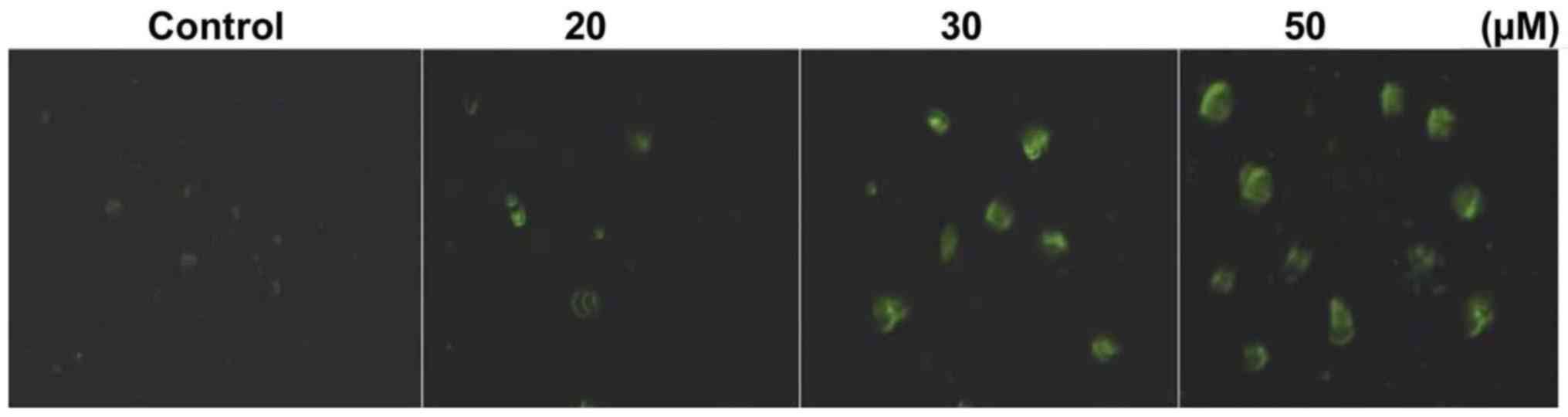
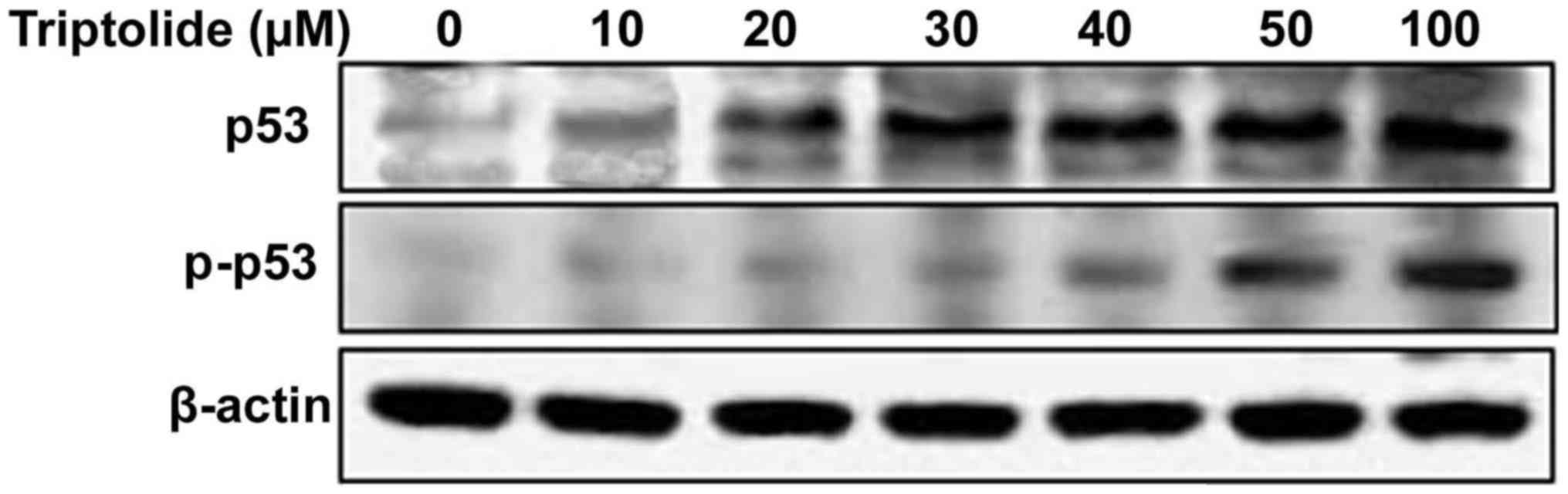
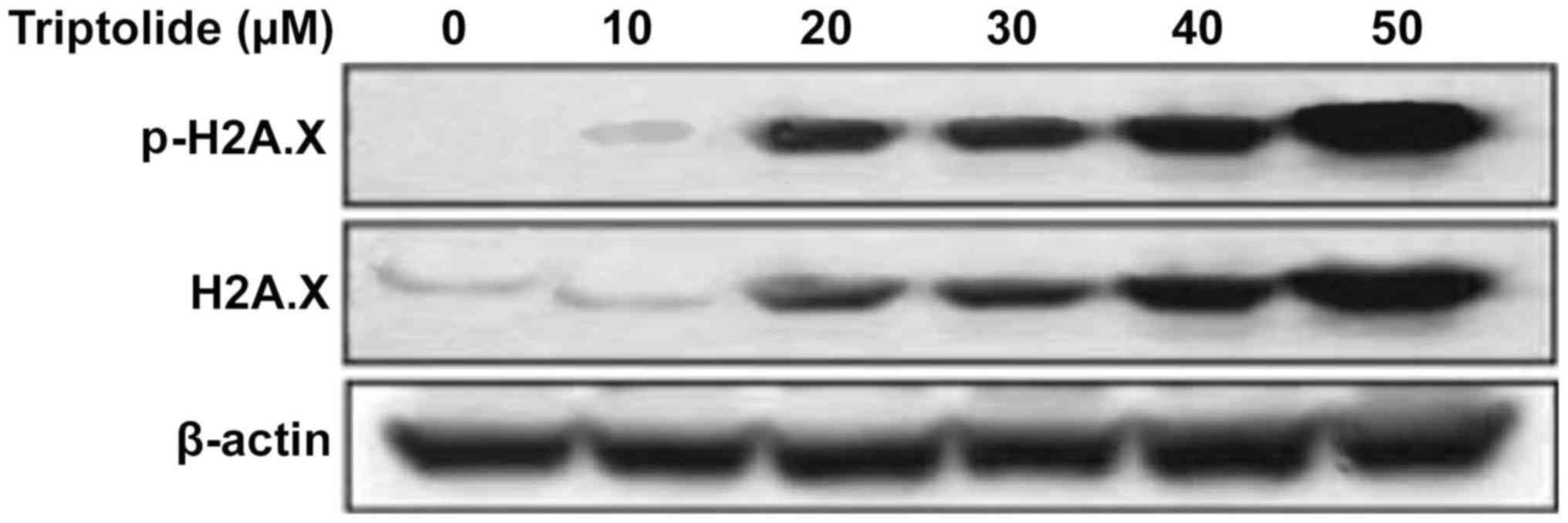
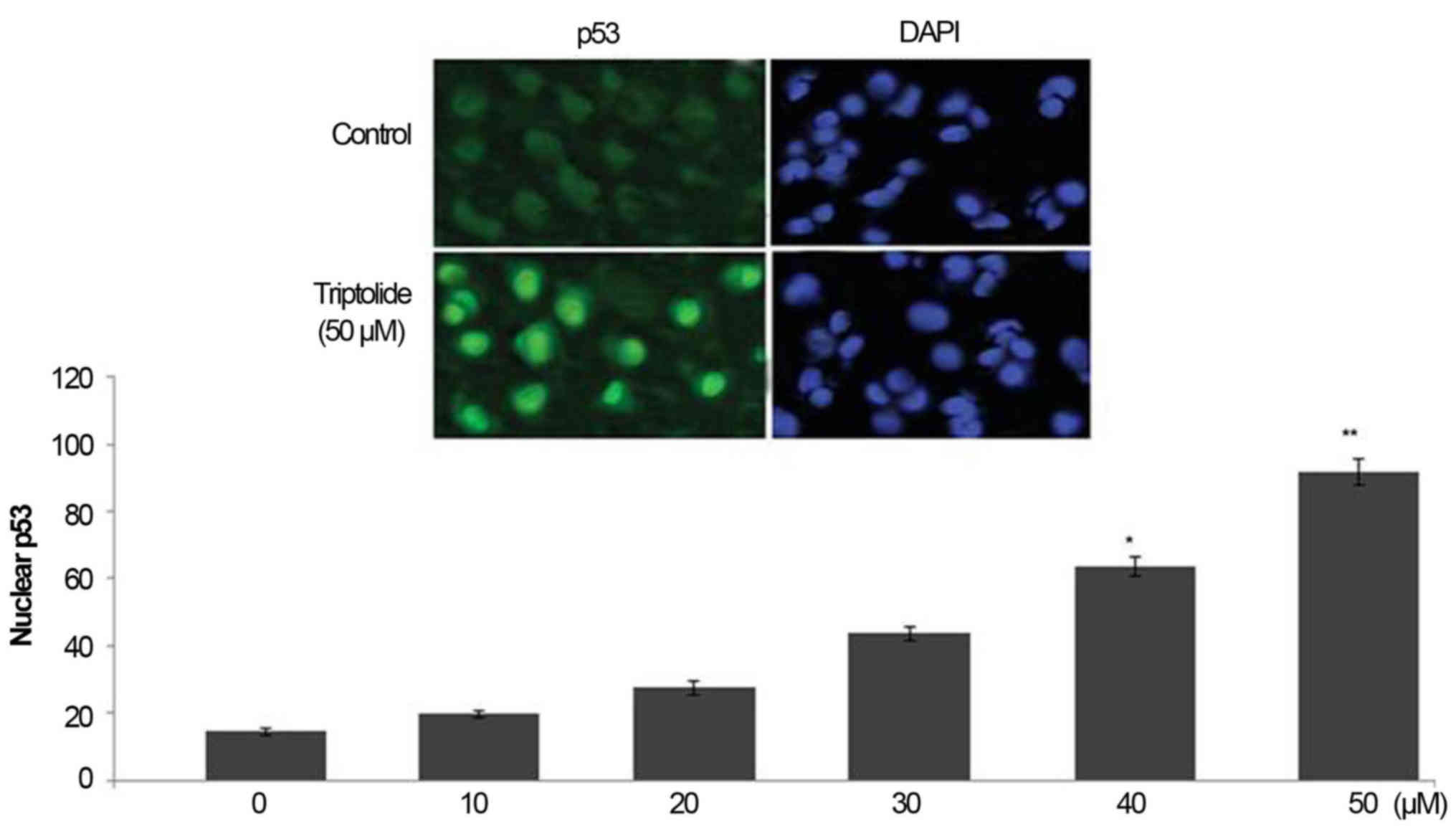
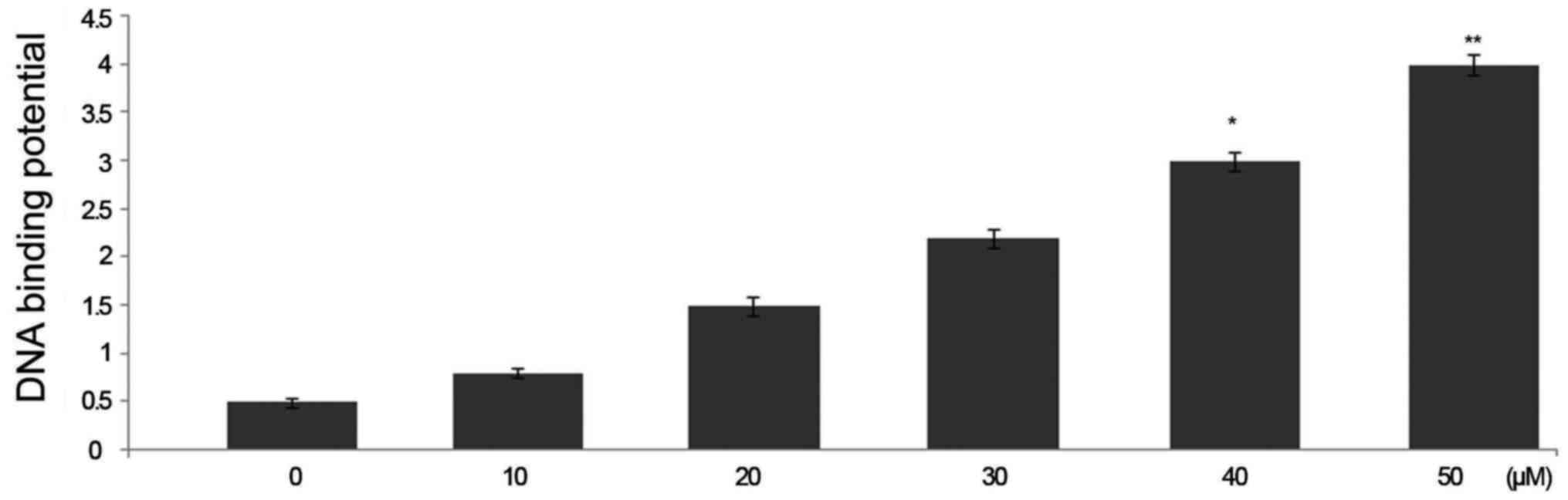
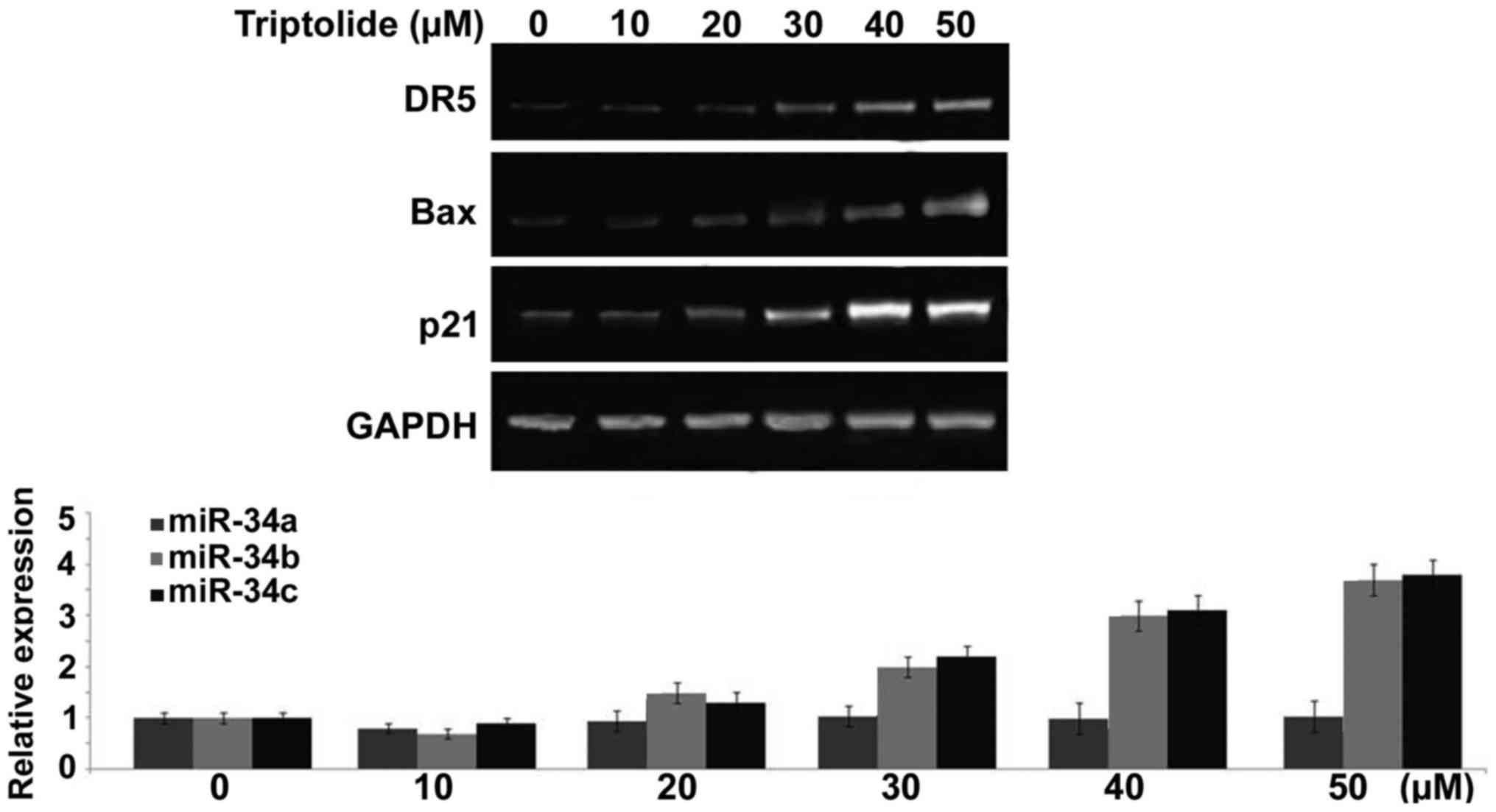
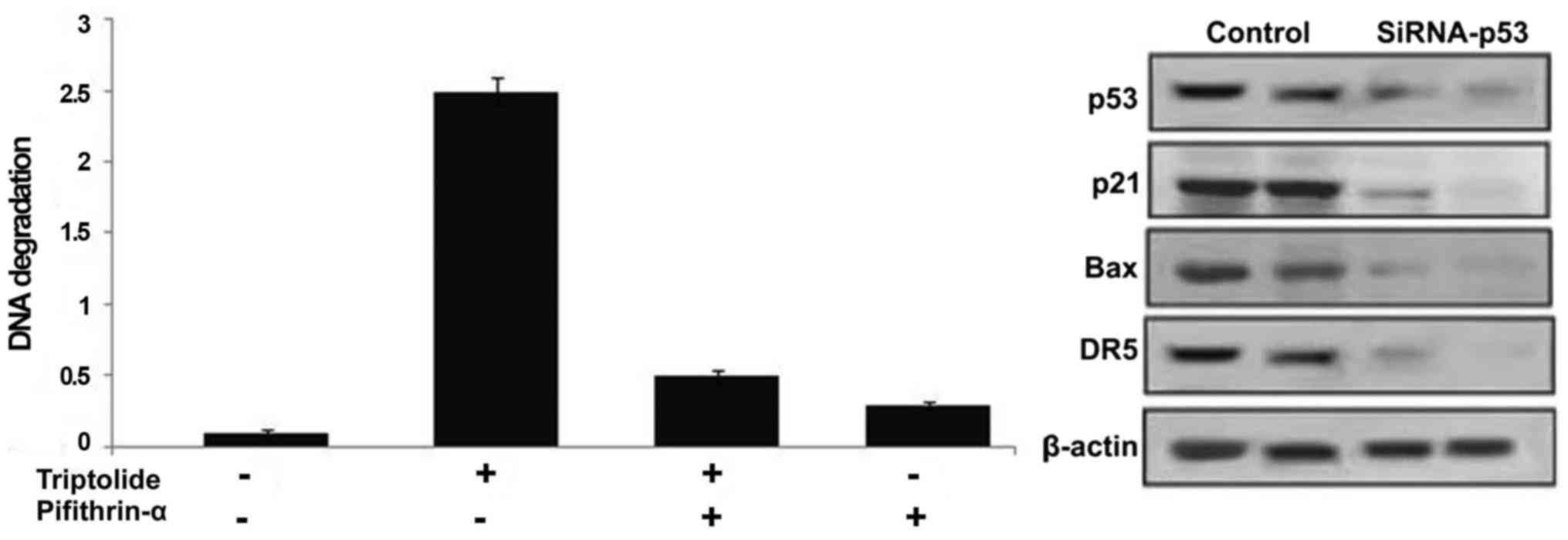
|
1
|
Zhen QS, Ye X and Wei ZJ: Recent progress
in research on Tripterygium: A male antifertility plant.
Contraception. 51:121–129. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Tengchaisri T, Chawengkirttikul R,
