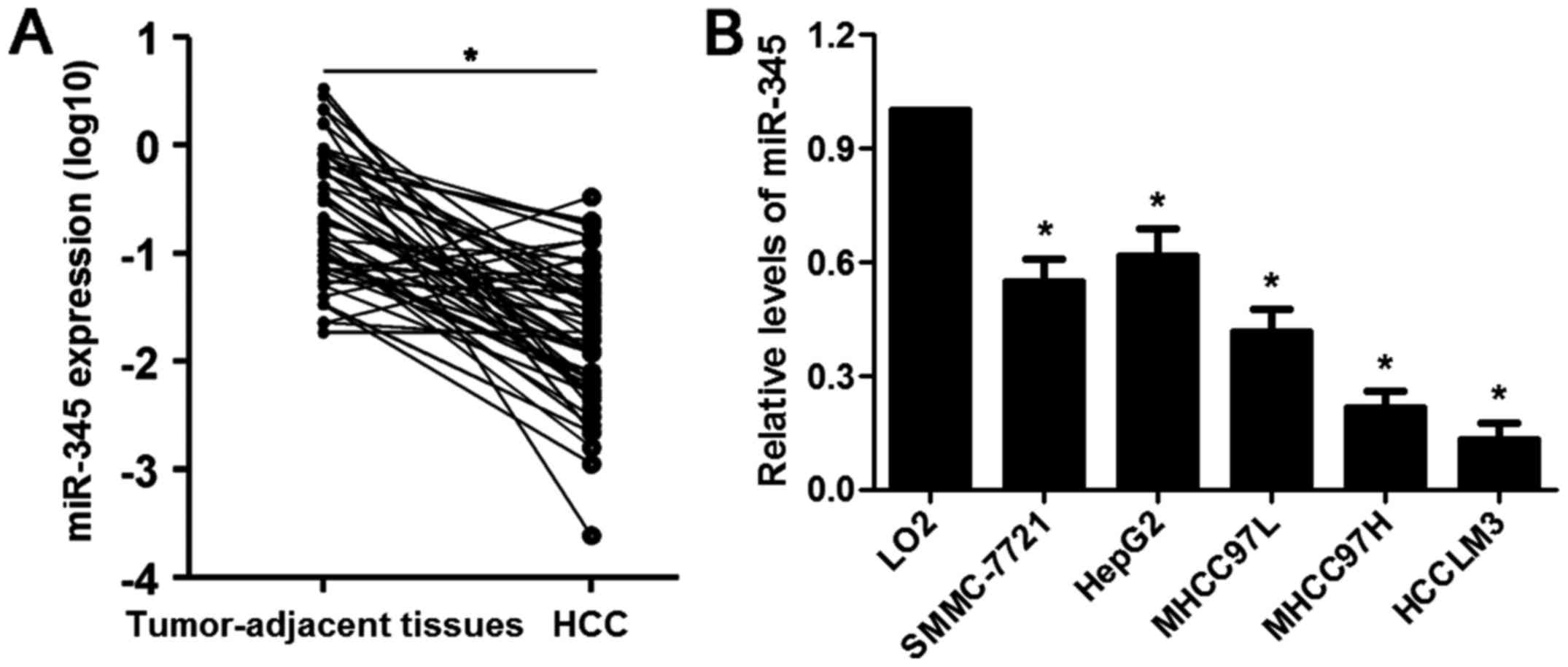
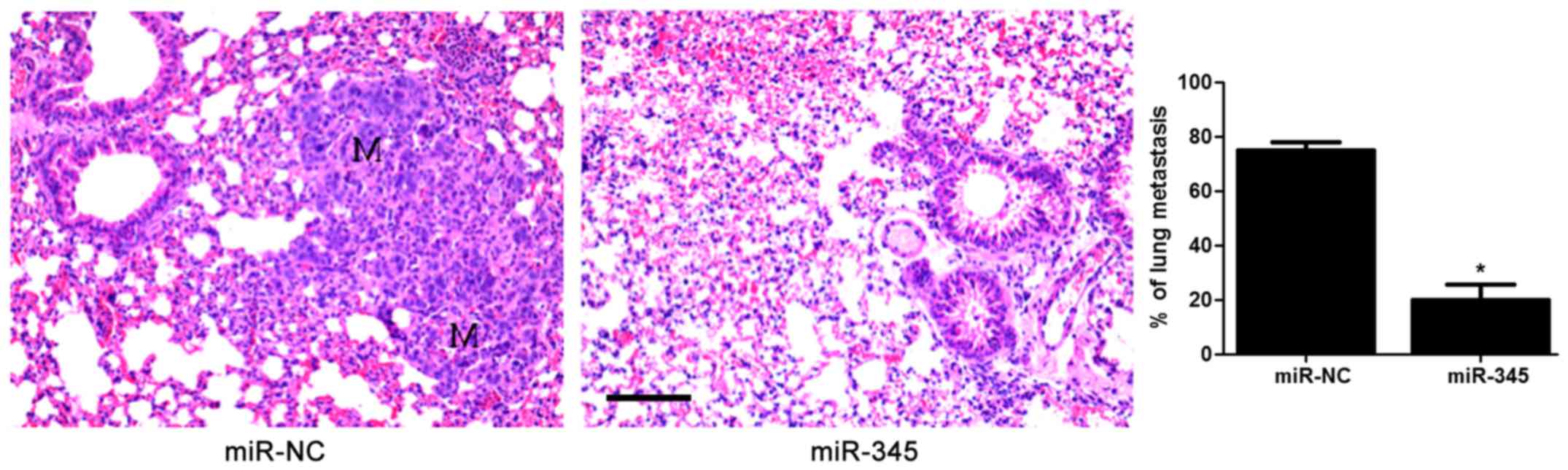
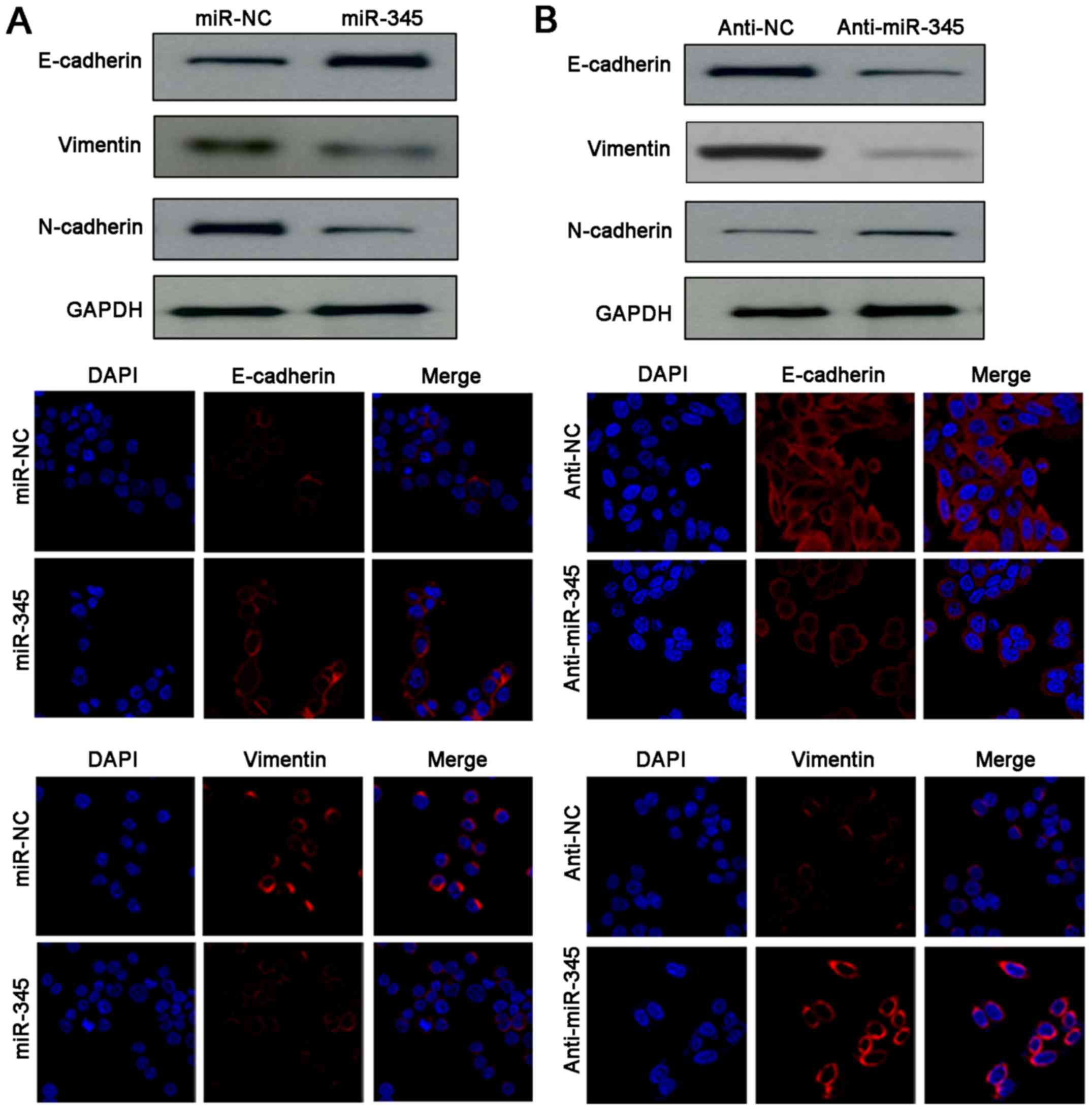
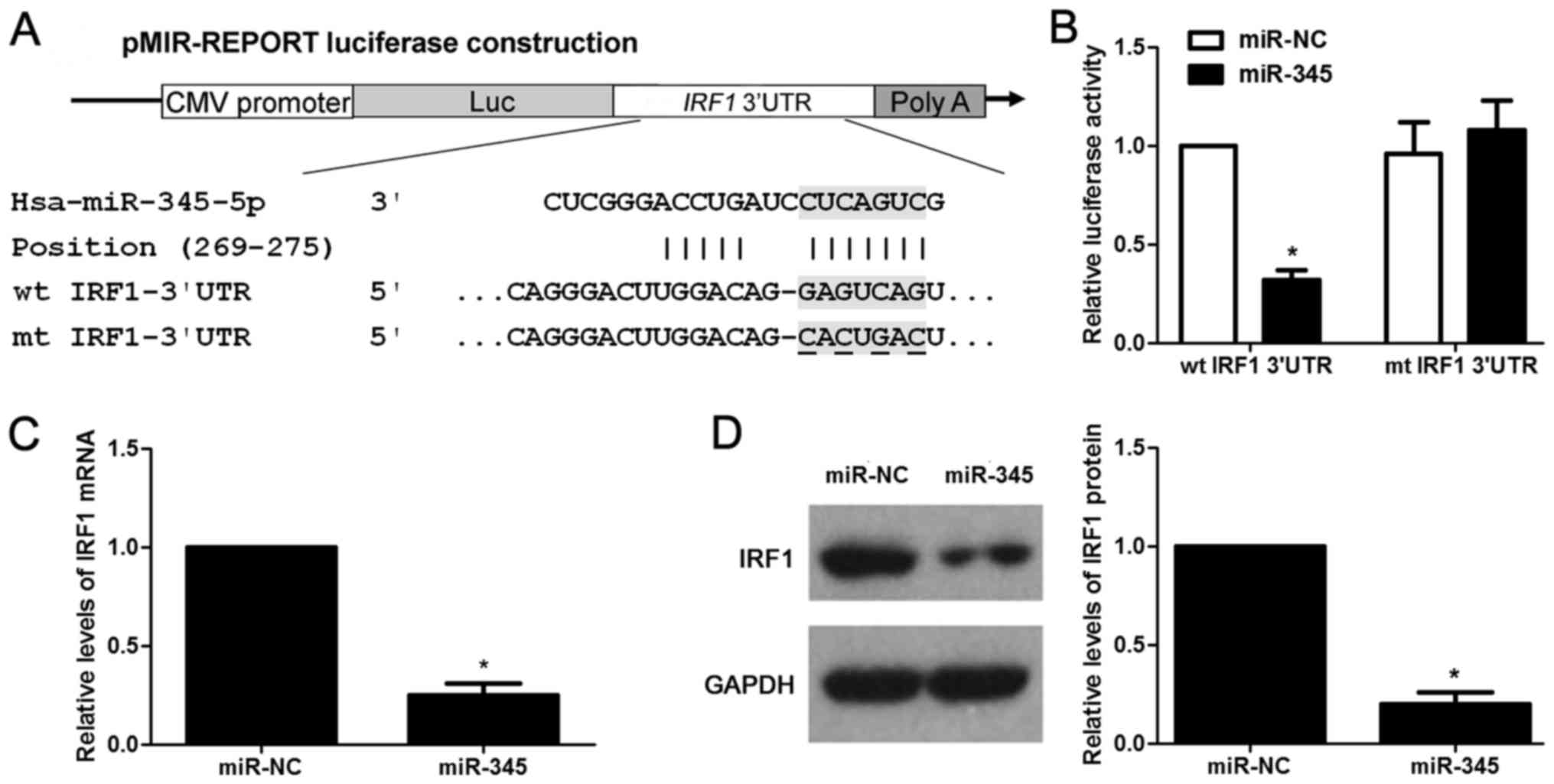
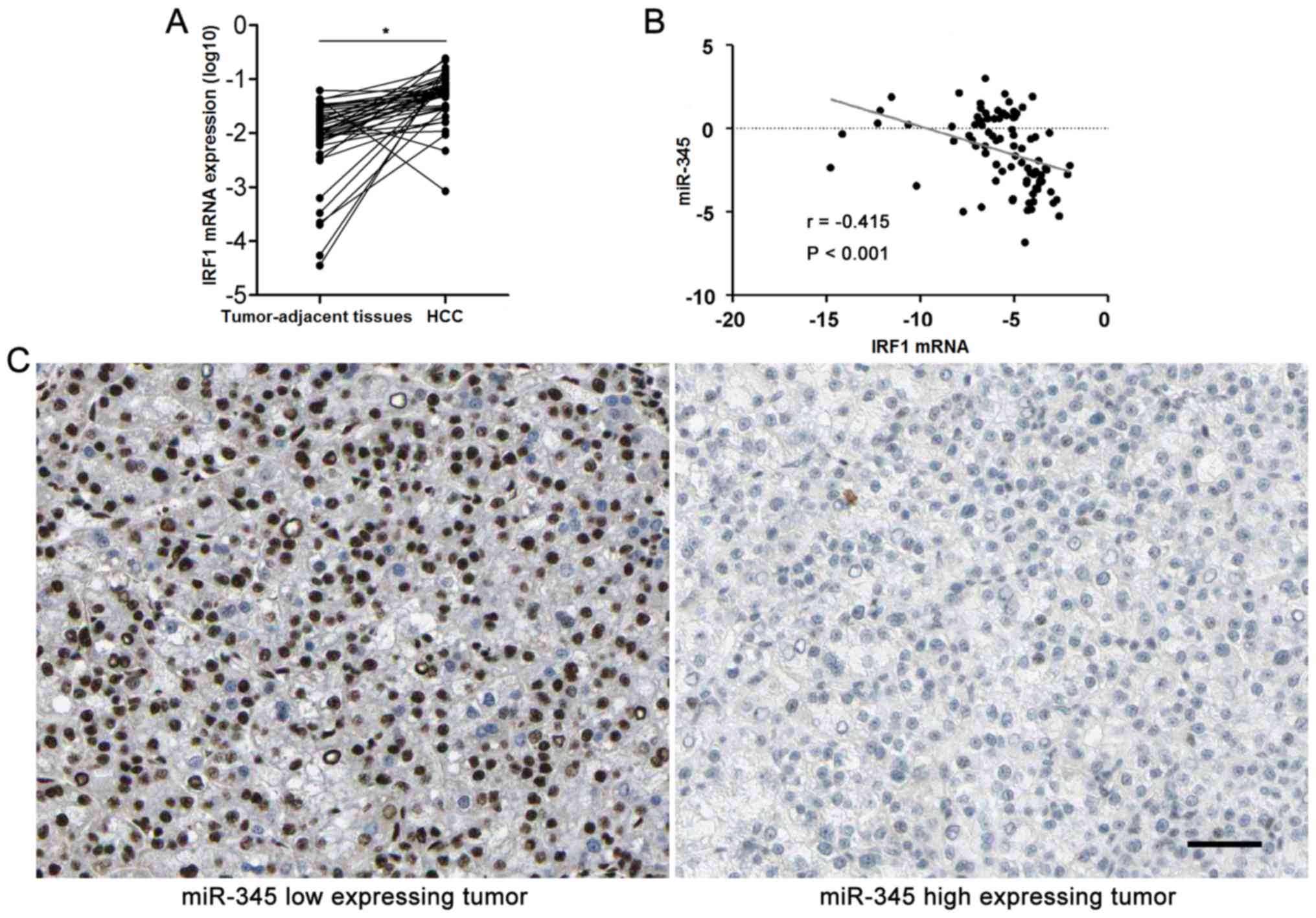
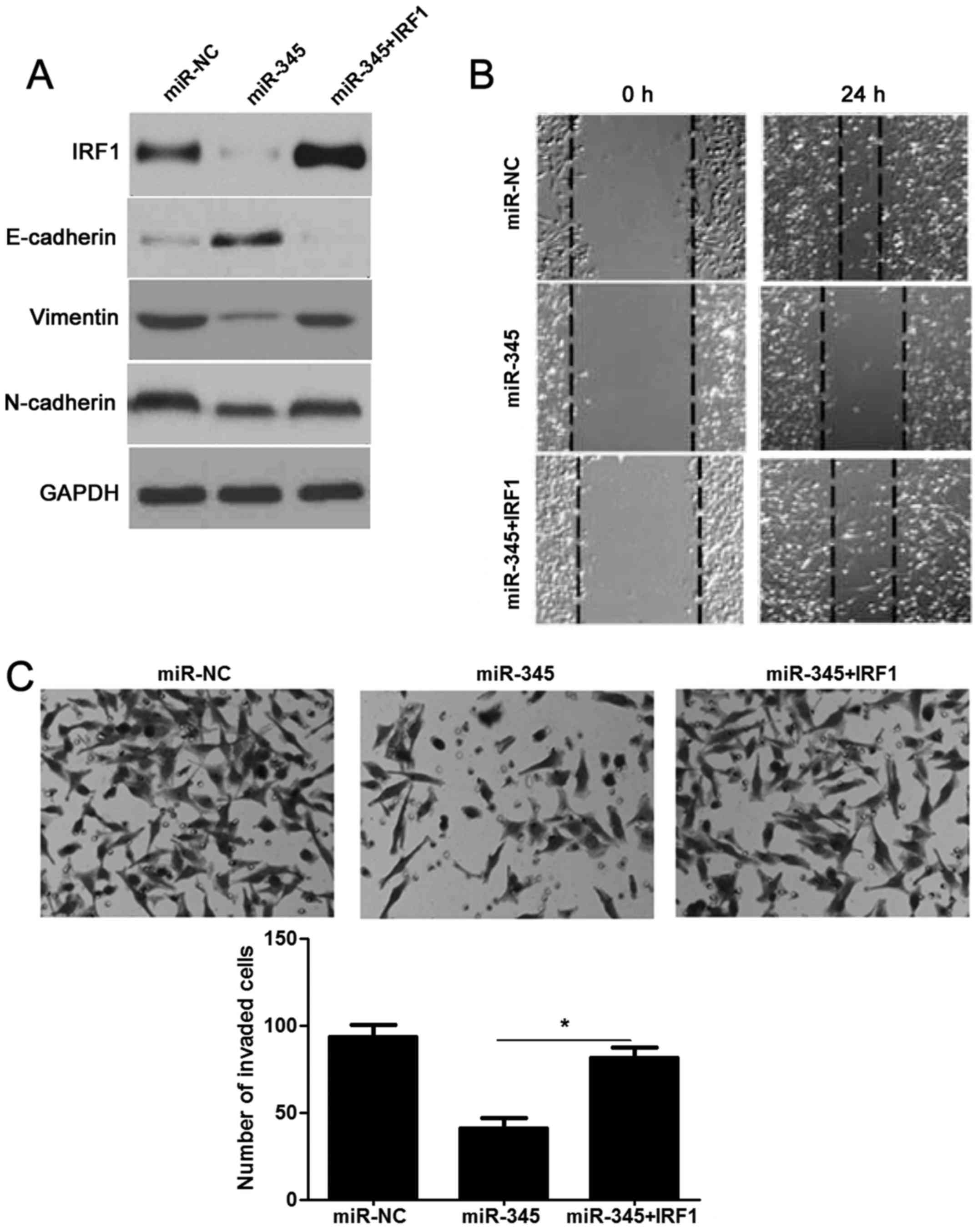
