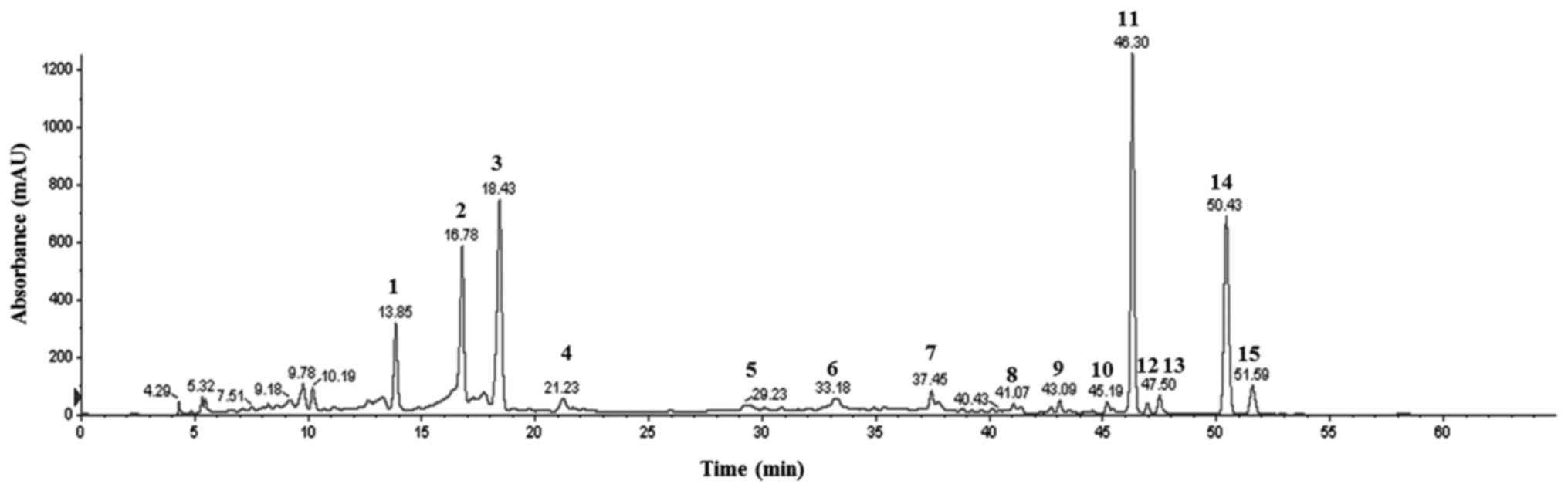
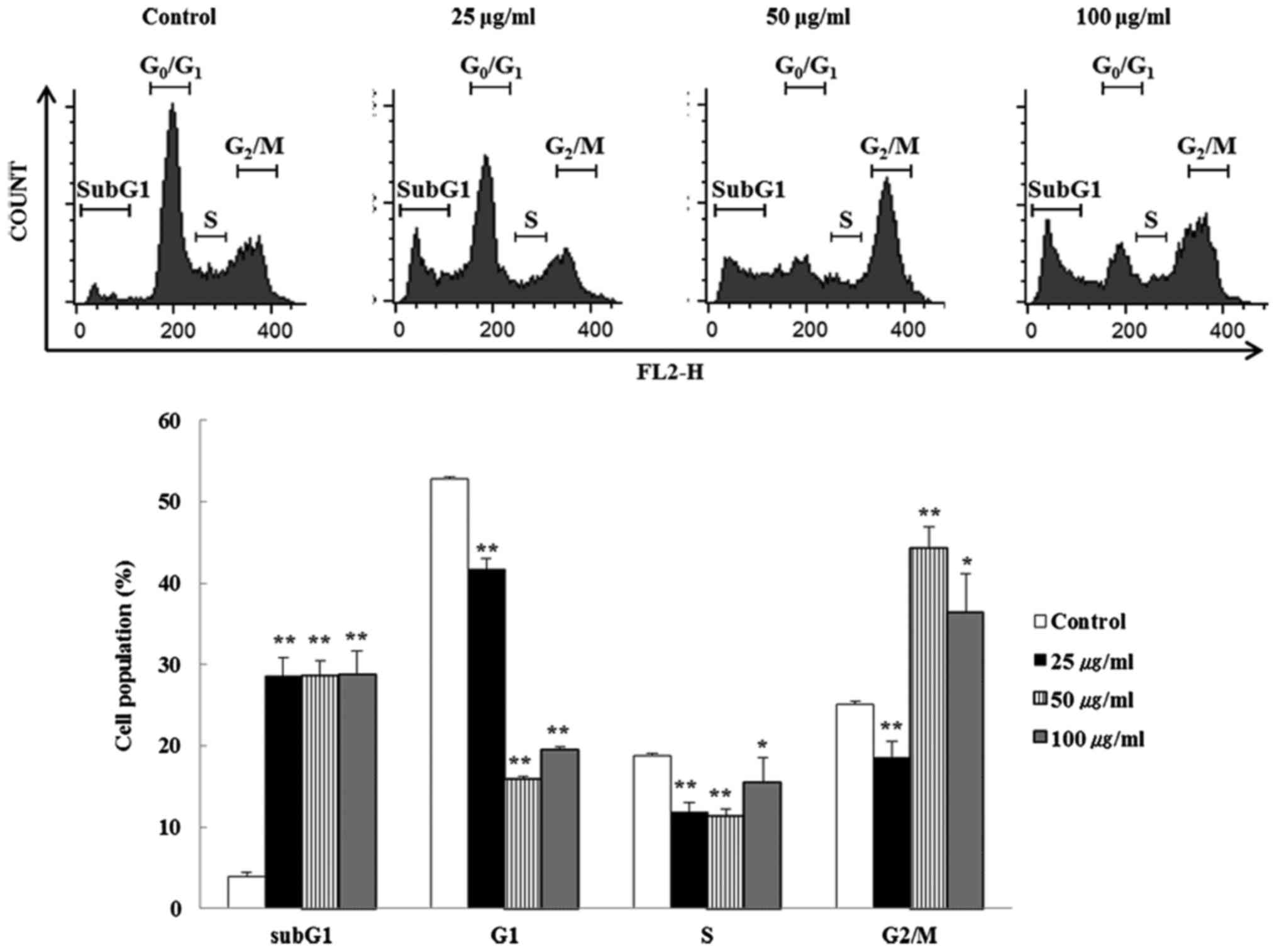
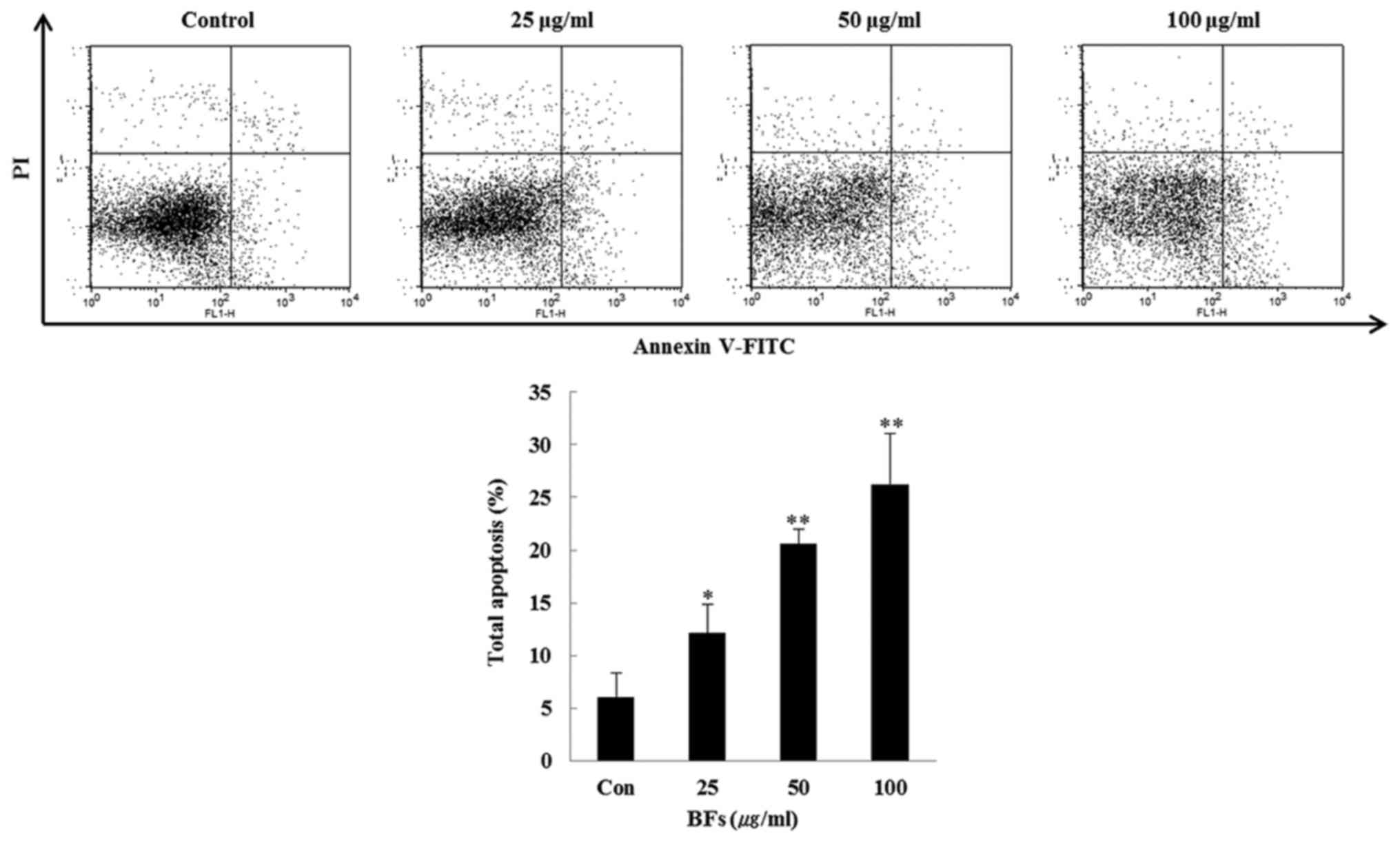
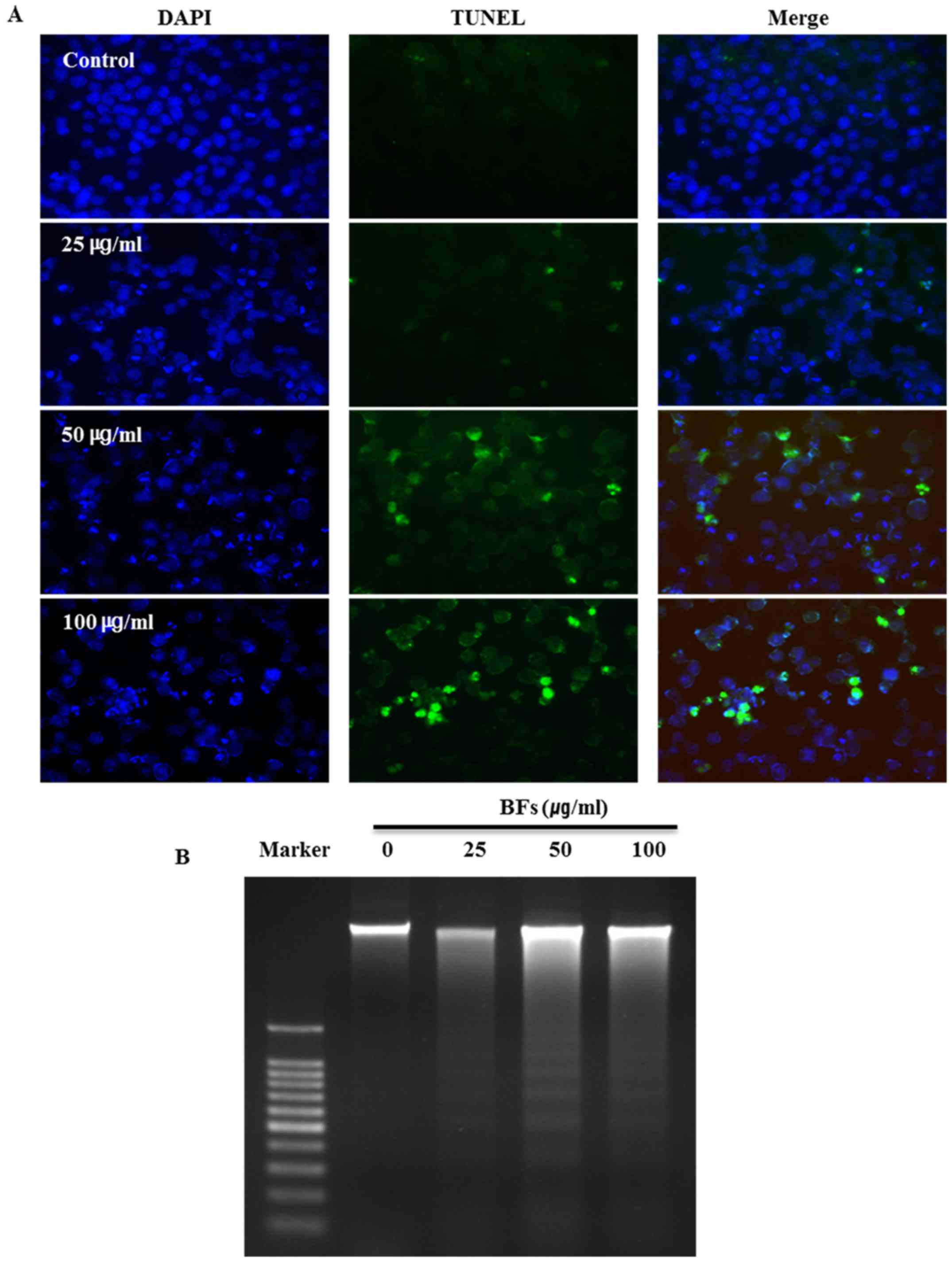
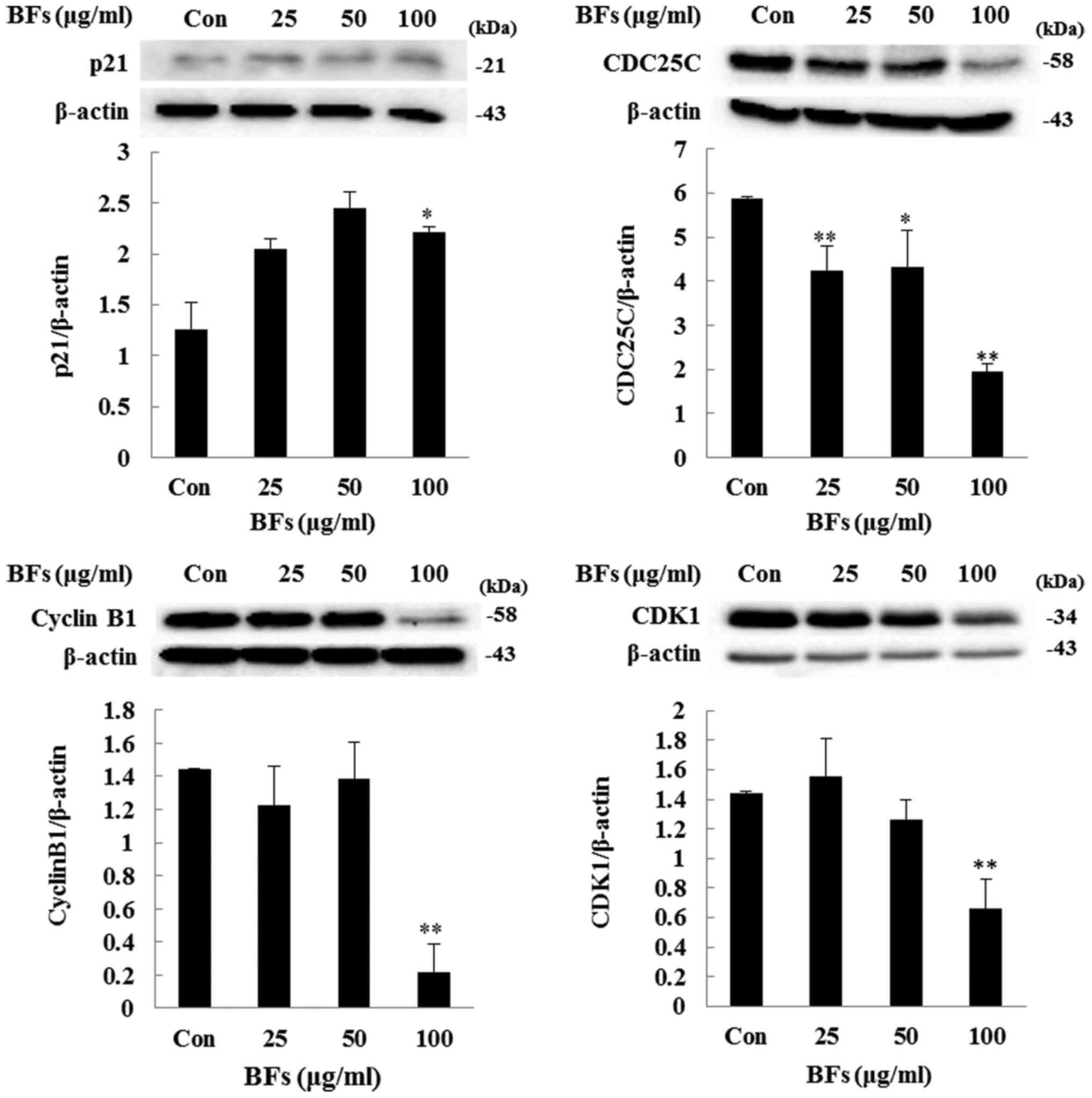
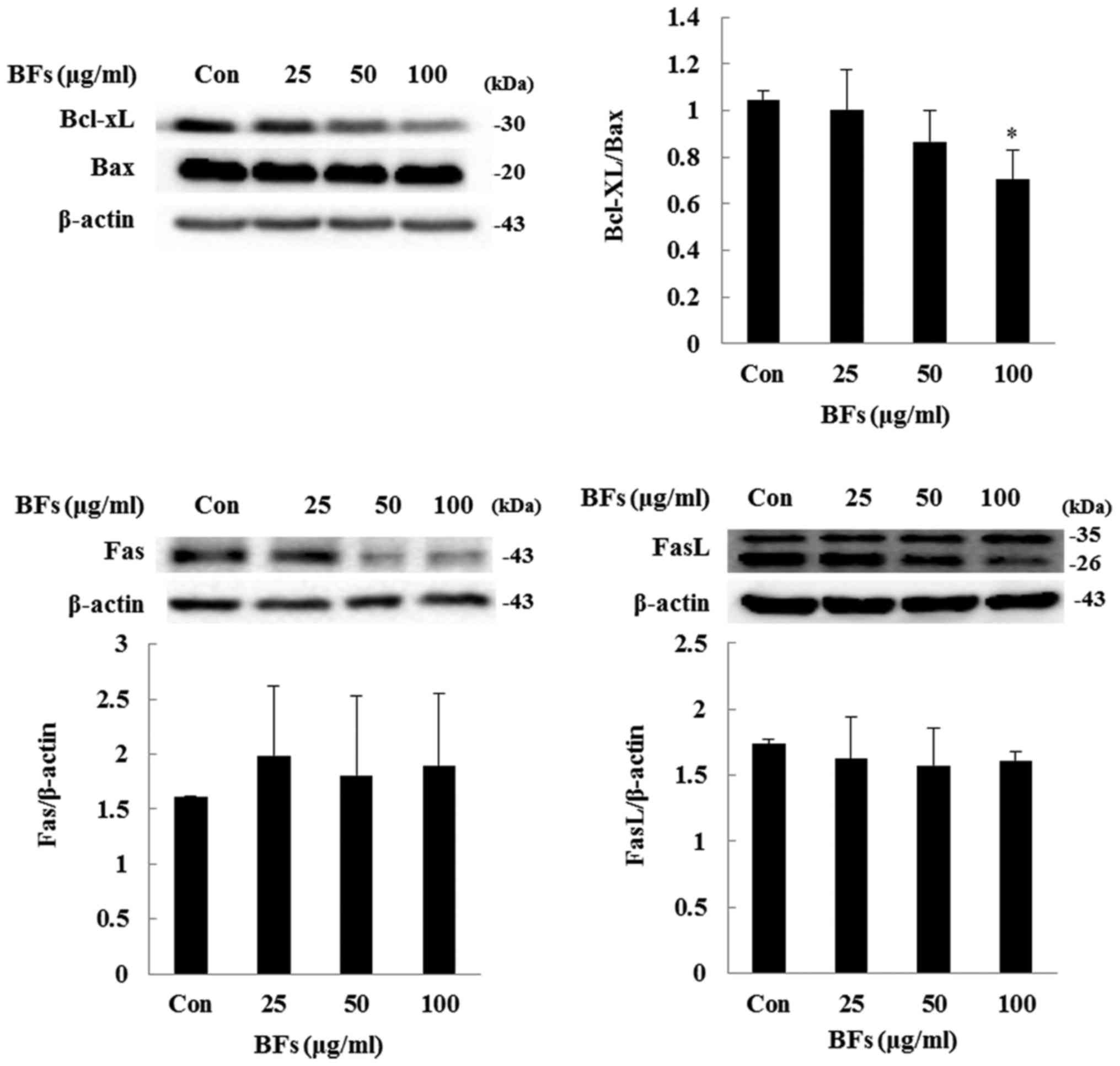
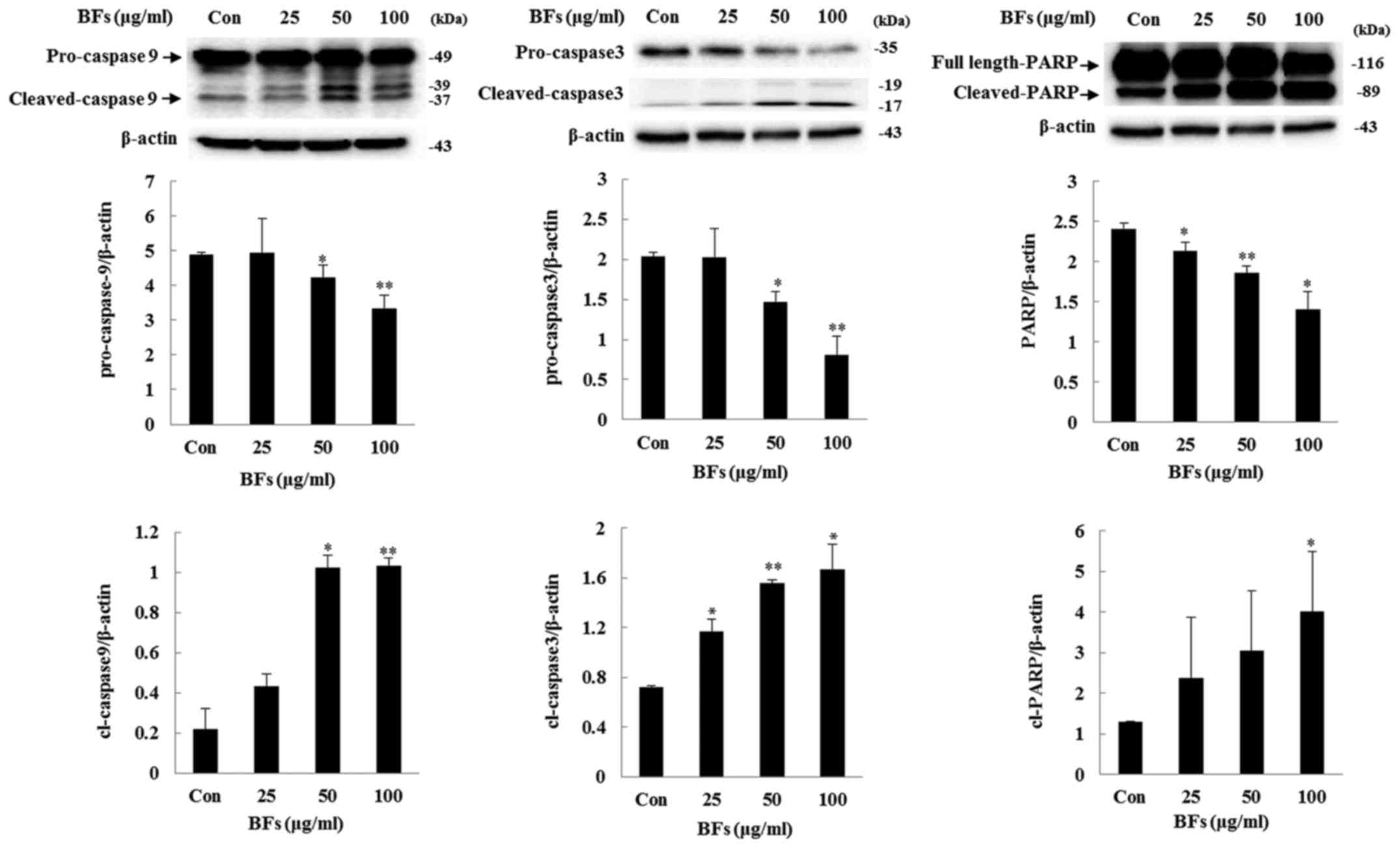
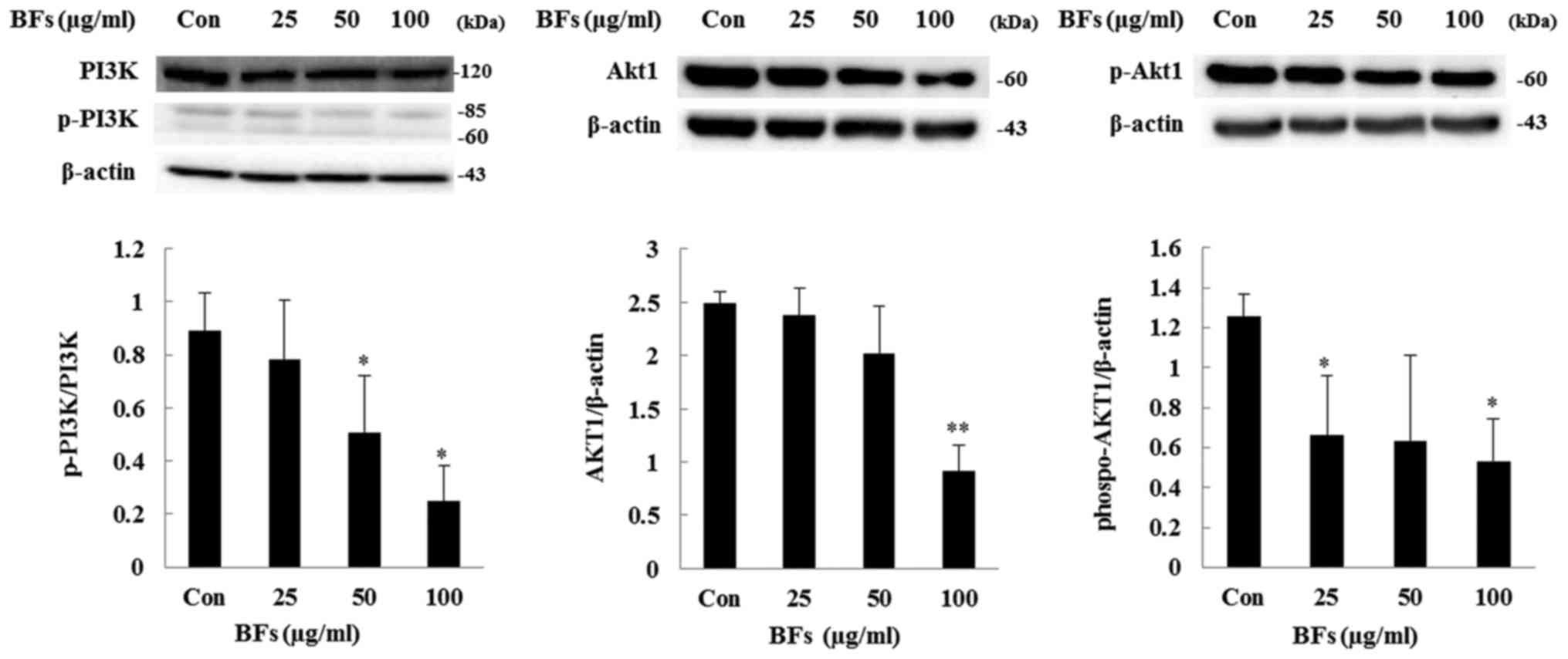
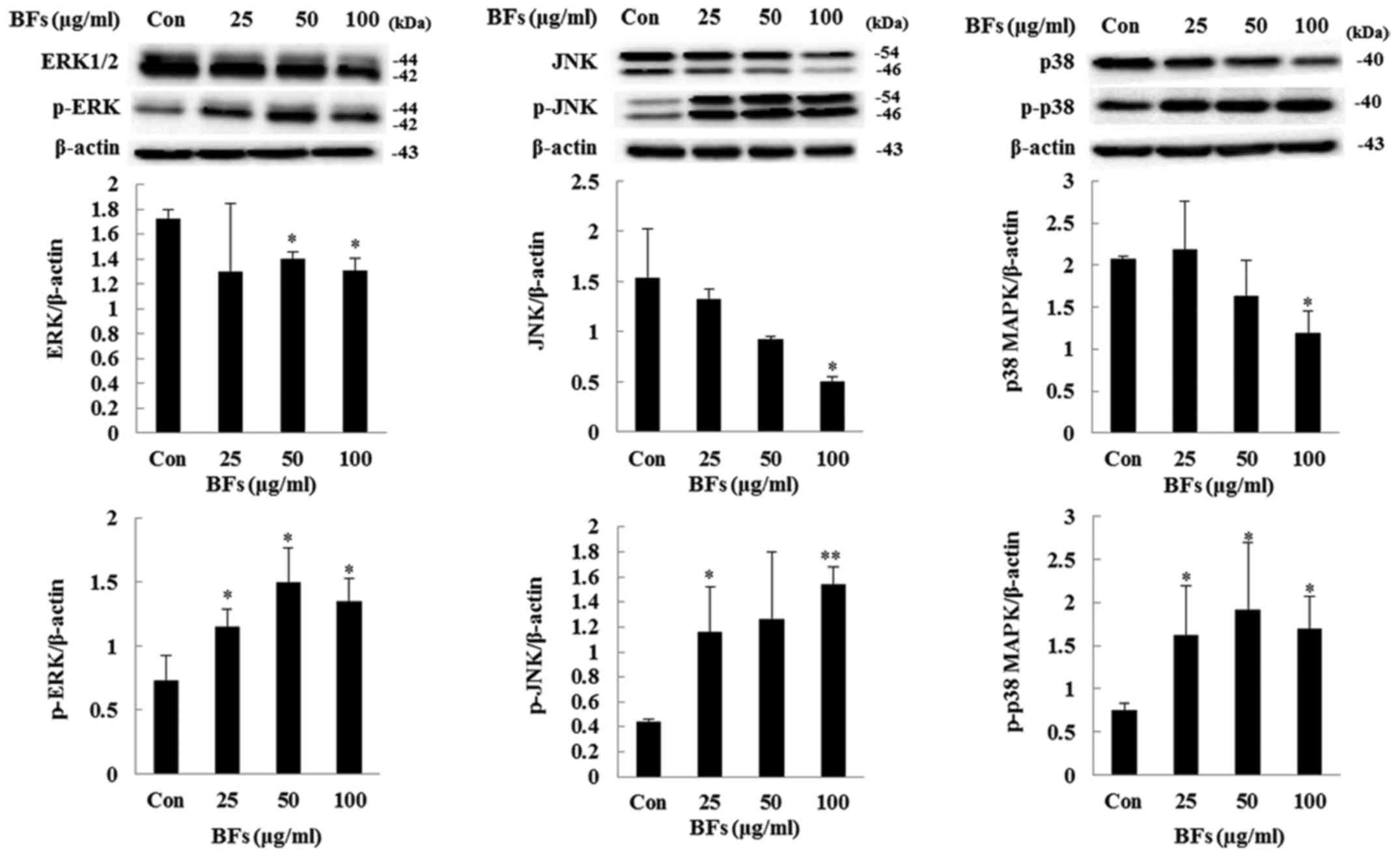
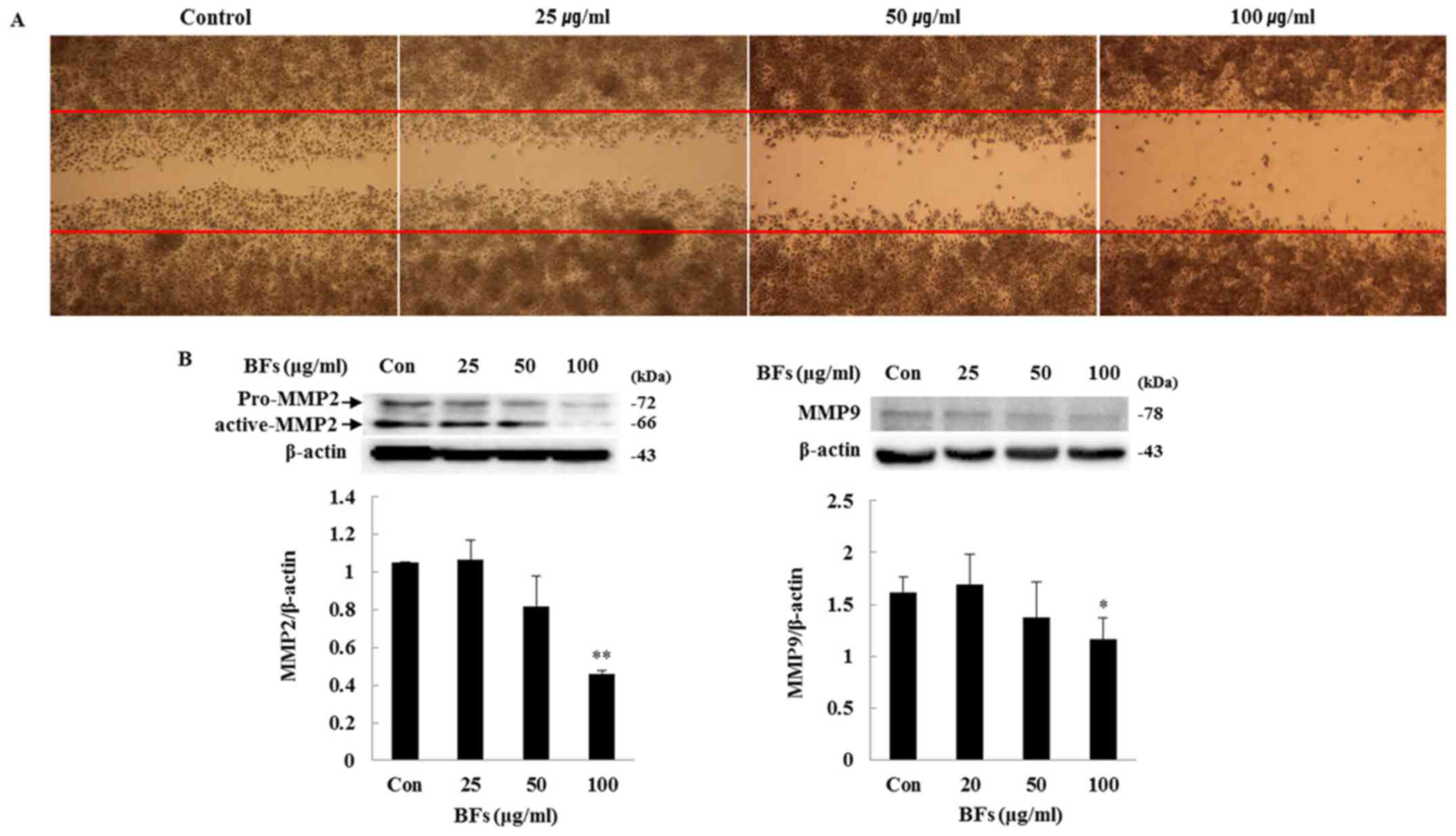
|
1
|
Schlachterman A, Craft WW Jr, Hilgenfeldt
E, Mitra A and Cabrera R: Current and future treatments for
hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. 21:8478–8491.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Manosroi A, Akazawa H, Kitdamrongtham W,
Akihisa T, Manosroi W and Manosroi J: Potent antiproliferative
effect on liver cancer of medicinal plants selected from the
thai/lanna medicinal plant recipe database 'MANOSROI III'. Evid
Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015:3971812015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Ren W, Qiao Z, Wang H, Zhu L and Zhang L:
Flavonoids: Promising anticancer agents. Med Res Rev. 23:519–534.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Tripoli E, Guardia ML, Giammanco S, Majo
DD and Giammanco M: Citrus flavonoids: Molecular structure,
biological activity and nutritional properties: A review. Food
Chem. 104:466–479. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Meiyanto E, Hermawan A and Anindyajati:
Natural products for cancer-targeted therapy: Citrus flavonoids as
potent chemopreventive agents. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 13:427–436.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lee HJ, Nagappan A, Park HS, Hong GE,
Yumnam S, Raha S, Saralamma VV, Lee WS, Kim EH and Kim GS:
Flavonoids isolated from Citrus platymamma induce
mitochondrial-dependent apoptosis in AGS cells by modulation of the
PI3K/AKT and MAPK pathways. Oncol Rep. 34:1517–1525.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Penjor T, Yamamoto M, Uehara M, Ide M,
Matsumoto N, Matsumoto R and Nagano Y: Phylogenetic relationships
of citrus and its relatives based on matK gene sequences. PLoS One.
