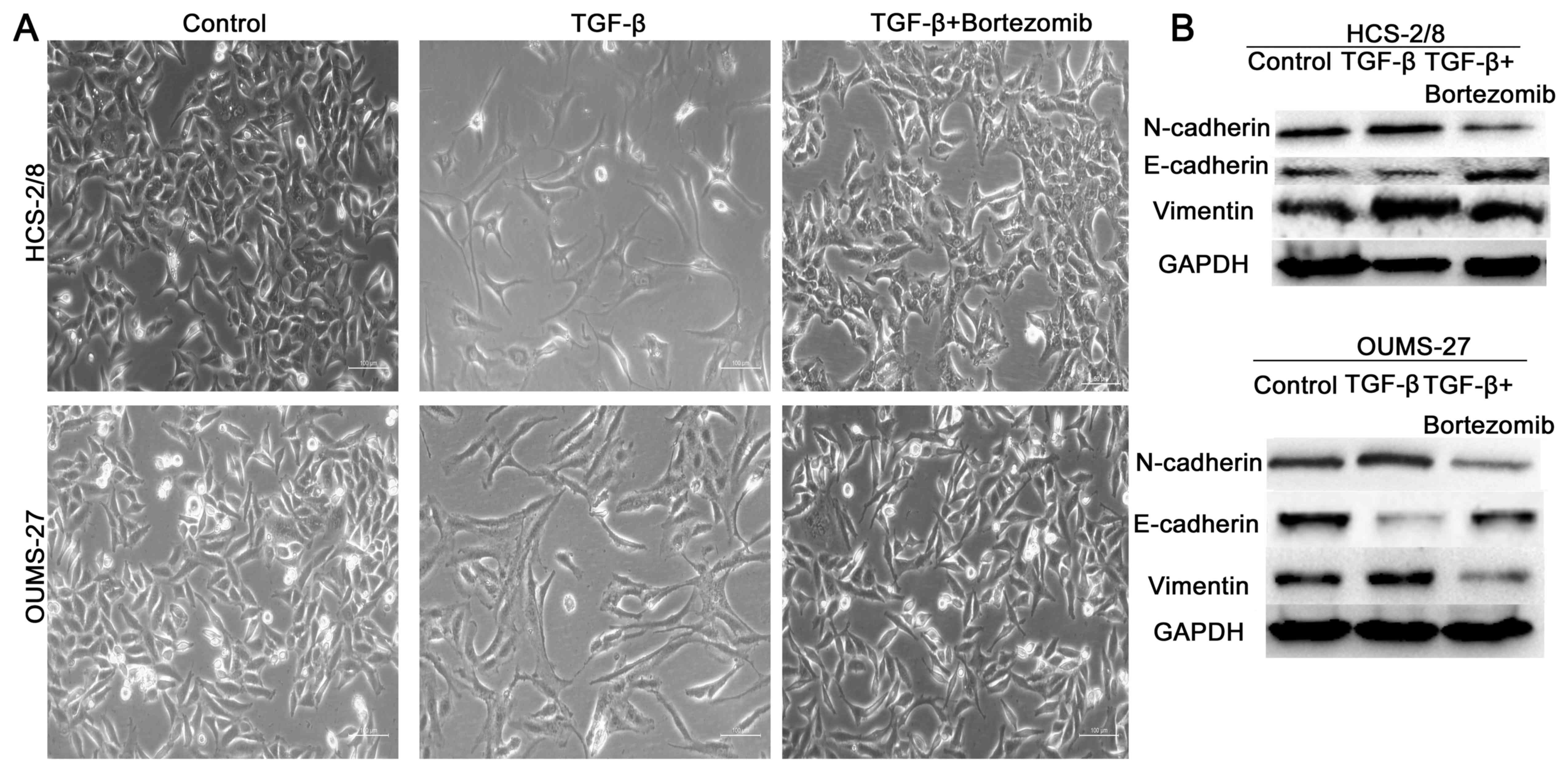
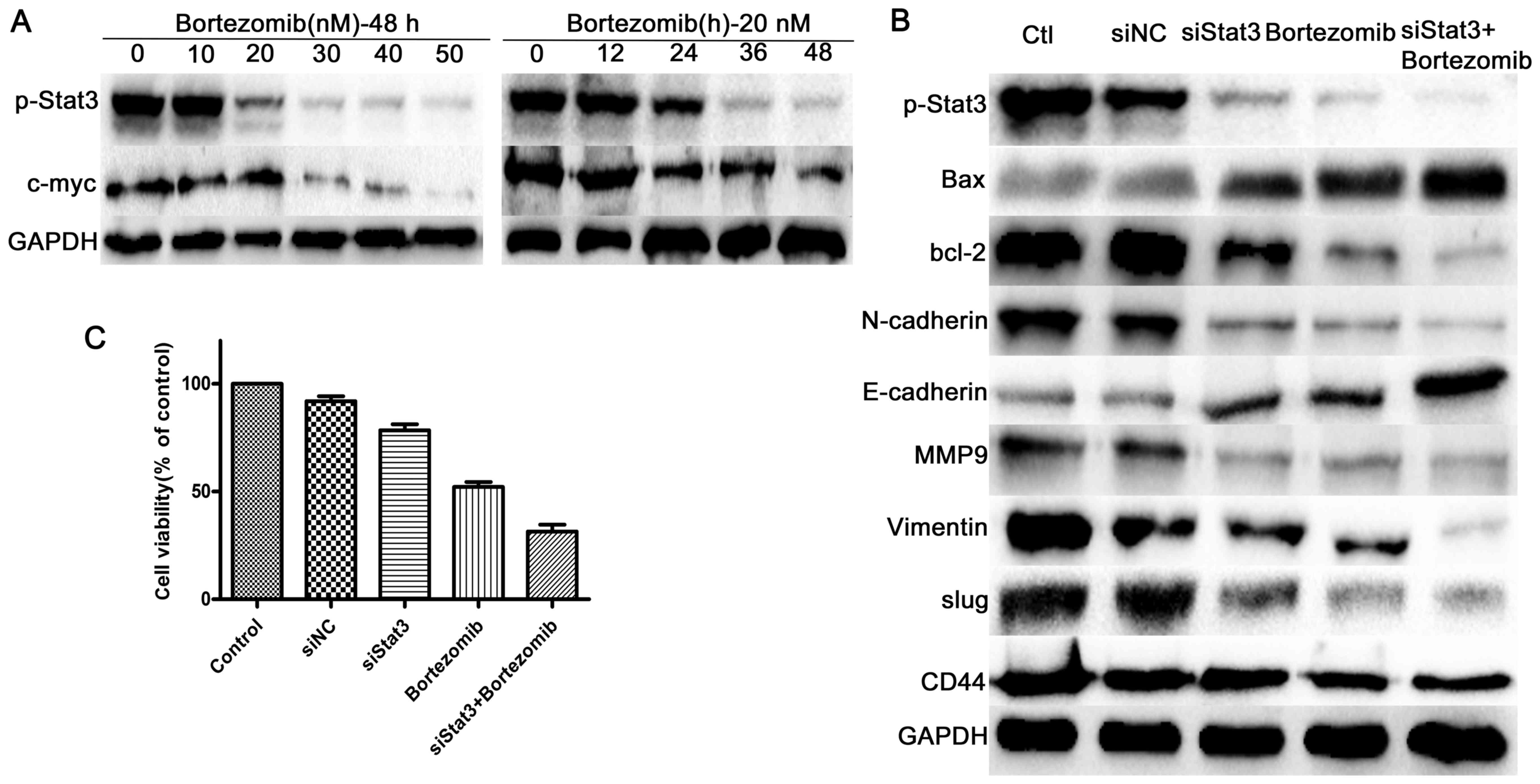
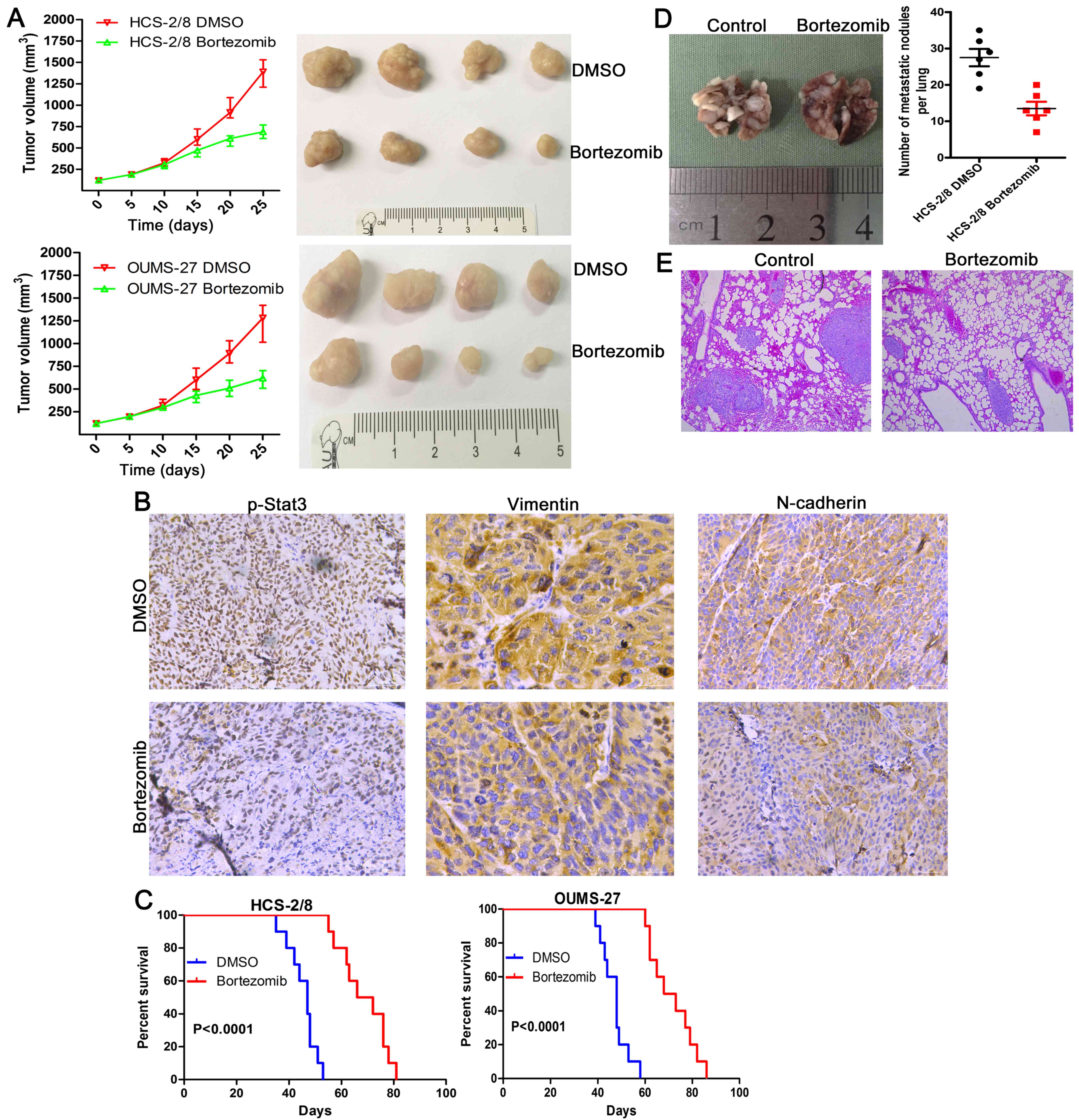
|
1
|
O'Neal LW and Ackerman LV: Chondrosarcoma
of bone. Cancer. 5:551–577. 1952. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lee FY, Mankin HJ, Fondren G, Gebhardt MC,
Springfield DS, Rosenberg AE and Jennings LC: Chondrosarcoma of
bone: An assessment of outcome. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 81:326–338.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bauer HC, Brosjo O, Kreicbergs A and
Lindholm J: Low risk of recurrence of enchondroma and low-grade
chondrosarcoma in extremities. 80 patients followed for 2–25 years.
Acta Orthop Scand. 66:283–288. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Eriksson AI, Schiller A and Mankin HJ: The
management of chondrosarcoma of bone. Clin Orthop Relat Res. (153):
44–66. 1980.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bovée JV, Cleton-Jansen AM, Taminiau AH
and Hogendoorn PC: Emerging pathways in the development of
chondrosarcoma of bone and implications for targeted treatment.