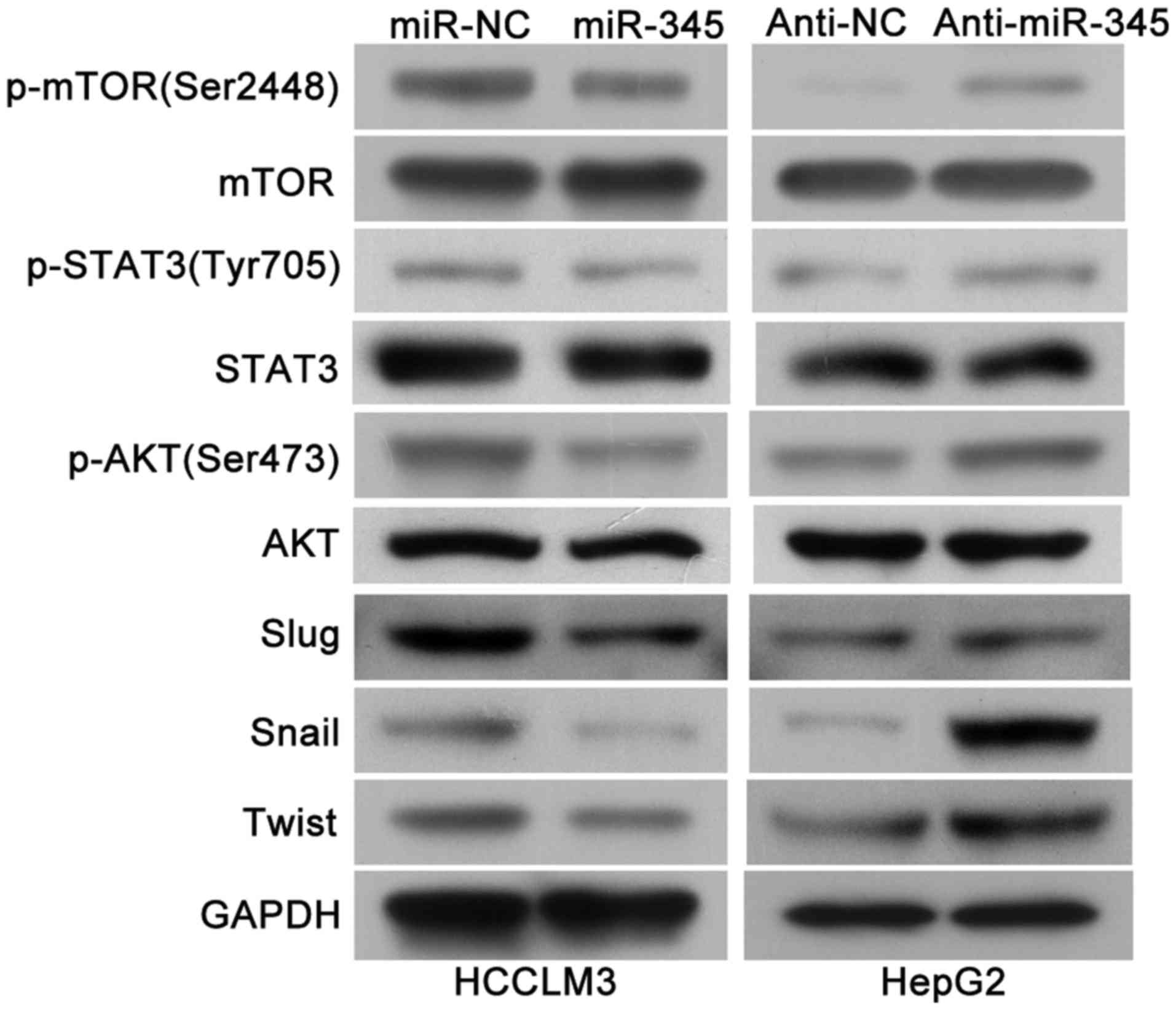
|
1
|
Forner A, Llovet JM and Bruix J:
Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 379:1245–1255. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bruix J and Sherman M; American
Association for the Study of Liver Diseases: Management of
hepatocellular carcinoma: An update. Hepatology. 53:1020–1022.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Calin GA and Croce CM: MicroRNA signatures
in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:857–866. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Garzon R, Calin GA and Croce CM: MicroRNAs
in cancer. Annu Rev Med. 60:167–179. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Guled M, Lahti L, Lindholm PM, Salmenkivi
K, Bagwan I, Nicholson AG and Knuutila S: CDKN2A, NF2, and JUN are
dysregulated among other genes by miRNAs in malignant mesothelioma
- A miRNA microarray analysis. Genes Chromosomes Cancer.
48:615–623. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cervigne NK, Reis PP, Machado J, Sadikovic
B, Bradley G, Galloni NN, Pintilie M, Jurisica I, Perez-Ordonez B,
Gilbert R, et al: Identification of a microRNA signature associated
with progression of leukoplakia to oral carcinoma. Hum Mol Genet.
