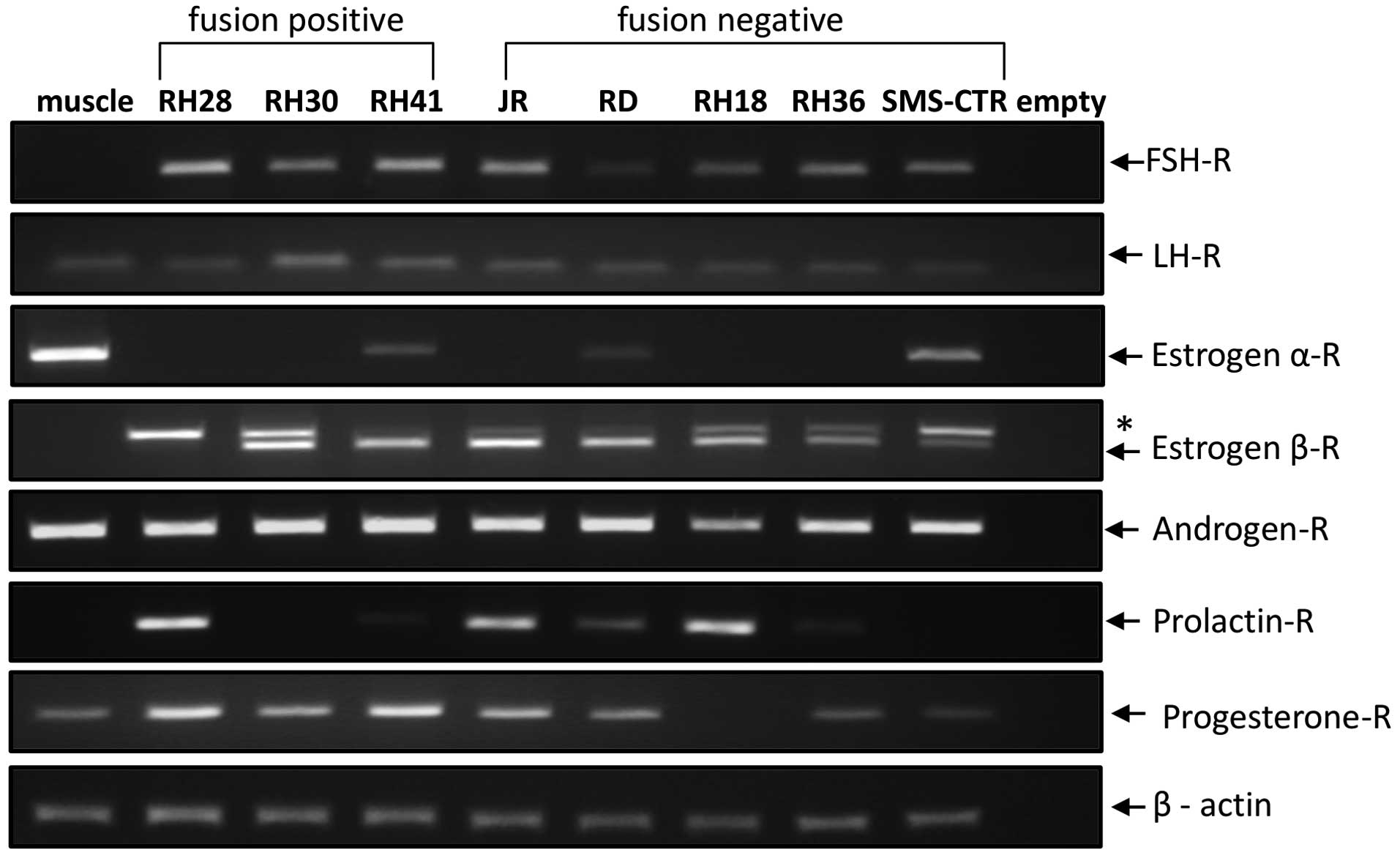
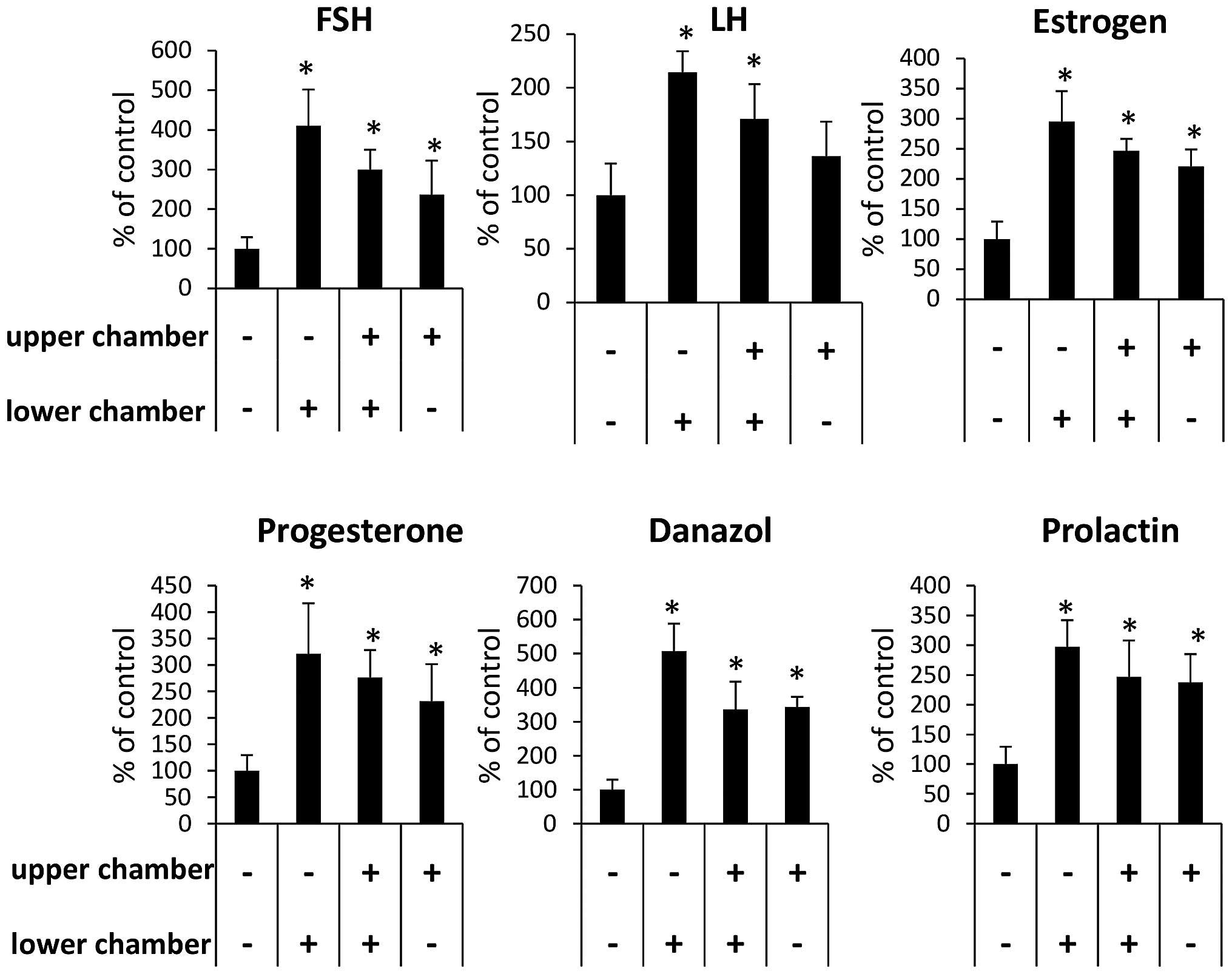
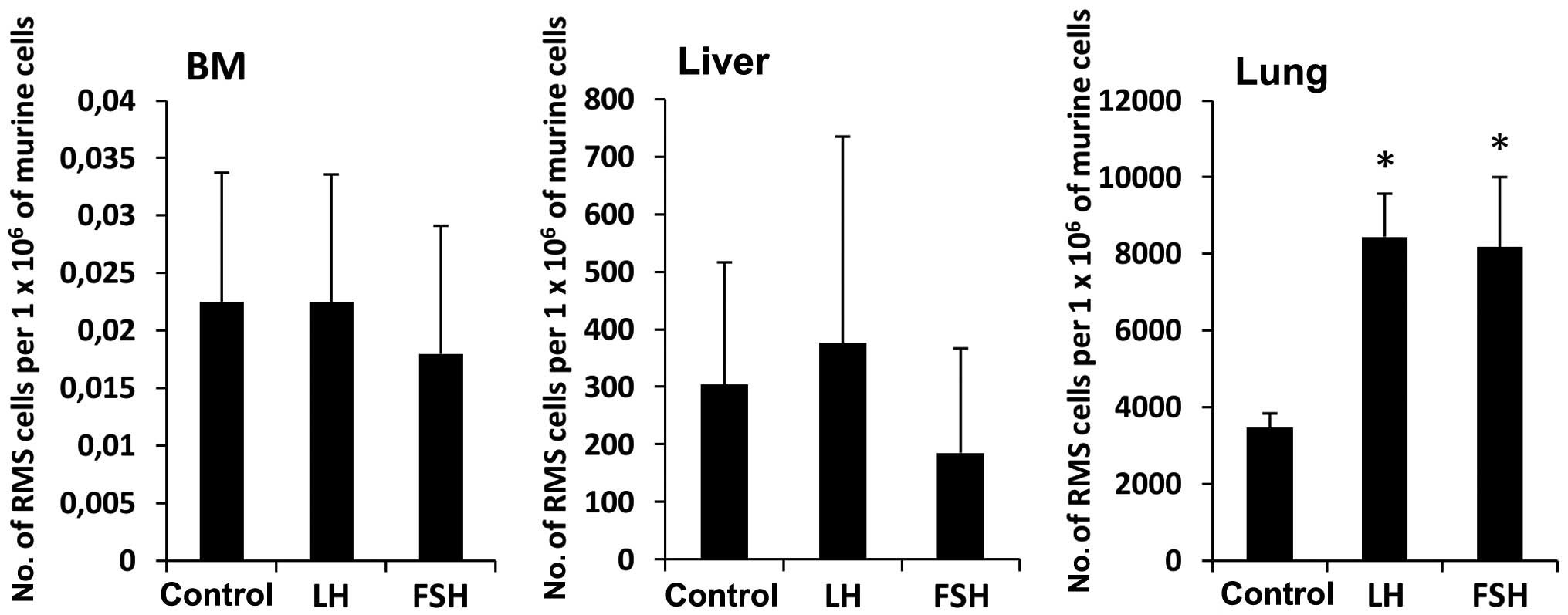
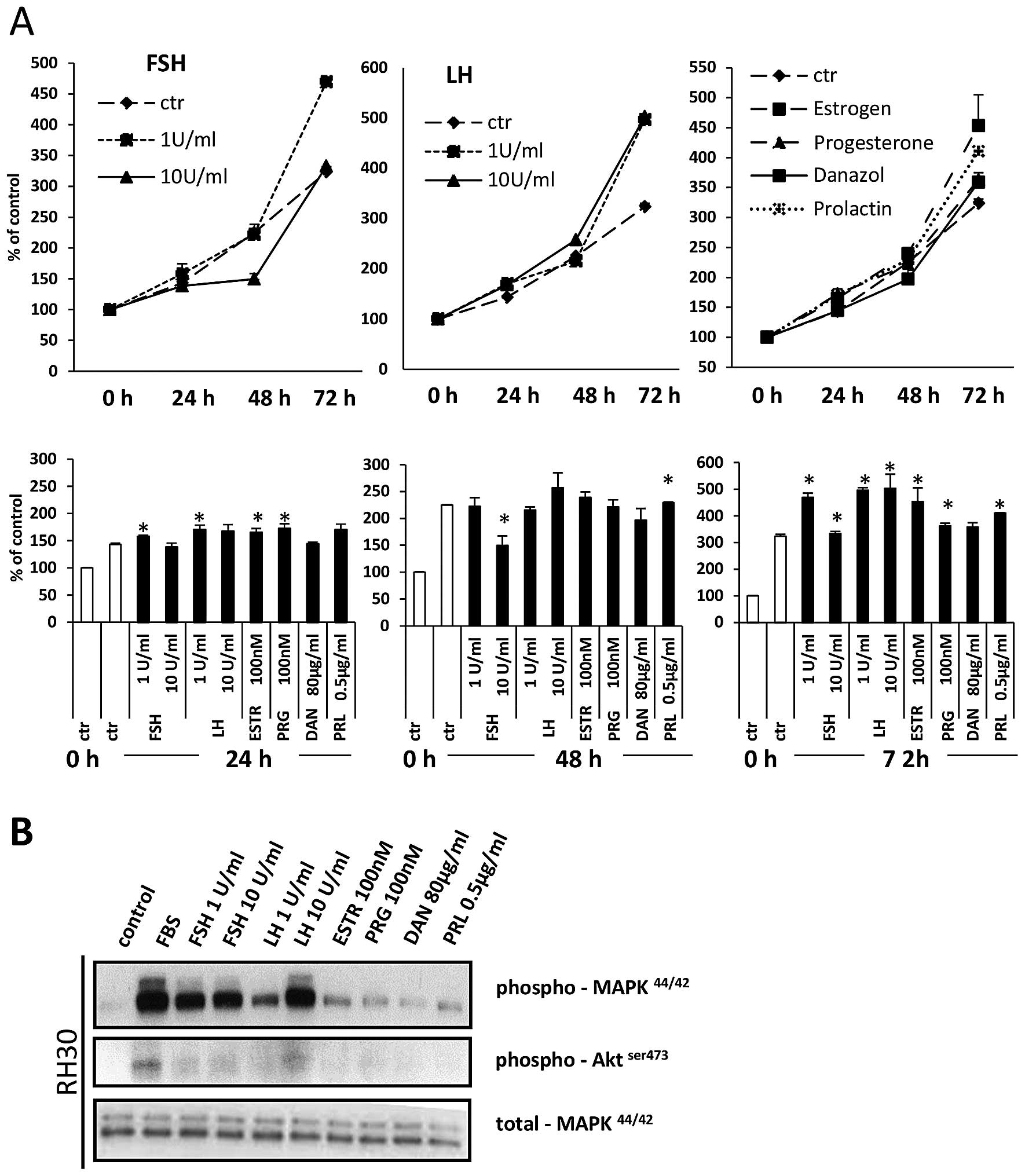
|
1
|
Gurney JG, Severson RK, Davis S and
Robison LL: Incidence of cancer in children in the United States.
Sex-, race-, and 1-year age-specific rates by histologic type.
Cancer. 75:2186–2195. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Huh WW and Skapek SX: Childhood
rhabdomyosarcoma: New insight on biology and treatment. Curr Oncol
Rep. 12:402–410. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sultan I, Qaddoumi I, Yaser S,
Rodriguez-Galindo C and Ferrari A: Comparing adult and pediatric
rhabdomyosarcoma in the surveillance, epidemiology and end results
program, 1973 to 2005: An analysis of 2,600 patients. J Clin Oncol.
27:3391–3397. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sandberg AA, Stone JF, Czarnecki L and
Cohen JD: Hematologic masquerade of rhabdomyosarcoma. Am J Hematol.
68:51–57. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Newton WA Jr, Gehan EA, Webber BL, Marsden
HB, van Unnik AJ, Hamoudi AB, Tsokos MG, Shimada H, Harms D,
Schmidt D, et al: Classification of rhabdomyosarcomas and related
sarcomas. Pathologic aspects and proposal for a new classification
- an Intergroup Rhabdomyosarcoma Study. Cancer. 76:1073–1085. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Davis RJ, D'Cruz CM, Lovell MA, Biegel JA
and Barr FG: Fusion of PAX7 to FKHR by the variant t(1;13)(p36;q14)
translocation in alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma. Cancer Res.
