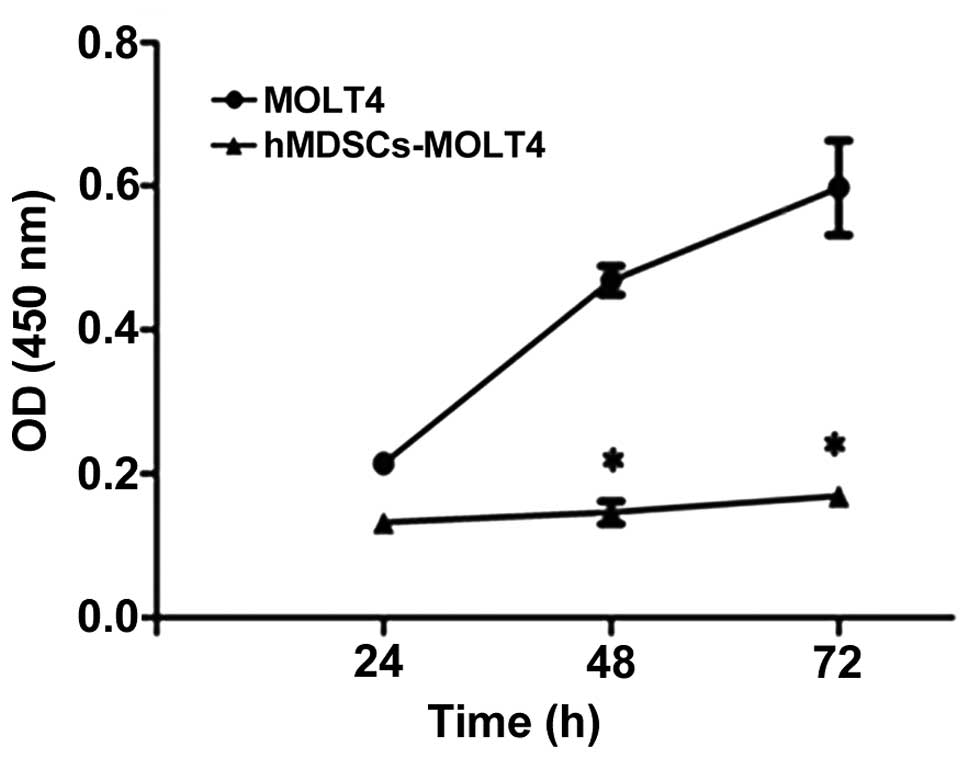
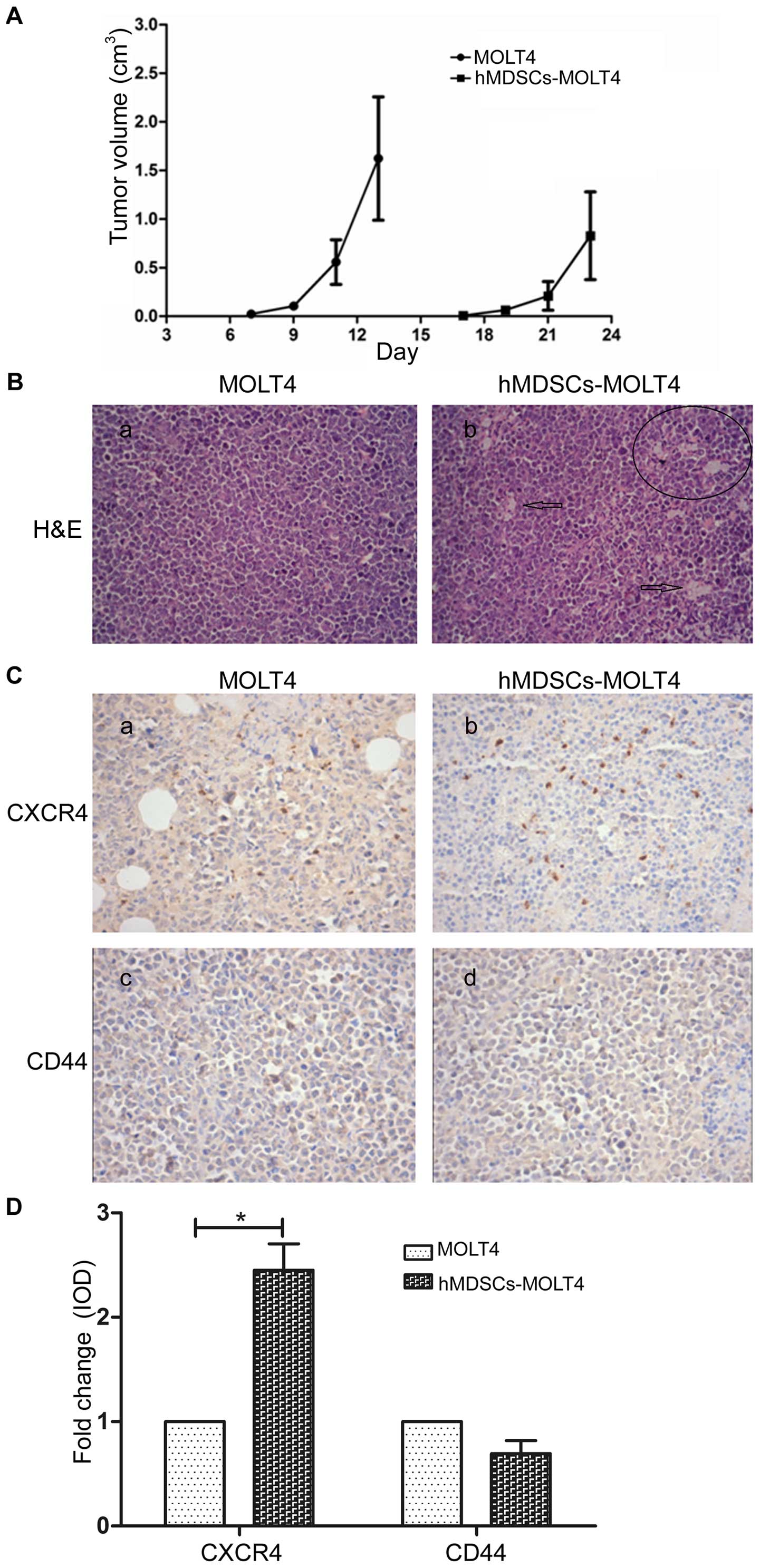
|
1
|
Vyas P, Appelbaum FR and Craddock C:
Allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation for acute myeloid
leukemia. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 21:8–15. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Lang F, Wojcik B and Rieger MA: Stem cell
hierarchy and clonal evolution in acute lymphoblastic leukemia.
Stem Cells Int. 2015:1371642015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Krause DS and Van Etten RA: Right on
target: Eradicating leukemic stem cells. Trends Mol Med.
13:470–481. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lane SW, Scadden DT and Gilliland DG: The
leukemic stem cell niche: Current concepts and therapeutic
opportunities. Blood. 114:1150–1157. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Schulenburg A, Blatt K, Cerny-Reiterer S,
Sadovnik I, Herrmann H, Marian B, Grunt TW, Zielinski CC and Valent
P: Cancer stem cells in basic science and in translational
oncology: Can we translate into clinical application? J Hematol
Oncol. 8:162015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Dallas NA, Xia L, Fan F, Gray MJ, Gaur P,
van Buren G II, Samuel S, Kim MP, Lim SJ and Ellis LM:
Chemoresistant colorectal cancer cells, the cancer stem cell
phenotype, and increased sensitivity to insulin-like growth
