|
1
|
Renehan A, Gleave EN, Hancock BD, Smith P
and McGurk M: Long-term follow-up of over 1000 patients with
salivary gland tumours treated in a single centre. Br J Surg.
83:1750–1754. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Liu J, Shao C, Tan ML, Mu D, Ferris RL and
Ha PK: Molecular biology of adenoid cystic carcinoma. Head Neck.
34:1665–1677. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Rettig EM, Tan M, Ling S, Yonescu R,
Bishop JA, Fakhry C and Ha PK: MYB rearrangement and
clinicopathologic characteristics in head and neck adenoid cystic
carcinoma. Laryngoscope. 125:E292–E299. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Moskaluk CA: Adenoid cystic carcinoma:
Clinical and molecular features. Head Neck Pathol. 7:17–22. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ho AS, Kannan K, Roy DM, Morris LG, Ganly
I, Katabi N, Ramaswami D, Walsh LA, Eng S, Huse JT, et al: The
mutational landscape of adenoid cystic carcinoma. Nat Genet.
45:791–798. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Stephens PJ, Davies HR, Mitani Y, Van Loo
P, Shlien A, Tarpey PS, Papaemmanuil E, Cheverton A, Bignell GR,
Butler AP, et al: Whole exome sequencing of adenoid cystic
carcinoma. J Clin Invest. 123:2965–2968. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Holst VA, Marshall CE, Moskaluk CA and
Frierson HF Jr: KIT protein expression and analysis of c-kit gene
mutation in adenoid cystic carcinoma. Mod Pathol. 12:956–960.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Vila L, Liu H, Al-Quran SZ, Coco DP, Dong
HJ and Liu C: Identification of c-kit gene mutations in primary
adenoid cystic carcinoma of the salivary gland. Mod Pathol.
22:1296–1302. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tetsu O, Phuchareon J, Chou A, Cox DP,
Eisele DW and Jordan RCK: Mutations in the c-Kit gene disrupt
mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling during tumor development
in adenoid cystic carcinoma of the salivary glands. Neoplasia.
12:708–717. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sung JY, Ahn HK, Kwon JE, Jeong H, Baek
CH, Son YI, Ahn YC, Park K, Ahn MJ and Ko YH: Reappraisal of KIT
mutation in adenoid cystic carcinomas of the salivary gland. J Oral
Pathol Med. 41:415–423. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Frierson HF Jr and Moskaluk CA: Mutation
signature of adenoid cystic carcinoma: Evidence for transcriptional
and epigenetic reprogramming. J Clin Invest. 123:2783–2785. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ross JS, Wang K, Rand JV, Sheehan CE,
Jennings TA, Al-Rohil RN, Otto GA, Curran JC, Palmer G, Downing SR,
et al: Comprehensive genomic profiling of relapsed and metastatic
adenoid cystic carcinomas by next-generation sequencing reveals
potential new routes to targeted therapies. Am J Surg Pathol.
