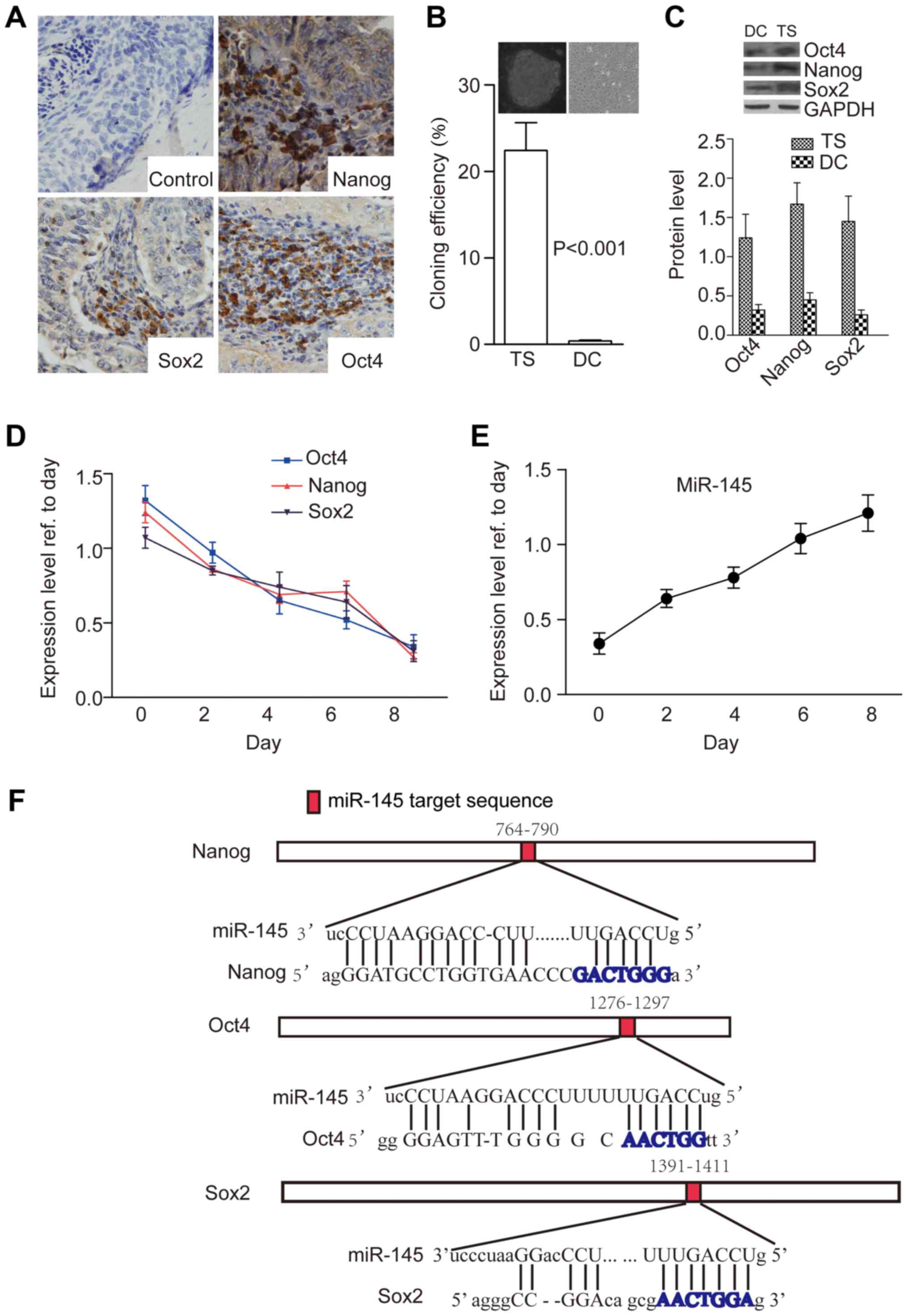
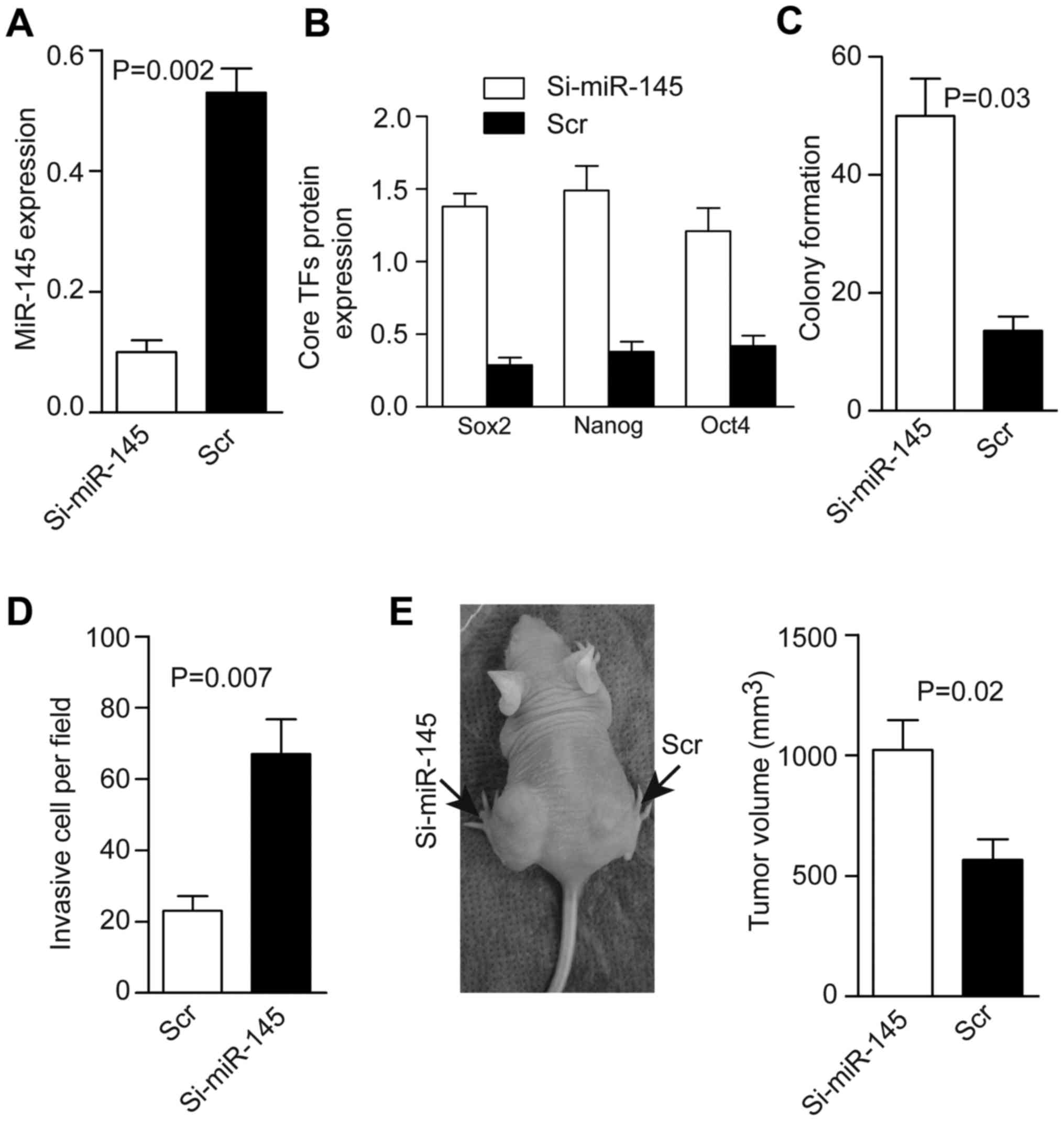
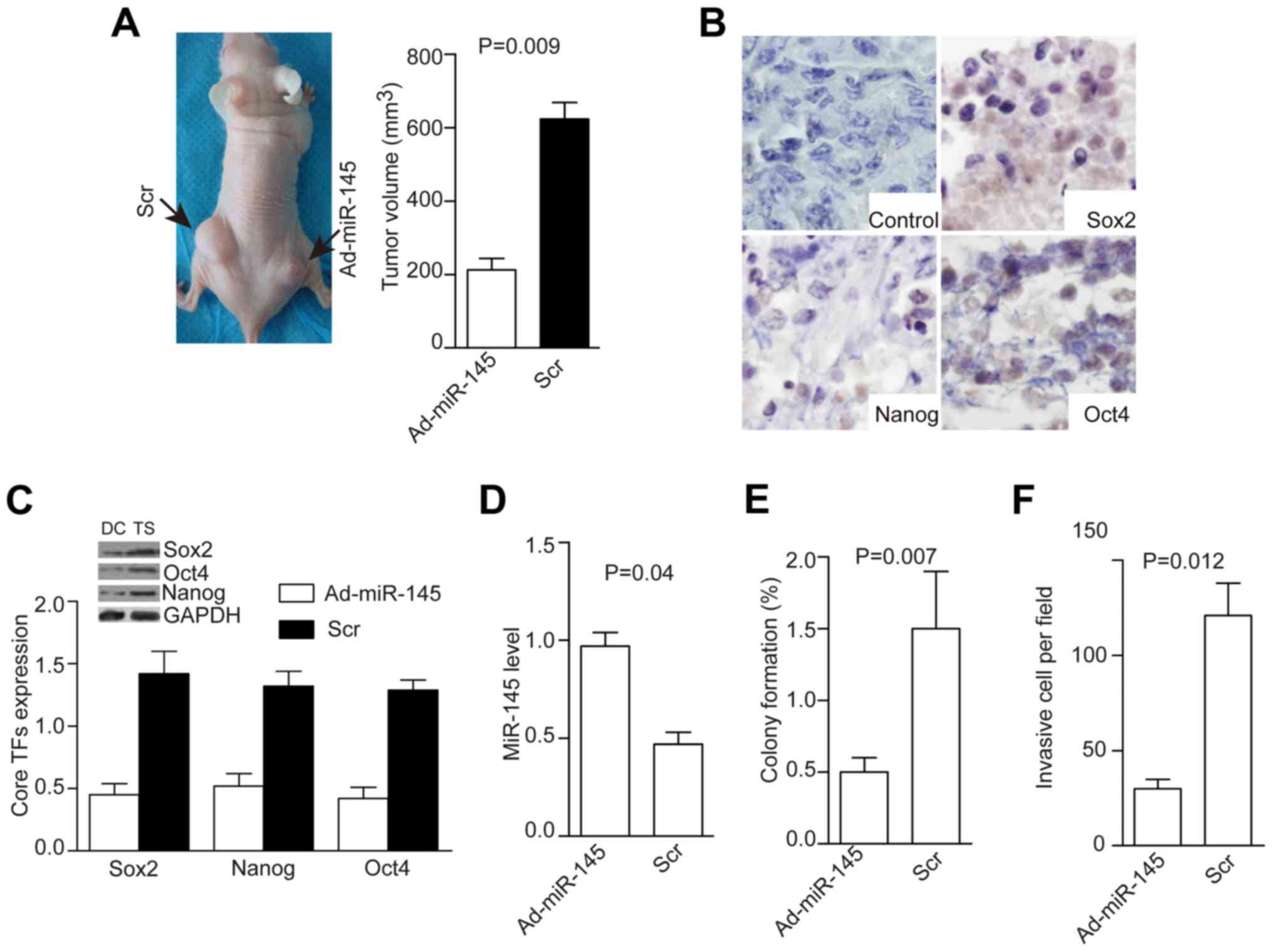
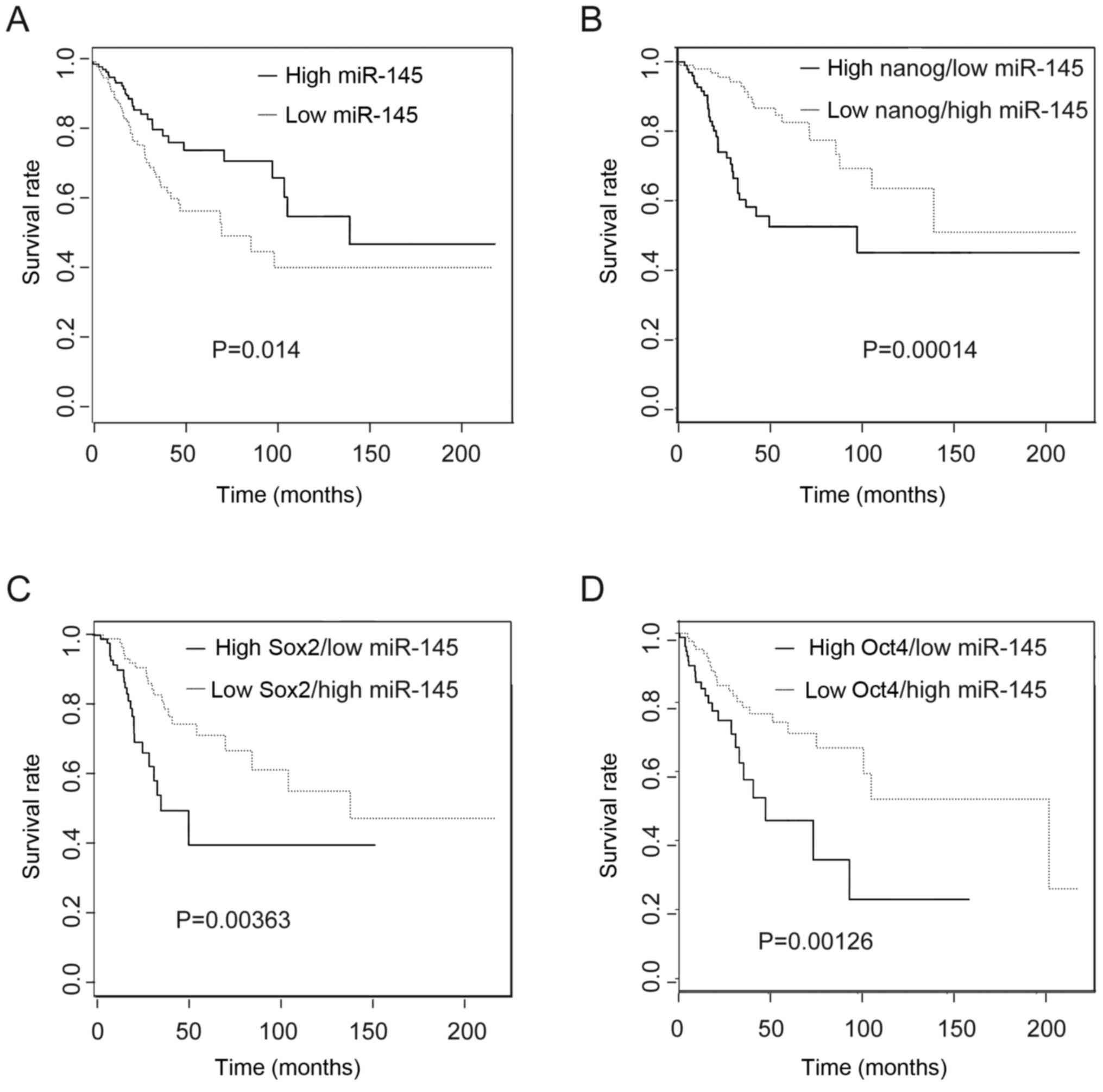
|
1
|
Li J, Kang LN and Qiao YL: Review of the
cervical cancer disease burden in mainland China. Asian Pac J
Cancer Prev. 12:1149–1153. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 65:5–29. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Shepherd JH: Cervical cancer. Best Pract
Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 26:293–309. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Shi JF, Canfell K, Lew JB and Qiao YL: The
