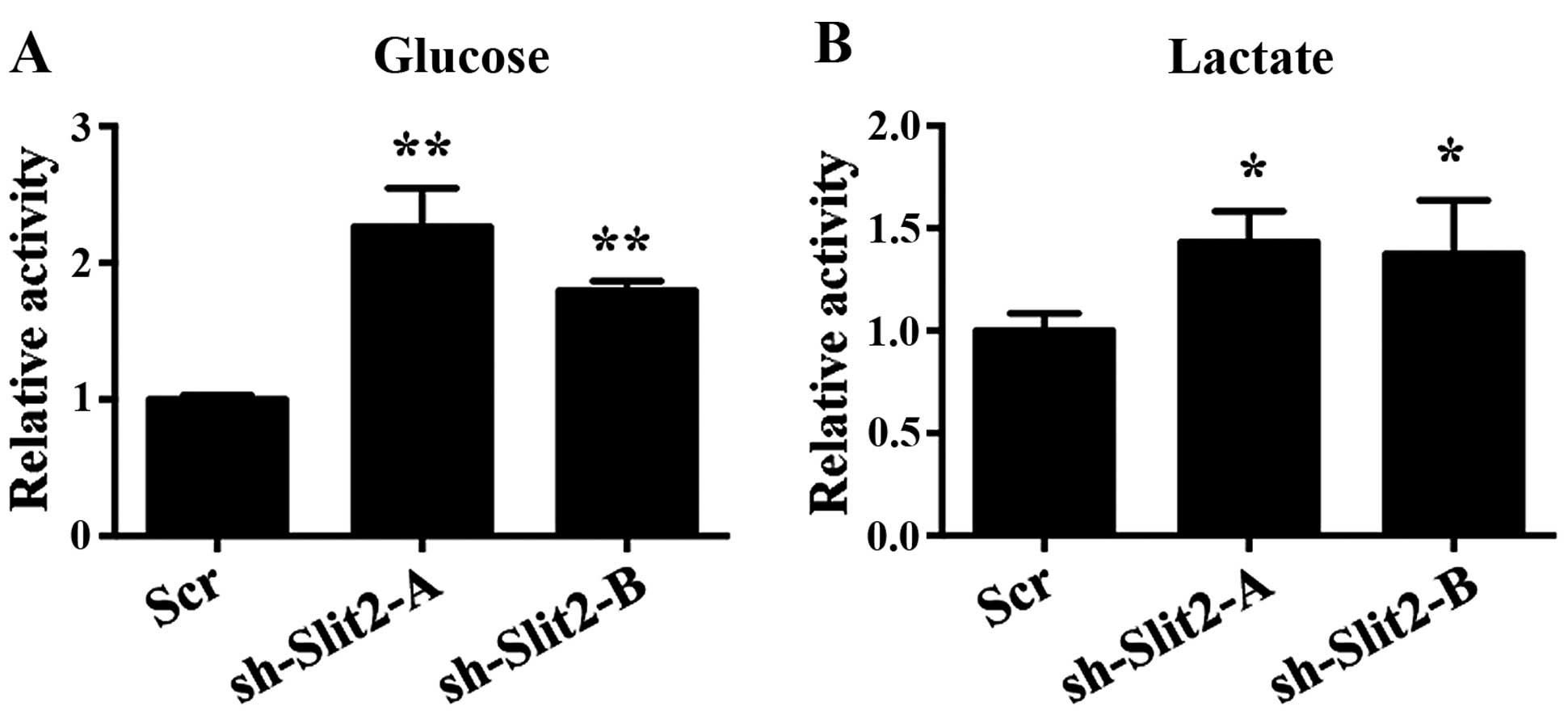
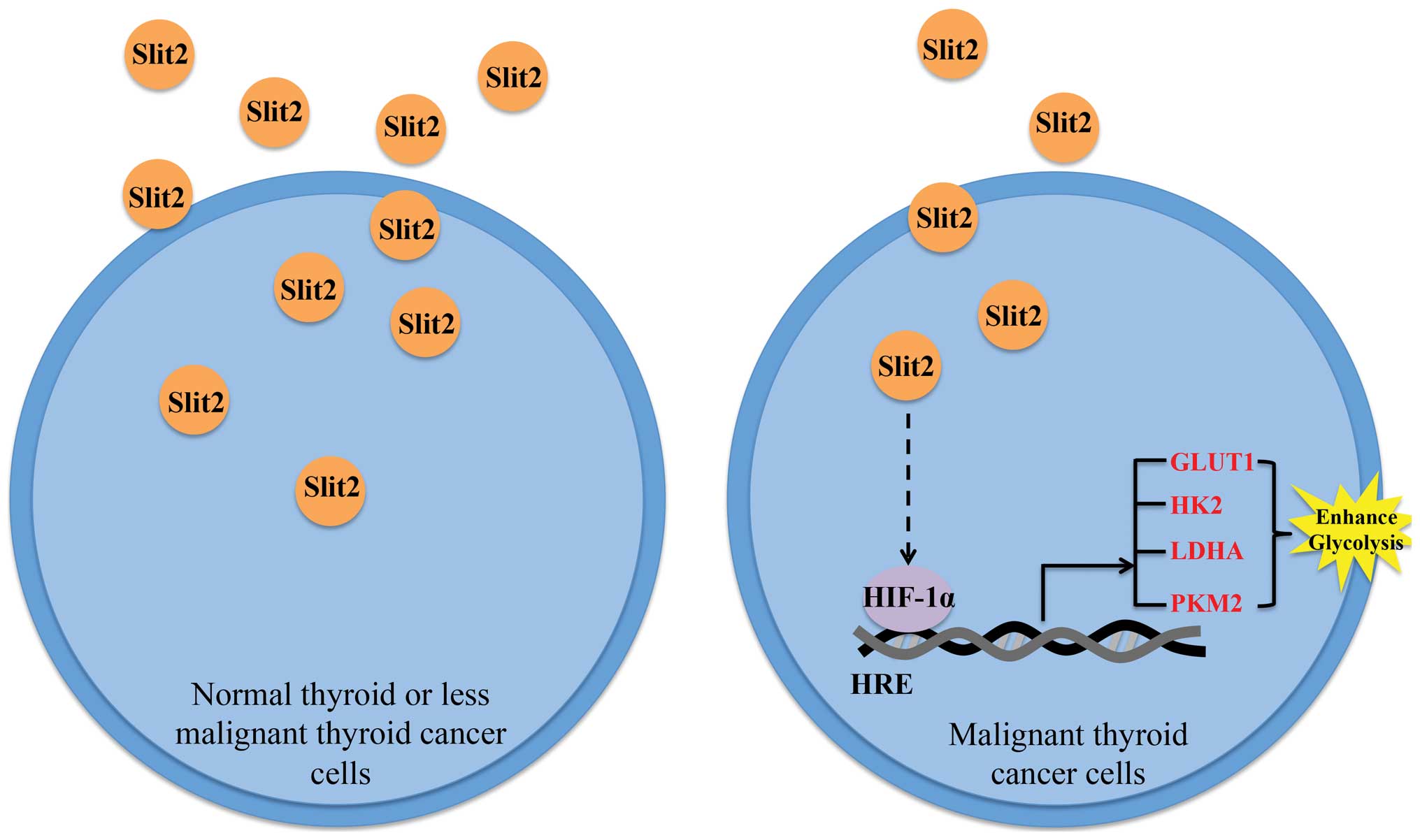
|
1
|
Faam B, Ghaffari MA, Ghadiri A and Azizi
F: Epigenetic modifications in human thyroid cancer. Biomed Rep.
3:3–8. 2015.
|
|
2
|
Kondo T, Ezzat S and Asa SL: Pathogenetic
mechanisms in thyroid follicular-cell neoplasia. Nat Rev Cancer.
6:292–306. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Patel KN and Shaha AR: Poorly
differentiated and anaplastic thyroid cancer. Cancer Control.
13:119–128. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chen AY, Jemal A and Ward EM: Increasing
incidence of differentiated thyroid cancer in the United States,
1988–2005. Cancer. 115:3801–3807. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Davies L and Welch HG: Increasing
incidence of thyroid cancer in the United States, 1973–2002. JAMA.
295:2164–2167. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Li Y, Nakamura M and Kakudo K: Targeting
of the BRAF gene in papillary thyroid carcinoma (Review). Oncol
Rep. 22:671–681. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Liu D, Hou J, Hu X, Wang X, Xiao Y, Mou Y
and De Leon H: Neuronal chemorepellent Slit2 inhibits vascular
smooth muscle cell migration by suppressing small GTPase Rac1
activation. Circ Res. 98:480–489. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wu W, Wong K, Chen J, Jiang Z, Dupuis S,
Wu JY and Rao Y: Directional guidance of neuronal migration in the
olfactory system by the protein Slit. Nature. 400:331–336. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Xu Y, Li WL, Fu L, Gu F and Ma YJ:
Slit2/Robo1 signaling in glioma migration and invasion. Neurosci
Bull. 26:474–478. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wong K, Ren XR, Huang YZ, Xie Y, Liu G,
Saito H, Tang H, Wen L, Brady-Kalnay SM, Mei L, et al: Signal
transduction in neuronal migration: Roles of GTPase activating
proteins and the small GTPase Cdc42 in the Slit-Robo pathway. Cell.
