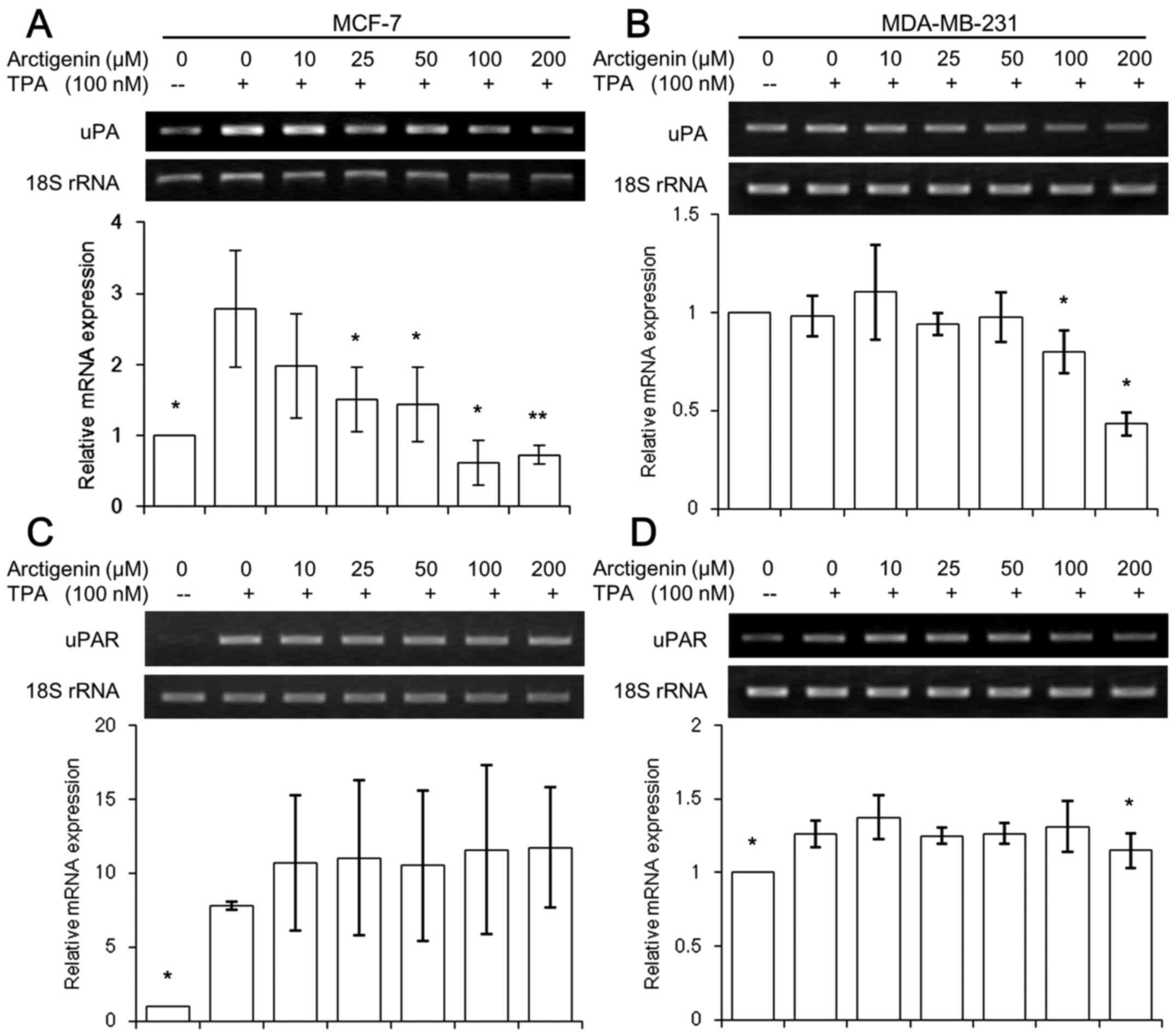
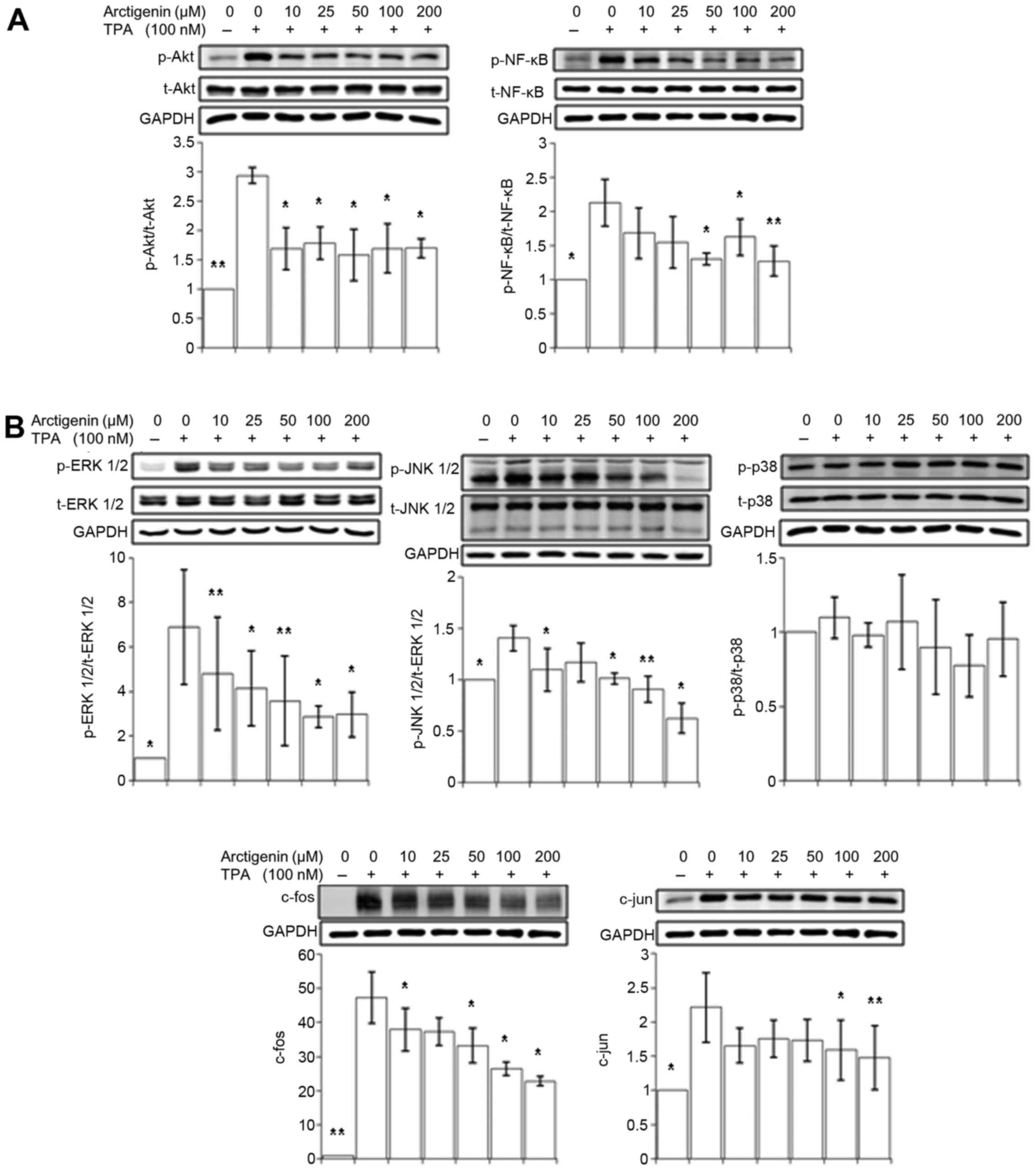
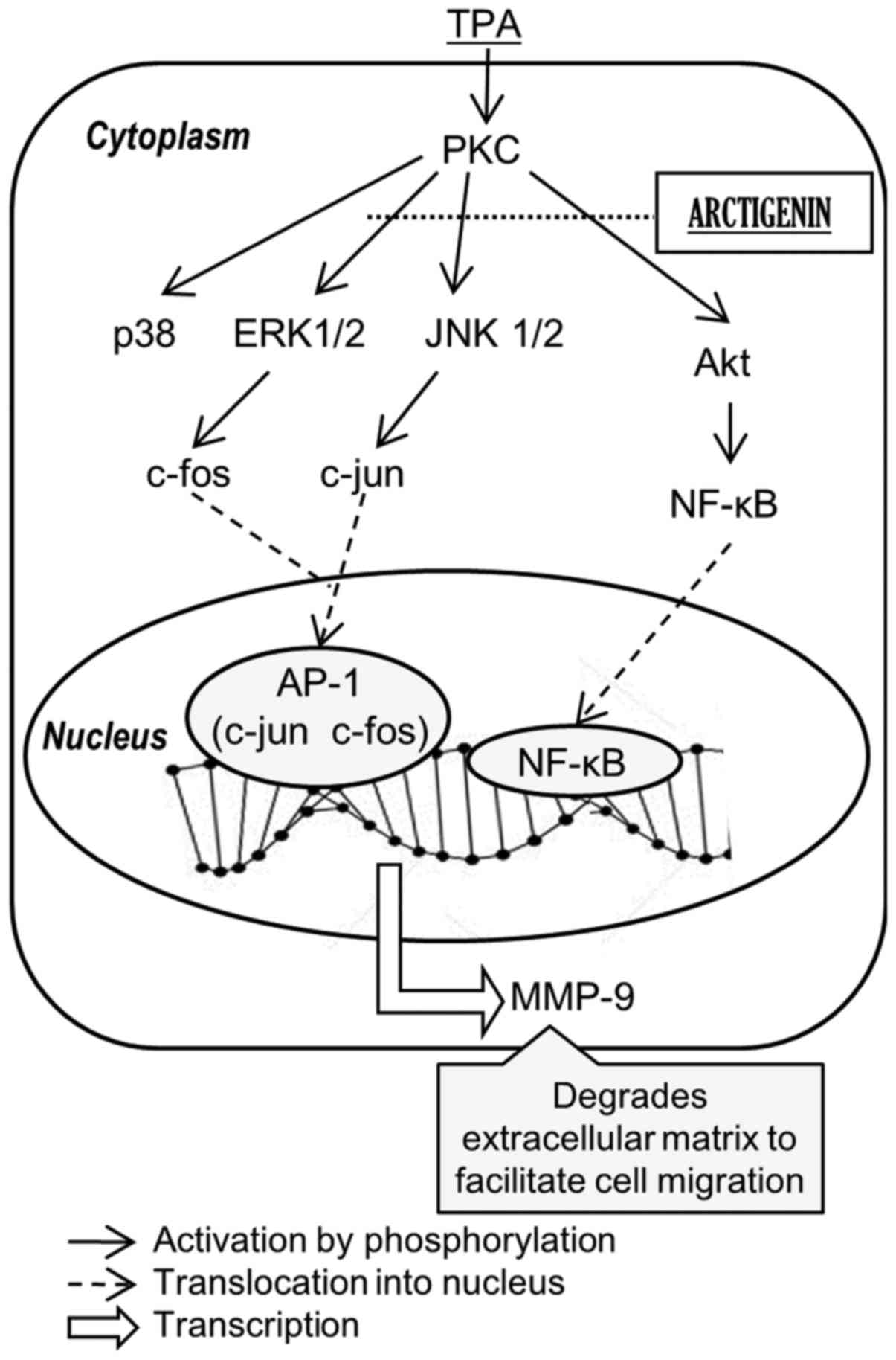
|
1
|
Gao H, Li G, Zhang J and Zeng J:
Arctigenin: A lignan from Arctium lappa. Acta Crystallogr Sect E
Struct Rep Online. 64:o15382008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kim Y, Hollenbaugh JA, Kim DH and Kim B:
Novel PI3K/Akt inhibitors screened by the cytoprotective function
of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Tat. PLoS One. 6:e217812011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hayashi K, Narutaki K, Nagaoka Y, Hayashi
T and Uesato S: Therapeutic effect of arctiin and arctigenin in
immunocompetent and immunocompromised mice infected with influenza
A virus. Biol Pharm Bull. 33:1199–1205. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Swarup V, Ghosh J, Mishra MK and Basu A:
Novel strategy for treatment of Japanese encephalitis using
arctigenin, a plant lignan. J Antimicrob Chemother. 61:679–688.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lee JY and Kim CJ: Arctigenin, a
phenylpropanoid dibenzylbutyrolactone lignan, inhibits type I–IV
allergic inflammation and pro-inflammatory enzymes. Arch Pharm Res.
