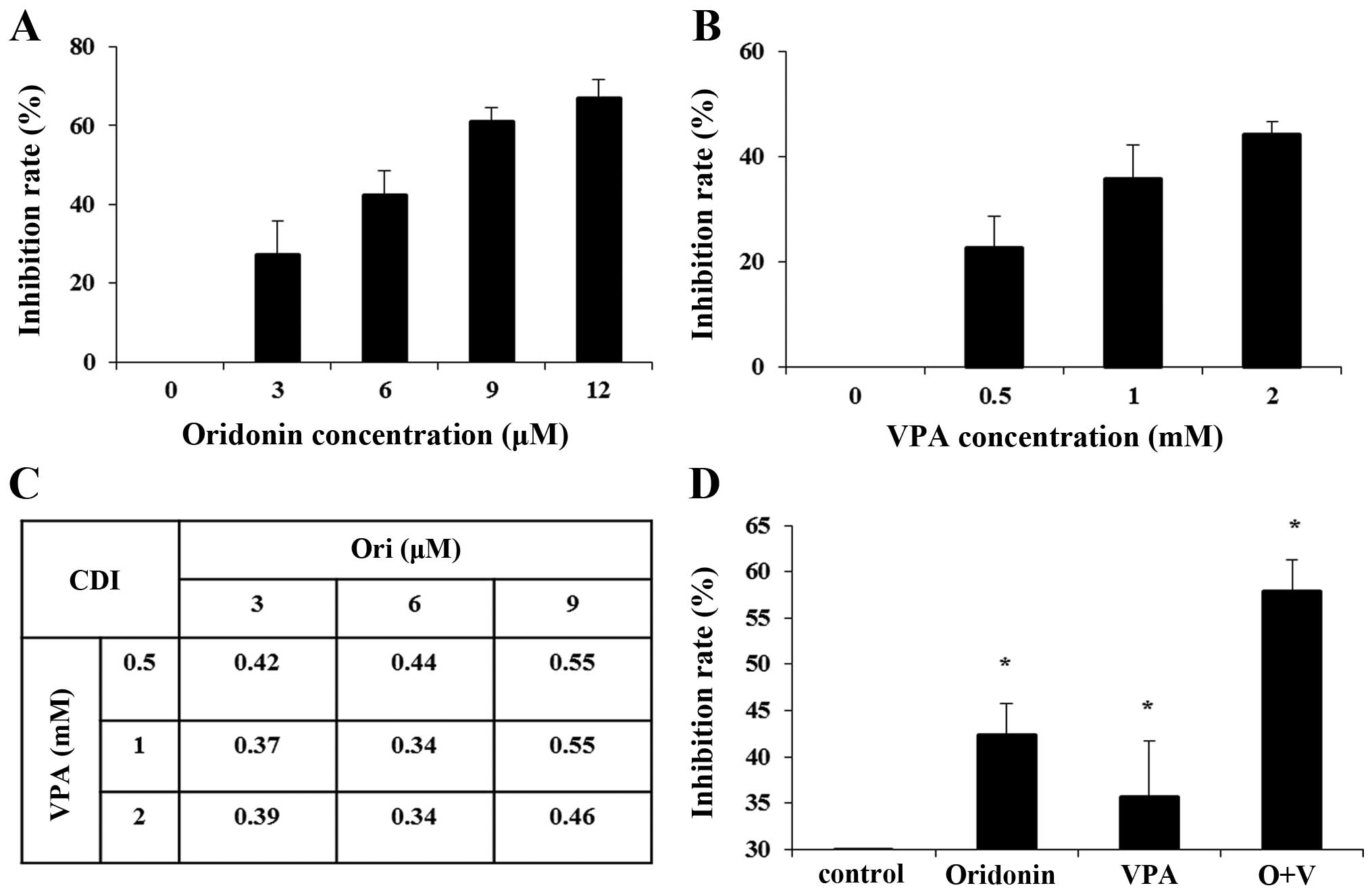
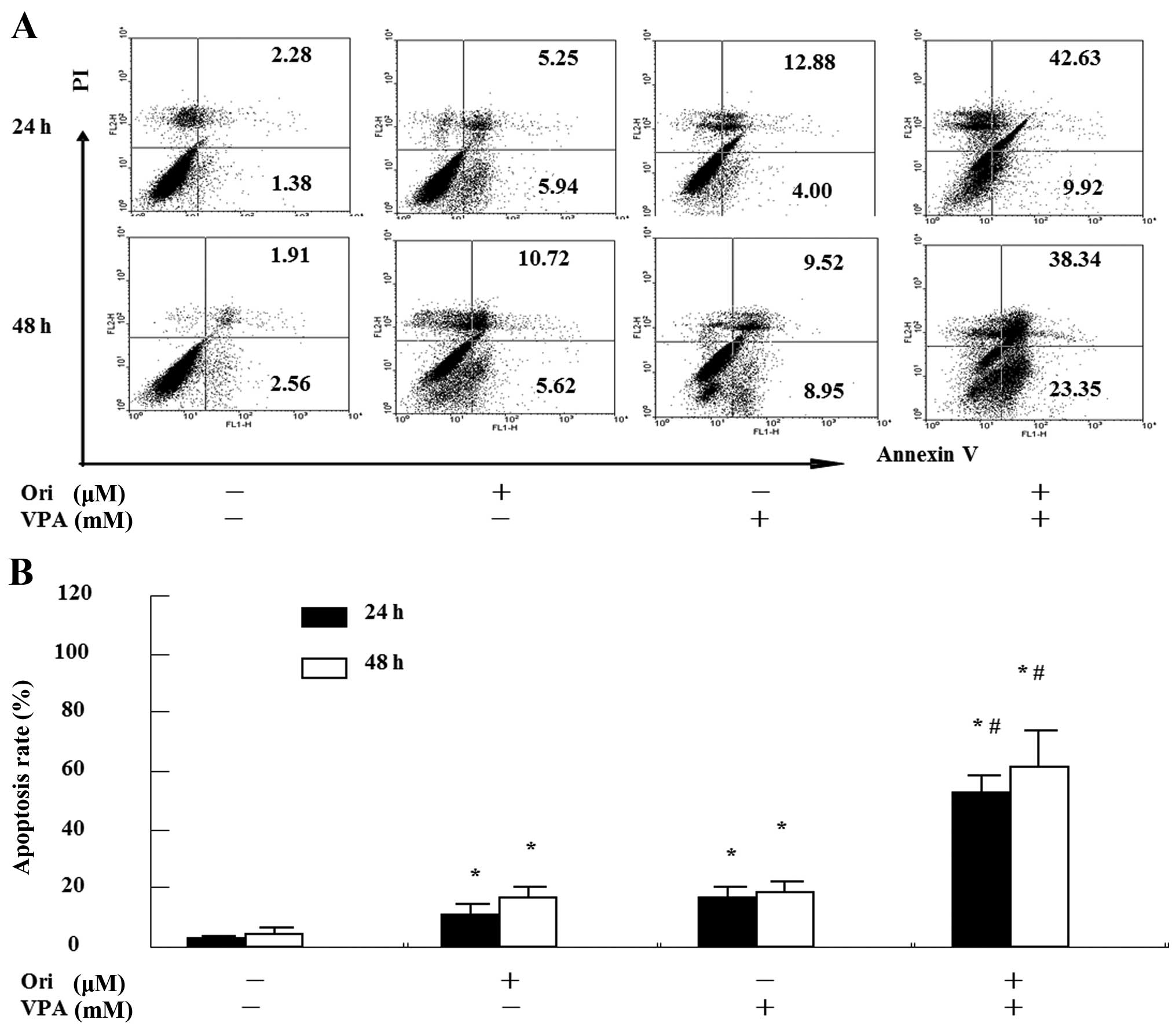
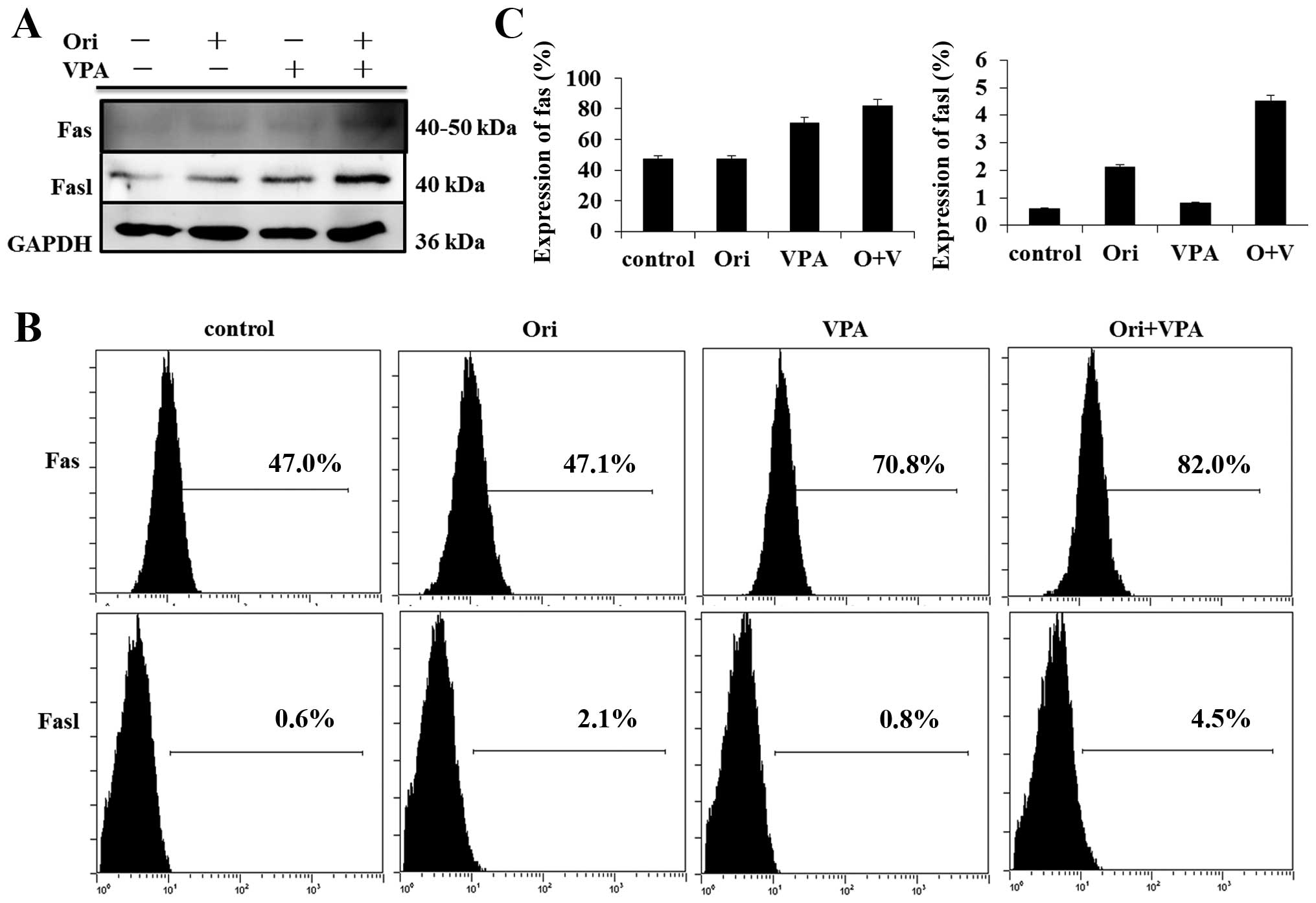
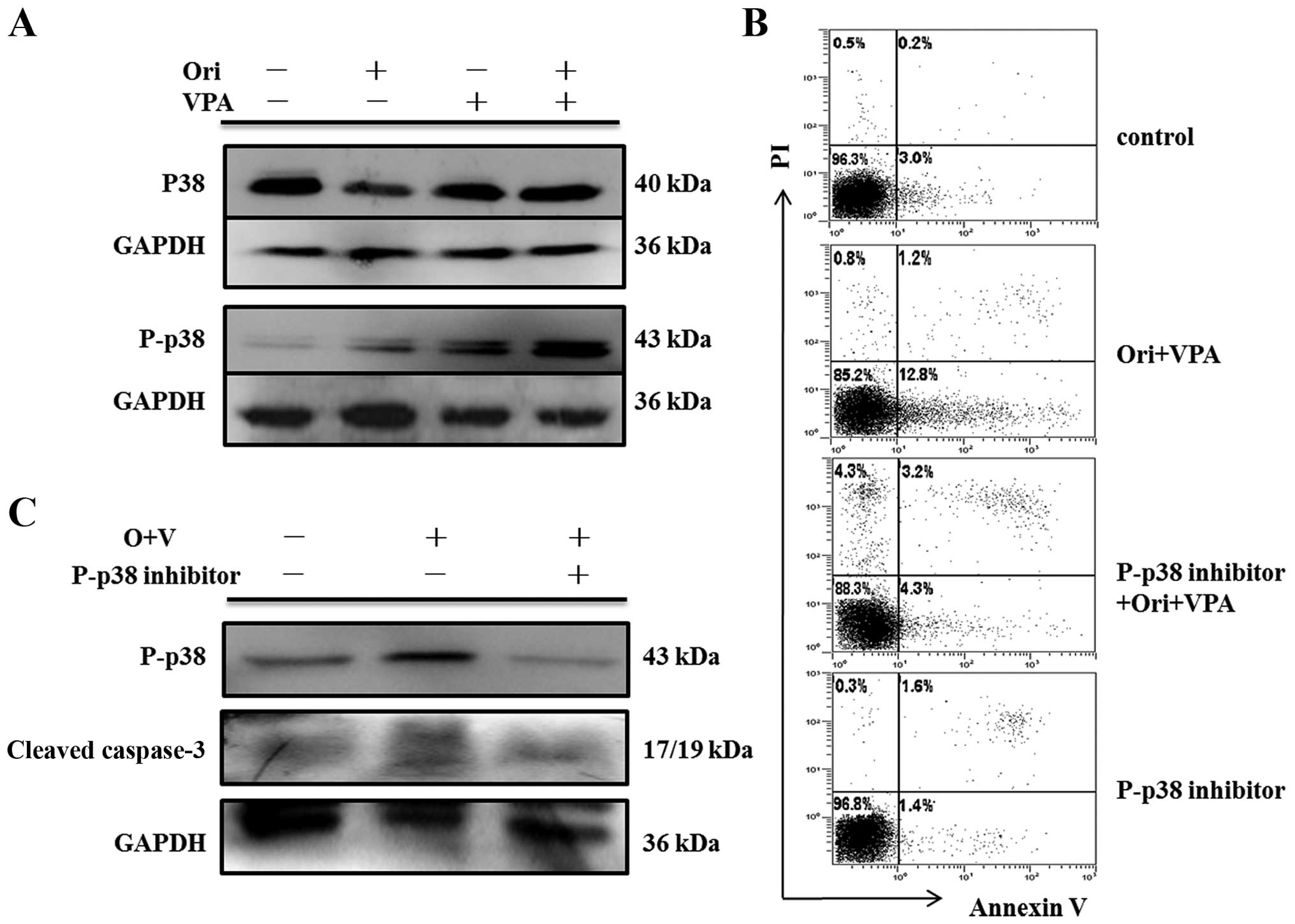
|
1
|
Lengfelder E, Hofmann WK and Nolte F:
Management of elderly patients with acute promyelocytic leukemia:
Progress and problems. Ann Hematol. 92:1181–1188. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chen Z, Chen GQ, Shen ZX, Chen SJ and Wang
ZY: Treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia with arsenic
compounds: In vitro and in vivo studies. Semin Hematol. 38:26–36.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Huang ME, Ye YC, Chen SR, Chai JR, Lu JX,
Zhoa L, Gu LJ and Wang ZY: Use of all-trans retinoic acid in the
treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia. Blood. 72:567–572.
