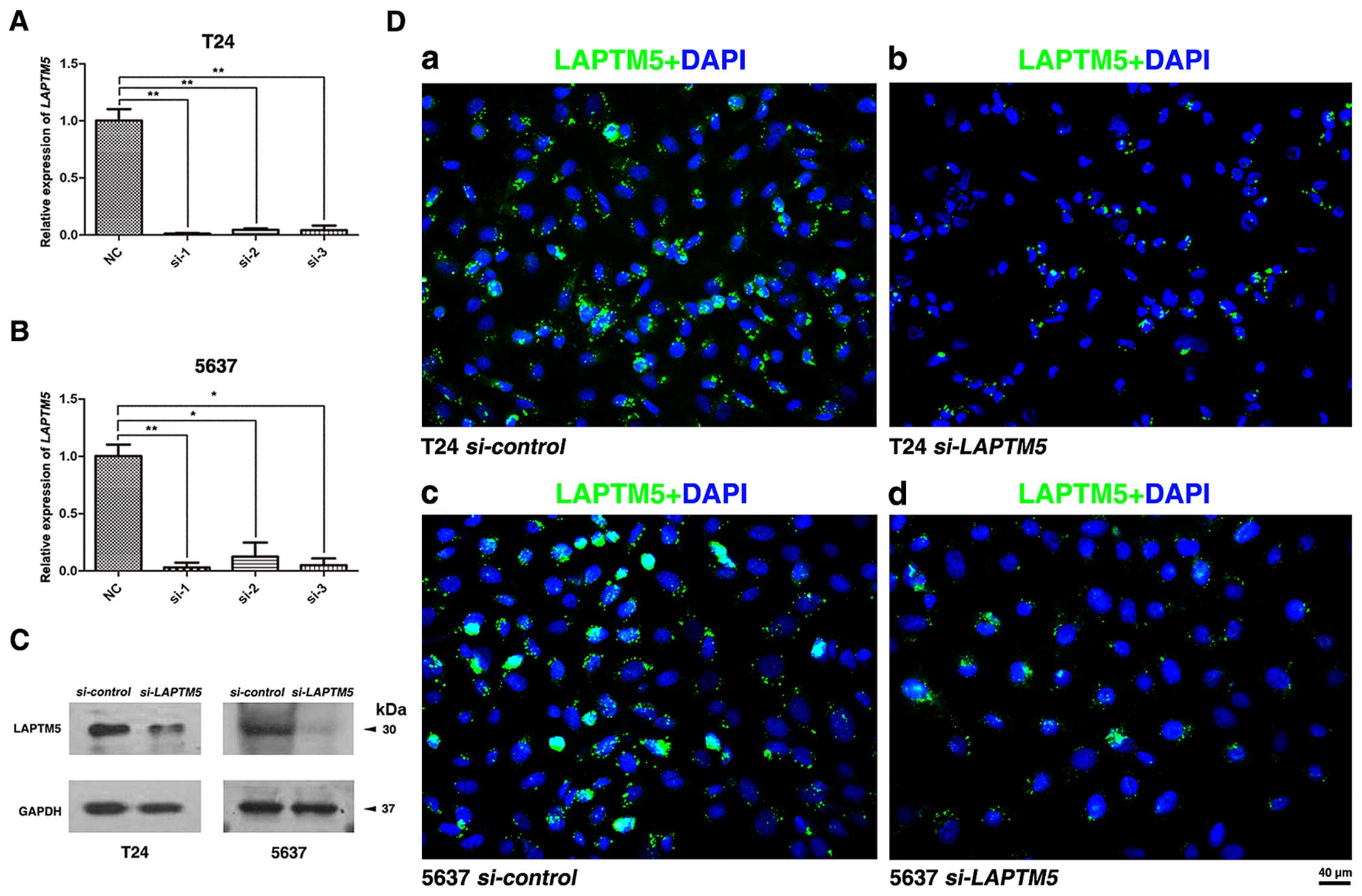
|
1
|
Burger M, Catto JW, Dalbagni G, Grossman
HB, Herr H, Karakiewicz P, Kassouf W, Kiemeney LA, La Vecchia C,
Shariat S, et al: Epidemiology and risk factors of urothelial
bladder cancer. Eur Urol. 63:234–241. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Rye PD, Nustad K and Stigbrand T: Tumor
marker workshops. Tumour Biol. 24:165–171. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Cao R, Meng Z, Liu T, Wang G, Qian G, Cao
T, Guan X, Dan H, Xiao Y and Wang X: Decreased TRPM7 inhibits
activities and induces apoptosis of bladder cancer cells via ERK1/2
pathway. Oncotarget. Sep 20–2016.Epub ahead of print.
|
|
4
|
Wang G, Cao R, Wang Y, Qian G, Dan HC,
Jiang W, Ju L, Wu M, Xiao Y and Wang X: Simvastatin induces cell
cycle arrest and inhibits proliferation of bladder cancer cells via
PPARγ signalling pathway. Sci Rep. 6:357832016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Ouchida R, Yamasaki S, Hikida M, Masuda K,
Kawamura K, Wada A, Mochizuki S, Tagawa M, Sakamoto A, Hatano M, et
al: A lysosomal protein negatively regulates surface T cell antigen
receptor expression by promoting CD3zeta-chain degradation.