burden of cervical cancer in China: Synthesis of the evidence. Int
J Cancer. 130:641–652. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Baccelli I and Trumpp A: The evolving
concept of cancer and metastasis stem cells. J Cell Biol.
198:281–293. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Liu A, Yu X and Liu S: Pluripotency
transcription factors and cancer stem cells: Small genes make a big
difference. Chin J Cancer. 32:483–487. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Li D, Mei H, Qi M, Yang D, Zhao X, Xiang
X, Pu J, Huang K, Zheng L and Tong Q: FOXD3 is a novel tumor
suppressor that affects growth, invasion, metastasis and
angiogenesis of neuroblastoma. Oncotarget. 4:2021–2044. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wang HY, Lian P and Zheng PS: SOX9, a
potential tumor suppressor in cervical cancer, transactivates
p21WAF1/CIP1 and suppresses cervical tumor growth. Oncotarget.
6:20711–20722. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Shen L, Huang X, Xie X, Su J, Yuan J and
Chen X: High expression of SOX2 and OCT4 indicates radiation
resistance and an independent negative prognosis in cervical
squamous cell carcinoma. J Histochem Cytochem. 62:499–509. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ji J, Wei X and Wang Y: Embryonic stem
cell markers Sox-2 and OCT4 expression and their correlation with
WNT signal pathway in cervical squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Clin
Exp Pathol. 7:2470–2476. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ding Y, Yu AQ, Li CL, Fang J, Zeng Y and
Li DS: TALEN-mediated Nanog disruption results in less
invasiveness, more chemosensitivity and reversal of EMT in Hela
cells. Oncotarget. 5:8393–8401. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Mathieu J and Ruohola-Baker H: Regulation
of stem cell populations by microRNAs. Adv Exp Med Biol.
