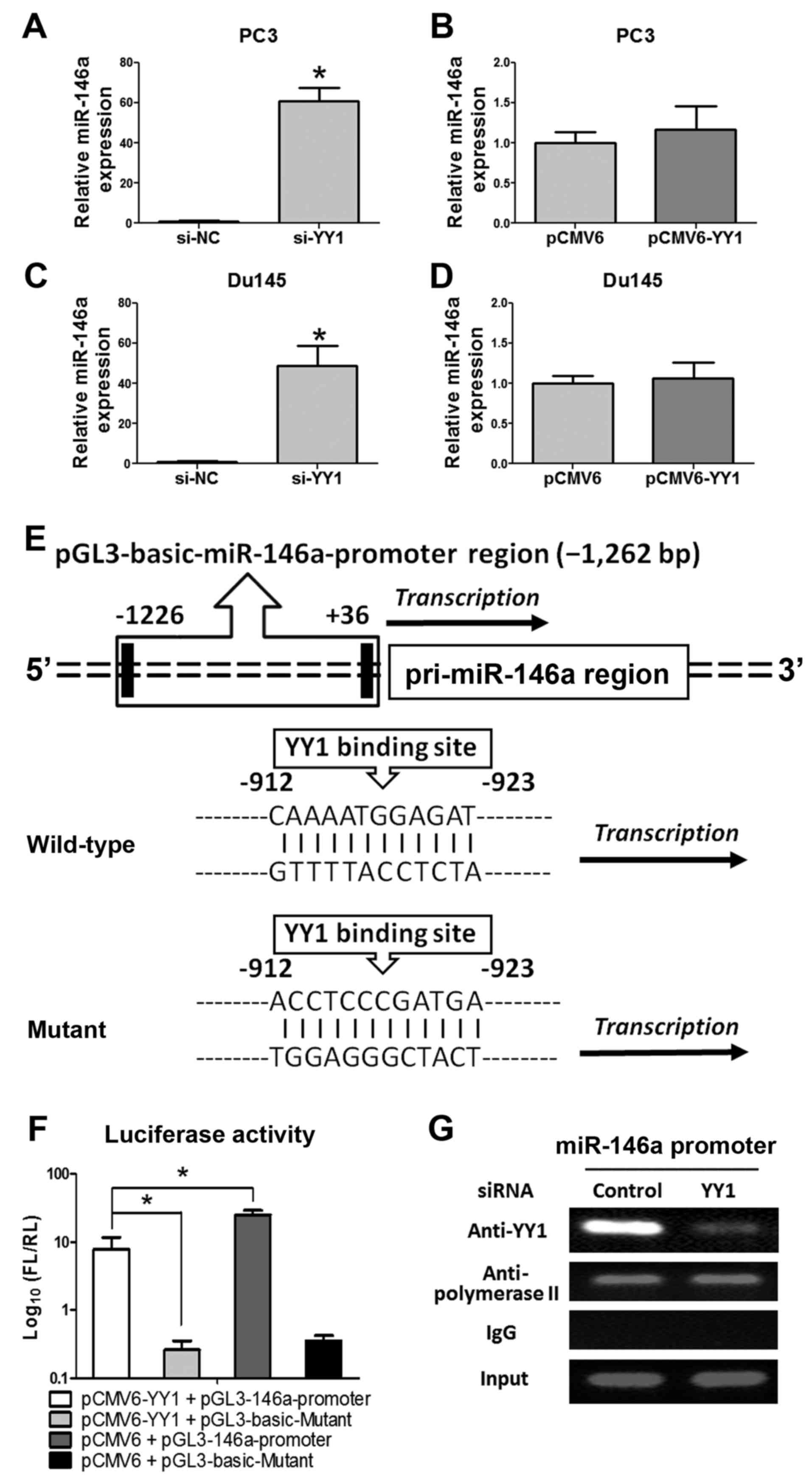
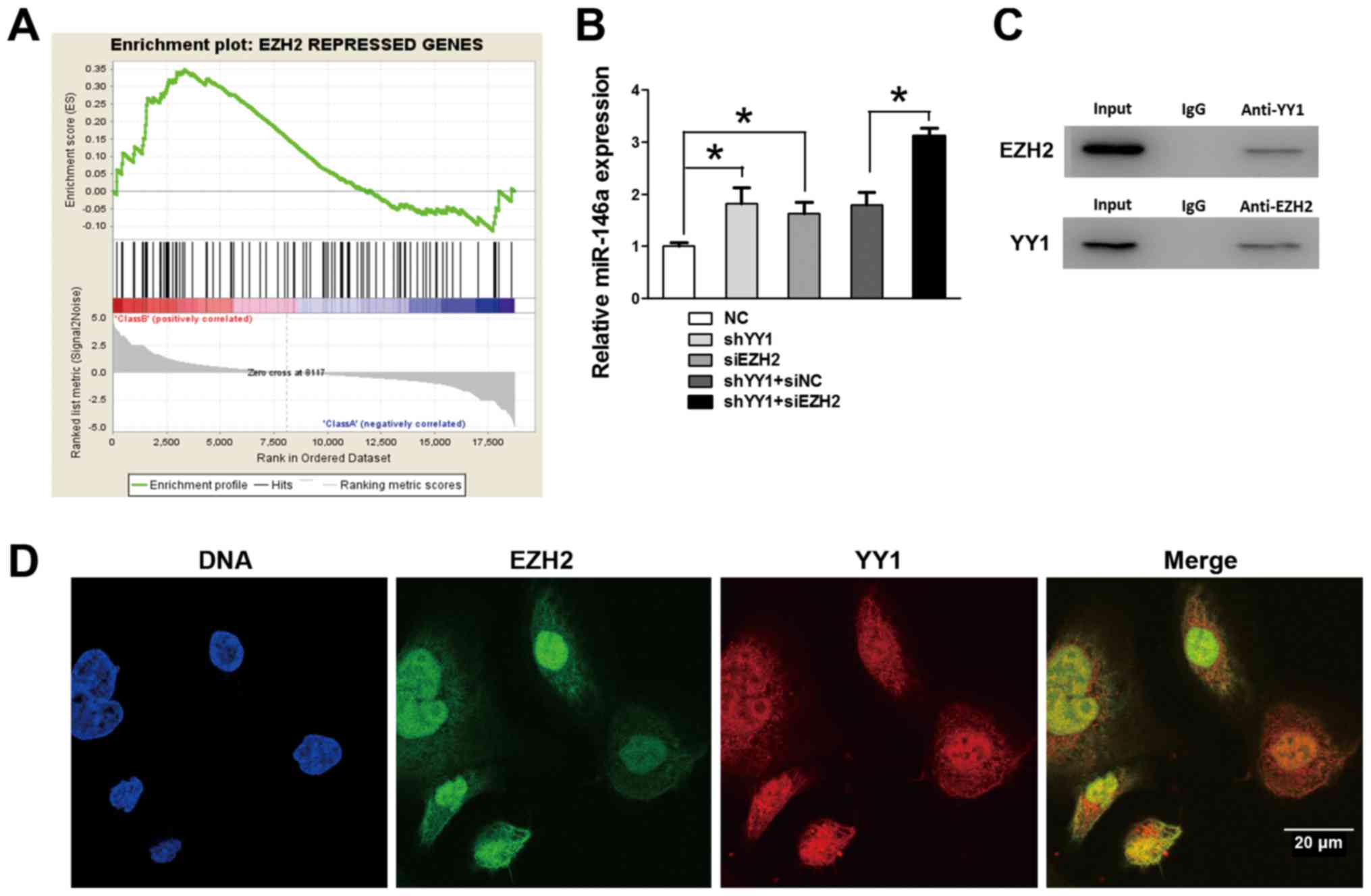
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 65:5–29. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Katzenwadel A and Wolf P: Androgen
deprivation of prostate cancer: Leading to a therapeutic dead end.