Rachaphaew N, Reutrakul V, Sangsuwan R and Sirisinha S: Antitumor
activity of triptolide against cholangiocarcinoma growth in vitro
and in hamsters. Cancer Lett. 133:169–175. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Hachida M, Lu H, Zhang X, Saito S,
Furutani Y, Matsuoka R, Hoshi H and Koyanagi H: Inhibitory effect
of triptolide on platelet derived growth factor-A and coronary
arteriosclerosis after heart transplantation. Transplant Proc.
31:2719–2723. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Carter BZ, Mak DH, Schober WD, McQueen T,
Harris D, Estrov Z, Evans RL and Andreeff M: Triptolide induces
caspase-dependent cell death mediated via the mitochondrial pathway
in leukemic cells. Blood. 108:630–637. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Cohen JJ: Apoptosis. Immunol Today.
14:126–130. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
White E: Life, death, and the pursuit of
apoptosis. Genes Dev. 10:1–15. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Williams GT and Smith CA: Molecular
regulation of apoptosis: Genetic controls on cell death. Cell.
74:777–779. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wyllie AH, Kerr JF and Currie AR: Cell
death: The significance of apoptosis. Int Rev Cytol. 68:251–306.
1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ma S, Chan KW and Guan XY: In search of
liver cancer stem cells. Stem Cell Rev. 4:179–192. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Tomuleasa C, Soritau O, Rus-Ciuca D, Pop
T, Todea D, Mosteanu O, Pintea B, Foris V, Susman S, Kacso G, et
al: Isolation and characterization of hepatic cancer cells with
stem-like properties from hepatocellular carcinoma. J
Gastrointestin Liver Dis. 19:61–67. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ricci-Vitiani L, Lombardi DG, Pilozzi E,
Biffoni M, Todaro M, Peschle C and De Maria R: Identification and
expansion of human colon-cancer-initiating cells. Nature.
