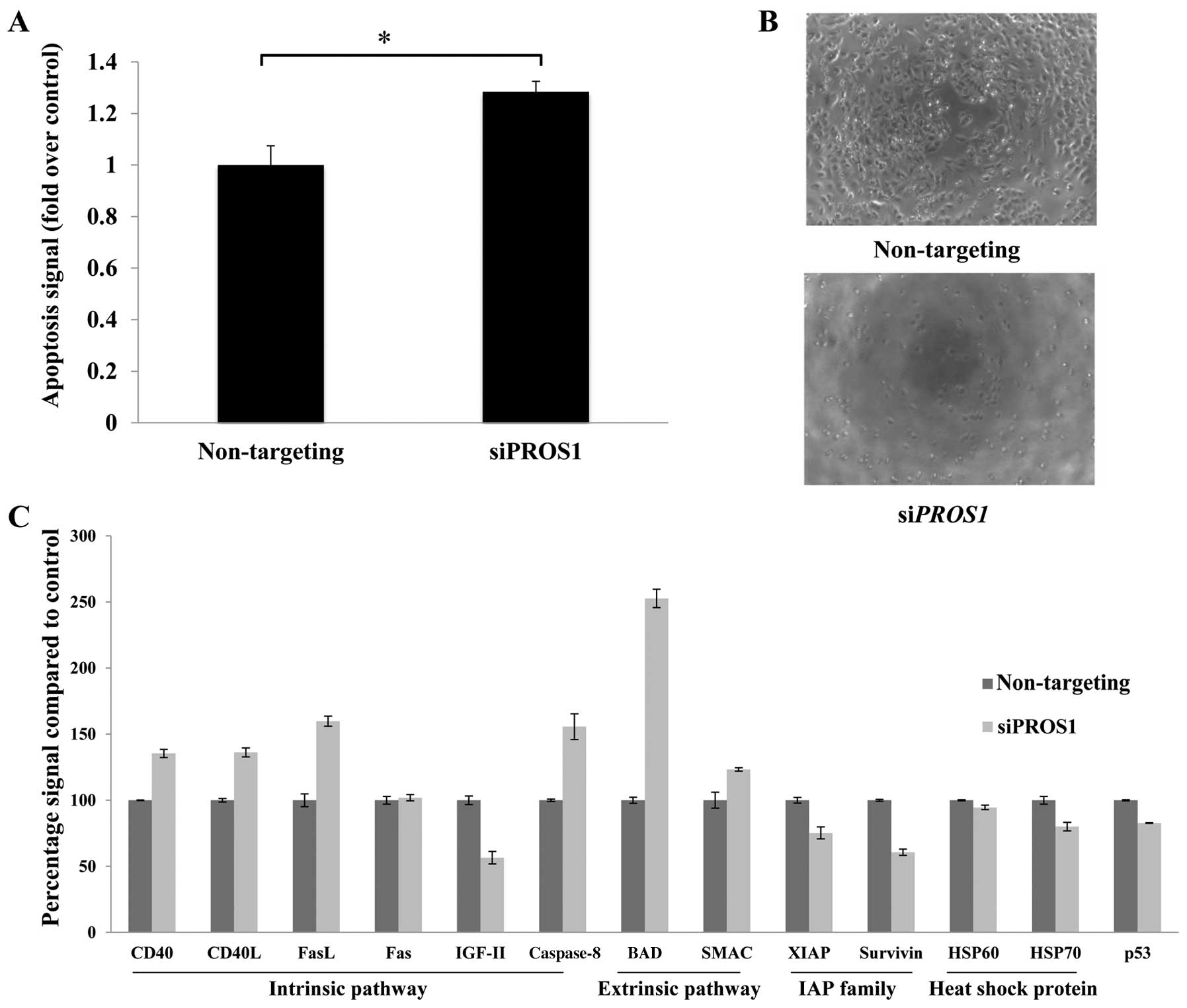
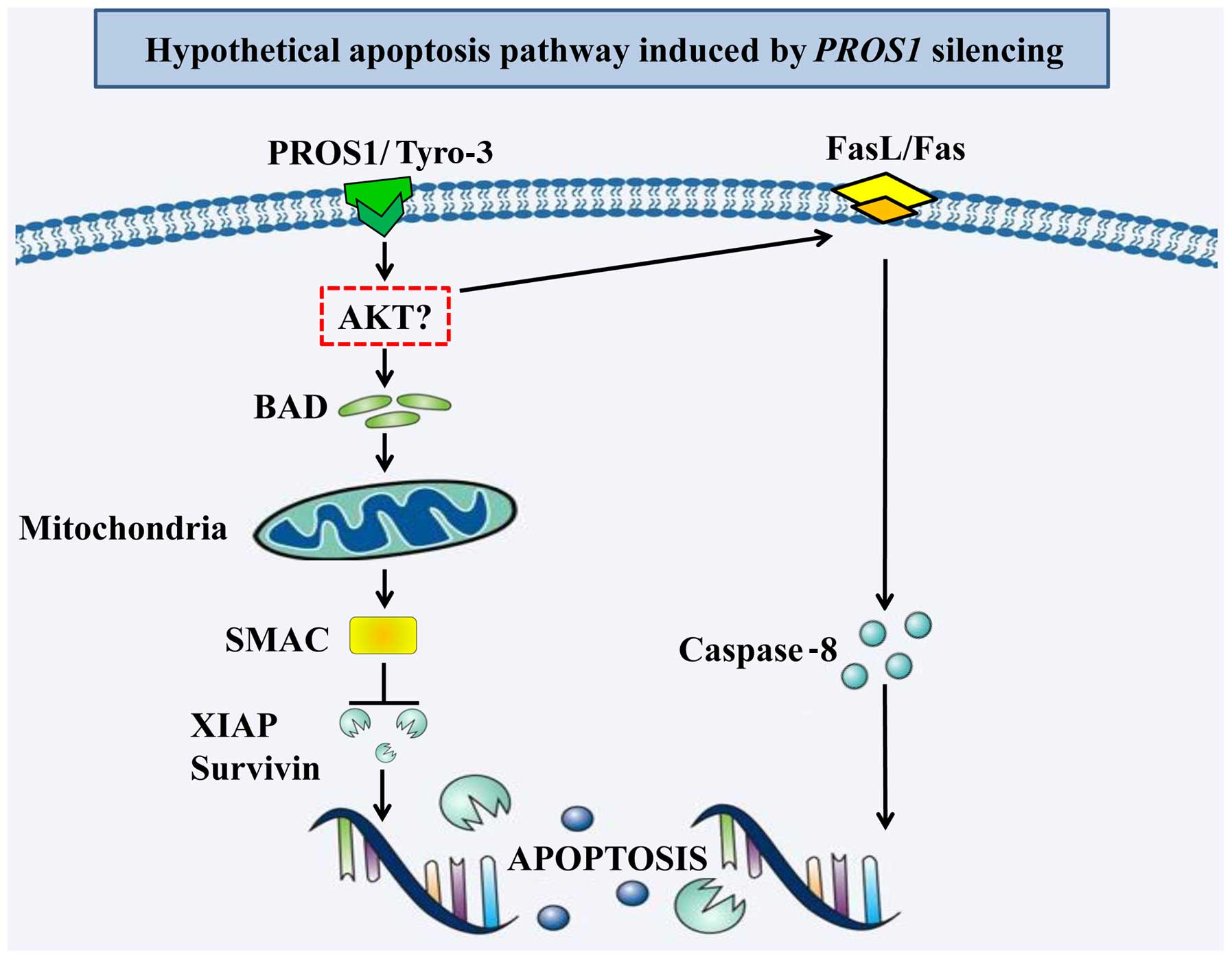
|
1
|
Omuro A and DeAngelis LM: Glioblastoma and
other malignant gliomas: A clinical review. JAMA. 310:1842–1850.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Davies AM, Weinberg U and Palti Y: Tumor
treating fields: A new frontier in cancer therapy. Ann N Y Acad
Sci. 1291:86–95. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Parpura V, Heneka MT, Montana V, Oliet
SHR, Schousboe A, Haydon PG, Stout RF Jr, Spray DC, Reichenbach A,
Pannicke T, et al: Glial cells in (patho)physiology. J Neurochem.