1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zhang L and Zhu X: Epidemiology, diagnosis
and treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia in children: The
experience in china. Mediterr J Hematol Infect Dis. 4:e20120122012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Tallman MS and Nabhan C: Management of
acute promyelocytic leukemia. Curr Oncol Rep. 4:381–389. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Douer D: Advances in the treatment of
relapsed acute promyelocytic leukemia. Acta Haematol. 107:1–17.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Tallman MS, Nabhan C, Feusner JH and Rowe
JM: Acute promyelocytic leukemia: Evolving therapeutic strategies.
Blood. 99:759–767. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sanz MA, Martín G and Lo Coco F: Choice of
chemotherapy in induction, consolidation and maintenance in acute
promyelocytic leukaemia. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol. 16:433–451.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Nasr R, Lallemand-Breitenbach V, Zhu J,
Guillemin MC and de Thé H: Therapy-induced PML/RARA proteolysis and
acute promyelocytic leukemia cure. Clin Cancer Res. 15:6321–6326.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Tomita A, Kiyoi H and Naoe T: Mechanisms
of action and resistance to all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) and
arsenic trioxide (As2O3) in acute
promyelocytic leukemia. Int J Hematol. 97:717–725. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hillestad LK: Acute promyelocytic
leukemia. Acta Med Scand. 159:189–194. 1957. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Liu JJ, Wu XY, Peng J, Pan XL and Lu HL:
Antiproliferation effects of oridonin on HL-60 cells. Ann Hematol.
83:691–695. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Gao F, Tang Q, Yang P, Fang Y, Li W and Wu
Y: Apoptosis inducing and differentiation enhancement effect of
oridonin on the all-trans-retinoic acid-sensitive and -resistant
acute promyelocytic leukemia cells. Int J Lab Hematol. 32(1p1):
e114–e122. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Zhou GB, Kang H, Wang L, Gao L, Liu P, Xie
J, Zhang FX, Weng XQ, Shen ZX, Chen J, et al: Oridonin, a
diterpenoid extracted from medicinal herbs, targets AML1-ETO fusion
protein and shows potent antitumor activity with low adverse
effects on t(8;21) leukemia in vitro and in vivo. Blood.
109:3441–3450. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Gao FH, Hu XH, Li W, Liu H, Zhang YJ, Guo
ZY, Xu MH, Wang ST, Jiang B, Liu F, et al: Oridonin induces
apoptosis and senescence in colorectal cancer cells by increasing
histone hyperacetylation and regulation of p16, p21, p27 and c-myc.
BMC Cancer. 10:6102010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chen G, Wang K, Yang BY, Tang B, Chen JX
and Hua ZC: Synergistic antitumor activity of oridonin and arsenic
trioxide on hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Int J Oncol.
40:139–147. 2012.
|
|
17
|
Marks PA, Richon VM and Rifkind RA:
Histone deacetylase inhibitors: Inducers of differentiation or
apoptosis of transformed cells. J Natl Cancer Inst. 92:1210–1216.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Konopleva M, Contractor R, Kurinna SM,
Chen W, Andreeff M and Ruvolo PP: The novel triterpenoid CDDO-Me
suppresses MAPK pathways and promotes p38 activation in acute
myeloid leukemia cells. Leukemia. 19:1350–1354. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Phiel CJ, Zhang F, Huang EY, Guenther mg,
Lazar MA and Klein PS: Histone deacetylase is a direct target of
valproic acid, a potent anticonvulsant, mood stabilizer, and
teratogen. J Biol Chem. 276:36734–36741. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Cimino G, Lo-Coco F, Fenu S, Travaglini L,
Finolezzi E, Mancini M, Nanni M, Careddu A, Fazi F, Padula F, et
al: Sequential valproic acid/all-trans retinoic acid treatment
reprograms differentiation in refractory and high-risk acute
myeloid leukemia. Cancer Res. 66:8903–8911. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tang R, Faussat AM, Majdak P, Perrot JY,
Chaoui D, Legrand O and Marie JP: Valproic acid inhibits
proliferation and induces apoptosis in acute myeloid leukemia cells
