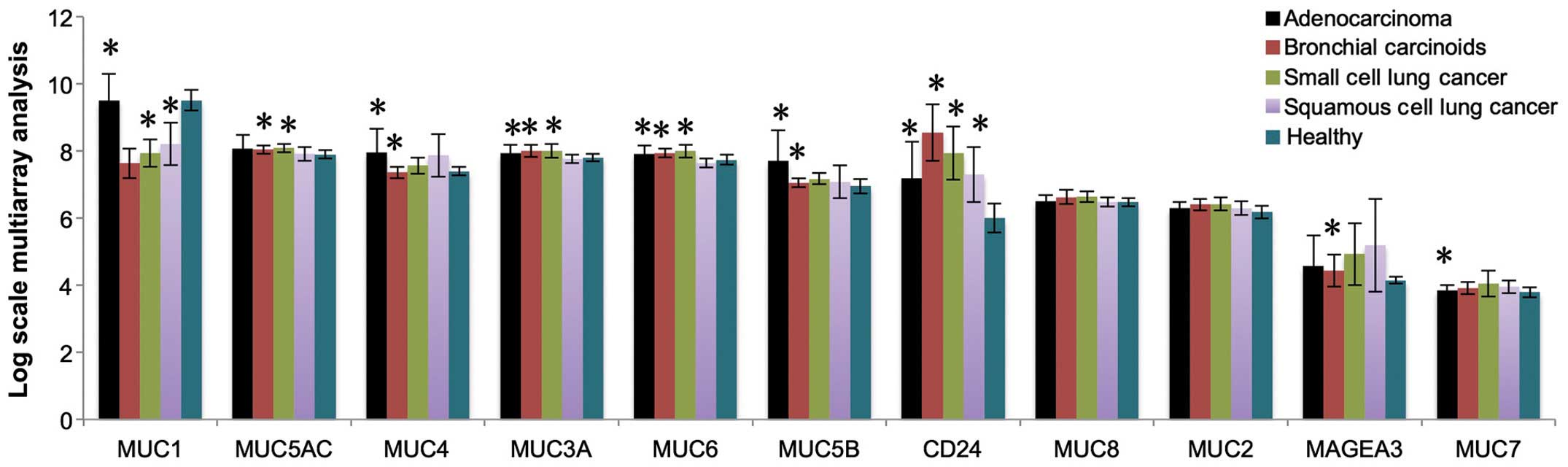
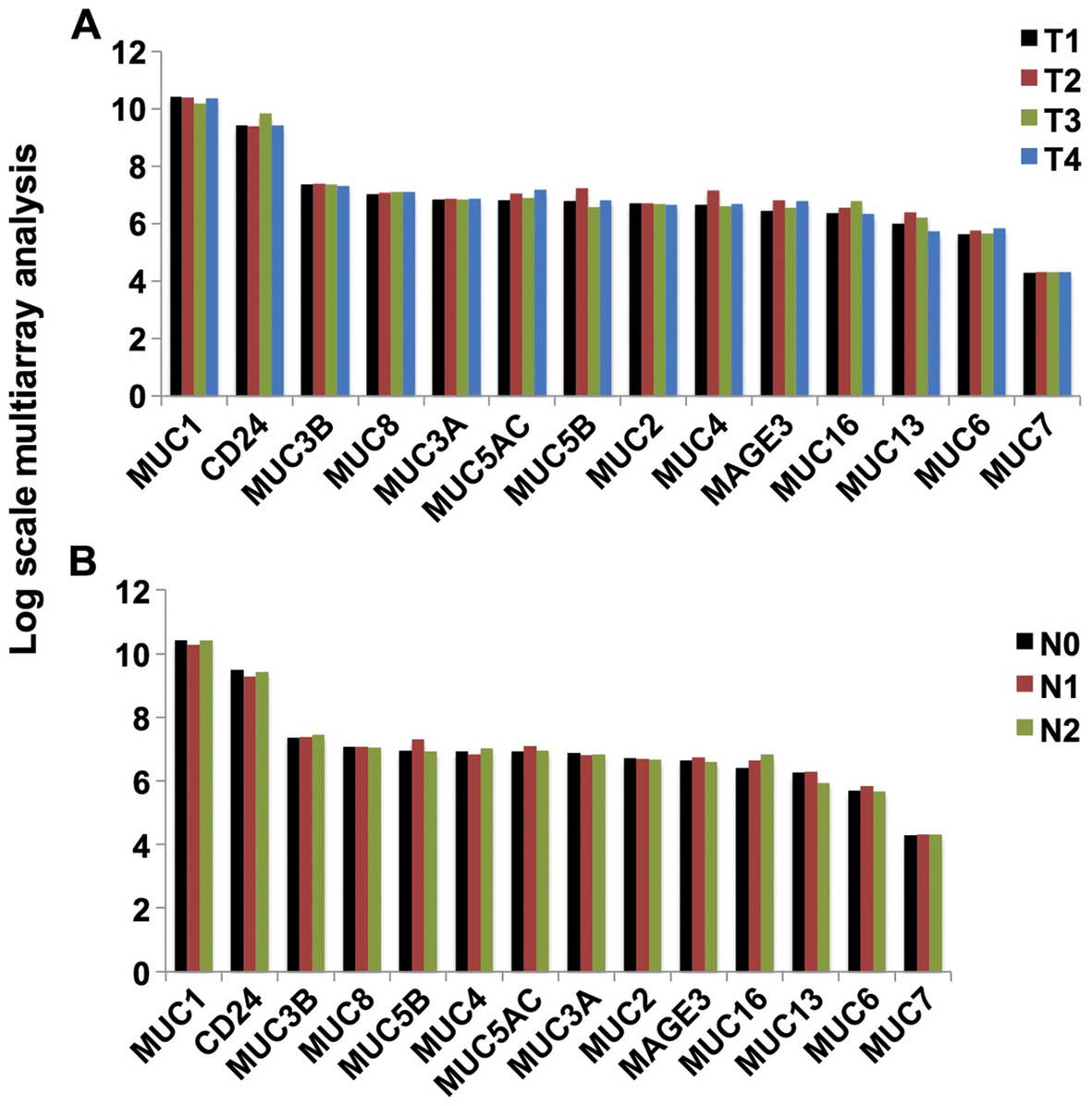
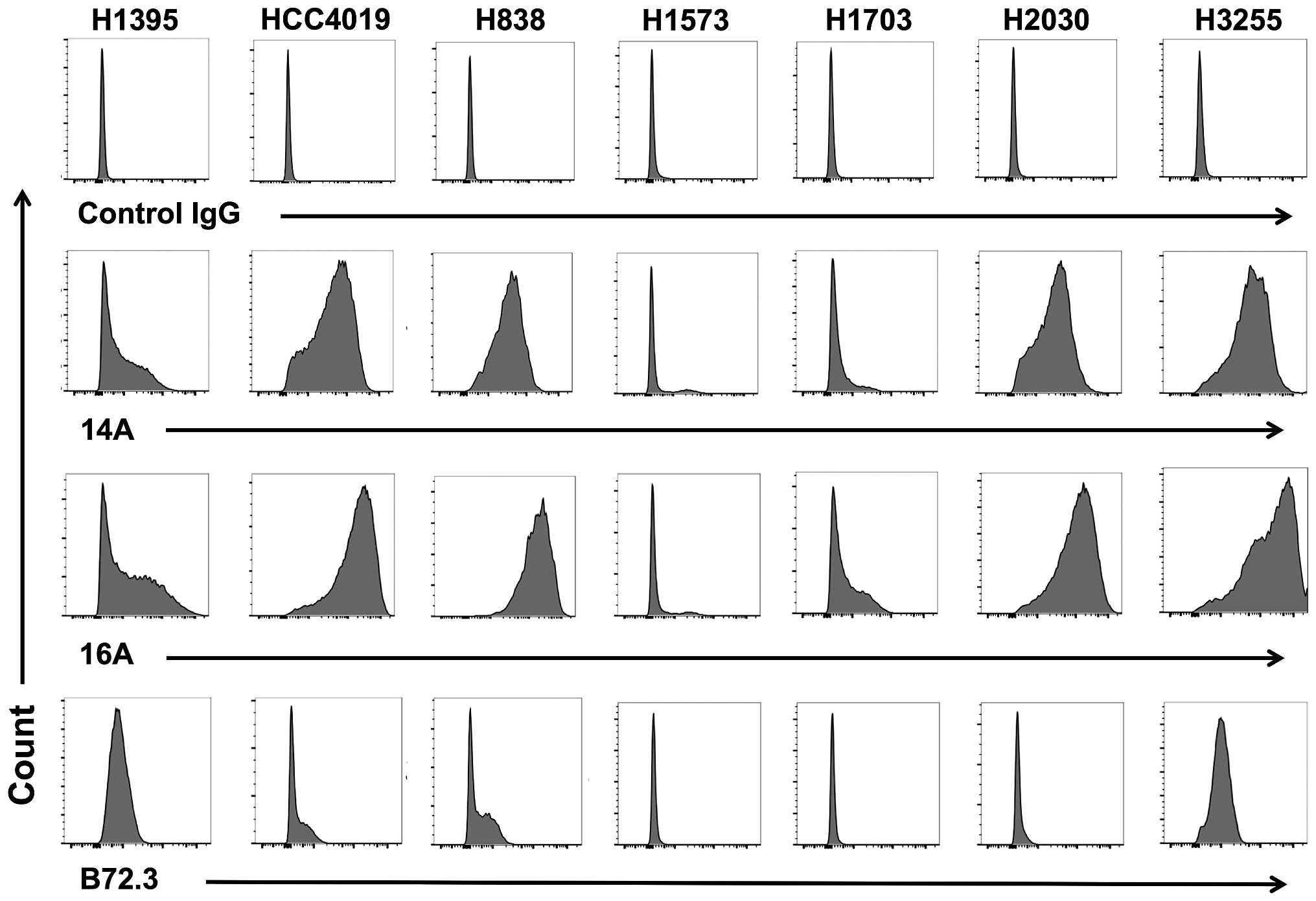
|
1
|
Hamid O, Robert C, Daud A, Hodi FS, Hwu
WJ, Kefford R, Wolchok JD, Hersey P, Joseph RW, Weber JS, et al:
Safety and tumor responses with lambrolizumab (anti-PD-1) in
melanoma. N Engl J Med. 369:134–144. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Brahmer JR, Tykodi SS, Chow LQ, Hwu WJ,
Topalian SL, Hwu P, Drake CG, Camacho LH, Kauh J, Odunsi K, et al:
Safety and activity of anti-PD-L1 antibody in patients with
advanced cancer. N Engl J Med. 366:2455–2465. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ahmad R, Alam M, Rajabi H and Kufe D: The