33:947–957. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kang HS, Lee JY and Kim CJ:
Anti-inflammatory activity of arctigenin from Forsythiae Fructus. J
Ethnopharmacol. 116:305–312. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yao X, Li G, Lü C, Xu H and Yin Z:
Arctigenin promotes degradation of inducible nitric oxide synthase
through CHIP-associated proteasome pathway and suppresses its
enzyme activity. Int Immunopharmacol. 14:138–144. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tsai WJ, Chang CT, Wang GJ, Lee TH, Chang
SF, Lu SC and Kuo YC: Arctigenin from Arctium lappa inhibits
interleukin-2 and interferon gene expression in primary human T
lymphocytes. Chin Med. 6:122011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cho MK, Park JW, Jang YP, Kim YC and Kim
SG: Potent inhibition of lipopolysaccharide-inducible nitric oxide
synthase expression by dibenzylbutyrolactone lignans through
inhibition of I-kappaBalpha phosphorylation and of p65 nuclear
translocation in macrophages. Int Immunopharmacol. 2:105–116. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Cho MK, Jang YP, Kim YC and Kim SG:
Arctigenin, a phenylpropanoid dibenzylbutyrolactone lignan,
inhibits MAP kinases and AP-1 activation via potent MKK inhibition:
The role in TNF-alpha inhibition. Int Immunopharmacol. 4:1419–1429.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Jeong JB, Hong SC, Jeong HJ and Koo JS:
Arctigenin induces cell cycle arrest by blocking the
phosphorylation of Rb via the modulation of cell cycle regulatory
proteins in human gastric cancer cells. Int Immunopharmacol.
11:1573–1577. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Susanti S, Iwasaki H, Itokazu Y, Nago M,
Taira N, Saitoh S and Oku H: Tumor specific cytotoxicity of
arctigenin isolated from herbal plant Arctium lappa L. J Nat Med.
66:614–621. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Awale S, Lu J, Kalauni SK, Kurashima Y,
Tezuka Y, Kadota S and Esumi H: Identification of arctigenin as an
antitumor agent having the ability to eliminate the tolerance of
cancer cells to nutrient starvation. Cancer Res. 66:1751–1757.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kim JY, Hwang JH, Cha MR, Yoon MY, Son ES,
Tomida A, Ko B, Song SW, Shin-ya K, Hwang YI, et al: Arctigenin
blocks the unfolded protein response and shows therapeutic
antitumor activity. J Cell Physiol. 224:33–40. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhang S, Li J, Song S, Li J, Tong R, Zang
Z, Jiang Q and Cai L: Integrated in silico and experimental methods
revealed that Arctigenin inhibited angiogenesis and HCT116 cell
migration and invasion through regulating the H1F4A and
wnt/β-catenin pathway. Mol Biosyst. 11:2878–2884. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hausott B, Greger H and Marian B:
Naturally occurring lignans efficiently induce apoptosis in
colorectal tumor cells. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 129:569–576. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Gu Y, Scheuer C, Feng D, Menger MD and
Laschke MW: Inhibition of angiogenesis: A novel antitumor mechanism
of the herbal compound arctigenin. Anticancer Drugs. 24:781–791.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Gu Y, Qi C, Sun X, Ma X, Zhang H, Hu L,
Yuan J and Yu Q: Arctigenin preferentially induces tumor cell death
under glucose deprivation by inhibiting cellular energy metabolism.
Biochem Pharmacol. 84:468–476. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Susanti S, Iwasaki H, Inafuku M, Taira N
and Oku H: Mechanism of arctigenin-mediated specific cytotoxicity
against human lung adenocarcinoma cell lines. Phytomedicine.
21:39–46. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yang S, Ma J, Xiao J, Lv X, Li X, Yang H,
Liu Y, Feng S and Zhang Y: Arctigenin anti-tumor activity in
bladder cancer T24 cell line through induction of cell-cycle arrest
and apoptosis. Anat Rec (Hoboken). 295:1260–1266. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Huang K, Li LA, Meng YG, You YQ, Fu XY and
Song L: Arctigenin promotes apoptosis in ovarian cancer cells via
the iNOS/NO/STAT3/survivin signalling. Basic Clin Pharmacol
Toxicol. 115:507–511. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hsieh CJ, Kuo PL, Hsu YC, Huang YF, Tsai
EM and Hsu YL: Arctigenin, a dietary phytoestrogen, induces
apoptosis of estrogen receptor-negative breast cancer cells through
the ROS/p38 MAPK pathway and epigenetic regulation. Free Radic Biol
Med. 67:159–170. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Jin JS, Lee JH and Hattori M: Ligand
binding affinities of arctigenin and its demethylated metabolites
to estrogen receptor alpha. Molecules. 18:1122–1127. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Matsumura A, Ghosh A, Pope GS and Darbre
PD: Comparative study of oestrogenic properties of eight
phytoestrogens in MCF7 human breast cancer cells. J Steroid Biochem
Mol Biol. 94:431–443. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Rice S and Whitehead SA: Phytoestrogens
and breast cancer–promoters or protectors? Endocr Relat Cancer.