Lancet Oncol. 6:599–607. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Gelderblom H, Hogendoorn PC, Dijkstra SD,
van Rijswijk CS, Krol AD, Taminiau AH and Bovée JV: The clinical
approach towards chondrosarcoma. Oncologist. 13:320–329. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yu H, Pardoll D and Jove R: STATs in
cancer inflammation and immunity: A leading role for STAT3. Nat Rev
Cancer. 9:798–809. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Darnell JE Jr: Reflections on STAT3,
STAT5, and STAT6 as fat STATs. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
93:6221–6224. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kijima T, Niwa H, Steinman RA, Drenning
SD, Gooding WE, Wentzel AL, Xi S and Grandis JR: STAT3 activation
abrogates growth factor dependence and contributes to head and neck
squamous cell carcinoma tumor growth in vivo. Cell Growth Differ.
13:355–362. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chen X, Ying Z, Lin X, Lin H, Wu J, Li M
and Song L: Acylglycerol kinase augments JAK2/STAT3 signaling in
esophageal squamous cells. J Clin Invest. 123:2576–2589. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bu LL, Deng WW, Huang CF, Liu B, Zhang WF
and Sun ZJ: Inhibition of STAT3 reduces proliferation and invasion
in salivary gland adenoid cystic carcinoma. Am J Cancer Res.
5:1751–1761. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Feng Y, Ke C, Tang Q, Dong H, Zheng X, Lin
W, Ke J, Huang J, Yeung SC and Zhang H: Metformin promotes
autophagy and apoptosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by
downregulating Stat3 signaling. Cell Death Dis. 5:e10882014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Anderson JL, Titz B, Akiyama R,
Komisopoulou E, Park A, Tap WD, Graeber TG and Denny CT:
Phosphoproteomic profiling reveals IL6-mediated paracrine signaling
within the Ewing sarcoma family of tumors. Mol Cancer Res.
12:1740–1754. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang J, Ni J, Yi S, Song D and Ding M:
Protein inhibitor of activated STAT xα depresses cyclin D and
cyclin D kinase, and contributes to the inhibition of osteosarcoma
cell progression. Mol Med Rep. 13:1645–1652. 2016.
|
|
15
|
Sandoval-Usme MC, Umaña-Pérez A, Guerra B,
Hernández-Perera O, García-Castellano JM, Fernández-Pérez L and
Sánchez-Gómez M: Simvastatin impairs growth hormone-activated
signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) signaling
pathway in UMR-106 osteosarcoma cells. PLoS One. 9:e877692014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kane RC, Farrell AT, Sridhara R and Pazdur
R: United States Food and Drug Administration approval summary:
Bortezomib for the treatment of progressive multiple myeloma after
one prior therapy. Clin Cancer Res. 12:2955–2960. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chen D, Frezza M, Schmitt S, Kanwar J and
Dou QP: Bortezomib as the first proteasome inhibitor anticancer
drug: Current status and future perspectives. Curr Cancer Drug
Targets. 11:239–253. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Cavo M: Proteasome inhibitor bortezomib
for the treatment of multiple myeloma. Leukemia. 20:1341–1352.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Shin DH, Chun YS, Lee DS, Huang LE and
Park JW: Bortezomib inhibits tumor adaptation to hypoxia by
stimulating the FIH-mediated repression of hypoxia-inducible
factor-1. Blood. 111:3131–3136. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Mackay H, Hedley D, Major P, Townsley C,
Mackenzie M, Vincent M, Degendorfer P, Tsao MS, Nicklee T, Birle D,
et al: A phase II trial with pharmacodynamic endpoints of the
proteasome inhibitor bortezomib in patients with metastatic
colorectal cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 11:5526–5533. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kim GP, Mahoney MR, Szydlo D, Mok TS,
Marshke R, Holen K, Picus J, Boyer M, Pitot HC, Rubin J, et al: An
international, multi-center phase II trial of bortezomib in
patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Invest New Drugs.
30:387–394. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Hideshima T, Chauhan D, Hayashi T, Akiyama
M, Mitsiades N, Mitsiades C, Podar K, Munshi NC, Richardson PG and
Anderson KC: Proteasome inhibitor PS-341 abrogates IL-6 triggered
signaling cascades via caspase-dependent downregulation of gp130 in
multiple myeloma. Oncogene. 22:8386–8393. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yang Z, Liu S, Zhu M, Zhang H, Wang J, Xu
Q, Lin K, Zhou X, Tao M, Li C and Zhu H: PS341 inhibits
hepatocellular and colorectal cancer cells through the FOXO3/CTNNB1
signaling pathway. Sci Rep. 6:220902016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tingting R, Wei G, Changliang P, Xinchang
L and Yi Y: Arsenic trioxide inhibits osteosarcoma cell
invasiveness via MAPK signaling pathway. Cancer Biol Ther.
