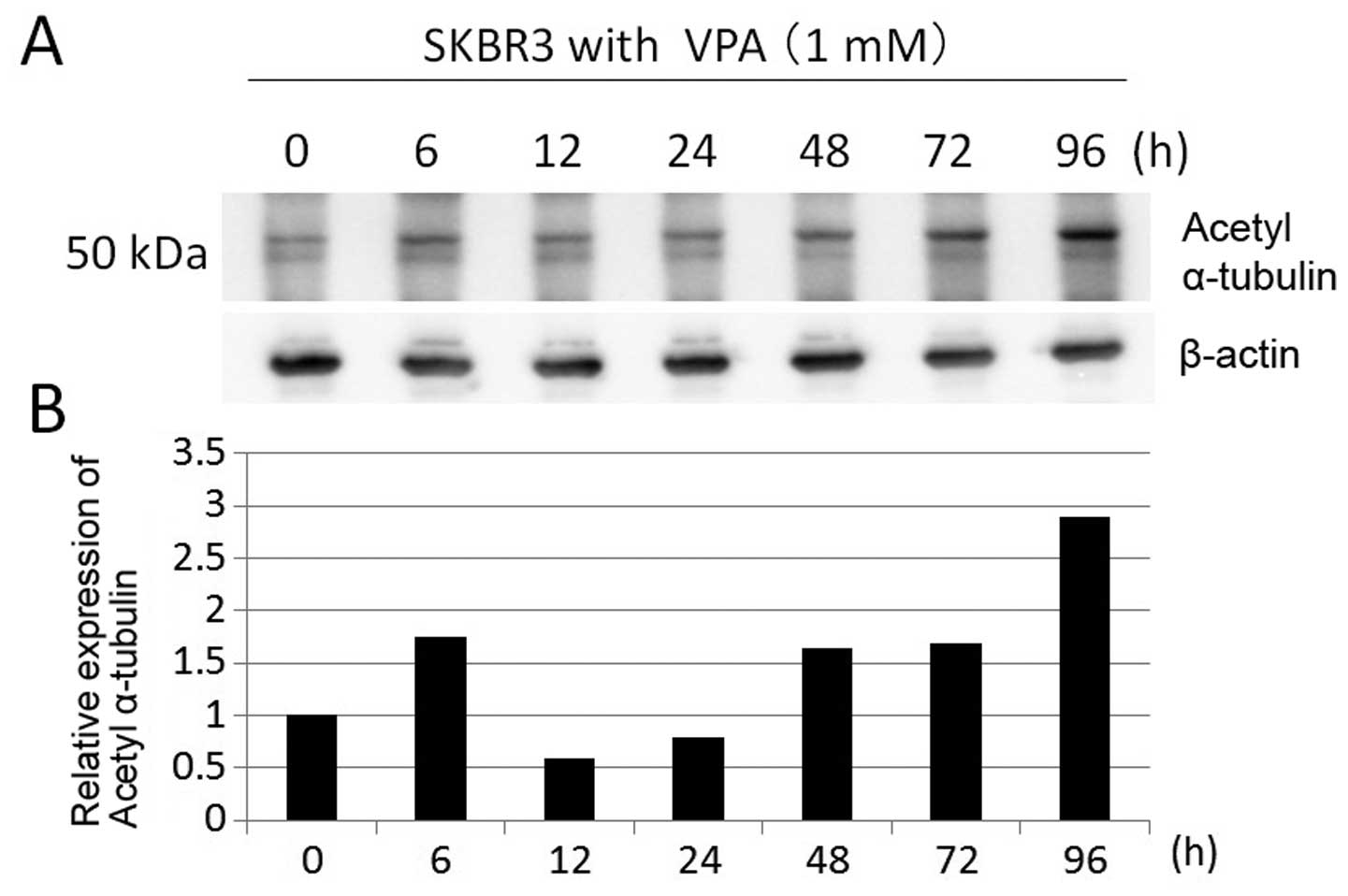
|
1
|
von Minckwitz G, Untch M, Blohmer JU,
Costa SD, Eidtmann H, Fasching PA, Gerber B, Eiermann W, Hilfrich
J, Huober J, et al: Definition and impact of pathologic complete
response on prognosis after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in various
intrinsic breast cancer subtypes. J Clin Oncol. 30:1796–1804. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Fang JY and Lu YY: Effects of histone
acetylation and DNA methylation on p21(WAF1) regulation. World J
Gastroenterol. 8:400–405. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Jenuwein T and Allis CD: Translating the
histone code. Science. 293:1074–1080. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Davie JR and Moniwa M: Control of
chromatin remodeling. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 10:303–325.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Bolden JE, Peart MJ and Johnstone RW:
Anticancer activities of histone deacetylase inhibitors. Nat Rev
Drug Discov. 5:769–784. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Monneret C: Histone deacetylase
inhibitors. Eur J Med Chem. 40:1–13. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sami S, Höti N, Xu HM, Shen Z and Huang X:
Valproic acid inhibits the growth of cervical cancer both in vitro
and in vivo. J Biochem. 144:357–362. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Krämer OH, Zhu P, Ostendorff HP,
Golebiewski M, Tiefenbach J, Peters MA, Brill B, Groner B, Bach I,
Heinzel T, et al: The histone deacetylase inhibitor valproic acid
selectively induces proteasomal degradation of HDAC2. EMBO J.