54:2869–2872. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Collins MH, Zhao H, Womer RB and Barr FG:
Proliferative and apoptotic differences between alveolar
rhabdomyosarcoma subtypes: A comparative study of tumors containing
PAX3-FKHR or PAX7-FKHR gene fusions. Med Pediatr Oncol. 37:83–89.
2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kashi VP, Hatley ME and Galindo RL:
Probing for a deeper understanding of rhabdomyosarcoma: Insights
from complementary model systems. Nat Rev Cancer. 15:426–439. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
MacKrell JG, Yaden BC, Bullock H, Chen K,
Shetler P, Bryant HU and Krishnan V: Molecular targets of androgen
signaling that characterize skeletal muscle recovery and
regeneration. Nucl Recept Signal. 13:e0052015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Carson JA and Manolagas SC: Effects of sex
steroids on bones and muscles: Similarities, parallels, and
putative interactions in health and disease. Bone. 80:67–78. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Velders M and Diel P: How sex hormones
promote skeletal muscle regeneration. Sports Med. 43:1089–1100.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Reiter BC, Kamanga-Sollo E, Pampusch MS,
White ME and Dayton WR: Epidermal growth factor receptor is
required for estradiol-stimulated bovine satellite cell
proliferation. Domest Anim Endocrinol. 48:48–55. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Dalerba P, Frascella E, Macino B,
Mandruzzato S, Zambon A, Rosolen A, Carli M, Ninfo V and Zanovello
P: MAGE, BAGE and GAGE gene expression in human rhabdomyosarcomas.
Int J Cancer. 93:85–90. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lifantseva N, Koltsova A, Krylova T,
Yakovleva T, Poljanskaya G and Gordeeva O: Expression patterns of
cancer-testis antigens in human embryonic stem cells and their cell
derivatives indicate lineage tracks. Stem Cells Int.
2011:7952392011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Anderson J, Gordon A, McManus A, Shipley J
and Pritchard-Jones K: Disruption of imprinted genes at chromosome
region 11p15.5 in paediatric rhabdomyosarcoma. Neoplasia.
1:340–348. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Roeb W, Boyer A, Cavenee WK and Arden KC:
PAX3-FOXO1 controls expression of the p57Kip2 cell-cycle regulator
through degradation of EGR1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
104:18085–18090. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Schneider G, Bowser MJ, Shin DM, Barr FG
and Ratajczak MZ: The paternally imprinted DLK1-GTL2 locus is
differentially methylated in embryonal and alveolar
rhabdomyosarcomas. Int J Oncol. 44:295–300. 2014.
|
|
18
|
Virchow R: Editorial Archive fuer
pathologische. Anatomie und Physiologie fuer klinische Medizin.
8:23–54. 1855.(In German).
|
|
19
|
Conheim J: Congenitales, quergestreiftes
muskelsarkon der nireren. Virchows Arch. 65:64–69. 1875.(In
German). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Aloisio GM, Nakada Y, Saatcioglu HD, Peña
CG, Baker MD, Tarnawa ED, Mukherjee J, Manjunath H, Bugde A,
Sengupta AL, et al: PAX7 expression defines germline stem cells in
the adult testis. J Clin Invest. 124:3929–3944. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
van Kruchten M, van der Marel P, de Munck
L, Hollema H, Arts H, Timmer-Bosscha H, de Vries E, Hospers G and
Reyners A: Hormone receptors as a marker of poor survival in
epithelial ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 138:634–639. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lønning PE: Poor-prognosis estrogen
receptor- positive disease: Present and future clinical solutions.
Ther Adv Med Oncol. 4:127–137. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
García-Cruz E, Piqueras M, Huguet J, Peri
L, Izquierdo L, Musquera M, Franco A, Alvarez-Vijande R, Ribal MJ
and Alcaraz A: Low testosterone levels are related to poor
prognosis factors in men with prostate cancer prior to treatment.