38:235–238. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Mitani Y, Li J, Rao PH, Zhao YJ, Bell D,
Lippman SM, Weber RS, Caulin C and El-Naggar AK: Comprehensive
analysis of the MYB-NFIB gene fusion in salivary adenoid cystic
carcinoma: Incidence, variability, and clinicopathologic
significance. Clin Cancer Res. 16:4722–4731. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
West RB, Kong C, Clarke N, Gilks T,
Lipsick JS, Cao H, Kwok S, Montgomery KD, Varma S and Le QT: MYB
expression and translocation in adenoid cystic carcinomas and other
salivary gland tumors with clinicopathologic correlation. Am J Surg
Pathol. 35:92–99. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
15
|
Brill LB II, Kanner WA, Fehr A, Andrén Y,
Moskaluk CA, Löning T, Stenman G and Frierson HF Jr: Analysis of
MYB expression and MYB-NFIB gene fusions in adenoid cystic
carcinoma and other salivary neoplasms. Mod Pathol. 24:1169–1176.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Persson M, Andrén Y, Moskaluk CA, Frierson
HF Jr, Cooke SL, Futreal PA, Kling T, Nelander S, Nordkvist A,
Persson F, et al: Clinically significant copy number alterations
and complex rearrangements of MYB and NFIB in head and neck adenoid
cystic carcinoma. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 51:805–817. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Persson M, Andrén Y, Mark J, Horlings HM,
Persson F and Stenman G: Recurrent fusion of MYB and NFIB
transcription factor genes in carcinomas of the breast and head and
neck. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:18740–18744. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Stenman G: Fusion oncogenes in salivary
gland tumors: Molecular and clinical consequences. Head Neck
Pathol. 7(Suppl 1): S12–S19. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Mitani Y, Rao PH, Futreal PA, Roberts DB,
Stephens PJ, Zhao YJ, Zhang L, Mitani M, Weber RS, Lippman SM, et
al: Novel chromosomal rearrangements and break points at the t(6;9)
in salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma: Association with MYB-NFIB
chimeric fusion, MYB expression, and clinical outcome. Clin Cancer
Res. 17:7003–7014. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Phuchareon J, Ohta Y, Woo JM, Eisele DW
and Tetsu O: Genetic profiling reveals cross-contamination and
misidentification of 6 adenoid cystic carcinoma cell lines: ACC2,
ACC3, ACCM, ACCNS, ACCS and CAC2. PLoS One. 4:e60402009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Moskaluk CA, Baras AS, Mancuso SA, Fan H,
Davidson RJ, Dirks DC, Golden WL and Frierson HF Jr: Development
and characterization of xenograft model systems for adenoid cystic
carcinoma. Lab Invest. 91:1480–1490. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Taylor SM and Jones PA: Multiple new
phenotypes induced in 10T1/2 and 3T3 cells treated with
5-azacytidine. Cell. 17:771–779. 1979. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Jones PA and Taylor SM: Cellular
differentiation, cytidine analogs and DNA methylation. Cell.
20:85–93. 1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Cameron EE, Bachman KE, Myöhänen S, Herman
JG and Baylin SB: Synergy of demethylation and histone deacetylase
inhibition in the re-expression of genes silenced in cancer. Nat
Genet. 21:103–107. 1999. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Jones PA and Taylor SM: Hemimethylated
duplex DNAs prepared from 5-azacytidine-treated cells. Nucleic
Acids Res. 9:2933–2947. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Taylor SM and Jones PA: Mechanism of
action of eukaryotic DNA methyltransferase. Use of
5-azacytosine-containing DNA. J Mol Biol. 162:679–692. 1982.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Herman JG and Baylin SB: Gene silencing in
cancer in association with promoter hypermethylation. N Engl J Med.
349:2042–2054. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Shao C, Sun W, Tan M, Glazer CA, Bhan S,
Zhong X, Fakhry C, Sharma R, Westra WH, Hoque MO, et al:
Integrated, genome-wide screening for hypomethylated oncogenes in
salivary gland adenoid cystic carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res.