121:4–27. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Huse JT, Holland E and DeAngelis LM:
Glioblastoma: Molecular analysis and clinical implications. Annu
Rev Med. 64:59–70. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Kanu OO, Hughes B, Di C, Lin N, Fu J,
Bigner DD, Yan H and Adamson C: Glioblastoma multiforme
oncogenomics and signaling pathways. Clin Med Oncol. 3:39–52.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Reardon DA, Conrad CA, Cloughesy T, Prados
MD, Friedman HS, Aldape KD, Mischel P, Xia J, DiLea C, Huang J, et
al: Phase I study of AEE788, a novel multitarget inhibitor of ErbB-
and VEGF-receptor-family tyrosine kinases, in recurrent
glioblastoma patients. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 69:1507–1518.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Vitucci M, Karpinich NO, Bash RE, Werneke
AM, Schmid RS, White KK, McNeill RS, Huff B, Wang S, Van Dyke T, et
al: Cooperativity between MAPK and PI3K signaling activation is
required for glioblastoma pathogenesis. Neuro Oncol. 15:1317–1329.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Akhavan D, Cloughesy TF and Mischel PS:
mTOR signaling in glioblastoma: Lessons learned from bench to
bedside. Neurooncol. 12:882–889. 2010.
|
|
9
|
Nakada M, Kita D, Watanabe T, Hayashi Y,
Teng L, Pyko IV and Hamada J: Aberrant signaling pathways in
glioma. Cancers (Basel). 3:3242–3278. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Ohgaki H and Kleihues P: Genetic pathways
to primary and secondary glioblastoma. Am J Pathol. 170:1445–1453.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhang C, Moore LM, Li X, Yung WKA and
Zhang W: IDH1/2 mutations target a key hallmark of cancer by
deregulating cellular metabolism in glioma. Neuro Oncol.
15:1114–1126. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Pierscianek D, Kim YH, Motomura K,
Mittelbronn M, Paulus W, Brokinkel B, Keyvani K, Wrede K, Nakazato
Y, Tanaka Y, et al: MET gain in diffuse astrocytomas is associated
with poorer outcome. Brain Pathol. 23:13–18. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Eisele G and Weller M: Targeting apoptosis
pathways in glioblastoma. Cancer Lett. 332:335–345. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Krakstad C and Chekenya M: Survival
signalling and apoptosis resistance in glioblastomas: Opportunities
for targeted therapeutics. Mol Cancer. 9:1352010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Panner A, Crane CA, Weng C, Feletti A,
Parsa AT and Pieper RO: A novel PTEN-dependent link to
ubiquitination controls FLIPS stability and TRAIL sensitivity in
glioblastoma multiforme. Cancer Res. 69:7911–7916. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ruano Y, Mollejo M, Camacho FI, Rodríguez
de Lope A, Fiaño C, Ribalta T, Martínez P, Hernández-Moneo JL and
Meléndez B: Identification of survival-related genes of the
phosphatidylinositol 3′-kinase signaling pathway in glioblastoma
multiforme. Cancer. 112:1575–1584. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Guvenc H, Pavlyukov MS, Joshi K, Kurt H,
Banasavadi-Siddegowda YK, Mao P, Hong C, Yamada R, Kwon CH, Bhasin
D, et al: Impairment of glioma stem cell survival and growth by a
novel inhibitor for Survivin-Ran protein complex. Clin Cancer Res.
19:631–642. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Catuogno S, Esposito CL, Quintavalle C,
Condorelli G, de Franciscis V and Cerchia L: Nucleic acids in human
glioma treatment: Innovative approaches and recent results. J
Signal Transduct. 2012:7351352012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jensen SA, Day ES, Ko CH, Hurley LA,
Luciano JP, Kouri FM, Merkel TJ, Luthi AJ, Patel PC, Cutler JI, et
al: Spherical nucleic acid nanoparticle conjugates as an RNAi-based
therapy for glioblastoma. Sci Transl Med. 5:209ra1522013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang Y, Zhang YF, Bryant J, Charles A,
Boado RJ and Pardridge WM: Intravenous RNA interference gene
therapy targeting the human epidermal growth factor receptor
prolongs survival in intracranial brain cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
10:3667–3677. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang XL, Xu R, Wu X, Gillespie D, Jensen R
and Lu ZR: Targeted systemic delivery of a therapeutic siRNA with a
multifunctional carrier controls tumor proliferation in mice. Mol
Pharm. 6:738–746. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bumcrot D, Manoharan M, Koteliansky V and
Sah DWY: RNAi therapeutics: A potential new class of pharmaceutical
drugs. Nat Chem Biol. 2:711–719. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Rolle K, Nowak S, Wyszko E, Nowak M,
Zukiel R, Piestrzeniewicz R, Gawronska I, Barciszewska MZ and
Barciszewski J: Promising human brain tumors therapy with
interference RNA intervention (iRNAi). Cancer Biol Ther. 9:396–406.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zukiel R, Nowak S, Wyszko E, Rolle K,
Gawronska I, Barciszewska MZ and Barciszewski J: Suppression of
human brain tumor with interference RNA specific for tenascin-C.