10:251–257. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sun Y, Guo W, Ren T, Liang W, Zhou W, Lu
Q, Jiao G and Yan T: Gli1 inhibition suppressed cell growth and
cell cycle progression and induced apoptosis as well as autophagy
depending on ERK1/2 activity in human chondrosarcoma cells. Cell
Death Dis. 5:e9792014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sun KX, Xia HW and Xia RL: Anticancer
effect of salidroside on colon cancer through inhibiting JAK2/STAT3
signaling pathway. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:615–621.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lamouille S, Xu J and Derynck R: Molecular
mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 15:178–196. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Xu J, Lamouille S and Derynck R:
TGF-beta-induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition. Cell Res.
19:156–172. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wake MS and Watson CJ: STAT3 the oncogene
- still eluding therapy? FEBS J. 282:2600–2611. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Stobbe-Maicherski N, Wolff S, Wolff C,
Abel J, Sydlik U, Frauenstein K and Haarmann-Stemmann T: The
interleukin-6-type cytokine oncostatin M induces aryl hydrocarbon
receptor expression in a STAT3-dependent manner in human HepG2
hepatoma cells. FEBS J. 280:6681–6690. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Salas S, Jiguet-Jiglaire C, Campion L,
Bartoli C, Frassineti F, Deville JL, Maues De Paula A, Forest F,
Jézéquel P, Gentet JC, et al: Correlation between ERK1 and STAT3
expression and chemoresistance in patients with conventional
osteosarcoma. BMC Cancer. 14:6062014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Dalla Via L, Nardon C and Fregona D:
Targeting the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway with inorganic compounds
to fight cancer: A challenge for the future. Future Med Chem.
4:525–543. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lee JH, Kim C, Kim SH, Sethi G and Ahn KS:
Farnesol inhibits tumor growth and enhances the anticancer effects
of bortezomib in multiple myeloma xenograft mouse model through the
modulation of STAT3 signaling pathway. Cancer Lett. 360:280–293.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kim JE, Lee JI, Jin DH, Lee WJ, Park GB,
Kim S, Kim YS, Wu TC, Hur DY and Kim D: Sequential treatment of HPV
E6 and E7-expressing TC-1 cells with bortezomib and celecoxib
promotes apoptosis through p-p38 MAPK-mediated downregulation of
cyclin D1 and CDK2. Oncol Rep. 31:2429–2437. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Liang YJ, Wang QY, Zhou CX, Yin QQ, He M,
Yu XT, Cao DX, Chen GQ, He JR and Zhao Q: MiR-124 targets Slug to
regulate epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis of breast
cancer. Carcinogenesis. 34:713–722. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Micalizzi DS, Farabaugh SM and Ford HL:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer: Parallels between
normal development and tumor progression. J Mammary Gland Biol
Neoplasia. 15:117–134. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Romero-Pérez L, López-García MÁ,
Díaz-Martín J, Biscuola M, Castilla MÁ, Tafe LJ, Garg K, Oliva E,
Matias-Guiu X, Soslow RA, et al: ZEB1 overexpression associated
with E-cadherin and microRNA-200 downregulation is characteristic
of undifferentiated endometrial carcinoma. Mod Pathol.
26:1514–1524. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Lim YY, Wright JA, Attema JL, Gregory PA,
Bert AG, Smith E, Thomas D, Lopez AF, Drew PA, Khew-Goodall Y, et
al: Epigenetic modulation of the miR-200 family is associated with
transition to a breast cancer stem-cell-like state. J Cell Sci.
126:2256–2266. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Liu RY, Zeng Y, Lei Z, Wang L, Yang H, Liu
Z, Zhao J and Zhang HT: JAK/STAT3 signaling is required for
TGF-β-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in lung cancer
cells. Int J Oncol. 44:1643–1651. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Yuan W, Li T, Mo X, Wang X, Liu B, Wang W,
Su Y, Xu L and Han W: Knockdown of CMTM3 promotes metastasis of
gastric cancer via the STAT3/Twist1/EMT signaling pathway.
Oncotarget. 7:29507–29519. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Tania M, Khan MA and Fu J: Epithelial to
mesenchymal transition inducing transcription factors and
metastatic cancer. Tumour Biol. 35:7335–7342. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|