22:3411–3420. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Göttlicher M, Minucci S, Zhu P, Krämer OH,
Schimpf A, Giavara S, Sleeman JP, Lo Coco F, Nervi C, Pelicci PG,
et al: Valproic acid defines a novel class of HDAC inhibitors
inducing differentiation of transformed cells. EMBO J.
20:6969–6978. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hrzenjak A, Moinfar F, Kremser ML,
Strohmeier B, Staber PB, Zatloukal K and Denk H: Valproate
inhibition of histone deacetylase 2 affects differentiation and
decreases proliferation of endometrial stromal sarcoma cells. Mol
Cancer Ther. 5:2203–2210. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Rocchi P, Tonelli R, Camerin C, Purgato S,
Fronza R, Bianucci F, Guerra F, Pession A and Ferreri AM:
p21Waf1/Cip1 is a common target induced by short-chain fatty acid
HDAC inhibitors (valproic acid, tributyrin and sodium butyrate) in
neuroblastoma cells. Oncol Rep. 13:1139–1144. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Takai N and Narahara H, Takai N and
Narahara H: Human endometrial and ovarian cancer cells: Histone
deacetylase inhibitors exhibit antiproliferative activity, potently
induce cell cycle arrest, and stimulate apoptosis. Curr Med Chem.
14:2548–2553. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yu X, Guo ZS, Marcu MG, Neckers L, Nguyen
DM, Chen GA and Schrump DS: Modulation of p53, ErbB1, ErbB2, and
Raf-1 expression in lung cancer cells by depsipeptide FR901228. J
Natl Cancer Inst. 94:504–513. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Blagosklonny MV, Robey R, Sackett DL, Du
L, Traganos F, Darzynkiewicz Z, Fojo T and Bates SE: Histone
deacetylase inhibitors all induce p21 but differentially cause
tubulin acetylation, mitotic arrest, and cytotoxicity. Mol Cancer
Ther. 1:937–941. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Catalano MG, Poli R, Pugliese M, Fortunati
N and Boccuzzi G: Valproic acid enhances tubulin acetylation and
apoptotic activity of paclitaxel on anaplastic thyroid cancer cell
lines. Endocr Relat Cancer. 14:839–845. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Fortunati N, Bertino S, Costantino L,
Bosco O, Vercellinatto I, Catalano MG and Boccuzzi G: Valproic acid
is a selective antiproliferative agent in estrogen-sensitive breast
cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 259:156–164. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Travaglini L, Vian L, Billi M, Grignani F
and Nervi C: Epigenetic reprogramming of breast cancer cells by
valproic acid occurs regardless of estrogen receptor status. Int J
Biochem Cell Biol. 41:225–234. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Zhang L, Wang G, Wang L, Song C, Leng Y,
Wang X and Kang J: VPA inhibits breast cancer cell migration by
specifically targeting HDAC2 and down-regulating Survivin. Mol Cell
Biochem. 361:39–45. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Nimmanapalli R, Fuino L, Bali P,
Gasparetto M, Glozak M, Tao J, Moscinski L, Smith C, Wu J, Jove R,
et al: Histone deacetylase inhibitor LAQ824 both lowers expression
and promotes proteasomal degradation of Bcr-Abl and induces
apoptosis of imatinib mesylate-sensitive or -refractory chronic
myelogenous leukemia-blast crisis cells. Cancer Res. 63:5126–5135.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hubbert C, Guardiola A, Shao R, Kawaguchi
Y, Ito A, Nixon A, Yoshida M, Wang XF and Yao TP: HDAC6 is a
microtubule-associated deacetylase. Nature. 417:455–458. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bali P, Pranpat M, Bradner J, Balasis M,
Fiskus W, Guo F, Rocha K, Kumaraswamy S, Boyapalle S, Atadja P, et
al: Inhibition of histone deacetylase 6 acetylates and disrupts the
chaperone function of heat shock protein 90: A novel basis for
antileukemia activity of histone deacetylase inhibitors. J Biol
Chem. 280:26729–26734. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bali P, Pranpat M, Swaby R, et al:
Activity of suberoylanilide hydroxamic Acid against human breast
cancer cells with amplification of her-2. Clin Cancer Res.