445:111–115. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Lee TK, Castilho A, Ma S and Ng IO: Liver
cancer stem cells: Implications for a new therapeutic target. Liver
Int. 29:955–965. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Vogelstein B, Lane D and Levine AJ:
Surfing the p53 network. Nature. 408:307–310. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ma L, Wagner J, Rice JJ, Hu W, Levine AJ
and Stolovitzky GA: A plausible model for the digital response of
p53 to DNA damage. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 102:14266–14271. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Harris SL and Levine AJ: The p53 pathway:
Positive and negative feedback loops. Oncogene. 24:2899–2908. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Levine AJ: p53, the cellular gatekeeper
for growth and division. Cell. 88:323–331. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bean LJ and Stark GR: Phosphorylation of
serines 15 and 37 is necessary for efficient accumulation of p53
following irradiation with UV. Oncogene. 20:1076–1084. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
She QB, Chen N and Dong Z: ERKs and p38
kinase phosphorylate p53 protein at serine 15 in response to UV
radiation. J Biol Chem. 275:20444–20449. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Vazquez A, Bond EE, Levine AJ and Bond GL:
The genetics of the p53 pathway, apoptosis and cancer therapy. Nat
Rev Drug Discov. 7:979–987. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yin Y, Terauchi Y, Solomon GG, Aizawa S,
Rangarajan PN, Yazaki Y, Kadowaki T and Barrett JC: Involvement of
p85 in p53-dependent apoptotic response to oxidative stress.
Nature. 391:707–710. 1998. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lowe SW, Ruley HE, Jacks T and Housman DE:
p53-dependent apoptosis modulates the cytotoxicity of anticancer
agents. Cell. 74:957–967. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Brugarolas J, Chandrasekaran C, Gordon JI,
Beach D, Jacks T and Hannon GJ: Radiation-induced cell cycle arrest
compromised by p21 deficiency. Nature. 377:552–557. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Miyashita T and Reed JC: Tumor suppressor
p53 is a direct transcriptional activator of the human bax gene.
Cell. 80:293–299. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Oda E, Ohki R, Murasawa H, Nemoto J,
Shibue T, Yamashita T, Tokino T, Taniguchi T and Tanaka N: Noxa, a
BH3-only member of the Bcl-2 family and candidate mediator of
p53-induced apoptosis. Science. 288:1053–1058. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yu J, Zhang L, Hwang PM, Kinzler KW and
Vogelstein B: PUMA induces the rapid apoptosis of colorectal cancer
cells. Mol Cell. 7:673–682. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Shieh SY, Ikeda M, Taya Y and Prives C:
DNA damage-induced phosphorylation of p53 alleviates inhibition by
MDM2. Cell. 91:325–334. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Prives C: Signaling to p53: Breaking the
MDM2-p53 circuit. Cell. 95:5–8. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Brew CT, Aronchik I, Hsu JC, Sheen JH,
Dickson RB, Bjeldanes LF and Firestone GL: Indole-3-carbinol
activates the ATM signaling pathway independent of DNA damage to
stabilize p53 and induce G1 arrest of human mammary epithelial
cells. Int J Cancer. 118:857–868. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Loehberg CR, Thompson T, Kastan MB,
Maclean KH, Edwards DG, Kittrell FS, Medina D, Conneely OM and
O'Malley BW: Ataxia telangiectasia-mutated and p53 are potential
mediators of chloroquine-induced resistance to mammary
carcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 67:12026–12033. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Jiang C, Hu H, Malewicz B, Wang Z and Lü
J: Selenite-induced p53 Ser-15 phosphorylation and caspase-mediated
apoptosis in LNCaP human prostate cancer cells. Mol Cancer Ther.
3:877–884. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhao R, Xiang N, Domann FE and Zhong W:
Expression of p53 enhances selenite-induced superoxide production
and apoptosis in human prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res.
66:2296–2304. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chang TC, Wentzel EA, Kent OA,
Ramachandran K, Mullendore M, Lee KH, Feldmann G, Yamakuchi M,
Ferlito M, Lowenstein CJ, et al: Transactivation of miR-34a by p53
broadly influences gene expression and promotes apoptosis. Mol
Cell. 26:745–752. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|