MUC1-C oncoprotein binds to the BH3 domain of the pro-apoptotic BAX
protein and blocks BAX function. J Biol Chem. 287:20866–20875.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Xu X, Wells A, Padilla MT, Kato K, Kim KC
and Lin Y: A signaling pathway consisting of miR-551b, catalase and
MUC1 contributes to acquired apoptosis resistance and
chemoresistance. Carcinogenesis. 35:2457–2466. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhang K, Sikut R and Hansson GC: A MUC1
mucin secreted from a colon carcinoma cell line inhibits target
cell lysis by natural killer cells. Cell Immunol. 176:158–165.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ogata S, Maimonis PJ and Itzkowitz SH:
Mucins bearing the cancer-associated sialosyl-Tn antigen mediate
inhibition of natural killer cell cytotoxicity. Cancer Res.
52:4741–4746. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Moreno M, Bontkes HJ, Scheper RJ, Kenemans
P, Verheijen RH and von Mensdorff-Pouilly S: High level of MUC1 in
serum of ovarian and breast cancer patients inhibits huHMFG-1
dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC). Cancer Lett.
257:47–55. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Belisle JA, Horibata S, Jennifer GA,
Petrie S, Kapur A, André S, Gabius HJ, Rancourt C, Connor J,
Paulson JC, et al: Identification of Siglec-9 as the receptor for
MUC16 on human NK cells, B cells, and monocytes. Mol Cancer.
