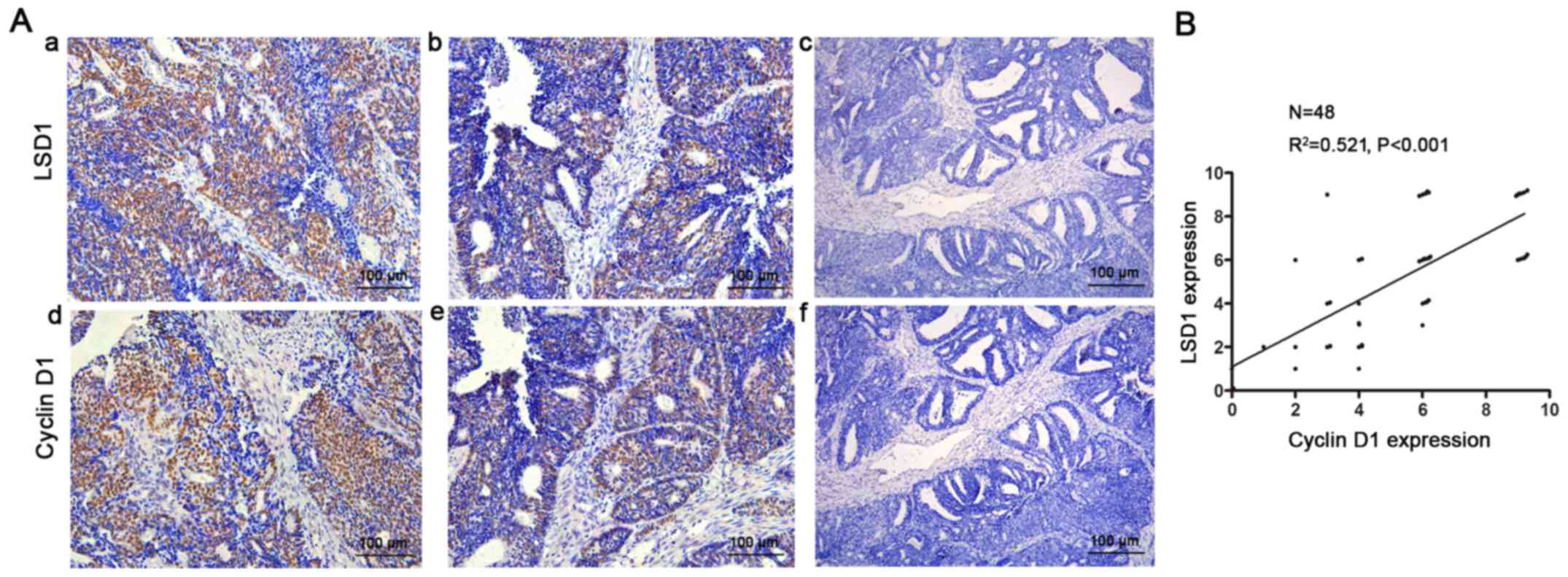
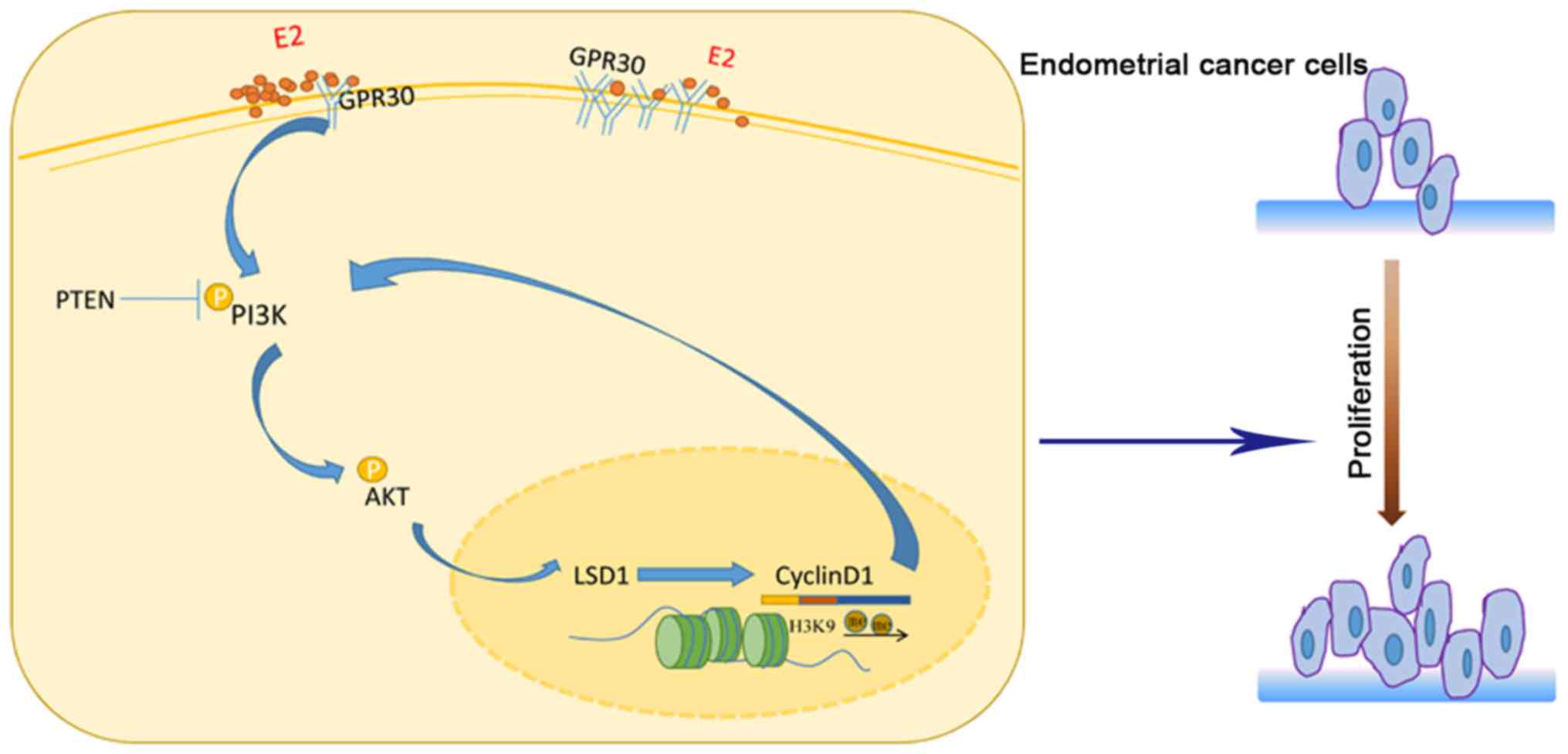
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:7–30. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Deligdisch L and Holinka CF: Endometrial
carcinoma: Two diseases? Cancer Detect Prev. 10:237–246.
1987.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Makker A and Goel MM: Tumor progression,
metastasis, and modulators of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in
endometrioid endometrial carcinoma: An update. Endocr Relat Cancer.
23:R85–R111. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Gibson WJ, Hoivik EA, Halle MK,
Taylor-Weiner A, Cherniack AD, Berg A, Holst F, Zack TI, Werner HM,
Staby KM, et al: The genomic landscape and evolution of endometrial
carcinoma progression and abdominopelvic metastasis. Nat Genet.
48:848–855. 2016. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Westin SN, Ju Z, Broaddus RR, Krakstad C,
Li J, Pal N, Lu KH, Coleman RL, Hennessy BT, Klempner SJ, et al:
PTEN loss is a context-dependent outcome determinant in obese and
non-obese endometrioid endometrial cancer patients. Mol Oncol.
9:1694–1703. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Slomovitz BM and Coleman RL: The
PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway as a therapeutic target in endometrial
cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 18:5856–5864. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Li Y, Jia Y, Che Q, Zhou Q, Wang K and Wan
XP: AMF/PGI-mediated tumorigenesis through MAPK-ERK signaling in