11:6382–6389. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kovacs JJ, Murphy PJ, Gaillard S, Zhao X,
Wu JT, Nicchitta CV, Yoshida M, Toft DO, Pratt WB and Yao TP: HDAC6
regulates Hsp90 acetylation and chaperone-dependent activation of
gluco-corticoid receptor. Mol Cell. 18:601–607. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Powers MV, Clarke PA and Workman P: Death
by chaperone: HSP90, HSP70 or both? Cell Cycle. 8:518–526. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Pratt WB and Toft DO: Regulation of
signaling protein function and trafficking by the hsp90/hsp70-based
chaperone machinery. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 228:111–133. 2003.
|
|
26
|
Boyault C, Zhang Y, Fritah S, Caron C,
Gilquin B, Kwon SH, Garrido C, Yao TP, Vourc'h C, Matthias P, et
al: HDAC6 controls major cell response pathways to cytotoxic
accumulation of protein aggregates. Genes Dev. 21:2172–2181. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhang Y, Li N, Caron C, Matthias G, Hess
D, Khochbin S and Matthias P: HDAC-6 interacts with and
deacetylates tubulin and microtubules in vivo. EMBO J.
22:1168–1179. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Furumai R, Matsuyama A, Kobashi N, Lee KH,
Nishiyama M, Nakajima H, Tanaka A, Komatsu Y, Nishino N, Yoshida M,
et al: FK228 (depsipeptide) as a natural prodrug that inhibits
class I histone deacetylases. Cancer Res. 62:4916–4921.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Neckers L: Hsp90 inhibitors as novel
cancer chemotherapeutic agents. Trends Mol Med. 8(Suppl): S55–S61.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Giacinti L, Giacinti C, Gabellini C,
Rizzuto E, Lopez M and Giordano A: Scriptaid effects on breast
cancer cell lines. J Cell Physiol. 227:3426–3433. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Olsen CM, Meussen-Elholm ET, Røste LS and
Taubøll E: Antiepileptic drugs inhibit cell growth in the human
breast cancer cell line MCF7. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 213:173–179.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chavez-Blanco A, Perez-Plasencia C,
Perez-Cardenas E, Carrasco-Legleu C, Rangel-Lopez E, Segura-Pacheco
B, Taja-Chayeb L, Trejo-Becerril C, Gonzalez-Fierro A, Candelaria
M, et al: Antineoplastic effects of the DNA methylation inhibitor
hydralazine and the histone deacetylase inhibitor valproic acid in
cancer cell lines. Cancer Cell Int. 6:22006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hodges-Gallagher L, Valentine CD, Bader SE
and Kushner PJ: Inhibition of histone deacetylase enhances the
anti-proliferative action of antiestrogens on breast cancer cells
and blocks tamoxifen-induced proliferation of uterine cells. Breast
Cancer Res Treat. 105:297–309. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Li GF, Qian TL, Li GS, Yang CX, Qin M,
Huang J, Sun M and Han YQ: Sodium valproate inhibits MDA-MB-231
breast cancer cell migration by upregulating NM23H1 expression.
Genet Mol Res. 11:77–86. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Huang X, Gao L, Wang S, Lee CK, Ordentlich
P and Liu B: HDAC inhibitor SNDX-275 induces apoptosis in
erbB2-overexpressing breast cancer cells via down-regulation of
erbB3 expression. Cancer Res. 69:8403–8411. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wang Y, Wang SY, Zhang XH, Zhao M, Hou CM,
Xu YJ, Du ZY and Yu XD: FK228 inhibits Hsp90 chaperone function in
K562 cells via hyperacetylation of Hsp70. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 356:998–1003. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Fuino L, Bali P, Wittmann S, Donapaty S,
Guo F, Yamaguchi H, Wang HG, Atadja P and Bhalla K: Histone
deacetylase inhibitor LAQ824 down-regulates Her-2 and sensitizes
human breast cancer cells to trastuzumab, taxotere, gemcitabine,
and epothilone B. Mol Cancer Ther. 2:971–984. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Scott GK, Marden C, Xu F, Kirk L and Benz
CC: Transcriptional repression of ErbB2 by histone deacetylase
inhibitors detected by a genomically integrated ErbB2
promoter-reporting cell screen. Mol Cancer Ther. 1:385–392.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Meng Q, Chen X, Sun L, Zhao C, Sui G and
Cai L: Carbamazepine promotes Her-2 protein degradation in breast
cancer cells by modulating HDAC6 activity and acetylation of Hsp90.
Mol Cell Biochem. 348:165–171. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|