Cancer Biol Ther. 5:1002–1007. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Rhodes DR, Yu J, Shanker K, Deshpande N,
Varambally R, Ghosh D, Barrette T, Pandey A and Chinnaiyan AM:
ONCOMINE: A cancer microarray database and integrated data-mining
platform. Neoplasia. 6:1–6. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Dahlbäck B: The tale of protein S and
C4b-binding protein, a story of affection. Thromb Haemost.
98:90–96. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hafizi S and Dahlbäck B: Gas6 and protein
S. Vitamin K-dependent ligands for the Axl receptor tyrosine kinase
subfamily. FEBS J. 273:5231–5244. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Saraon P, Musrap N, Cretu D, Karagiannis
GS, Batruch I, Smith C, Drabovich AP, Trudel D, van der Kwast T,
Morrissey C, et al: Proteomic profiling of androgen-independent
prostate cancer cell lines reveals a role for protein S during the
development of high grade and castration-resistant prostate cancer.
J Biol Chem. 287:34019–34031. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Suleiman L, Négrier C and Boukerche H:
Protein S: A multi-functional anticoagulant vitamin K-dependent
protein at the crossroads of coagulation, inflammation,
angiogenesis, and cancer. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 88:637–654. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lemke G: Biology of the TAM receptors.
Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 5:a0090762013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lemke G and Rothlin CV: Immunobiology of
the TAM receptors. Nat Rev Immunol. 8:327–336. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Linger RMA, Keating AK, Earp HS and Graham
DK: Taking aim at Mer and Axl receptor tyrosine kinases as novel
therapeutic targets in solid tumors. Expert Opin Ther Targets.
14:1073–1090. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wimmel A, Rohner I, Ramaswamy A, Heidtmann
HH, Seitz R, Kraus M and Schuermann M: Synthesis and secretion of
the anticoagulant protein S and coexpression of the Tyro3 receptor
in human lung carcinoma cells. Cancer. 86:43–49. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Keating AK, Kim GK, Jones AE, Donson AM,
Ware K, Mulcahy JM, Salzberg DB, Foreman NK, Liang X, Thorburn A,
et al: Inhibition of Mer and Axl receptor tyrosine kinases in
astrocytoma cells leads to increased apoptosis and improved
chemosensitivity. Mol Cancer Ther. 9:1298–1307. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Stitt TN, Conn G, Gore M, Lai C, Bruno J,
Radziejewski C, Mattsson K, Fisher J, Gies DR, Jones PF, et al: The
anticoagulation factor protein S and its relative, Gas6, are
ligands for the Tyro 3/Axl family of receptor tyrosine kinases.
Cell. 80:661–670. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Saraon P, Jarvi K and Diamandis EP:
High-throughput proteomic analysis identifies protein s as a
modulator of high grade and castrate-resistant prostate cancer.
Cancer Res (AACR Annual Meeting abstracts). 72(8 Suppl):
LB-2932012.
|
|
38
|
Lemke G and Burstyn-Cohen T: TAM receptors
and the clearance of apoptotic cells. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1209:23–29.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Guo H, Barrett TM, Zhong Z, Fernández JA,
Griffin JH, Freeman RS and Zlokovic BV: Protein S blocks the
extrinsic apoptotic cascade in tissue plasminogen
activator/N-methyl D-aspartate-treated neurons via Tyro3-Akt-FKHRL1
signaling pathway. Mol Neurodegener. 6:132011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wang Y, Moncayo G, Morin P Jr, Xue G,
Grzmil M, Lino MM, Clément-Schatlo V, Frank S, Merlo A and Hemmings
BA: Mer receptor tyrosine kinase promotes invasion and survival in
glioblastoma multiforme. Oncogene. 32:872–882. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Simpson KJ, Selfors LM, Bui J, Reynolds A,
Leake D, Khvorova A and Brugge JS: Identification of genes that
regulate epithelial cell migration using an siRNA screening
approach. Nat Cell Biol. 10:1027–1038. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Vajkoczy P, Knyazev P, Kunkel A, Capelle
HH, Behrndt S, von Tengg-Kobligk H, Kiessling F, Eichelsbacher U,
Essig M, Read TA, et al: Dominant-negative inhibition of the Axl
receptor tyrosine kinase suppresses brain tumor cell growth and
invasion and prolongs survival. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
103:5799–5804. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|