endometrial carcinoma. Oncotarget. 6:26373–26387. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wang Y, van der Zee M, Fodde R and Blok
LJ: Wnt/β-catenin and sex hormone signaling in endometrial
homeostasis and cancer. Oncotarget. 1:674–684. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Strahl BD and Allis CD: The language of
covalent histone modifications. Nature. 403:41–45. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Elsheikh SE, Green AR, Rakha EA, Powe DG,
Ahmed RA, Collins HM, Soria D, Garibaldi JM, Paish CE, Ammar AA, et
al: Global histone modifications in breast cancer correlate with
tumor phenotypes, prognostic factors, and patient outcome. Cancer
Res. 69:3802–3809. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Shi Y, Lan F, Matson C, Mulligan P,
Whetstine JR, Cole PA, Casero RA and Shi Y: Histone demethylation
mediated by the nuclear amine oxidase homolog LSD1. Cell.
119:941–953. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zuchegna C, Aceto F, Bertoni A, Romano A,
Perillo B, Laccetti P, Gottesman ME, Avvedimento EV and Porcellini
A: Mechanism of retinoic acid-induced transcription: Histone code,
DNA oxidation and formation of chromatin loops. Nucleic Acids Res.
42:11040–11055. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lim S, Janzer A, Becker A, Zimmer A,
Schüle R, Buettner R and Kirfel J: Lysine-specific demethylase 1
(LSD1) is highly expressed in ER-negative breast cancers and a
biomarker predicting aggressive biology. Carcinogenesis.