factor-I receptor inhibition. Cancer Res. 69:1951–1957. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Khan IN, Al-Karim S, Bora RS, Chaudhary AG
and Saini KS: Cancer stem cells: A challenging paradigm for
designing targeted drug therapies. Drug Discov Today. 20:1205–1216.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Li HZ, Yi TB and Wu ZY: Suspension culture
combined with chemotherapeutic agents for sorting of breast cancer
stem cells. BMC Cancer. 8:1352008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Liu YM, Li XF, Liu H and Wu XL:
Ultrasound-targeted micro-bubble destruction-mediated
downregulation of CD133 inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition,
stemness and migratory ability of liver cancer stem cells. Oncol
Rep. 34:2977–2986. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Becker MW and Jordan CT: Leukemia stem
cells in 2010: Current understanding and future directions. Blood
Rev. 25:75–81. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kornblau SM, Qutub A, Yao H, York H, Qiu
YH, Graber D, Ravandi F, Cortes J, Andreeff M, Zhang N, et al:
Proteomic profiling identifies distinct protein patterns in acute
myelogenous leukemia CD34+CD38− stem-like
cells. PLoS One. 8:e784532013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Amaya CN and Bryan BA: Enrichment of the
embryonic stem cell reprogramming factors Oct4, Nanog, Myc, and
Sox2 in benign and malignant vascular tumors. BMC Clin Pathol.