expressing P-gp and MRP1. Leukemia. 18:1246–1251. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chou TC: Theoretical basis, experimental
design, and computerized simulation of synergism and antagonism in
drug combination studies. Pharmacol Rev. 58:621–681. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Liu J, Bi G, Wen P, Yang W, Ren X, Tang T,
Xie C, Dong W and Jiang G: Down-regulation of CD44 contributes to
the differentiation of HL-60 cells induced by ATRA or HMBA. Cell
Mol Immunol. 4:59–63. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Shimizu S, Narita M and Tsujimoto Y: Bcl-2
family proteins regulate the release of apoptogenic cytochrome c by
the mitochondrial channel VDAC. Nature. 399:483–487. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Constantinou C, Papas KA and Constantinou
AI: Caspase-independent pathways of programmed cell death: The
unraveling of new targets of cancer therapy? Curr Cancer Drug
Targets. 9:717–728. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sun KW, Ma YY, Guan TP, Xia YJ, Shao CM,
Chen LG, Ren YJ, Yao HB, Yang Q and He XJ: Oridonin induces
apoptosis in gastric cancer through Apaf-1, cytochrome c and
caspase-3 signaling pathway. World J Gastroenterol. 18:7166–7174.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Bao R, Shu Y, Wu X, Weng H, Ding Q, Cao Y,
Li M, Mu J, Wu W, Ding Q, et al: Oridonin induces apoptosis and
cell cycle arrest of gallbladder cancer cells via the mitochondrial
pathway. BMC Cancer. 14:2172014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kawagoe R, Kawagoe H and Sano K: Valproic
acid induces apoptosis in human leukemia cells by stimulating both
caspase-dependent and -independent apoptotic signaling pathways.
Leuk Res. 26:495–502. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ramos S: Cancer chemoprevention and
chemotherapy: Dietary polyphenols and signalling pathways. Mol Nutr
Food Res. 52:507–526. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhang W and Liu HT: MAPK signal pathways
in the regulation of cell proliferation in mammalian cells. Cell
Res. 12:9–18. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lunghi P, Tabilio A, Dall'Aglio PP, Ridolo
E, Carlo-Stella C, Pelicci PG and Bonati A: Downmodulation of ERK
activity inhibits the proliferation and induces the apoptosis of
primary acute myelogenous leukemia blasts. Leukemia. 17:1783–1793.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wu J, Wong WW, Khosravi F, Minden MD and
Penn LZ: Blocking the Raf/MEK/ERK pathway sensitizes acute
myelogenous leukemia cells to lovastatin-induced apoptosis. Cancer
Res. 64:6461–6468. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Jin S, Shen JN, Wang J, Huang G and Zhou
JG: Oridonin induced apoptosis through Akt and MAPKs signaling
pathways in human osteosarcoma cells. Cancer Biol Ther. 6:261–268.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wang H, Ye Y, Chui JH, Zhu GY, Li YW, Fong
DW and Yu ZL: Oridonin induces G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis
through MAPK and p53 signaling pathways in HepG2 cells. Oncol Rep.
24:647–651. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
McCubrey JA, Steelman LS, Chappell WH,
Abrams SL, Wong EW, Chang F, Lehmann B, Terrian DM, Milella M,
Tafuri A, et al: Roles of the Raf/MEK/ERK pathway in cell growth,
malignant transformation and drug resistance. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1773:1263–1284. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Henson ES and Gibson SB: Surviving cell
death through epidermal growth factor (EGF) signal transduction
pathways: Implications for cancer therapy. Cell Signal.
18:2089–2097. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Bu HQ, Liu DL, Wei WT, Chen L, Huang H, Li
Y and Cui JH: Oridonin induces apoptosis in SW1990 pancreatic
cancer cells via p53- and caspase-dependent induction of p38 MAPK.
Oncol Rep. 31:975–982. 2014.
|
|
38
|
Chiu CC, Chen JY, Lin KL, Huang CJ, Lee
JC, Chen BH, Chen WY, Lo YH, Chen YL, Tseng CH, et al: p38 MAPK and
NF-kappaB pathways are involved in naphtho[1,2-b] furan-4,5-dione
induced anti-proliferation and apoptosis of human hepatoma cells.
Cancer Lett. 295:92–99. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|