Immunity. 29:33–43. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Seimiya M, O-Wang J, Bahar R, Kawamura K,
Wang Y, Saisho H and Tagawa M: Stage-specific expression of
Clast6/E3/LAPTM5 during B cell differentiation: Elevated expression
in human B lymphomas. Int J Oncol. 22:301–304. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Adra CN, Zhu S, Ko JL, Guillemot JC,
Cuervo AM, Kobayashi H, Horiuchi T, Lelias JM, Rowley JD and Lim B:
LAPTM5: A novel lysosomal-associated multispanning membrane protein
preferentially expressed in hematopoietic cells. Genomics.
35:328–337. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Pak Y, Glowacka WK, Bruce MC, Pham N and
Rotin D: Transport of LAPTM5 to lysosomes requires association with
the ubiquitin ligase Nedd4, but not LAPTM5 ubiquitination. J Cell
Biol. 175:631–645. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ingham RJ, Gish G and Pawson T: The Nedd4
family of E3 ubiquitin ligases: Functional diversity within a
common modular architecture. Oncogene. 23:1972–1984. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang X, Trotman LC, Koppie T, Alimonti A,
Chen Z, Gao Z, Wang J, Erdjument-Bromage H, Tempst P, Cordon-Cardo
C, et al: NEDD4-1 is a proto-oncogenic ubiquitin ligase for PTEN.
Cell. 128:129–139. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Shao GZ, Zhou RL, Zhang QY, Zhang Y, Liu
JJ, Rui JA, Wei X and Ye DX: Molecular cloning and characterization
of LAPTM4B, a novel gene upregulated in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Oncogene. 22:5060–5069. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhang H, Wei Q, Liu R, Qi S, Liang P, Qi
C, Wang A, Sheng B, Li L and Xu Y: Overexpression of LAPTM4B-35: A
novel marker of poor prognosis of prostate cancer. PLoS One.
9:e910692014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Xiao M, Jia S, Wang H, Wang J, Huang Y and
Li Z: Overexpression of LAPTM4B: An independent prognostic marker
in breast cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 139:661–667. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Huber MA, Kraut N and Beug H: Molecular
requirements for epithelial-mesenchymal transition during tumor
progression. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 17:548–558. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Nieto MA: Epithelial plasticity: A common
theme in embryonic and cancer cells. Science. 342:12348502013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yang J and Weinberg RA:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition: At the crossroads of development
and tumor metastasis. Dev Cell. 14:818–829. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wei SC, Fattet L and Yang J: The forces
behind EMT and tumor metastasis. Cell Cycle. 14:2387–2388. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yilmaz M and Christofori G: EMT, the
cytoskeleton, and cancer cell invasion. Cancer Metastasis Rev.
28:15–33. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Glowacka WK, Alberts P, Ouchida R, Wang JY
and Rotin D: LAPTM5 protein is a positive regulator of
proinflammatory signaling pathways in macrophages. J Biol Chem.
287:27691–27702. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Park JS, Kwon JK, Kim HR, Kim HJ, Kim BS
and Jung JY: Farnesol induces apoptosis of DU145 prostate cancer
cells through the PI3K/Akt and MAPK pathways. Int J Mol Med.
33:1169–1176. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gupta J, Igea A, Papaioannou M,
Lopez-Casas PP, Llonch E, Hidalgo M, Gorgoulis VG and Nebreda AR:
Pharmacological inhibition of p38 MAPK reduces tumor growth in
patient-derived xenografts from colon tumors. Oncotarget.
6:8539–8551. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Wheelock MJ and Johnson KR: Cadherins as
modulators of cellular phenotype. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol.
19:207–235. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Harris TJ and Peifer M: Decisions,
decisions: Beta-catenin chooses between adhesion and transcription.
Trends Cell Biol. 15:234–237. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Bolós V, Peinado H, Pérez-Moreno MA, Fraga
MF, Esteller M and Cano A: The transcription factor Slug represses
E-cadherin expression and induces epithelial to mesenchymal
transitions: A comparison with Snail and E47 repressors. J Cell
Sci. 116:499–511. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Li Y, Wu Y, Abbatiello TC, Wu WL, Kim JR,
Sarkissyan M, Sarkissyan S, Chung SS, Elshimali Y and Vadgama JV:
Slug contributes to cancer progression by direct regulation of ERα
signaling pathway. Int J Oncol. 46:1461–1472. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Sun Y, Song GD, Sun N, Chen JQ and Yang
SS: Slug overexpression induces stemness and promotes
hepatocellular carcinoma cell invasion and metastasis. Oncol Lett.
7:1936–1940. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Xiao Y, Karnati S, Qian G, Nenicu A, Fan
W, Tchatalbachev S, Höland A, Hossain H, Guillou F, Lüers GH, et
al: Cre-mediated stress affects sirtuin expression levels,
peroxisome biogenesis and metabolism, antioxidant and
proinflammatory signaling pathways. PLoS One. 7:e410972012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Meloche S and Pouysségur J: The ERK1/2
mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway as a master regulator of
the G1- to S-phase transition. Oncogene. 26:3227–3239. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
MacCorkle RA and Tan TH: Mitogen-activated
protein kinases in cell-cycle control. Cell Biochem Biophys.
43:451–461. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Tsai SC, Huang WW, Huang WC, Lu CC, Chiang
JH, Peng SF, Chung JG, Lin YH, Hsu YM, Amagaya S, et al:
ERK-modulated intrinsic signaling and G(2)/M phase arrest
contribute to the induction of apoptotic death by allyl
isothiocyanate in MDA-MB-468 human breast adenocarcinoma cells. Int
J Oncol. 41:2065–2072. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|