Cancer Lett. 367:12–17. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hua K, Jin J, Zhang H, Zhao B, Wu C, Xu H
and Fang L: MicroRNA-7 inhibits proliferation, migration and
invasion of thyroid papillary cancer cells via targeting CKS2. Int
J Oncol. 49:1531–1540. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Li J, Yang X, Guan H, Mizokami A, Keller
ET, Xu X, Liu X, Tan J, Hu L, Lu Y, et al: Exosome-derived
microRNAs contribute to prostate cancer chemoresistance. Int J
Oncol. 49:838–846. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Xu B, Wang N, Wang X, Tong N, Shao N, Tao
J, Li P, Niu X, Feng N, Zhang L, et al: MiR-146a suppresses tumor
growth and progression by targeting EGFR pathway and in a
p-ERK-dependent manner in castration-resistant prostate cancer.
Prostate. 72:1171–1178. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Sun Q, Zhao X, Liu X, Wang Y, Huang J,
Jiang B, Chen Q and Yu J: miR-146a functions as a tumor suppressor
in prostate cancer by targeting Rac1. Prostate. 74:1613–1621. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Xu B, Huang Y, Niu X, Tao T, Jiang L, Tong
N, Chen S, Liu N, Zhu W and Chen M: Hsa-miR-146a-5p modulates
androgen-independent prostate cancer cells apoptosis by targeting
ROCK1. Prostate. 75:1896–1903. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Liu R, Yi B, Wei S, Yang WH, Hart KM,
Chauhan P, Zhang W, Mao X, Liu X, Liu CG, et al:
FOXP3-miR-146-NF-κB axis and therapy for precancerous lesions in
prostate. Cancer Res. 75:1714–1724. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bhalla SS, Robitaille L and Nemer M:
Cooperative activation by GATA-4 and YY1 of the cardiac B-type
natriuretic peptide promoter. J Biol Chem. 276:11439–11445. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lee MY, Lu A and Gudas LJ: Transcriptional
regulation of Rex1 (zfp42) in normal prostate epithelial cells and
prostate cancer cells. J Cell Physiol. 224:17–27. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Luo J, Zhou X, Ge X, Liu P, Cao J, Lu X,
Ling Y and Zhang S: Upregulation of Ying Yang 1 (YY1) suppresses
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma development through heme
oxygenase-1. Cancer Sci. 104:1544–1551. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Xu B, Feng NH, Li PC, Tao J, Wu D, Zhang
ZD, Tong N, Wang JF, Song NH, Zhang W, et al: A functional
polymorphism in Pre-miR-146a gene is associated with prostate
cancer risk and mature miR-146a expression in vivo. Prostate.
70:467–472. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Tao T, Wang Y, Luo H, Yao L, Wang L, Wang
J, Yan W, Zhang J, Wang H, Shi Y, et al: Involvement of
FOS-mediated miR-181b/miR-21 signalling in the progression of
malignant gliomas. Eur J Cancer. 49:3055–3063. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Taganov KD, Boldin MP, Chang KJ and
Baltimore D: NF-kappaB-dependent induction of microRNA miR-146, an
inhibitor targeted to signaling proteins of innate immune
responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:12481–12486. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhang B, Wang LL, Ren RJ, Dammer EB, Zhang
YF, Huang Y, Chen SD and Wang G: MicroRNA-146a represses LRP2
translation and leads to cell apoptosis in Alzheimer's disease.
FEBS Lett. 590:2190–2200. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Tsang DP, Wu WK, Kang W, Lee YY, Wu F, Yu
Z, Xiong L, Chan AW, Tong JH, Yang W, et al: Yin Yang 1-mediated
epigenetic silencing of tumour-suppressive microRNAs activates
nuclear factor-κB in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Pathol.