786:329–351. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Xu N, Papagiannakopoulos T, Pan G, Thomson
JA and Kosik KS: MicroRNA-145 regulates OCT4, SOX2, and KLF4 and
represses pluripotency in human embryonic stem cells. Cell.
137:647–658. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Khan S, Ebeling MC, Zaman MS, Sikander M,
Yallapu MM, Chauhan N, Yacoubian AM, Behrman SW, Zafar N, Kumar D,
et al: MicroRNA-145 targets MUC13 and suppresses growth and
invasion of pancreatic cancer. Oncotarget. 5:7599–7609. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Cui SY, Wang R and Chen LB: MicroRNA-145:
A potent tumour suppressor that regulates multiple cellular
pathways. J Cell Mol Med. 18:1913–1926. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Arndt GM, Dossey L, Cullen LM, Lai A,
Druker R, Eisbacher M, Zhang C, Tran N, Fan H, Retzlaff K, et al:
Characterization of global microRNA expression reveals oncogenic
potential of miR-145 in metastatic colorectal cancer. BMC Cancer.
9:3742009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Inamoto T, Taniguchi K, Takahara K,
Iwatsuki A, Takai T, Komura K, Yoshikawa Y, Uchimoto T, Saito K,
Tanda N, et al: Intravesical administration of exogenous
microRNA-145 as a therapy for mouse orthotopic human bladder cancer
xenograft. Oncotarget. 6:21628–21635. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wu Y, Liu S, Xin H, Jiang J, Younglai E,
Sun S and Wang H: Up-regulation of microRNA-145 promotes
differentiation by repressing OCT4 in human endometrial
adenocarcinoma cells. Cancer. 117:3989–3998. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhou X, Gao Q, Wang J, Zhang X, Liu K and
Duan Z: Linc-RNA-RoR acts as a 'sponge' against mediation of the
differentiation of endometrial cancer stem cells by microRNA-145.
Gynecol Oncol. 133:333–339. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Alvarado AG, Turaga SM, Sathyan P,
Mulkearns-Hubert EE, Otvos B, Silver DJ, Hale JS, Flavahan WA, Zinn
PO, Sinyuk M, et al: Coordination of self-renewal in glioblastoma
by integration of adhesion and microRNA signaling. Neuro-oncol.
18:656–666. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Wang Y, Xu Z, Jiang J, Xu C, Kang J, Xiao
L, Wu M, Xiong J, Guo X and Liu H: Endogenous miRNA sponge
lincRNA-RoR regulates Oct4, Nanog, and Sox2 in human embryonic stem
cell self-renewal. Dev Cell. 25:69–80. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kim SJ, Oh JS, Shin JY, Lee KD, Sung KW,
Nam SJ and Chun KH: Development of microRNA-145 for therapeutic
application in breast cancer. J Control Release. 155:427–434. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Crosbie EJ, Einstein MH, Franceschi S and
Kitchener HC: Human papillomavirus and cervical cancer. Lancet.
382:889–899. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Gunasekharan V and Laimins LA: Human
papillomaviruses modulate microRNA 145 expression to directly
control genome amplification. J Virol. 87:6037–6043. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Luo W, Li S, Peng B, Ye Y, Deng X and Yao
K: Embryonic stem cells markers SOX2, OCT4 and Nanog expression and
their correlations with epithelial-mesenchymal transition in
nasopharyngeal carcinoma. PLoS One. 8:e563242013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wang X, Tang S, Le SY, Lu R, Rader JS,
Meyers C and Zheng ZM: Aberrant expression of oncogenic and
tumor-suppressive microRNAs in cervical cancer is required for
cancer cell growth. PLoS One. 3:e25572008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chhabra R and Saini N: MicroRNAs in cancer
stem cells: Current status and future directions. Tumour Biol.
35:8395–8405. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ibrahim AF, Weirauch U, Thomas M,
Grünweller A, Hartmann RK and Aigner A: MicroRNA replacement
therapy for miR-145 and miR-33a is efficacious in a model of colon
carcinoma. Cancer Res. 71:5214–5224. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Takagi T, Iio A, Nakagawa Y, Naoe T,
Tanigawa N and Akao Y: Decreased expression of microRNA-143 and
-145 in human gastric cancers. Oncology. 77:12–21. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|