9:1182010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kuemmel A, Single K, Bittinger F, Faldum
A, Schmidt LH, Sebastian M, Micke P, Taube C, Buhl R and Wiewrodt
R: TA-MUC1 epitope in non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer.
63:98–105. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Devine PL, Birrell GW, Quin RJ and Shield
PW: Monoclonal antibodies recognising sialyl-Tn: Production and
application to immunochemistry. Dis Markers. 12:175–186. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Longenecker BM, Willans DJ, MacLean GD,
Selvaraj S, Suresh MR and Noujaim AA: Monoclonal antibodies and
synthetic tumor-associated glycoconjugates in the study of the
expression of Thomsen-Friedenreich-like and Tn-like antigens on
human cancers. J Natl Cancer Inst. 78:489–496. 1987.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Nguyen PL, Niehans GA, Cherwitz DL, Kim YS
and Ho SB: Membrane-bound (MUC1) and secretory (MUC2, MUC3, and
MUC4) mucin gene expression in human lung cancer. Tumour Biol.
17:176–192. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Snijdewint FG, von Mensdorff-Pouilly S,
Karuntu-Wanamarta AH, Verstraeten AA, Livingston PO, Hilgers J and
Kenemans P: Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity can be
induced by MUC1 peptide vaccination of breast cancer patients. Int
J Cancer. 93:97–106. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Vassilaros S, Tsibanis A, Tsikkinis A,
Pietersz GA, McKenzie IF and Apostolopoulos V: Up to 15-year
clinical follow-up of a pilot Phase III immunotherapy study in
stage II breast cancer patients using oxidized mannan-MUC1.
Immunotherapy. 5:1177–1182. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kimura T, McKolanis JR, Dzubinski LA,
Islam K, Potter DM, Salazar AM, Schoen RE and Finn OJ: MUC1 vaccine
for individuals with advanced adenoma of the colon: A cancer
immunoprevention feasibility study. Cancer Prev Res (Phila).
6:18–26. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Ramanathan RK, Lee KM, McKolanis J,
Hitbold E, Schraut W, Moser AJ, Warnick E, Whiteside T, Osborne J,
Kim H, et al: Phase I study of a MUC1 vaccine composed of different
doses of MUC1 peptide with SB-AS2 adjuvant in resected and locally
advanced pancreatic cancer. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 54:254–264.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Shedden K, Taylor JM, Enkemann SA, Tsao
MS, Yeatman TJ, Gerald WL, Eschrich S, Jurisica I, Giordano TJ,
Misek DE, et al; Director's Challenge Consortium for the Molecular
Classification of Lung Adenocarcinoma. Gene expression-based
survival prediction in lung adenocarcinoma: A multi-site, blinded
validation study. Nat Med. 14:822–827. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wilson CL and Miller CJ: Simpleaffy: A
BioConductor package for Affymetrix Quality Control and data
analysis. Bioinformatics. 21:3683–3685. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Bhattacharjee A, Richards WG, Staunton J,
Li C, Monti S, Vasa P, Ladd C, Beheshti J, Bueno R, Gillette M, et
al: Classification of human lung carcinomas by mRNA expression
profiling reveals distinct adenocarcinoma subclasses. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 98:13790–13795. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Irizarry RA, Bolstad BM, Collin F, Cope
LM, Hobbs B and Speed TP: Summaries of Affymetrix GeneChip probe
level data. Nucleic Acids Res. 31:e152003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
R Development Core Team. R: A Language and
Environment for Statistical Computing: the R Foundation for
Statistical Computing. Vienna: 2011
|
|
22
|
Song W, Delyria ES, Chen J, Huang W, Lee
JS, Mittendorf EA, Ibrahim N, Radvanyi LG, Li Y, Lu H, et al: MUC1
glycopeptide epitopes predicted by computational glycomics. Int J
Oncol. 41:1977–1984. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Reddish MA, Jackson L, Koganty RR, Qiu D,
Hong W and Longenecker BM: Specificities of anti-sialyl-Tn and
anti-Tn monoclonal antibodies generated using novel clustered
synthetic glycopeptide epitopes. Glycoconj J. 14:549–560. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Colcher D, Hand PH, Nuti M and Schlom J: A
spectrum of monoclonal antibodies reactive with human mammary tumor
cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 78:3199–3203. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Schietinger A, Philip M, Yoshida BA, Azadi
P, Liu H, Meredith SC and Schreiber H: A mutant chaperone converts
a wild-type protein into a tumor-specific antigen. Science.