BJU Int. 110:E541–E546. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ryu WS, Kim JH, Jang YJ, Park SS, Um JW,
Park SH, Kim SJ, Mok YJ and Kim CS: Expression of estrogen
receptors in gastric cancer and their clinical significance. J Surg
Oncol. 106:456–461. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang AG, Lee KY, Kim SY, Choi JY, Lee KH,
Kim WH, Wang HJ, Kim JM, Park MG, Yeom YI, et al: The expression of
estrogen receptors in hepatocellular carcinoma in Korean patients.
Yonsei Med J. 47:811–816. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Siegfried JM, Hershberger PA and Stabile
LP: Estrogen receptor signaling in lung cancer. Semin Oncol.
36:524–531. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhou JH, Kim KB, Myers JN, Fox PS, Ning J,
Bassett RL, Hasanein H and Prieto VG: Immunohistochemical
expression of hormone receptors in melanoma of pregnant women,
nonpregnant women, and men. Am J Dermatopathol. 36:74–79. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Nakamura Y, Tanaka F, Nagahara H, Ieta K,
Haraguchi N, Mimori K, Sasaki A, Inoue H, Yanaga K and Mori M: Opa
interacting protein 5 (OIP5) is a novel cancer-testis specific gene
in gastric cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 14:885–892. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Song MH, Choi KU, Shin DH, Lee CH and Lee
SY: Identification of the cancer/testis antigens AKAP3 and CTp11 by
SEREX in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 28:1792–1798.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Su C, Xu Y, Li X, Ren S, Zhao C, Hou L, Ye
Z and Zhou C: Predictive and prognostic effect of CD133 and
cancer-testis antigens in stage Ib-IIIA non-small cell lung cancer.
Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:5509–5518. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sigalotti L, Fratta E, Coral S, Tanzarella
S, Danielli R, Colizzi F, Fonsatti E, Traversari C, Altomonte M and
Maio M: Intratumor heterogeneity of cancer/testis antigens
expression in human cutaneous melanoma is methylation-regulated and
functionally reverted by 5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine. Cancer Res.
64:9167–9171. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yasuoka H, Tsujimoto M, Fujita S, Yamasaki
T, Kashihara H, Nishio Y, Kodama R, Inagaki M, Oishi H, Sanke T, et
al: Coexistence of a clear cell adenocarcinoma and an adenosarcoma
with a heterologous rhabdomyosarcoma in an endometriotic cyst of
the ovary: A case study. Int J Gynecol Pathol. 28:362–366. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kim DW, Shin JH, Lee HJ, Hong YO, Joo JE
and Kim EK: Spindle cell rhabdomyosacoma of uterus: A case study.
Korean J Pathol. 47:388–391. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Poniewierska-Baran A, Suszynska M, Sun W,
Abdelbaset-Ismail A, Schneider G, Barr FG and Ratajczak MZ: Human
rhabdomyosarcoma cells express functional erythropoietin receptor:
Potential therapeutic implications. Int J Oncol. 47:1989–1997.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kamel HK, Maas D and Duthie EH Jr: Role of
hormones in the pathogenesis and management of sarcopenia. Drugs
Aging. 19:865–877. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Baumgartner RN, Koehler KM, Gallagher D,
Romero L, Heymsfield SB, Ross RR, Garry PJ and Lindeman RD:
Epidemiology of sarcopenia among the elderly in New Mexico. Am J
Epidemiol. 147:755–763. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zacharin M, Waters K, Chow CW, Crock P and
McKelvie P: Recurrent rhabdomyosarcoma after 25 years: A possible
association with estrogen and progestogen therapy. J Pediatr
Hematol Oncol. 19:477–481. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Dagher R and Helman L: Rhabdomyosarcoma:
An overview. Oncologist. 4:34–44. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Nguyen DX, Bos PD and Massagué J:
Metastasis: From dissemination to organ-specific colonization. Nat
Rev Cancer. 9:274–284. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zlotnik A, Burkhardt AM and Homey B:
Homeostatic chemokine receptors and organ-specific metastasis. Nat
Rev Immunol. 11:597–606. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Coghlin C and Murray GI: Current and
emerging concepts in tumour metastasis. J Pathol. 222:1–15. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Petrie RJ, Doyle AD and Yamada KM: Random
versus directionally persistent cell migration. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 10:538–549. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Jankowski K, Kucia M, Wysoczynski M, Reca
R, Zhao D, Trzyna E, Trent J, Peiper S, Zembala M, Ratajczak J, et
al: Both hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) and stromal-derived
factor-1 regulate the metastatic behavior of human rhabdomyosarcoma
cells, but only HGF enhances their resistance to radiochemotherapy.
