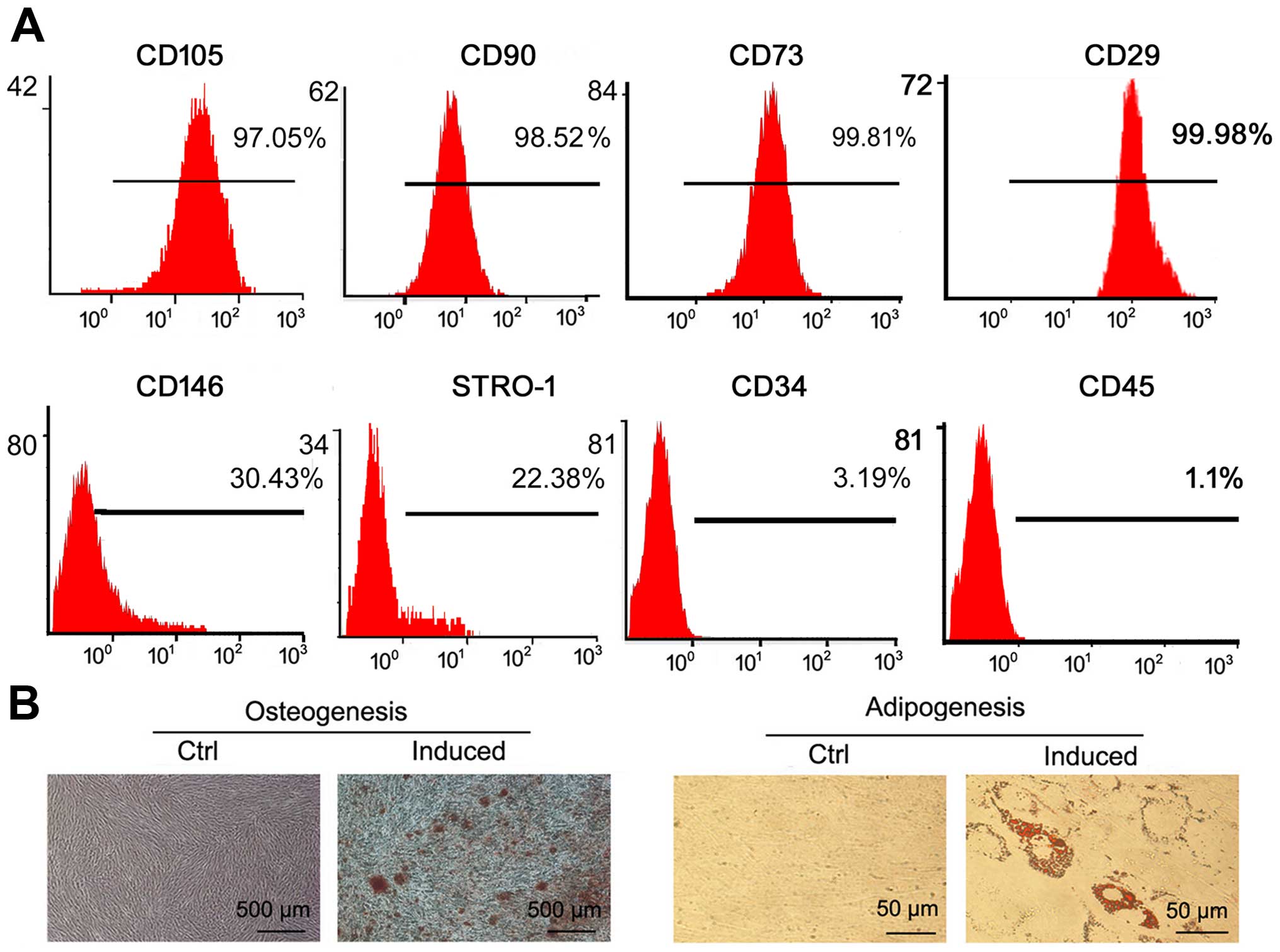
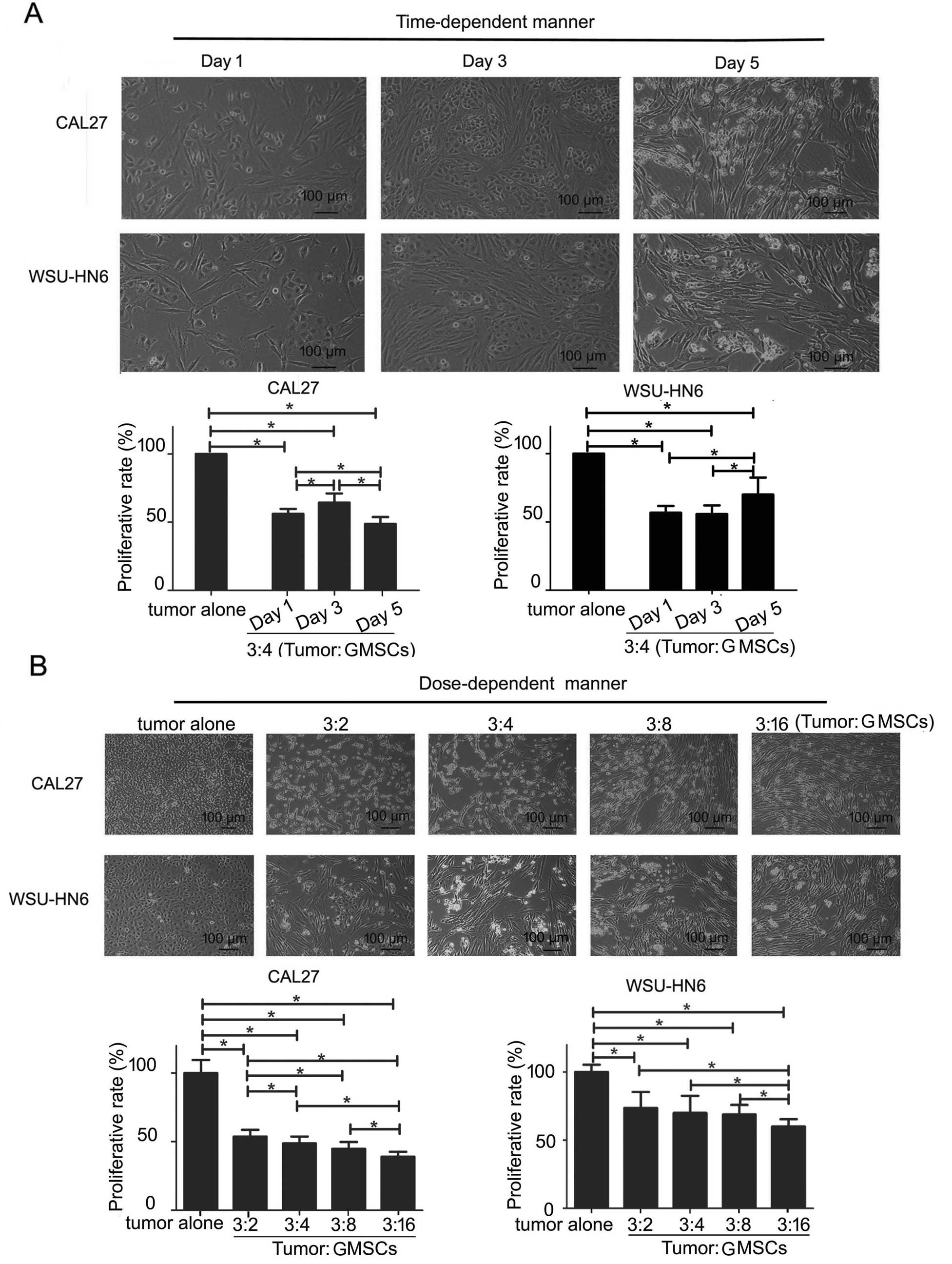
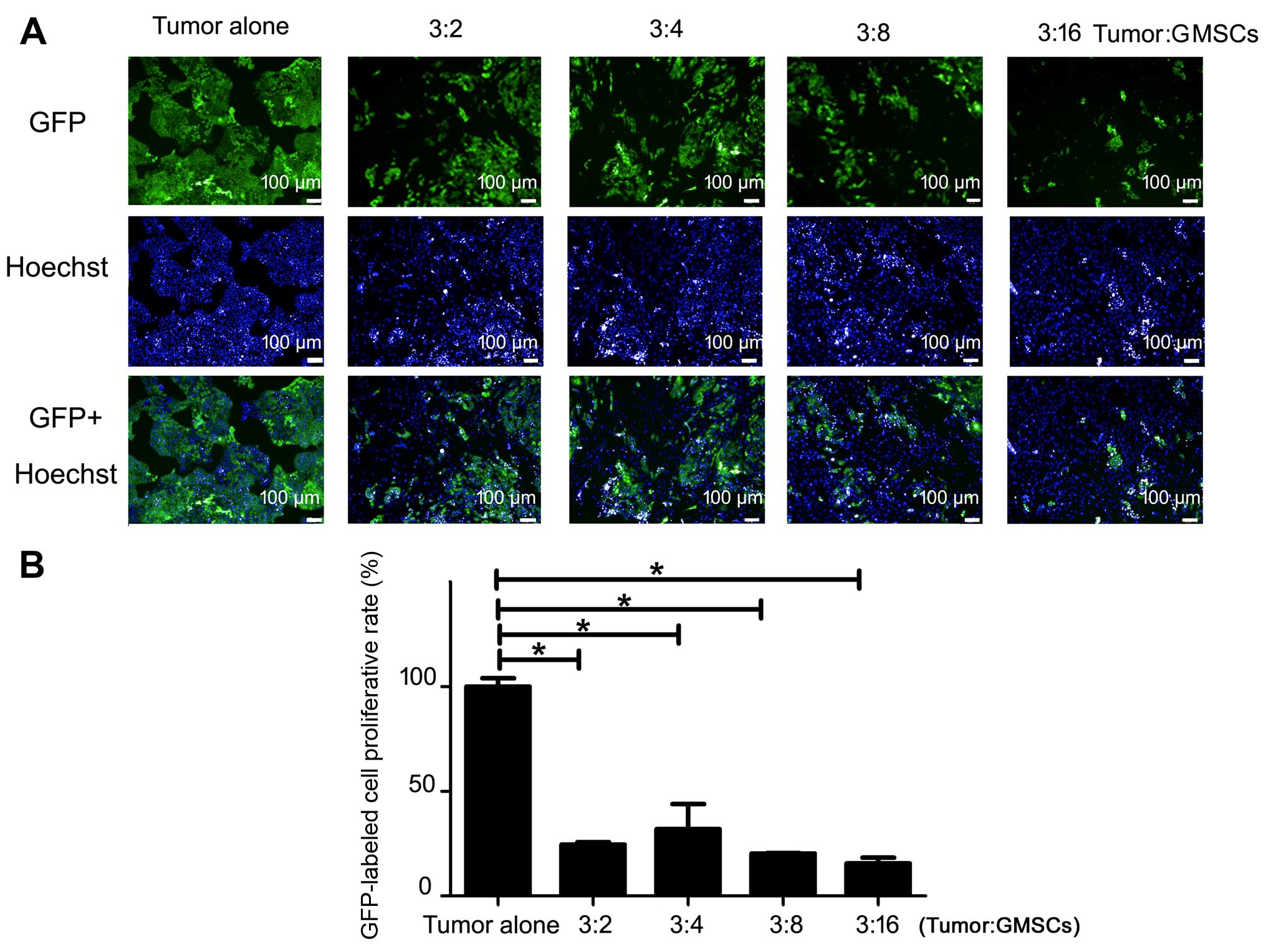
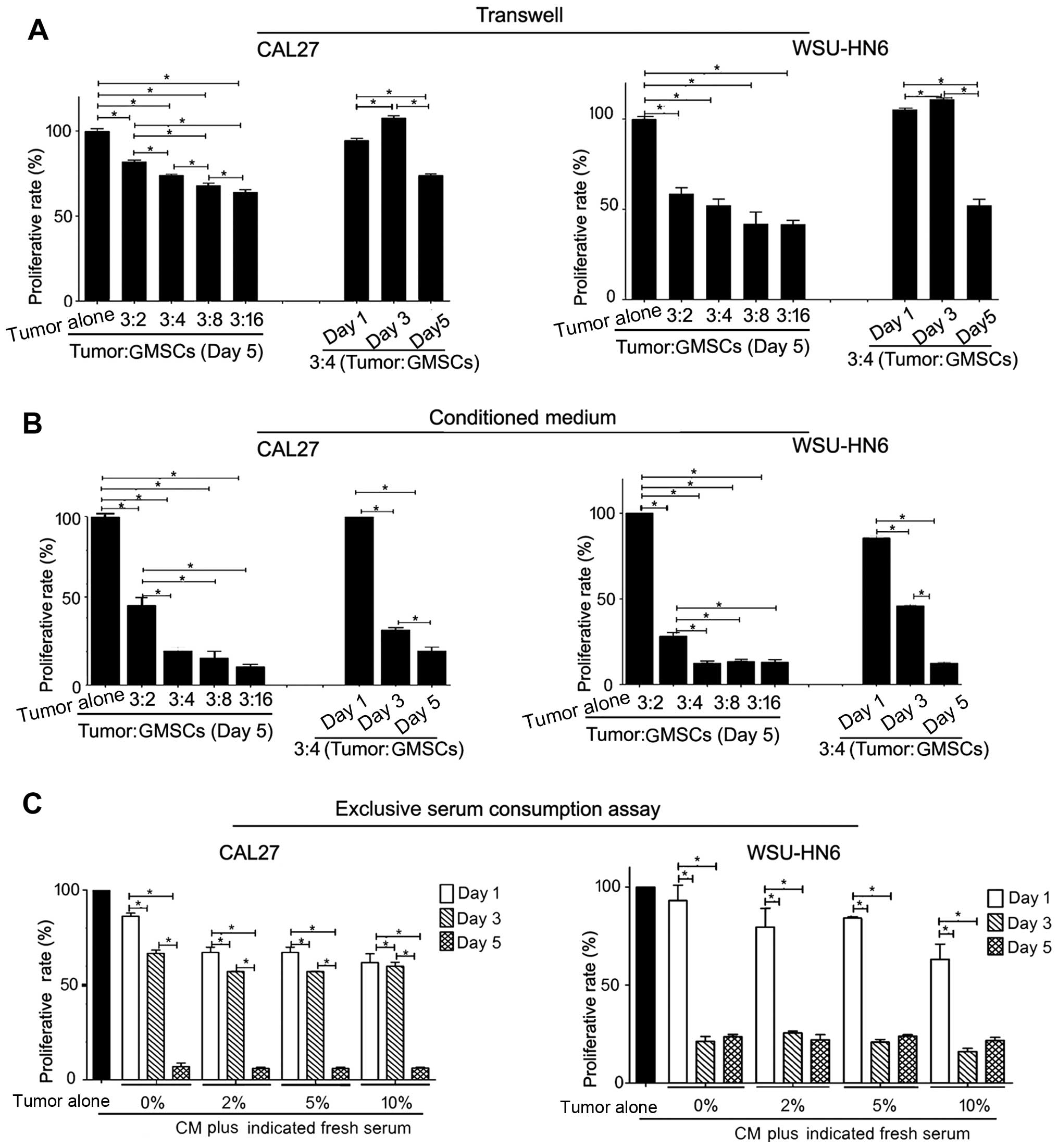
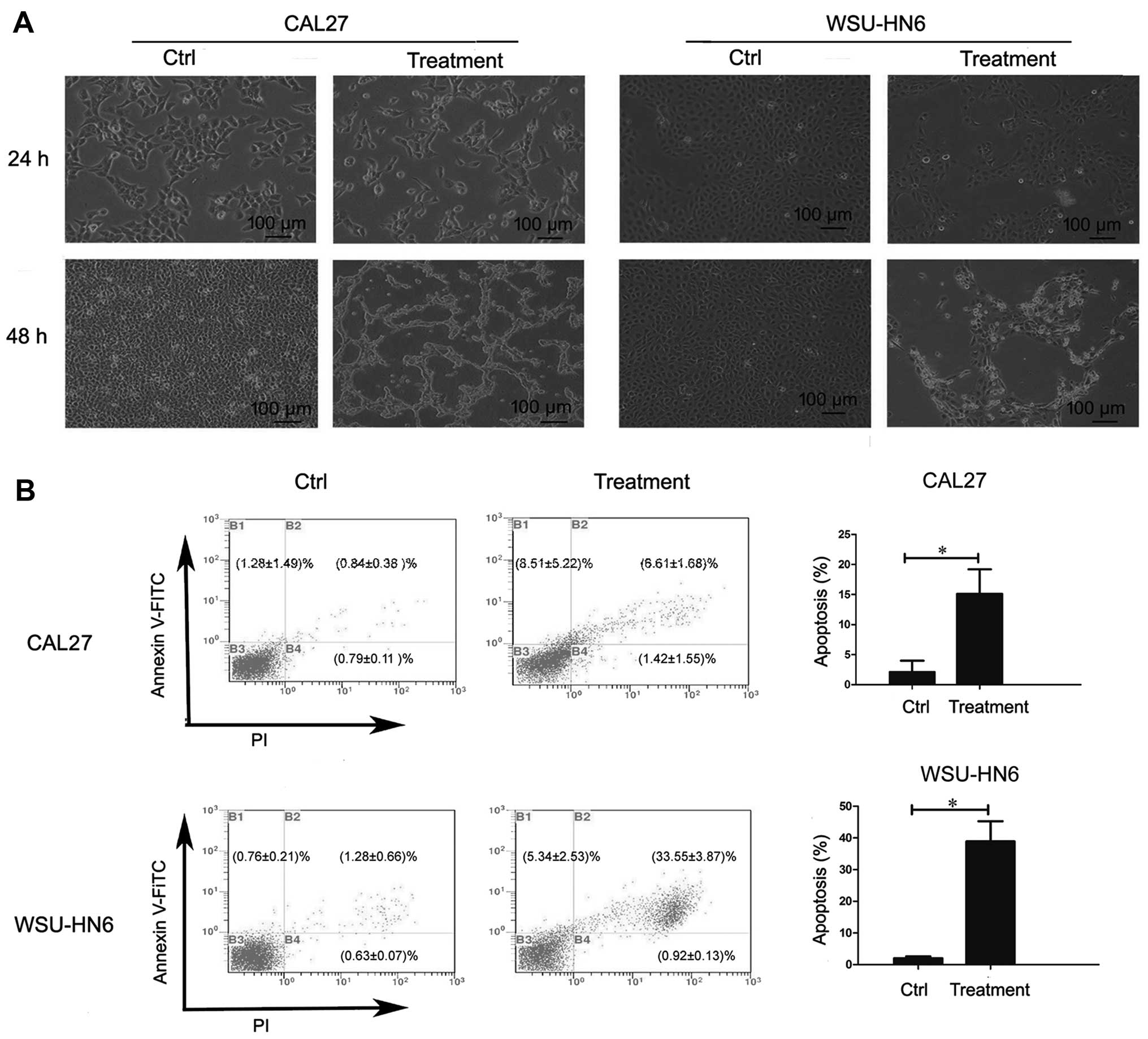
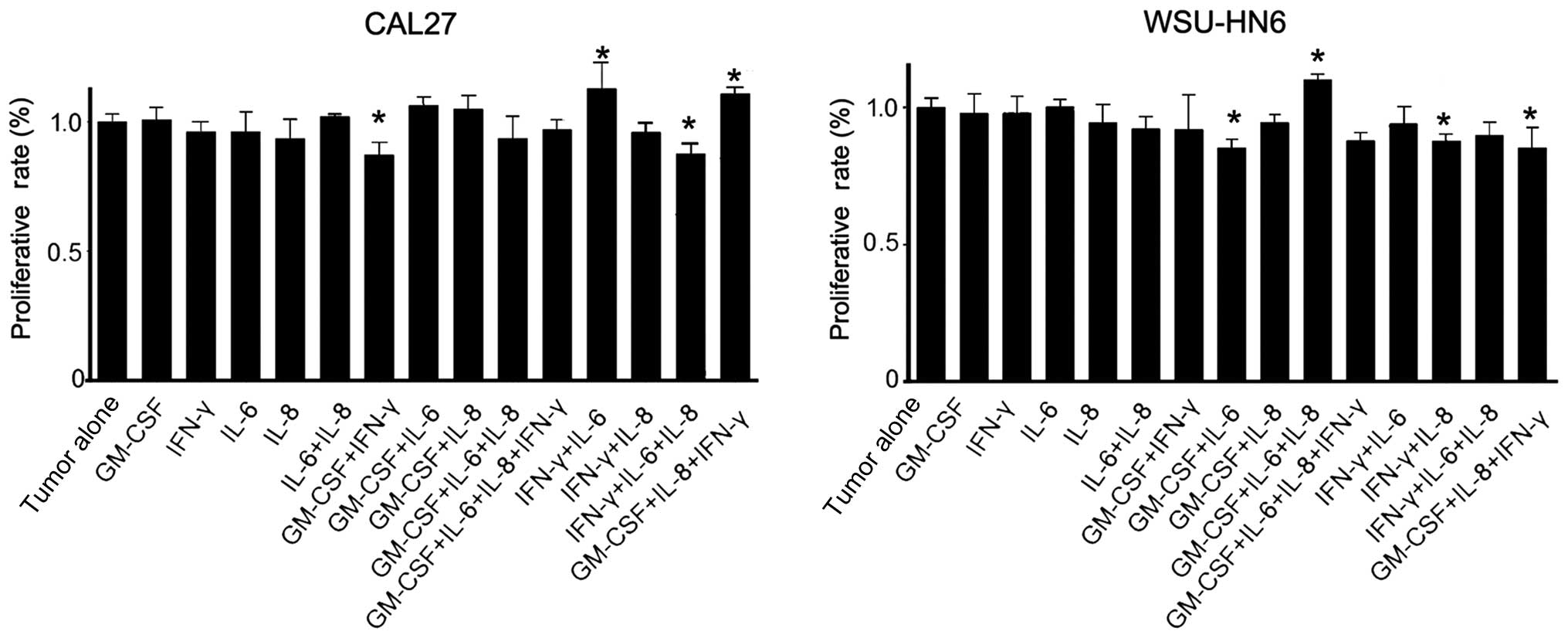