314:304–308. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Vierbuchen MJ, Fruechtnicht W, Brackrock
S, Krause KT and Zienkiewicz TJ: Quantitative lectin-histochemical
and immunohistochemical studies on the occurrence of alpha(2,3)-
and alpha(2,6)-linked sialic acid residues in colorectal
carcinomas. Relation to clinicopathologic features. Cancer.
76:727–735. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Steentoft C, Vakhrushev SY, Joshi HJ, Kong
Y, Vester-Christensen MB, Schjoldager KT, Lavrsen K, Dabelsteen S,
Pedersen NB, Marcos-Silva L, et al: Precision mapping of the human
O-GalNAc glycoproteome through SimpleCell technology. EMBO J.
32:1478–1488. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yang Z, Halim A, Narimatsu Y, Jitendra
Joshi H, Steentoft C, Schjoldager KT, Alder Schulz M, Sealover NR,
Kayser KJ, Paul Bennett E, et al: The GalNAc-type O-Glycoproteome
of CHO cells characterized by the SimpleCell strategy. Mol Cell
Proteomics. 13:3224–3235. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Levery SB, Steentoft C, Halim A, Narimatsu
Y, Clausen H and Vakhrushev SY: Advances in mass spectrometry
driven O-glycoproteomics. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1850.33–42.
2015.
|
|
30
|
Lakshminarayanan V, Thompson P, Wolfert
MA, Buskas T, Bradley JM, Pathangey LB, Madsen CS, Cohen PA,
Gendler SJ and Boons GJ: Immune recognition of tumor-associated
mucin MUC1 is achieved by a fully synthetic aberrantly glycosylated
MUC1 tripartite vaccine. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 109:261–266. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
31
|
Dokurno P, Bates PA, Band HA, Stewart LM,
Lally JM, Burchell JM, Taylor-Papadimitriou J, Snary D, Sternberg
MJ and Freemont PS: Crystal structure at 1.95 A resolution of the
breast tumour-specific antibody SM3 complexed with its peptide
epitope reveals novel hypervariable loop recognition. J Mol Biol.
284:713–728. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Möller H, Serttas N, Paulsen H, Burchell
JM, Taylor-Papadimitriou J and Meyer Bernd: NMR-based determination
of the binding epitope and conformational analysis of MUC-1
glycopeptides and peptides bound to the breast cancer-selective
monoclonal antibody SM3. Eur J Biochem. 269:1444–1455. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Spencer DI, Missailidis S, Denton G,
Murray A, Brady K, Matteis CI, Searle MS, Tendler SJ and Price MR:
Structure/activity studies of the anti-MUC1 monoclonal antibody
C595 and synthetic MUC1 mucin-core-related peptides and
glycopeptides. Biospectroscopy. 5:79–91. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Matsumoto-Takasaki A, Hanashima S, Aoki A,
Yuasa N, Ogawa H, Sato R, Kawakami H, Mizuno M, Nakada H, Yamaguchi
Y, et al: Surface plasmon resonance and NMR analyses of anti
Tn-antigen MLS128 monoclonal antibody binding to two or three
consecutive Tn-antigen clusters. J Biochem. 151:273–282. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Ibrahim NK, Murray JL, Zhou D, Mittendorf
EA, Sample D, Tautchin M and Miles D: Survival Advantage in
Patients with Metastatic Breast Cancer Receiving Endocrine Therapy
plus Sialyl Tn-KLH Vaccine: Post Hoc Analysis of a Large Randomized
Trial. J Cancer. 4:577–584. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Forsström B, Axnäs BB, Stengele KP, Bühler
J, Albert TJ, Richmond TA, Hu FJ, Nilsson P, Hudson EP, Rockberg J,
et al: Proteome-wide epitope mapping of antibodies using
ultra-dense peptide arrays. Mol Cell Proteomics. 13:1585–1597.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|