17:4320–4330. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Shao C, Bai W, Junn JC, Uemura M,
Hennessey PT, Zaboli D, Sidransky D, Califano JA and Ha PK:
Evaluation of MYB promoter methylation in salivary adenoid cystic
carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 47:251–255. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
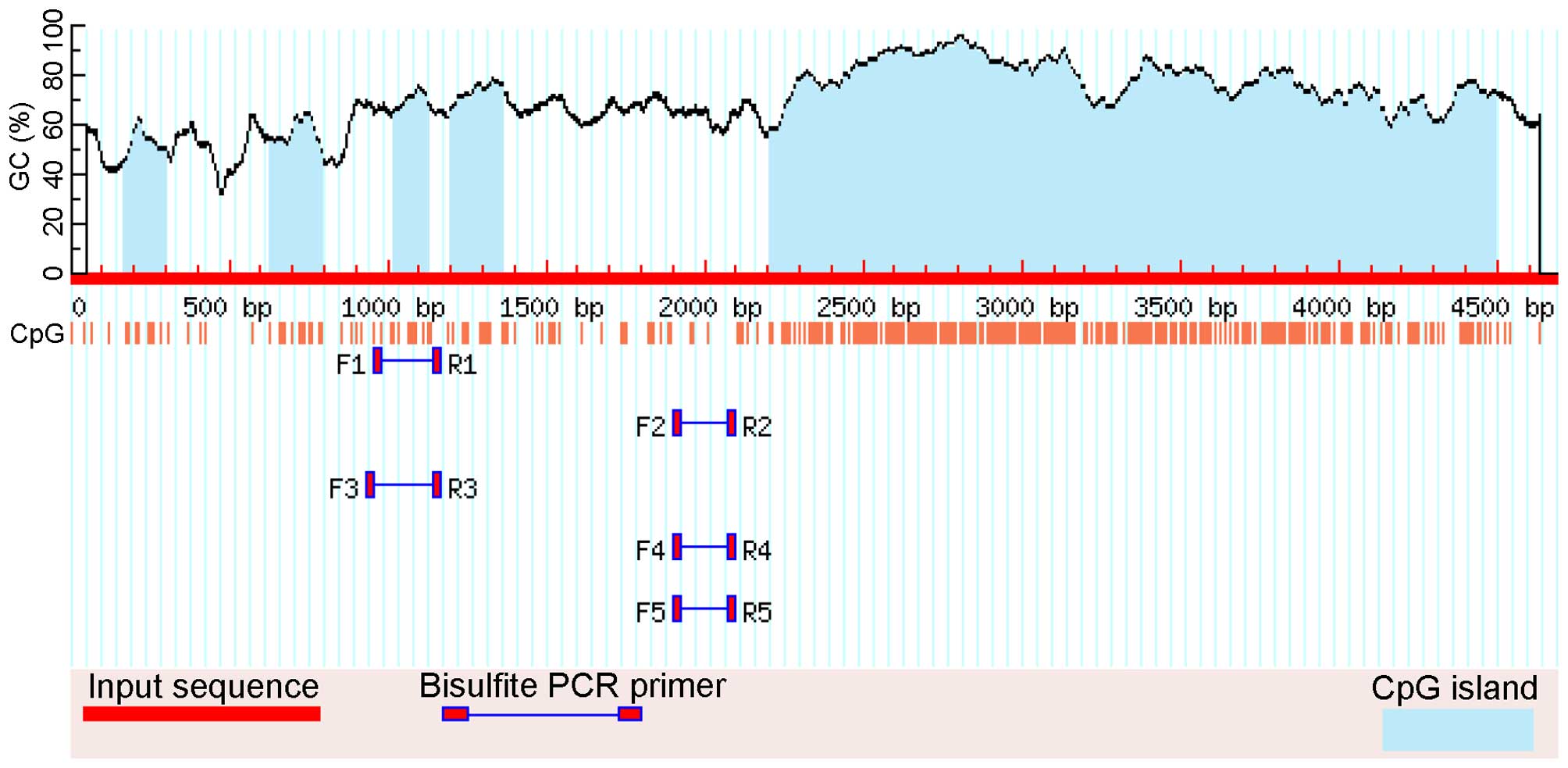
Li LC and Dahiya R: MethPrimer: Designing
primers for methylation PCRs. Bioinformatics. 18:1427–1431. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kim MS, Louwagie J, Carvalho B, Terhaar
Sive Droste JS, Park HL, Chae YK, Yamashita K, Liu J, Ostrow KL,
Ling S, et al: Promoter DNA methylation of oncostatin m receptor-β
as a novel diagnostic and therapeutic marker in colon cancer. PLoS
One. 4:e65552009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Durr ML, Mydlarz WK, Shao C, Zahurak ML,
Chuang AY, Hoque MO, Westra WH, Liegeois NJ, Califano JA, Sidransky
D, et al: Quantitative methylation profiles for multiple tumor
suppressor gene promoters in salivary gland tumors. PLoS One.