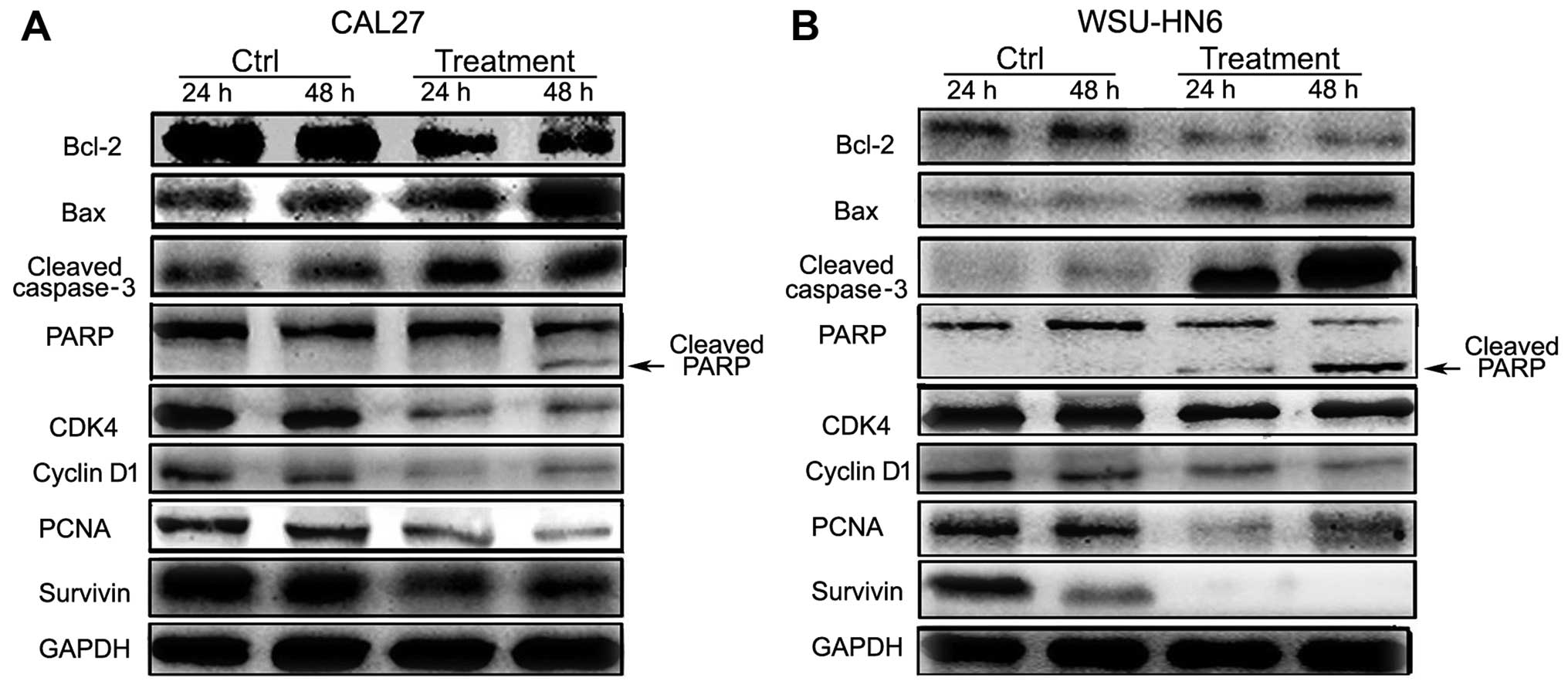
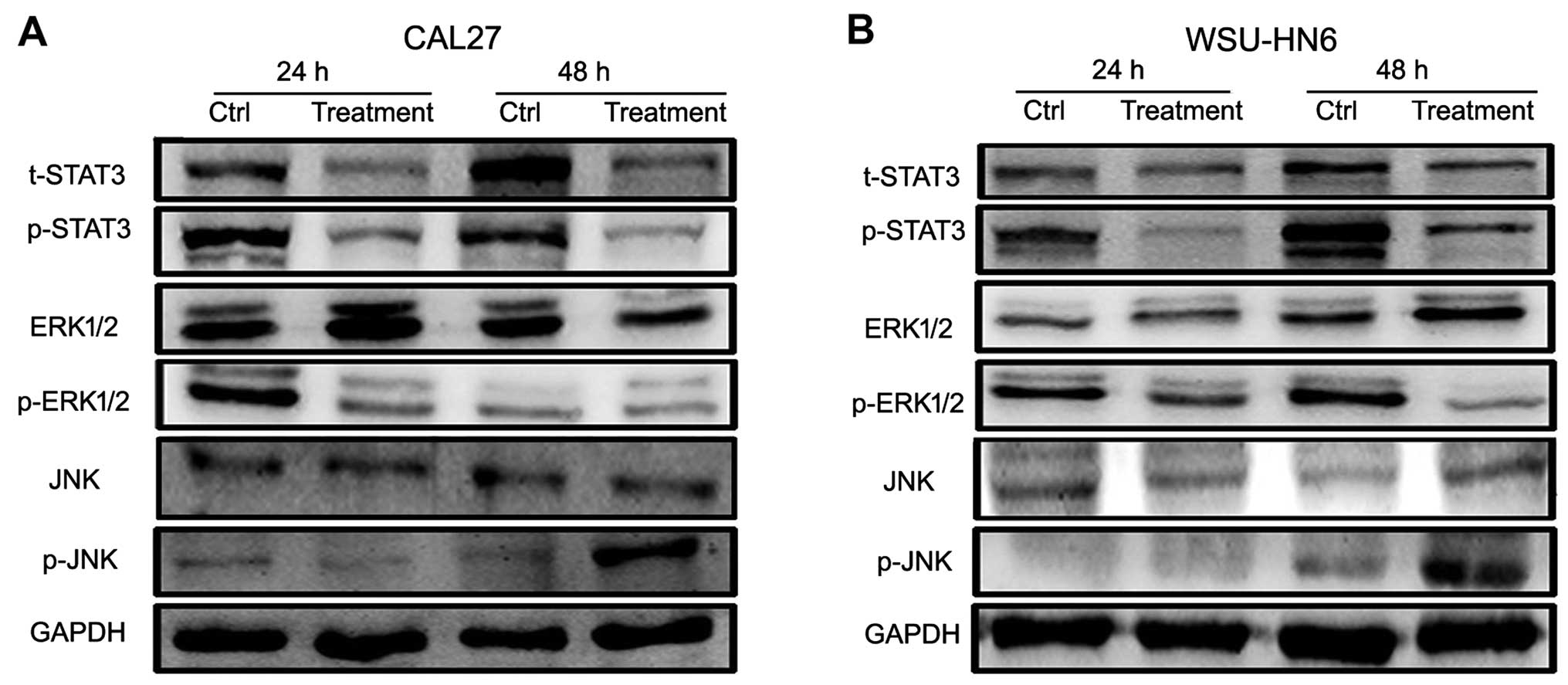
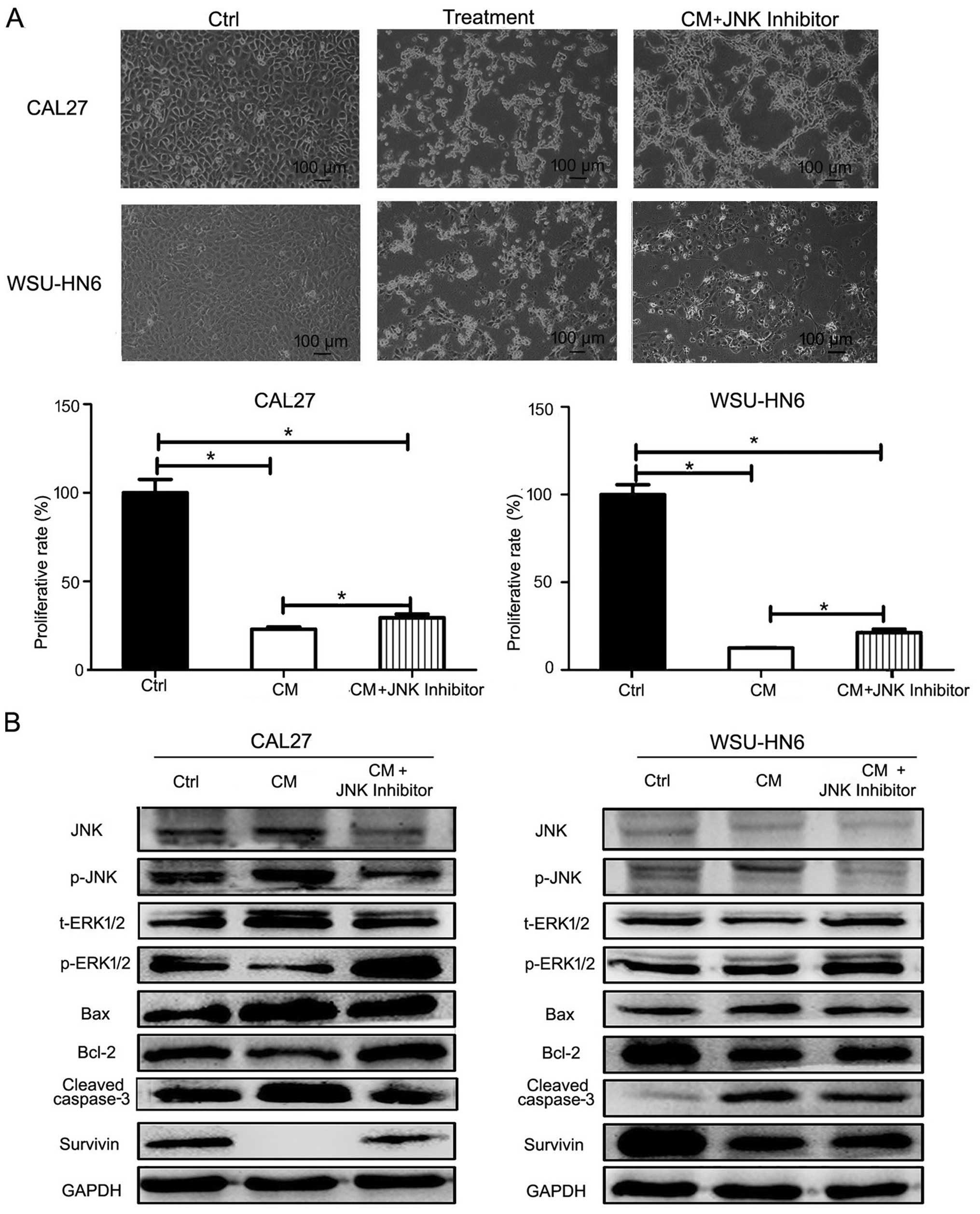
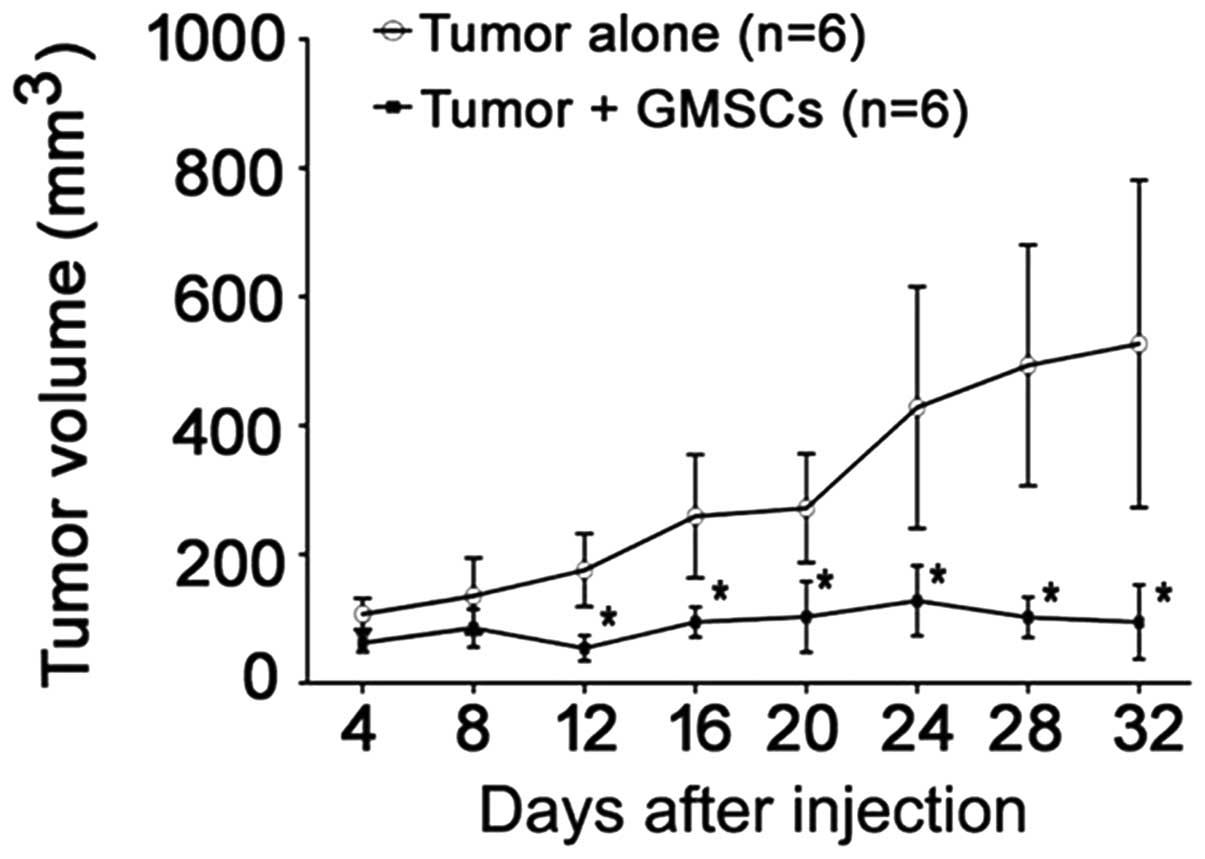
|
1
|
Bernardo ME and Fibbe WE: Mesenchymal
stromal cells: Sensors and switchers of inflammation. Cell Stem
Cell. 13:392–402. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ryu H, Oh JE, Rhee KJ, Baik SK, Kim J,
Kang SJ, Sohn JH, Choi E, Shin HC, Kim YM, et al: Adipose
tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells cultured at high density
express IFN-β and suppress the growth of MCF-7 human breast cancer
cells. Cancer Lett. 352:220–227. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zhu Y, Sun Z, Han Q, Liao L, Wang J, Bian
C, Li J, Yan X, Liu Y, Shao C, et al: Human mesenchymal stem cells
inhibit cancer cell proliferation by secreting DKK-1. Leukemia.
23:925–933. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kucerova L, Matuskova M, Hlubinova K,
Altanerova V and Altaner C: Tumor cell behaviour modulation by
mesenchymal stromal cells. Mol Cancer. 9:1292010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Song N, Gao L, Qiu H, Huang C, Cheng H,
Zhou H, Lv S, Chen L and Wang J: Mouse bone marrow-derived
mesenchymal stem cells inhibit leukemia/lymphoma cell proliferation
in vitro and in a mouse model of allogeneic bone marrow transplant.