107:209–221. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wong K, Park HT, Wu JY and Rao Y: Slit
proteins: Molecular guidance cues for cells ranging from neurons to
leukocytes. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 12:583–591. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Qiu H, Zhu J, Yu J, Pu H and Dong R: SLIT2
is epigenetically silenced in ovarian cancers and suppresses growth
when activated. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 12:791–795.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Dallol A, Morton D, Maher ER and Latif F:
SLIT2 axon guidance molecule is frequently inactivated in
colorectal cancer and suppresses growth of colorectal carcinoma
cells. Cancer Res. 63:1054–1058. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Dallol A, Da Silva NF, Viacava P, Minna
JD, Bieche I, Maher ER and Latif F: SLIT2, a human homologue of the
Drosophila Slit2 gene, has tumor suppressor activity and is
frequently inactivated in lung and breast cancers. Cancer Res.
62:5874–5880. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Shi R, Yang Z, Liu W, Liu B, Xu Z and
Zhang Z: Knockdown of Slit2 promotes growth and motility in gastric
cancer cells via activation of AKT/β-catenin. Oncol Rep.
31:812–818. 2014.
|
|
16
|
Shi R, Liu W, Liu B, Xu Z, Chen L and
Zhang Z: Slit2 expression and its correlation with subcellular
localization of β-catenin in gastric cancer. Oncol Rep.
30:1883–1889. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Dallol A, Krex D, Hesson L, Eng C, Maher
ER and Latif F: Frequent epigenetic inactivation of the SLIT2 gene
in gliomas. Oncogene. 22:4611–4616. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Jin J, You H, Yu B, Deng Y, Tang N, Yao G,
Shu H, Yang S and Qin W: Epigenetic inactivation of SLIT2 in human
hepatocellular carcinomas. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 379:86–91.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Chang PH, Hwang-Verslues WW, Chang YC,
Chen CC, Hsiao M, Jeng YM, Chang KJ, Lee EY, Shew JY and Lee WH:
Activation of Robo1 signaling of breast cancer cells by Slit2 from
stromal fibroblast restrains tumorigenesis via blocking
PI3K/Akt/β-catenin pathway. Cancer Res. 72:4652–4661. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhou WJ, Geng ZH, Chi S, Zhang W, Niu XF,
Lan SJ, Ma L, Yang X, Wang LJ, Ding YQ, et al: Slit-Robo signaling
induces malignant transformation through Hakai-mediated E-cadherin
degradation during colorectal epithelial cell carcinogenesis. Cell
Res. 21:609–626. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Muñoz-Pinedo C, El Mjiyad N and Ricci JE:
Cancer metabolism: Current perspectives and future directions. Cell
Death Dis. 3:e2482012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Dang CV: Links between metabolism and
cancer. Genes Dev. 26:877–890. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Deberardinis RJ, Sayed N, Ditsworth D and
Thompson CB: Brick by brick: Metabolism and tumor cell growth. Curr
Opin Genet Dev. 18:54–61. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Cairns RA, Harris IS and Mak TW:
Regulation of cancer cell metabolism. Nat Rev Cancer. 11:85–95.
2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Meijer TW, Kaanders JH, Span PN and
Bussink J: Targeting hypoxia, HIF-1, and tumor glucose metabolism
to improve radiotherapy efficacy. Clin Cancer Res. 18:5585–5594.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Denko NC: Hypoxia, HIF1 and glucose
metabolism in the solid tumour. Nat Rev Cancer. 8:705–713. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Keith B, Johnson RS and Simon MC: HIF1α
and HIF2α: Sibling rivalry in hypoxic tumour growth and
progression. Nat Rev Cancer. 12:9–22. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Pereira KM, Chaves FN, Viana TS, Carvalho
FS, Costa FW, Alves AP and Sousa FB: Oxygen metabolism in oral
cancer: HIF and GLUTs (Review). Oncol Lett. 6:311–316.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Bertout JA, Patel SA and Simon MC: The
impact of O2 availability on human cancer. Nat Rev Cancer.
8:967–975. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Le A, Cooper CR, Gouw AM, Dinavahi R,
Maitra A, Deck LM, Royer RE, Vander Jagt DL, Semenza GL and Dang
CV: Inhibition of lactate dehydrogenase A induces oxidative stress
and inhibits tumor progression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
107:2037–2042. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Vaupel P, Mayer A and Höckel M: Tumor
hypoxia and malignant progression. Methods Enzymol. 381:335–354.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Semenza GL: Defining the role of
hypoxia-inducible factor 1 in cancer biology and therapeutics.
Oncogene. 29:625–634. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|