13:995–1015. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lephart ED: Modulation of aromatase by
phytoestrogens. Enzyme Res. 2015:5946562015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Whitehead SA and Lacey M: Phytoestrogens
inhibit aromatase but not 17beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (HSD)
type 1 in human granulosa-luteal cells: Evidence for FSH induction
of 17beta-HSD. Hum Reprod. 18:487–494. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Low YL, Taylor JI, Grace PB, Dowsett M,
Scollen S, Dunning AM, Mulligan AA, Welch AA, Luben RN, Khaw KT, et
al: Phytoestrogen exposure correlation with plasma estradiol in
postmenopausal women in European Prospective Investigation of
Cancer and Nutrition-Norfolk may involve diet-gene interactions.
Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 14:213–220. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
DeSantis C, Ma J, Bryan L and Jemal A:
Breast cancer statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 64:52–62. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Jung KW, Won YJ, Kong HJ, Oh CM, Seo HG
and Lee JS: Cancer statistics in Korea: Incidence, mortality,
survival and prevalence in 2010. Cancer Res Treat. 45:1–14. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Straatman K: Wound healing assay.
University of Leicester, College of Medicine, Biological Sciences
and Psychology, Advanced Imaging Facilities; 2008
|
|
32
|
Loughlin DT and Artlett CM: Modification
of collagen by 3-deoxyglucosone alters wound healing through
differential regulation of p38 MAP kinase. PLoS One. 6:e186762011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lee K, Shin J, Kwon Y, Moon D and Nam K:
Suppression of cancer progression and metastasis in HT-29 human
colorectal adenocarcinomas by deep sea water. Biotechnol Bioprocess
Eng. 18:194–200. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Mehner C, Hockla A, Miller E, Ran S,
Radisky DC and Radisky ESR: Tumor cell-produced matrix
metalloproteinase 9 (MMP-9) drives malignant progression and
metastasis of basal-like triple negative breast cancer. Oncotarget.
5:2736–2749. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Holst-Hansen C, Johannessen B,
Høyer-Hansen G, Rømer J, Ellis V and Brünner N: Urokinase-type
plasminogen activation in three human breast cancer cell lines
correlates with their in vitro invasiveness. Clin Exp Metastasis.
14:297–307. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Lungu G, Covaleda L, Mendes O,
Martini-Stoica H and Stoica G: FGF-1-induced matrix
metalloproteinase-9 expression in breast cancer cells is mediated
by increased activities of NF-kappaB and activating protein-1. Mol
Carcinog. 47:424–435. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Moritani S, Nomura M, Takeda Y and
Miyamoto K: Cytotoxic components of bardanae fructus (goboshi).
Biol Pharm Bull. 19:1515–1517. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
McCawley LJ and Matrisian LM: Matrix
metalloproteinases: Multifunctional contributors to tumor
progression. Mol Med Today. 6:149–156. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Duffy MJ: The urokinase plasminogen
activator system: Role in malignancy. Curr Pharm Des. 10:39–49.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Cheepala SB, Yin W, Syed Z, Gill JN,
McMillian A, Kleiner HE, Lynch M, Loganantharaj R, Trutschl M, Cvek
U, et al: Identification of the B-Raf/Mek/Erk MAP kinase pathway as
a target for all-trans retinoic acid during skin cancer promotion.
Mol Cancer. 8:272009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Lilleholt LL, Johansen C, Arthur JS,
Funding A, Bibby BM, Kragballe K and Iversen L: Role of p38
mitogen-activated protein kinase isoforms in murine skin
inflammation induced by 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol 13-acetate. Acta
Derm Venereol. 91:271–278. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|