Int J Mol Med. 36:139–149. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Huang WH, Chang MC, Tsai KS, Hung MC, Chen
HL and Hung SC: Mesenchymal stem cells promote growth and
angiogenesis of tumors in mice. Oncogene. 32:4343–4354. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Egusa H, Okita K, Kayashima H, Yu G,
Fukuyasu S, Saeki M, Matsumoto T, Yamanaka S and Yatani H: Gingival
fibroblasts as a promising source of induced pluripotent stem
cells. PLoS One. 5:e127432010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Liu J, Yu F, Sun Y, Jiang B, Zhang W, Yang
J, Xu GT, Liang A and Liu S: Concise reviews: Characteristics and
potential applications of human dental tissue-derived mesenchymal
stem cells. Stem Cells. 33:627–638. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Xu X, Chen C, Akiyama K, Chai Y, Le AD,
Wang Z and Shi S: Gingivae contain neural-crest- and
mesoderm-derived mesenchymal stem cells. J Dent Res. 92:825–832.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Tomar GB, Srivastava RK, Gupta N,
Barhanpurkar AP, Pote ST, Jhaveri HM, Mishra GC and Wani MR: Human
gingiva-derived mesenchymal stem cells are superior to bone
marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells for cell therapy in
regenerative medicine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 393:377–383.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang F, Yu M, Yan X, Wen Y, Zeng Q, Yue W,
Yang P and Pei X: Gingiva-derived mesenchymal stem cell-mediated
therapeutic approach for bone tissue regeneration. Stem Cells Dev.
20:2093–2102. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Petersen PE: Oral cancer prevention and
control - the approach of the World Health Organization. Oral
Oncol. 45:454–460. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Zhang Z, Han Y, Song J, Luo R, Jin X, Mu
D, Su S, Ji X, Ren YF and Liu H: Interferon-γ regulates the
function of mesenchymal stem cells from oral lichen planus via
indoleamine 2,3-dioxy-genase activity. J Oral Pathol Med. 44:15–27.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Hung BP, Hutton DL, Kozielski KL, Bishop
CJ, Naved B, Green JJ, Caplan AI, Gimble JM, Dorafshar AH and
Grayson WL: Platelet-derived growth factor BB enhances osteogenesis
of adipose-derived but not bone marrow-derived mesenchymal
stromal/stem cells. Stem Cells. 33:2773–2784. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lei M, Li K, Li B, Gao LN, Chen FM and Jin
Y: Mesenchymal stem cell characteristics of dental pulp and
periodontal ligament stem cells after in vivo transplantation.
Biomaterials. 35:6332–6343. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Motaln H, Gruden K, Hren M, Schichor C,
Primon M, Rotter A and Lah TT: Human mesenchymal stem cells exploit
the immune response mediating chemokines to impact the phenotype of
glioblastoma. Cell Transplant. 21:1529–1545. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Thiery JP: Epithelial-mesenchymal
transitions in tumour progression. Nat Rev Cancer. 2:442–454. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Quail DF and Joyce JA: Microenvironmental
regulation of tumor progression and metastasis. Nat Med.
19:1423–1437. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Liu R, Wei S, Chen J and Xu S: Mesenchymal
stem cells in lung cancer tumor microenvironment: Their biological
properties, influence on tumor growth and therapeutic implications.
Cancer Lett. 353:145–152. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Urbanek K, Cesselli D, Rota M, Nascimbene
A, De Angelis A, Hosoda T, Bearzi C, Boni A, Bolli R, Kajstura J,
et al: Stem cell niches in the adult mouse heart. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 103:9226–9231. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sun Z, Wang S and Zhao RC: The roles of
mesenchymal stem cells in tumor inflammatory microenvironment. J
Hematol Oncol. 7:142014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Qiao L, Xu ZL, Zhao TJ, Ye LH and Zhang
XD: Dkk-1 secreted by mesenchymal stem cells inhibits growth of
breast cancer cells via depression of Wnt signalling. Cancer Lett.
269:67–77. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Klopp AH, Gupta A, Spaeth E, Andreeff M
and Marini F III : Concise review: Dissecting a discrepancy in the
literature: do mesenchymal stem cells support or suppress tumor
growth? Stem Cells. 29:11–19. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Qiao L, Xu Z, Zhao T, Zhao Z, Shi M, Zhao
RC, Ye L and Zhang X: Suppression of tumorigenesis by human
mesenchymal stem cells in a hepatoma model. Cell Res. 18:500–507.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Um HD: Bcl-2 family proteins as regulators
of cancer cell invasion and metastasis: A review focusing on
mitochondrial respiration and reactive oxygen species. Oncotarget.
7:5193–5203. 2016.
|
|
26
|
Su TH, Shiau CW, Jao P, Liu CH, Liu CJ,
Tai WT, Jeng YM, Yang HC, Tseng TC, Huang HP, et al: Sorafenib and
its derivative SC-1 exhibit antifibrotic effects through signal
transducer and activator of transcription 3 inhibition. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 112:7243–7248. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Li Y, Liu D, Zhou Y, Li Y, Xie J, Lee RJ,
Cai Y and Teng L: Silencing of survivin expression leads to reduced
proliferation and cell cycle arrest in cancer cells. J Cancer.
6:1187–1194. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sheridan C, Brumatti G, Elgendy M, Brunet
M and Martin SJ: An ERK-dependent pathway to Noxa expression
regulates apoptosis by platinum-based chemotherapeutic drugs.
Oncogene. 29:6428–6441. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wier EM, Fu K, Hodgson A, Sun X and Wan F:
Caspase-3 cleaved p65 fragment dampens NF-κB-mediated
anti-apoptotic transcription by interfering with the p65/RPS3
interaction. FEBS Lett. 589:3581–3587. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Bogoyevitch MA and Kobe B: Uses for JNK:
The many and varied substrates of the c-Jun N-terminal kinases.
Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 70:1061–1095. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|