31:512–520. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Nagasawa S, Sedukhina AS, Nakagawa Y,
Maeda I, Kubota M, Ohnuma S, Tsugawa K, Ohta T, Roche-Molina M,
Bernal JA, et al: LSD1 overexpression is associated with poor
prognosis in basal-like breast cancer, and sensitivity to PARP
inhibition. PLoS One. 10:e01180022015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kashyap V, Ahmad S, Nilsson EM, Helczynski
L, Kenna S, Persson JL, Gudas LJ and Mongan NP: The lysine specific
demethylase-1 (LSD1/KDM1A) regulates VEGF-A expression in prostate
cancer. Mol Oncol. 7:555–566. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Qin Y, Zhu W, Xu W, Zhang B, Shi S, Ji S,
Liu J, Long J, Liu C, Liu L, et al: LSD1 sustains pancreatic cancer
growth via maintaining HIF1α-dependent glycolytic process. Cancer
Lett. 347:225–232. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chen C, Ge J, Lu Q, Ping G, Yang C and
Fang X: Expression of lysine-specific demethylase 1 in human
epithelial ovarian cancer. J Ovarian Res. 8:282015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mohammad HP, Smitheman KN, Kamat CD, Soong
D, Federowicz KE, Van Aller GS, Schneck JL, Carson JD, Liu Y,
Butticello M, et al: A DNA hypomethylation signature predicts
antitumor activity of LSD1 inhibitors in SCLC. Cancer Cell.
28:57–69. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Fiskus W, Sharma S, Shah B, Portier BP,
Devaraj SG, Liu K, Iyer SP, Bearss D and Bhalla KN: Highly
effective combination of LSD1 (KDM1A) antagonist and pan-histone
deacetylase inhibitor against human AML cells. Leukemia.
28:2155–2164. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Theisen ER, Gajiwala S, Bearss J, Sorna V,
Sharma S and Janat-Amsbury M: Reversible inhibition of lysine
specific demethylase 1 is a novel anti-tumor strategy for poorly
differentiated endometrial carcinoma. BMC Cancer. 14:7522014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Liu YD, Dai M, Yang SS, Xiao M, Meng FL
and Chen XW: Overexpression of lysine-specific demethylase 1 is
associated with tumor progression and unfavorable prognosis in
Chinese patients with endometrioid endometrial adenocarcinoma. Int
J Gynecol Cancer. 25:1453–1460. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Cai C, He HH, Gao S, Chen S, Yu Z, Gao Y,
Chen S, Chen MW, Zhang J, Ahmed M, et al: Lysine-specific
demethylase 1 has dual functions as a major regulator of androgen
receptor transcriptional activity. Cell Rep. 9:1618–1627. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bennesch MA, Segala G, Wider D and Picard
D: LSD1 engages a corepressor complex for the activation of the
estrogen receptor α by estrogen and cAMP. Nucleic Acids Res.
44:8655–8670. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Pollock JA, Larrea MD, Jasper JS,
McDonnell DP and McCafferty DG: Lysine-specific histone demethylase
1 inhibitors control breast cancer proliferation in ERα-dependent
and -independent manners. ACS Chem Biol. 7:1221–1231. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sun G, Alzayady K, Stewart R, Ye P, Yang
S, Li W and Shi Y: Histone demethylase LSD1 regulates neural stem
cell proliferation. Mol Cell Biol. 30:1997–2005. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yokoyama A, Takezawa S, Schüle R, Kitagawa
H and Kato S: Transrepressive function of TLX requires the histone
demethylase LSD1. Mol Cell Biol. 28:3995–4003. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chen J, Bai M, Ning C, Xie B, Zhang J,
Liao H, Xiong J, Tao X, Yan D, Xi X, et al: Gankyrin facilitates
follicle-stimulating hormone-driven ovarian cancer cell
proliferation through the PI3K/AKT/HIF-1α/cyclin D1 pathway.
Oncogene. 35:2506–2517. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Shao G, Wang J, Li Y, Liu X, Xie X, Wan X,
Yan M, Jin J, Lin Q, Zhu H, et al: Lysine-specific demethylase 1
mediates epidermal growth factor signaling to promote cell
migration in ovarian cancer cells. Sci Rep. 5:153442015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Liu Y, Zhang J, Qian W, Dong Y, Yang Y,
Liu Z, Feng Y, Ma D, Zhang Z and Wu S: Gankyrin is frequently
overexpressed in cervical high grade disease and is associated with
cervical carcinogenesis and metastasis. PLoS One. 9:e950432014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Jin X, Gossett DR, Wang S, Yang D, Cao Y,
Chen J, Guo R, Reynolds RK and Lin J: Inhibition of AKT survival
pathway by a small molecule inhibitor in human endometrial cancer
cells. Br J Cancer. 91:1808–1812. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chen Y, Jiang J, Zhao M, Luo X, Liang Z,
Zhen Y, Fu Q, Deng X, Lin X, Li L, et al: microRNA-374a suppresses
colon cancer progression by directly reducing CCND1 to inactivate
the PI3K/AKT pathway. Oncotarget. 7:41306–41319. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Torres-Padilla ME, Parfitt DE, Kouzarides
T and Zernicka-Goetz M: Histone arginine methylation regulates
pluripotency in the early mouse embryo. Nature. 445:214–218. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Prossnitz ER, Arterburn JB, Smith HO,
Oprea TI, Sklar LA and Hathaway HJ: Estrogen signaling through the
transmembrane G protein-coupled receptor GPR30. Annu Rev Physiol.