5:e108282010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ling S, Chang X, Schultz L, Lee TK, Chaux
A, Marchionni L, Netto GJ, Sidransky D and Berman DM: An
EGFR-ERK-SOX9 signaling cascade links urothelial development and
regeneration to cancer. Cancer Res. 71:3812–3821. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Bell D, Roberts D, Karpowicz M, Hanna EY,
Weber RS and El-Naggar AK: Clinical significance of Myb protein and
downstream target genes in salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma.
Cancer Biol Ther. 12:569–573. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Bell A, Bell D, Weber RS and El-Naggar AK:
CpG island methylation profiling in human salivary gland adenoid
cystic carcinoma. Cancer. 117:2898–2909. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Santoro B, Grant SGN, Bartsch D and Kandel
ER: Interactive cloning with the SH3 domain of N-src identifies a
new brain specific ion channel protein, with homology to eag and
cyclic nucleotide-gated channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
94:14815–14820. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Santoro B, Liu DT, Yao H, Bartsch D,
Kandel ER, Siegelbaum SA and Tibbs GR: Identification of a gene
encoding a hyperpolarization-activated pacemaker channel of brain.
Cell. 93:717–729. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ludwig A, Zong X, Jeglitsch M, Hofmann F
and Biel M: A family of hyperpolarization-activated mammalian
cation channels. Nature. 393:587–591. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Gauss R, Seifert R and Kaupp UB: Molecular
identification of a hyperpolarization-activated channel in sea
urchin sperm. Nature. 393:583–587. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Ludwig A, Zong X, Stieber J, Hullin R,
Hofmann F and Biel M: Two pacemaker channels from human heart with
profoundly different activation kinetics. EMBO J. 18:2323–2329.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Vaccari T, Moroni A, Rocchi M, Gorza L,
Bianchi ME, Beltrame M and DiFrancesco D: The human gene coding for
HCN2, a pacemaker channel of the heart. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1446:419–425. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Seifert R, Scholten A, Gauss R, Mincheva
A, Lichter P and Kaupp UB: Molecular characterization of a slowly
gating human hyperpolarization-activated channel predominantly
expressed in thalamus, heart, and testis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
96:9391–9396. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Ishii TM, Takano M, Xie LH, Noma A and
Ohmori H: Molecular characterization of the
hyperpolarization-activated cation channel in rabbit heart
sinoatrial node. J Biol Chem. 274:12835–12839. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Clapham DE: Not so funny anymore: Pacing
channels are cloned. Neuron. 21:5–7. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Hofmann F, Biel M and Kaupp UB:
International Union of Pharmacology. LI. Nomenclature and
structure-function relationships of cyclic nucleotide-regulated
channels. Pharmacol Rev. 57:455–462. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Pape HC: Queer current and pacemaker: The
hyperpolarization-activated cation current in neurons. Annu Rev
Physiol. 58:299–327. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Stieber J, Hofmann F and Ludwig A:
Pacemaker channels and sinus node arrhythmia. Trends Cardiovasc
Med. 14:23–28. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
DiFrancesco D: The role of the funny
current in pacemaker activity. Circ Res. 106:434–446. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Lang F and Stournaras C: Ion channels in
cancer: Future perspectives and clinical potential. Philos Trans R
Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 369:201301082014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Benarroch EE: HCN channels: Function and
clinical implications. Neurology. 80:304–310. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Norberg E, Karlsson M, Korenovska O,
Szydlowski S, Silberberg G, Uhlén P, Orrenius S and Zhivotovsky B:
Critical role for hyperpolarization-activated cyclic
nucleotide-gated channel 2 in the AIF-mediated apoptosis. EMBO J.
29:3869–3878. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Michels G, Brandt MC, Zagidullin N, Khan
IF, Larbig R, van Aaken S, Wippermann J and Hoppe UC: Direct
evidence for calcium conductance of hyperpolarization-activated
cyclic nucleotide-gated channels and human native If at
physiological calcium concentrations. Cardiovasc Res. 78:466–475.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|