8:e625742013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Shimizu T and Yano K: A post-labeling
method for multiplexed and multicolored genotyping analysis of SSR,
indel and SNP markers in single tube with bar-coded split tag
(BStag). BMC Res Notes. 4:1612011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Elmore S: Apoptosis: A review of
programmed cell death. Toxicol Pathol. 35:495–516. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Pietenpol JA and Stewart ZA: Cell cycle
checkpoint signaling: Cell cycle arrest versus apoptosis.
Toxicology. 181–182:475–481. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Hsu SC, Kuo CL, Lin JP, Lee JH, Lin CC, Su
CC, Lin HJ and Chung JG: Crude extracts of Euchresta formosana
radix induce cytotoxicity and apoptosis in human hepatocellular
carcinoma cell line (Hep3B). Anticancer Res. 27B:2415–2425.
2007.
|
|
12
|
Nair SV, Hettihewa M and Rupasinghe HP:
Apoptotic and inhibitory effects on cell proliferation of
hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cells by methanol leaf extract of
Costus speciosus. BioMed Res Int. 2014:6370982014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yoon SB, Lee YJ, Park SK, Kim HC, Bae H,
Kim HM, Ko SG, Choi HY, Oh MS and Park W: Anti-inflammatory effects
of Scutellaria baicalensis water extract on LPS-activated RAW 264.7
macrophages. J Ethnopharmacol. 125:286–290. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Granado-Serrano AB, Martín MA, Bravo L,
Goya L and Ramos S: Quercetin induces apoptosis via caspase
activation, regulation of Bcl-2, and inhibition of PI-3-kinase/Akt
and ERK pathways in a human hepatoma cell line (HepG2). J Nutr.