15:182015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yin X, Zhang BH, Zheng SS, Gao DM, Qiu SJ,
Wu WZ and Ren ZG: Coexpression of gene Oct4 and Nanog initiates
stem cell characteristics in hepatocellular carcinoma and promotes
epithelial-mesenchymal transition through activation of Stat3/Snail
signaling. J Hematol Oncol. 8:232015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jeter CR, Liu B, Liu X, Chen X, Liu C,
Calhoun-Davis T, Repass J, Zaehres H, Shen JJ and Tang DG: NANOG
promotes cancer stem cell characteristics and prostate cancer
resistance to androgen deprivation. Oncogene. 30:3833–3845. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Jeter CR, Badeaux M, Choy G, Chandra D,
Patrawala L, Liu C, Calhoun-Davis T, Zaehres H, Daley GQ and Tang
DG: Functional evidence that the self-renewal gene NANOG regulates
human tumor development. Stem Cells. 27:993–1005. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lessard J and Sauvageau G: Bmi-1
determines the proliferative capacity of normal and leukaemic stem
cells. Nature. 423:255–260. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Han AR, Lee JY, Kim HJ, min WS, Park G and
Kim SH: A CXCR4 antagonist leads to tumor suppression by activation
of immune cells in a leukemia-induced microenvironment. Oncol Rep.
34:2880–2888. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Dubrovska A, Elliott J, Salamone RJ,
Telegeev GD, Stakhovsky AE, Schepotin IB, Yan F, Wang Y, Bouchez
LC, Kularatne SA, et al: CXCR4 expression in prostate cancer
progenitor cells. PLoS One. 7:e312262012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Dubrovska A, Hartung A, Bouchez LC, Walker
JR, Reddy VA, Cho CY and Schultz PG: CXCR4 activation maintains a
stem cell population in tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer cells
through AhR signalling. Br J Cancer. 107:43–52. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Tavernier E, Aanei C, Solly F,
Flandrin-Gresta P, Campos L and Guyotat D: CXCR4: A new therapeutic
target of the leukaemic cell? Role of the SDF-1/CXCR4 axis in acute
myeloid leukaemia. Bull Cancer. 101:593–604. 2014.(In French).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Williams DA and Cancelas JA: Leukaemia:
Niche retreats for stem cells. Nature. 444:827–828. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Liu C, Kelnar K, Liu B, Chen X,
Calhoun-Davis T, Li H, Patrawala L, Yan H, Jeter C, Honorio S, et
al: The microRNA miR-34a inhibits prostate cancer stem cells and
metastasis by directly repressing CD44. Nat Med. 17:211–215. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Erb U, Megaptche AP, Gu X, Büchler MW and
Zöller M: CD44 standard and CD44v10 isoform expression on leukemia
cells distinctly influences niche embedding of hematopoietic stem
cells. J Hematol Oncol. 7:292014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Assanhou AG, Li W, Zhang L, Xue L, Kong L,
Sun H, Mo R and Zhang C: Reversal of multidrug resistance by
co-delivery of paclitaxel and lonidamine using a TPGS and
hyaluronic acid dual-functionalized liposome for cancer treatment.
Biomaterials. 73:284–295. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hämmerle B, Yañez Y, Palanca S, Cañete A,
Burks DJ, Castel V and Font de Mora J: Targeting neuroblastoma stem
cells with retinoic acid and proteasome inhibitor. PLoS One.
8:e767612013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wang X, Liu Q, Hou B, Zhang W, Yan M, Jia
H, Li H, Yan D, Zheng F, Ding W, et al: Concomitant targeting of
multiple key transcription factors effectively disrupts cancer stem
cells enriched in side population of human pancreatic cancer cells.
PLoS One. 8:e739422013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Guo P, Gao A, Zhang G, Han H and Zhou Q:
Decoding the knots of initiation of oncogenic
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in tumor progression. Curr Cancer
Drug Targets. 13:996–1011. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wu A, Loutherback K, Lambert G,
Estévez-Salmerón L, Tlsty TD, Austin RH and Sturm JC: Cell motility
and drug gradients in the emergence of resistance to chemotherapy.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 110:16103–16108. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Stiehl T, Baran N, Ho AD and
Marciniak-Czochra A: Cell division patterns in acute myeloid
leukemia stem-like cells determine clinical course: A model to
predict patient survival. Cancer Res. 75:940–949. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Prud'homme GJ: Cancer stem cells and novel
targets for antitumor strategies. Curr Pharm Des. 18:2838–2849.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Carter BZ, Mak DH, Cortes J and Andreeff
M: The elusive chronic myeloid leukemia stem cell: Does it matter
and how do we eliminate it? Semin Hematol. 47:362–370. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|