Cancer Res. 63:7926–7935. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Kalebic T, Tsokos M and Helman LJ: In vivo
treatment with antibody against IGF-1 receptor suppresses growth of
human rhabdomyosarcoma and down-regulates p34cdc2. Cancer Res.
54:5531–5534. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Rezvani G, Lui JC, Barnes KM and Baron J:
A set of imprinted genes required for normal body growth also
promotes growth of rhabdomyosarcoma cells. Pediatr Res. 71:32–38.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Libura J, Drukala J, Majka M, Tomescu O,
Navenot JM, Kucia M, Marquez L, Peiper SC, Barr FG,
Janowska-Wieczorek A, et al: CXCR4-SDF-1 signaling is active in
rhabdomyosarcoma cells and regulates locomotion, chemotaxis, and
adhesion. Blood. 100:2597–2606. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Tarnowski M, Grymula K, Liu R, Tarnowska
J, Drukala J, Ratajczak J, Mitchell RA, Ratajczak MZ and Kucia M:
Macrophage migration inhibitory factor is secreted by
rhabdomyosarcoma cells, modulates tumor metastasis by binding to
CXCR4 and CXCR7 receptors and inhibits recruitment of
cancer-associated fibroblasts. Mol Cancer Res. 8:1328–1343. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Wysoczynski M, Miekus K, Jankowski K,
Wanzeck J, Bertolone S, Janowska-Wieczorek A, Ratajczak J and
Ratajczak MZ: Leukemia inhibitory factor: A newly identified
metastatic factor in rhabdomyosarcomas. Cancer Res. 67:2131–2140.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Schneider G, Bryndza E, Abdel-Latif A,
Ratajczak J, Maj M, Tarnowski M, Klyachkin YM, Houghton P, Morris
AJ, Vater A, et al: Bioactive lipids S1P and C1P are prometastatic
factors in human rhabdomyosarcoma, and their tissue levels increase
in response to radio/chemotherapy. Mol Cancer Res. 11:793–807.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Schneider G, Sellers ZP, Abdel-Latif A,
Morris AJ and Ratajczak MZ: Bioactive lipids, LPC and LPA, are
novel prometastatic factors and their tissue levels increase in
response to radio/chemotherapy. Mol Cancer Res. 12:1560–1573. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Hou Q and Gorski J: Estrogen receptor and
progesterone receptor genes are expressed differentially in mouse
embryos during preimplantation development. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
90:9460–9464. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Crocoll A, Zhu CC, Cato AC and Blum M:
Expression of androgen receptor mRNA during mouse embryogenesis.
Mech Dev. 72:175–178. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Ratajczak MZ, Zuba-Surma EK, Wysoczynski
M, Ratajczak J and Kucia M: Very small embryonic-like stem cells:
Characterization, developmental origin, and biological
significance. Exp Hematol. 36:742–751. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Mierzejewska K, Borkowska S, Suszynska E,
Suszynska M, Poniewierska-Baran A, Maj M, Pedziwiatr D, Adamiak M,
Abdel-Latif A, Kakar SS, et al: Hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells
express several functional sex hormone receptors-novel evidence for
a potential developmental link between hematopoiesis and primordial
germ cells. Stem Cells Dev. 24:927–937. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Zuba-Surma EK, Kucia M, Wu W, Klich I,
Lillard JW Jr, Ratajczak J and Ratajczak MZ: Very small
embryonic-like stem cells are present in adult murine organs:
ImageStream-based morphological analysis and distribution studies.
Cytometry A. 73A:1116–1127. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|