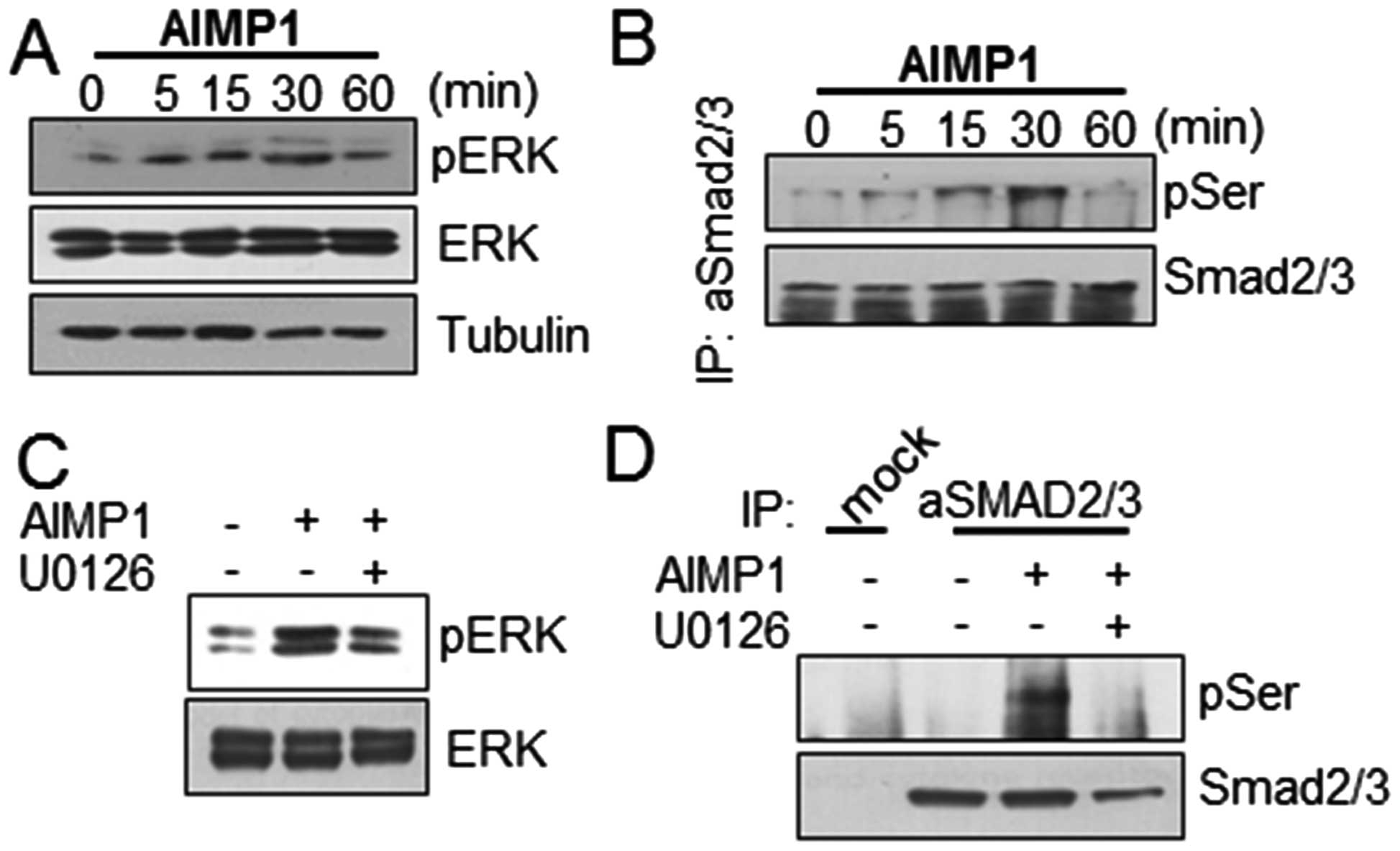
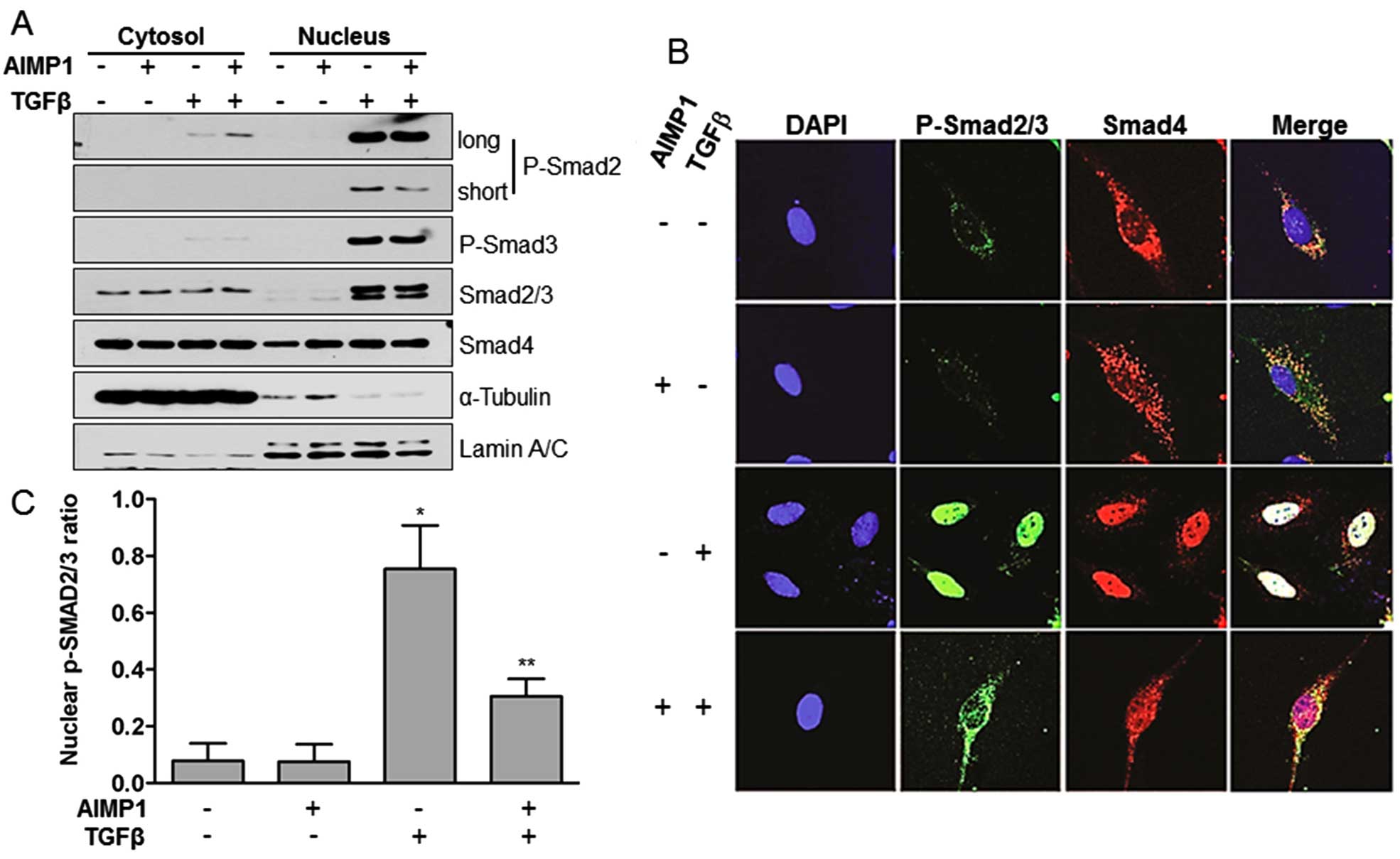
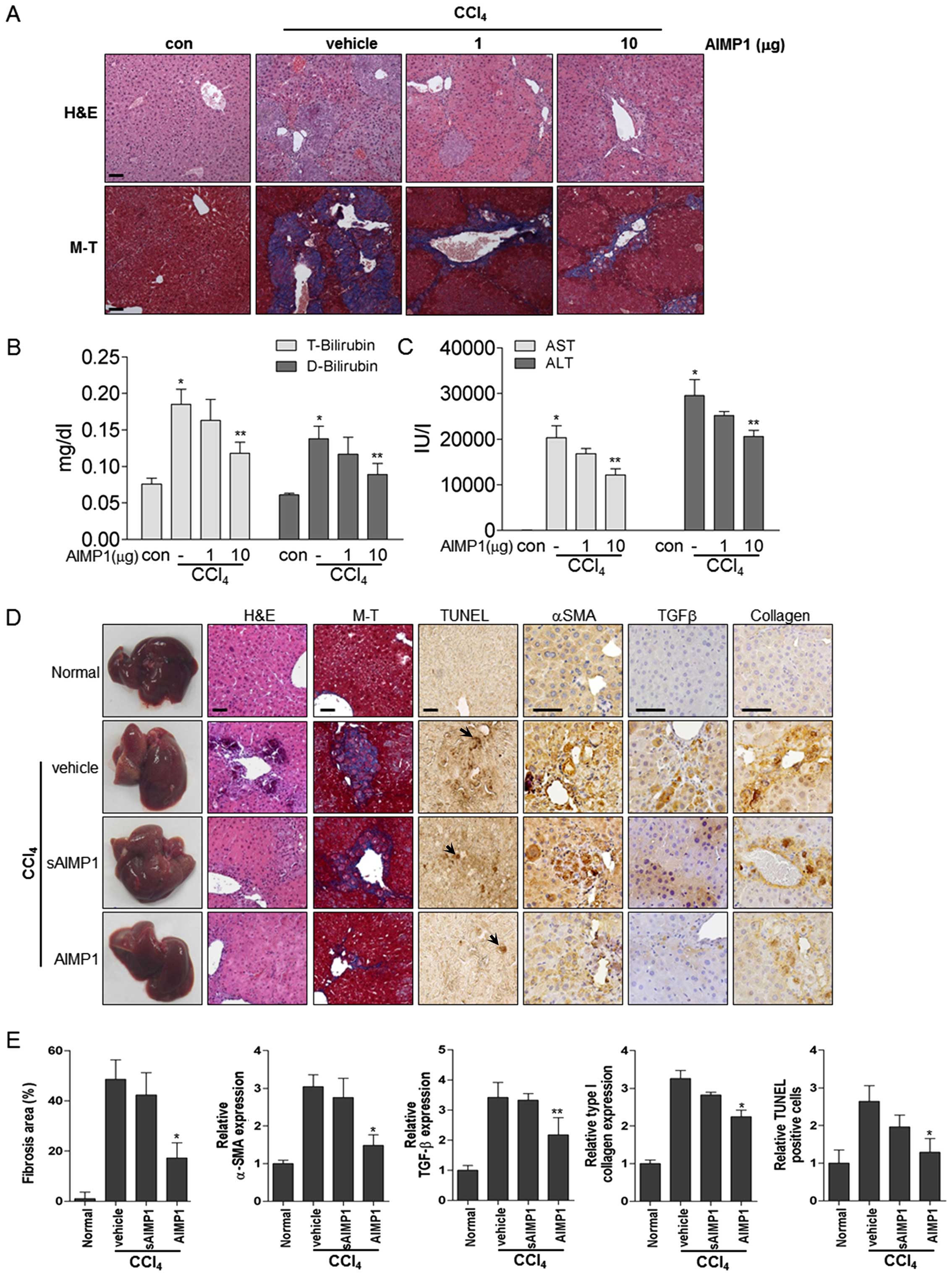
|
1
|
Friedman SL: Mechanisms of hepatic
fibrogenesis. Gastroenterology. 134:1655–1669. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Li JT, Liao ZX, Ping J, Xu D and Wang H:
Molecular mechanism of hepatic stellate cell activation and
antifibrotic therapeutic strategies. J Gastroenterol. 43:419–428.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Russo FP, Alison MR, Bigger BW, Amofah E,
Florou A, Amin F, Bou-Gharios G, Jeffery R, Iredale JP and Forbes
SJ: The bone marrow functionally contributes to liver fibrosis.