18:4818–4829. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Pogribny IP, Filkowski JN, Tryndyak VP,
Golubov A, Shpyleva SI and Kovalchuk O: Alterations of microRNAs
and their targets are associated with acquired resistance of MCF-7
breast cancer cells to cisplatin. Int J Cancer. 127:1785–1794.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tang JT, Wang JL, Du W, Hong J, Zhao SL,
Wang YC, Xiong H, Chen HM and Fang JY: MicroRNA 345, a
methylation-sensitive microRNA is involved in cell proliferation
and invasion in human colorectal cancer. Carcinogenesis.
32:1207–1215. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Schou JV, Rossi S, Jensen BV, Nielsen DL,
Pfeiffer P, Høgdall E, Yilmaz M, Tejpar S, Delorenzi M, Kruhøffer
M, et al: miR-345 in metastatic colorectal cancer: A non-invasive
biomarker for clinical outcome in non-KRAS mutant patients treated
with 3rd line cetuximab and irinotecan. PLoS One. 9:e998862014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chen L, Li X and Chen X: Prognostic
significance of tissue miR-345 downregulation in non-small cell
lung cancer. Int J Clin Exp Med. 8:20971–20976. 2015.
|
|
11
|
Srivastava SK, Bhardwaj A, Arora S, Tyagi
N, Singh S, Andrews J, McClellan S, Wang B and Singh AP:
MicroRNA-345 induces apoptosis in pancreatic cancer cells through
potentiation of caspase-dependent and -independent pathways. Br J
Cancer. 113:660–668. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chen QG, Zhou W, Han T, Du SQ, Li ZH,
Zhang Z, Shan GY and Kong CZ: MiR-345 suppresses proliferation,
migration and invasion by targeting Smad1 in human prostate cancer.
J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 142:213–224. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Shiu TY, Huang SM, Shih YL, Chu HC, Chang
WK and Hsieh TY: Hepatitis C virus core protein down-regulates
p21(Waf1/Cip1) and inhibits curcumin-induced apoptosis through
microRNA-345 targeting in human hepatoma cells. PLoS One.
8:e610892013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jiang J, Gusev Y, Aderca I, Mettler TA,
Nagorney DM, Brackett DJ, Roberts LR and Schmittgen TD: Association
of MicroRNA expression in hepatocellular carcinomas with hepatitis
infection, cirrhosis, and patient survival. Clin Cancer Res.
14:419–427. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lin YH, Wu MH, Liao CJ, Huang YH, Chi HC,
Wu SM, Chen CY, Tseng YH, Tsai CY, Chung IH, et al: Repression of
microRNA-130b by thyroid hormone enhances cell motility. J Hepatol.
62:1328–1340. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhu Z, Zhang X, Wang G and Zheng H: Role
of MicroRNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepat Mon. 14:e186722014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yao Y, Suo AL, Li ZF, Liu LY, Tian T, Ni
L, Zhang WG, Nan KJ, Song TS and Huang C: MicroRNA profiling of
human gastric cancer. Mol Med Rep. 2:963–970. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Jansson MD and Lund AH: MicroRNA and
cancer. Mol Oncol. 6:590–610. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kröger A, Ortmann D, Krohne TU, Mohr L,
Blum HE, Hauser H and Geissler M: Growth suppression of the
hepatocellular carcinoma cell line Hepa1-6 by an activatable
interferon regulatory factor-1 in mice. Cancer Res. 61:2609–2617.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Li P, Du Q, Cao Z, Guo Z, Evankovich J,
Yan W, Chang Y, Shao L, Stolz DB, Tsung A, et al: Interferon-γ
induces autophagy with growth inhibition and cell death in human
hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells through interferon-regulatory
factor-1 (IRF-1). Cancer Lett. 314:213–222. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Moriyama Y, Nishiguchi S, Tamori A, Koh N,
Yano Y, Kubo S, Hirohashi K and Otani S: Tumor-suppressor effect of
interferon regulatory factor-1 in human hepatocellular carcinoma.
Clin Cancer Res. 7:1293–1298. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tanaka M, Katayama F, Kato H, Tanaka H,
Wang J, Qiao YL and Inoue M: Hepatitis B and C virus infection and
hepatocellular carcinoma in China: A review of epidemiology and
control measures. J Epidemiol. 21:401–416. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|