70:165–190. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ge X, Guo R, Qiao Y, Zhang Y, Lei J, Wang
X, Li L and Hu D: The G protein-coupled receptor GPR30 mediates the
nontranscriptional effect of estrogen on the activation of PI3K/Akt
pathway in endometrial cancer cells. Int J Gynecol Cancer.
23:52–59. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Wei Y, Zhang Z, Liao H, Wu L, Wu X, Zhou
D, Xi X, Zhu Y and Feng Y: Nuclear estrogen receptor-mediated Notch
signaling and GPR30-mediated PI3K/AKT signaling in the regulation
of endometrial cancer cell proliferation. Oncol Rep. 27:504–510.
2012.
|
|
36
|
Zhang J, Yang Y, Zhang Z, He Y, Liu Z, Yu
Y, Wu S, Cai B and Feng Y: Gankyrin plays an essential role in
estrogen-driven and GPR30-mediated endometrial carcinoma cell
proliferation via the PTEN/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Cancer Lett.
339:279–287. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Wang Y, Zhu Y, Wang Q, Hu H, Li Z, Wang D,
Zhang W, Qi B, Ye J, Wu H, et al: The histone demethylase LSD1 is a
novel oncogene and therapeutic target in oral cancer. Cancer Lett.
374:12–21. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Thambyrajah R, Mazan M, Patel R, Moignard
V, Stefanska M, Marinopoulou E, Li Y, Lancrin C, Clapes T, Möröy T,
et al: GFI1 proteins orchestrate the emergence of haematopoietic
stem cells through recruitment of LSD1. Nat Cell Biol. 18:21–32.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Lin Y, Kang T and Zhou BP: Doxorubicin
enhances Snail/LSD1-mediated PTEN suppression in a PARP1-dependent
manner. Cell Cycle. 13:1708–1716. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Hecht JL and Mutter GL: Molecular and
pathologic aspects of endometrial carcinogenesis. J Clin Oncol.
24:4783–4791. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Ono H, Katagiri H, Funaki M, Anai M,
Inukai K, Fukushima Y, Sakoda H, Ogihara T, Onishi Y, Fujishiro M,
et al: Regulation of phosphoinositide metabolism, Akt
phosphorylation, and glucose transport by PTEN (phosphatase and
tensin homolog deleted on chromosome 10) in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Mol
Endocrinol. 15:1411–1422. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Yang CH, Almomen A, Wee YS, Jarboe EA,
Peterson CM and Janát-Amsbury MM: An estrogen-induced endometrial
hyperplasia mouse model recapitulating human disease progression
and genetic aberrations. Cancer Med. 4:1039–1050. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Seiler R, Thalmann GN, Rotzer D, Perren A
and Fleischmann A: CCND1/CyclinD1 status in metastasizing bladder
cancer: a prognosticator and predictor of chemotherapeutic
response. Modern Pathol. 27:87–95. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Dreyer JH, Hauck F, Barros MH and
Niedobitek G: pRb and cyclinD1 complement p16 as
immunohistochemical surrogate markers of HPV infection in head and
neck cancer. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. Dec 9–2015.Epub
ahead of print. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Umekita Y, Ohi Y, Sagara Y and Yoshida H:
Overexpression of cyclinD1 predicts for poor prognosis in estrogen
receptor-negative breast cancer patients. Int J Cancer. 98:415–418.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Zhong Z, Yeow WS, Zou C, Wassell R, Wang
C, Pestell RG, Quong JN and Quong AA: Cyclin D1/cyclin-dependent
kinase 4 interacts with filamin A and affects the migration and
invasion potential of breast cancer cells. Cancer Res.
70:2105–2114. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Sun X, Tang SC, Xu C, Wang C, Qin S, Du N,
Liu J, Zhang Y, Li X, Luo G, et al: DICER1 regulated let-7
expression levels in p53-induced cancer repression requires cyclin
D1. J Cell Mol Med. 19:1357–1365. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Maiques-Diaz A and Somervaille TC: LSD1:
Biologic roles and therapeutic targeting. Epigenomics. 8:1103–1116.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|