Gastroenterology. 130:1807–1821. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Pinzani M and Rombouts K: Liver fibrosis:
From the bench to clinical targets. Dig Liver Dis. 36:231–242.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Iredale JP, Benyon RC, Arthur MJ, Ferris
WF, Alcolado R, Winwood PJ, Clark N and Murphy G: Tissue inhibitor
of metal-loproteinase-1 messenger RNA expression is enhanced
relative to interstitial collagenase messenger RNA in experimental
liver injury and fibrosis. Hepatology. 24:176–184. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cheng JH, She H, Han YP, Wang J, Xiong S,
Asahina K and Tsukamoto H: Wnt antagonism inhibits hepatic stellate
cell activation and liver fibrosis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver
Physiol. 294:G39–G49. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Yoshiji H, Noguchi R, Kuriyama S, Ikenaka
Y, Yoshii J, Yanase K, Namisaki T, Kitade M, Masaki T and Fukui H:
Imatinib mesylate (STI-571) attenuates liver fibrosis development
in rats. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 288:G907–G913.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Son MK, Ryu YL, Jung KH, Lee H, Lee HS,
Yan HH, Park HJ, Ryu JK, Suh JK, Hong S, et al: HS-173, a novel
PI3K inhibitor, attenuates the activation of hepatic stellate cells
in liver fibrosis. Sci Rep. 3:34702013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bueno M, Salgado S, Beas-Zárate C and
Armendariz-Borunda J: Urokinase-type plasminogen activator gene
therapy in liver cirrhosis is mediated by collagens gene expression
down-regulation and up-regulation of MMPs, HGF and VEGF. J Gene
Med. 8:1291–1299. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Anselmi K, Stolz DB, Nalesnik M, Watkins
SC, Kamath R and Gandhi CR: Gliotoxin causes apoptosis and necrosis
of rat Kupffer cells in vitro and in vivo in the absence of
oxidative stress: Exacerbation by caspase and serine protease
inhibition. J Hepatol. 47:103–113. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Shackel N and Rockey D: In pursuit of the
‘Holy Grail’ - stem cells, hepatic injury, fibrogenesis and repair.
Hepatology. 41:16–18. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
LeRoy EC, Trojanowska MI and Smith EA:
Cytokines and human fibrosis. Eur Cytokine Netw. 1:215–219.
1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kane CJ, Hebda PA, Mansbridge JN and
Hanawalt PC: Direct evidence for spatial and temporal regulation of
transforming growth factor beta 1 expression during cutaneous wound
healing. J Cell Physiol. 148:157–173. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wahl SM, Hunt DA, Wakefield LM,
McCartney-Francis N, Wahl LM, Roberts AB and Sporn MB: Transforming
growth factor type beta induces monocyte chemotaxis and growth
factor production. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 84:5788–5792. 1987.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Funaba M, Zimmerman CM and Mathews LS:
Modulation of Smad2-mediated signaling by extracellular
signal-regulated kinase. J Biol Chem. 277:41361–41368. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Matsuura I, Wang G, He D and Liu F:
Identification and characterization of ERK MAP kinase
phosphorylation sites in Smad3. Biochemistry. 44:12546–12553. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Mulder KM: Role of Ras and Mapks in
TGFbeta signaling. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 11:23–35. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kretzschmar M, Doody J, Timokhina I and
Massagué J: A mechanism of repression of TGFbeta/Smad signaling by
oncogenic Ras. Genes Dev. 13:804–816. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Conery AR, Cao Y, Thompson EA, Townsend CM
Jr, Ko TC and Luo K: Akt interacts directly with Smad3 to regulate
the sensitivity to TGF-beta induced apoptosis. Nat Cell Biol.
6:366–372. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Song K, Wang H, Krebs TL and Danielpour D:
Novel roles of Akt and mTOR in suppressing TGF-beta/ALK5-mediated
Smad3 activation. EMBO J. 25:58–69. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Remy I, Montmarquette A and Michnick SW:
PKB/Akt modulates TGF-beta signalling through a direct interaction
with Smad3. Nat Cell Biol. 6:358–365. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Takayama S, Murakami S, Miki Y, Ikezawa K,
Tasaka S, Terashima A, Asano T and Okada H: Effects of basic
fibroblast growth factor on human periodontal ligament cells. J
Periodontal Res. 32:667–675. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Silverio-Ruiz KG, Martinez AE, Garlet GP,
Barbosa CF, Silva JS, Cicarelli RM, Valentini SR, Abi-Rached RS and
Junior CR: Opposite effects of bFGF and TGF-beta on collagen
metabolism by human periodontal ligament fibroblasts. Cytokine.
39:130–137. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Quevillon S, Agou F, Robinson JC and
Mirande M: The p43 component of the mammalian multi-synthetase
complex is likely to be the precursor of the endothelial
monocyte-activating polypeptide II cytokine. J Biol Chem.
272:32573–32579. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Matschurat S, Knies UE, Person V, Fink L,
Stoelcker B, Ebenebe C, Behrensdorf HA, Schaper J and Clauss M:
Regulation of EMAP II by hypoxia. Am J Pathol. 162:93–103. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Park SG, Shin H, Shin YK, Lee Y, Choi EC,
Park BJ and Kim S: The novel cytokine p43 stimulates dermal
fibroblast proliferation and wound repair. Am J Pathol.