238:651–664. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Seligson D, Horvath S, Huerta-Yepez S,
Hanna S, Garban H, Roberts A, Shi T, Liu X, Chia D, Goodglick L, et
al: Expression of transcription factor Yin Yang 1 in prostate
cancer. Int J Oncol. 27:131–141. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Deng Z, Cao P, Wan MM and Sui G: Yin Yang
1: A multifaceted protein beyond a transcription factor.
Transcription. 1:81–84. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Thorvaldsen JL, Weaver JR and Bartolomei
MS: A YY1 bridge for X inactivation. Cell. 146:11–13. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Caggia S, Libra M, Malaponte G and Cardile
V: Modulation of YY1 and p53 expression by transforming growth
factor-β3 in prostate cell lines. Cytokine. 56:403–410. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sankar N, Baluchamy S, Kadeppagari RK,
Singhal G, Weitzman S and Thimmapaya B: p300 provides a corepressor
function by cooperating with YY1 and HDAC3 to repress c-Myc.
Oncogene. 27:5717–5728. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Aldiri I and Vetter ML: PRC2 during
vertebrate organogenesis: A complex in transition. Dev Biol.
367:91–99. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Xiong X, Zhang J, Liang W, Cao W, Qin S,
Dai L, Ye D and Liu Z: Fuse-binding protein 1 is a target of the
EZH2 inhibitor GSK343, in osteosarcoma cells. Int J Oncol.
49:623–628. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Varambally S, Dhanasekaran SM, Zhou M,
Barrette TR, Kumar-Sinha C, Sanda MG, Ghosh D, Pienta KJ, Sewalt
RG, Otte AP, et al: The polycomb group protein EZH2 is involved in
progression of prostate cancer. Nature. 419:624–629. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Bracken AP, Pasini D, Capra M, Prosperini
E, Colli E and Helin K: EZH2 is downstream of the pRB-E2F pathway,
essential for proliferation and amplified in cancer. EMBO J.
22:5323–5335. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wen S, Tian J, Niu Y, Li L, Yeh S and
Chang C: ASC-J9(®), and not Casodex or Enzalutamide, suppresses
prostate cancer stem/progenitor cell invasion via altering the
EZH2-STAT3 signals. Cancer Lett. 376:377–386. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kleer CG, Cao Q, Varambally S, Shen R, Ota
I, Tomlins SA, Ghosh D, Sewalt RG, Otte AP, Hayes DF, et al: EZH2
is a marker of aggressive breast cancer and promotes neoplastic
transformation of breast epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
100:11606–11611. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Cao Q, Mani RS, Ateeq B, Dhanasekaran SM,
Asangani IA, Prensner JR, Kim JH, Brenner JC, Jing X, Cao X, et al:
Coordinated regulation of polycomb group complexes through
microRNAs in cancer. Cancer Cell. 20:187–199. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhou L, Wang L, Lu L, Jiang P, Sun H and
Wang H: A novel target of microRNA-29, Ring1 and YY1-binding
protein (Rybp), negatively regulates skeletal myogenesis. J Biol
Chem. 287:25255–25265. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Weng W, Wang M, Xie S, Long Y, Li F, Sun
F, Yu Y and Li Z: YY1-C/EBPα-miR34a regulatory circuitry is
involved in renal cell carcinoma progression. Oncol Rep.
31:1921–1927. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ren G, Zhang G, Dong Z, Liu Z, Li L, Feng
Y, Su D, Zhang Y, Huang B and Lu J: Recruitment of HDAC4 by
transcription factor YY1 represses HOXB13 to affect cell growth in
AR-negative prostate cancers. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
41:1094–1101. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Wang H, Garzon R, Sun H, Ladner KJ, Singh
R, Dahlman J, Cheng A, Hall BM, Qualman SJ, Chandler DS, et al:
NF-kappaB-YY1-miR-29 regulatory circuitry in skeletal myogenesis
and rhabdomyosarcoma. Cancer Cell. 14:369–381. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|