136:2715–2721. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Park HS, Park KI, Lee DH, Kang SR,
Nagappan A, Kim JA, Kim EH, Lee WS, Shin SC, Hah YS, et al:
Polyphenolic extract isolated from Korean Lonicera japonica Thunb.
induce G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in HepG2 cells:
Involvements of PI3K/Akt and MAPKs. Food Chem Toxicol.
50:2407–2416. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Park KI, Park HS, Kang SR, Nagappan A, Lee
DH, Kim JA, Han DY and Kim GS: Korean Scutellaria baicalensis water
extract inhibits cell cycle G1/S transition by suppressing cyclin
D1 expression and matrix-metalloproteinase-2 activity in human lung
cancer cells. J Ethnopharmacol. 133:634–641. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Stamenkovic I: Matrix metalloproteinases
in tumor invasion and metastasis. Semin Cancer Biol. 10:415–433.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Hong GE, Kim JA, Nagappan A, Yumnam S, Lee
HJ, Kim EH, Lee WS, Shin SC, Park HS and Kim GS: Flavonoids
identified from Korean Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi inhibit
inflammatory signaling by suppressing activation of NF-κB and MAPK
in RAW 264.7 cells. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.
2013:9120312013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Saralamma VV, Nagappan A, Hong GE, Lee HJ,
Yumnam S, Raha S, Heo JD, Lee SJ, Lee WS, Kim EH, et al: Poncirin
induces apoptosis in AGS human gastric cancer cells through
extrinsic apoptotic pathway by up-regulation of fas ligand. Int J
Mol Sci. 16:22676–22691. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kim MS, Bak Y, Park YS, Lee DH, Kim JH,
Kang JW, Song HH, Oh SR and Yoon DY: Wogonin induces apoptosis by
suppressing E6 and E7 expressions and activating intrinsic
signaling pathways in HPV-16 cervical cancer cells. Cell Biol
Toxicol. 29:259–272. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Park HY, Kim GY, Moon SK, Kim WJ, Yoo YH
and Choi YH: Fucoidan inhibits the proliferation of human urinary
bladder cancer T24 cells by blocking cell cycle progression and
inducing apoptosis. Molecules. 19:5981–5998. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Jokinen E, Laurila N and Koivunen JP:
Alternative dosing of dual PI3K and MEK inhibition in cancer
therapy. BMC Cancer. 12:6122012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wagner EF and Nebreda AR: Signal
integration by JNK and p38 MAPK pathways in cancer development. Nat
Rev Cancer. 9:537–549. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kumar S and Pandey AK: Chemistry and
biological activities of flavonoids: An overview. Sci World J.
2013:1627502013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Rawson NE, Ho C and Li S: Efficacious
anti-cancer property of flavonoids from citrus peels. Food Sci Hum
Wellness. 3:104–109. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: The next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Park KI, Park HS, Nagappan A, Hong GE, Lee
DH, Kang SR, Kim JA, Zhang J, Kim EH, Lee WS, et al: Induction of
the cell cycle arrest and apoptosis by flavonoids isolated from
Korean Citrus aurantium L. in non-small-cell lung cancer cells.
Food Chem. 135:2728–2735. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Jain MV, Paczulla AM, Klonisch T, Dimgba
FN, Rao SB, Roberg K, Schweizer F, Lengerke C, Davoodpour P,
Palicharla VR, et al: Interconnections between apoptotic,
autophagic and necrotic pathways: Implications for cancer therapy
development. J Cell Mol Med. 17:12–29. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wada T and Penninger JM: Mitogen-activated
protein kinases in apoptosis regulation. Oncogene. 23:2838–2849.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chien CC, Wu MS, Shen SC, Ko CH, Chen CH,
Yang LL and Chen YC: Activation of JNK contributes to
evodiamine-induced apoptosis and G2/M arrest in human colorectal
carcinoma cells: A structure-activity study of evodiamine. PLoS
One. 9:e997292014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wang X, Martindale JL and Holbrook NJ:
Requirement for ERK activation in cisplatin-induced apoptosis. J
Biol Chem. 275:39435–39443. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
He X, Zhu Z, Johnson C, Stoops J, Eaker
AE, Bowen W and DeFrances MC: PIK3IP1, a negative regulator of
PI3K, suppresses the development of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Cancer Res. 68:5591–5598. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Liu X, Shi Y, Han EK, Chen Z, Rosenberg
SH, Giranda VL, Luo Y and Ng SC: Downregulation of Akt1 inhibits
anchorage-independent cell growth and induces apoptosis in cancer
cells. Neoplasia. 3:278–286. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lou L, Ye W, Chen Y, Wu S, Jin L, He J,
Tao X, Zhu J, Chen X, Deng A, et al: Ardipusilloside inhibits
survival, invasion and metastasis of human hepatocellular carcinoma
cells. Phytomedicine. 19:603–608. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhao XL, Sun T, Che N, Sun D, Zhao N, Dong
XY, Gu Q, Yao Z and Sun BC: Promotion of hepatocellular carcinoma
metastasis through matrix metalloproteinase activation by
epithelial-mesenchymal transition regulator Twist1. J Cell Mol Med.
15:691–700. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Huang YT, Hwang JJ, Lee PP, Ke FC, Huang
JH, Huang CJ, Kandaswami C, Middleton E Jr and Lee MT: Effects of
luteolin and quercetin, inhibitors of tyrosine kinase, on cell
growth and metastasis-associated properties in A431 cells
overexpressing epidermal growth factor receptor. Br J Pharmacol.
128:999–1010. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Shi MD, Liao YC, Shih YW and Tsai LY:
Nobiletin attenuates metastasis via both ERK and PI3K/Akt pathways
in HGF-treated liver cancer HepG2 cells. Phytomedicine. 20:743–752.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|