166:387–398. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Park SG, Kang YS, Kim JY, Lee CS, Ko YG,
Lee WJ, Lee KU, Yeom YI and Kim S: Hormonal activity of AIMP1/p43
for glucose homeostasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:14913–14918.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ko YG, Park H, Kim T, Lee JW, Park SG,
Seol W, Kim JE, Lee WH, Kim SH, Park JE, et al: A cofactor of tRNA
synthetase, p43, is secreted to up-regulate proinflammatory genes.
J Biol Chem. 276:23028–23033. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Park SG, Kang YS, Ahn YH, Lee SH, Kim KR,
Kim KW, Koh GY, Ko YG and Kim S: Dose-dependent biphasic activity
of tRNA synthetase-associating factor, p43, in angiogenesis. J Biol
Chem. 277:45243–45248. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Park H, Park SG, Lee JW, Kim T, Kim G, Ko
YG and Kim S: Monocyte cell adhesion induced by a human
aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase-associated factor, p43: Identification of
the related adhesion molecules and signal pathways. J Leukoc Biol.
71:223–230. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kim E, Kim SH, Kim S and Kim TS: The novel
cytokine p43 induces IL-12 production in macrophages via NF-kappaB
activation, leading to enhanced IFN-gamma production in
CD4+ T cells. J Immunol. 176:256–264. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Kim E, Kim SH, Kim S, Cho D and Kim TS:
AIMP1/p43 protein induces the maturation of bone marrow-derived
dendritic cells with T helper type 1-polarizing ability. J Immunol.
180:2894–2902. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kim SY, Son WS, Park MC, Kim CM, Cha BH,
Yoon KJ, Lee SH and Park SG: ARS-interacting multi-functional
protein 1 induces proliferation of human bone marrow-derived
mesenchymal stem cells by accumulation of β-catenin via fibroblast
growth factor receptor 2-mediated activation of Akt. Stem Cells
Dev. 22:2630–2640. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lee JH, Lee H, Joung YK, Jung KH, Choi JH,
Lee DH, Park KD and Hong SS: The use of low molecular weight
heparin-pluronic nanogels to impede liver fibrosis by inhibition
the TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway. Biomaterials. 32:1438–1445. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Coffer PJ, Jin J and Woodgett JR: Protein
kinase B (c-Akt): A multifunctional mediator of
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activation. Biochem J. 335:1–13.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Xu L, Hui AY, Albanis E, Arthur MJ,
O'Byrne SM, Blaner WS, Mukherjee P, Friedman SL and Eng FJ: Human
hepatic stellate cell lines, LX-1 and LX-2: New tools for analysis
of hepatic fibrosis. Gut. 54:142–151. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Kretzschmar M, Doody J and Massagué J:
Opposing BMP and EGF signalling pathways converge on the TGF-beta
family mediator Smad1. Nature. 389:618–622. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Chen SJ, Yuan W, Mori Y, Levenson A,
Trojanowska M and Varga J: Stimulation of type I collagen
transcription in human skin fibroblasts by TGF-beta: Involvement of
Smad 3. J Invest Dermatol. 112:49–57. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Qi Z, Atsuchi N, Ooshima A, Takeshita A
and Ueno H: Blockade of type beta transforming growth factor
signaling prevents liver fibrosis and dysfunction in the rat. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 96:2345–2349. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Bataller R and Brenner DA: Liver fibrosis.
J Clin Invest. 115:209–218. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Wynn TA: Common and unique mechanisms
regulate fibrosis in various fibroproliferative diseases. J Clin
Invest. 117:524–529. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Han JM, Park SG, Lee Y and Kim S:
Structural separation of different extracellular activities in
aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase-interacting multi-functional protein,
p43/AIMP1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 342:113–118. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Friedman SL: Molecular regulation of
hepatic fibrosis, an integrated cellular response to tissue injury.
J Biol Chem. 275:2247–2250. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Gressner AM: Cytokines and cellular
crosstalk involved in the activation of fat-storing cells. J
Hepatol. 22(Suppl): 28–36. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Bissell DM, Wang SS, Jarnagin WR and Roll
FJ: Cell-specific expression of transforming growth factor-beta in
rat liver. Evidence for autocrine regulation of hepatocyte
proliferation. J Clin Invest. 96:447–455. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Chen A and Davis BH: The DNA binding
protein BTEB mediates acetaldehyde-induced, jun N-terminal
kinase-dependent alphaI(I) collagen gene expression in rat hepatic
stellate cells. Mol Cell Biol. 20:2818–2826. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|